Integrated Farming System [อินเดีย]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Srikanta Kumar Parida
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1085 - อินเดีย
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Pradhan Gandhi
อินเดีย
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Pradhan Damodar
อินเดีย
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Panda R.K
Central Soil & Water Conservation Research & Training Institute
อินเดีย
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Mohanty B.B
Sarvodaya Samiti
อินเดีย
ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Sarvodaya Samiti - อินเดีย1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.5 Reference to Questionnaire(s) on SLM Approaches (documented using WOCAT)

PARTICIPATORY APPROACH IN IDCWDP, DANIDA [อินเดีย]
Participatory approach for holistic and intigrated development of the defined area on watershed basis involving all level of stake holders.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Srikanta Kumar Parida
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
Growing of crops for food, fodder trees and fibre forest in a compact patch.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
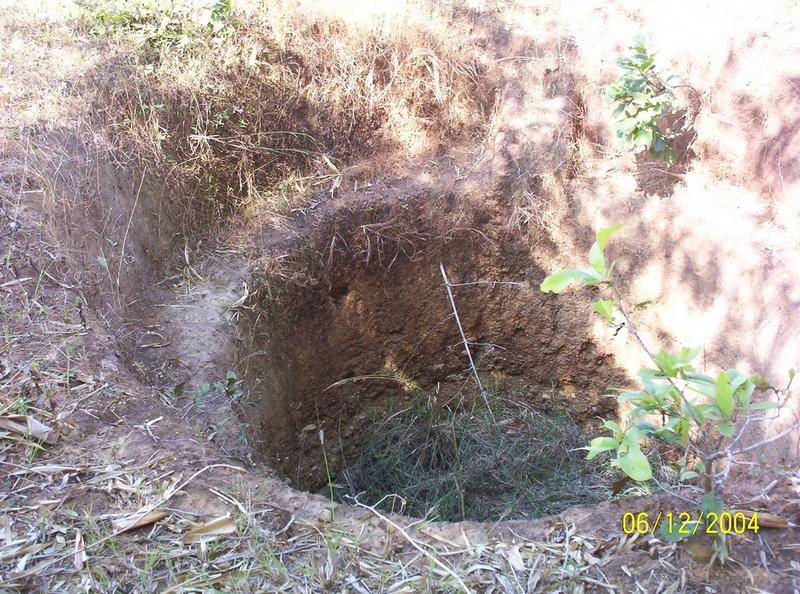
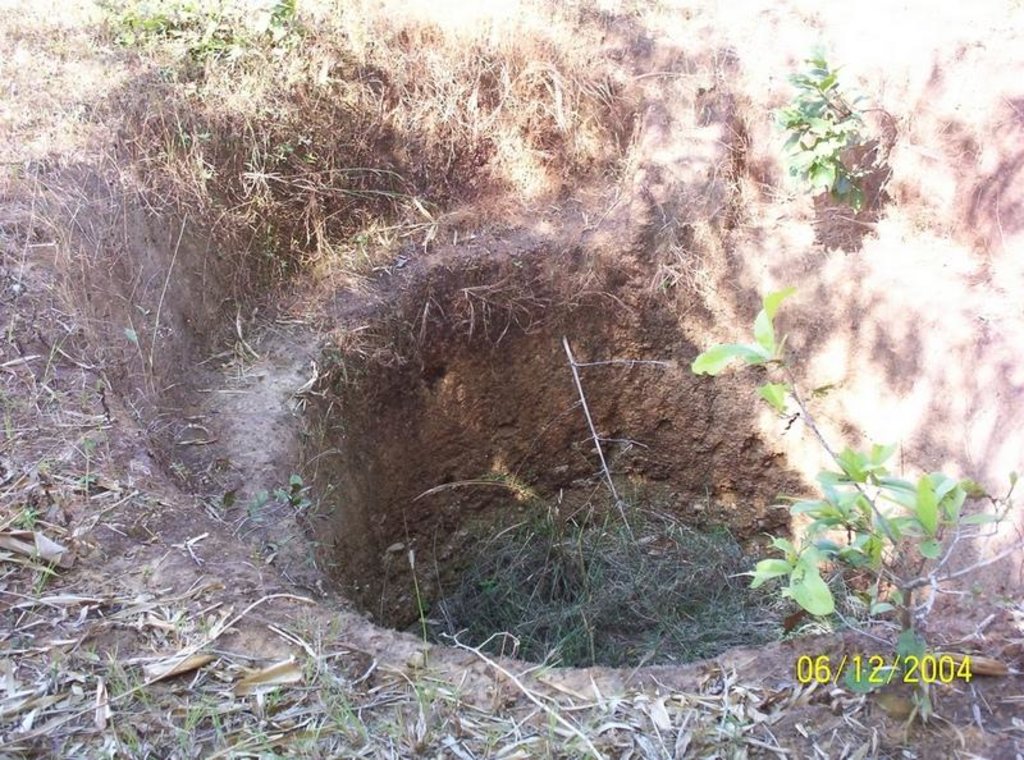
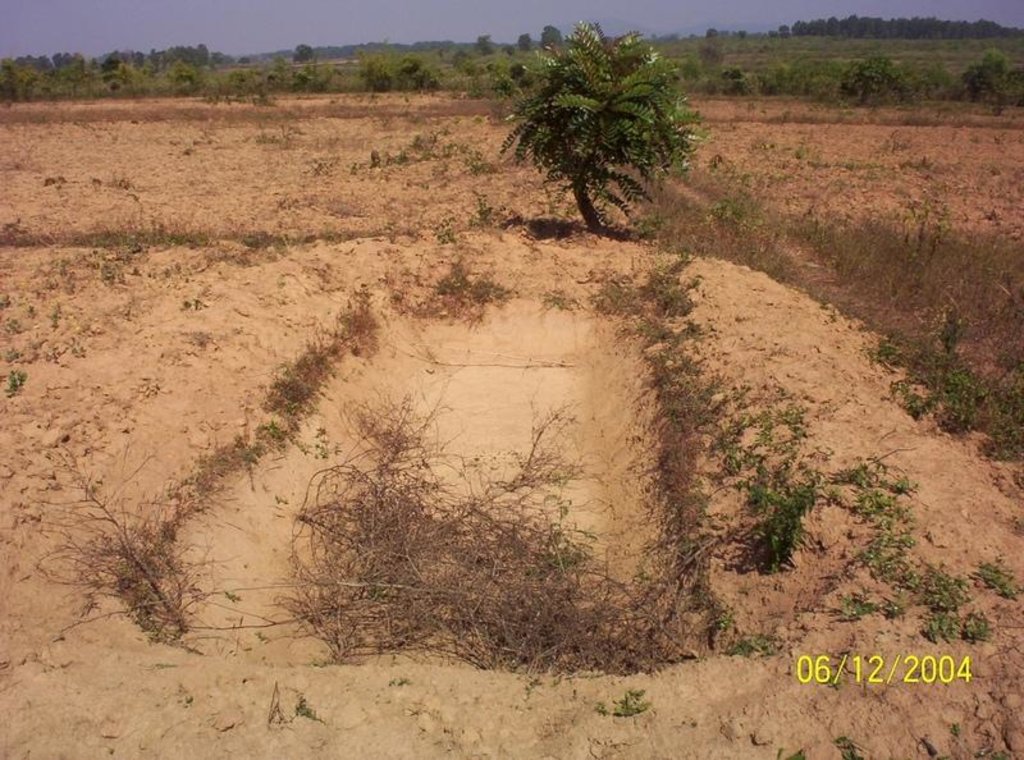
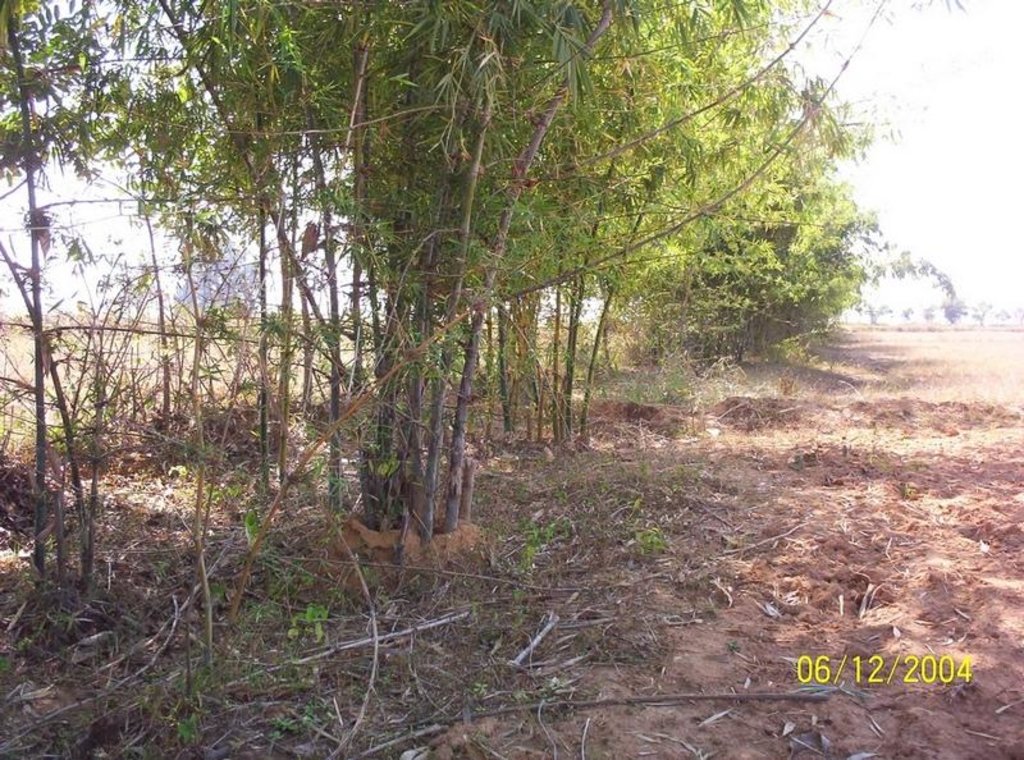
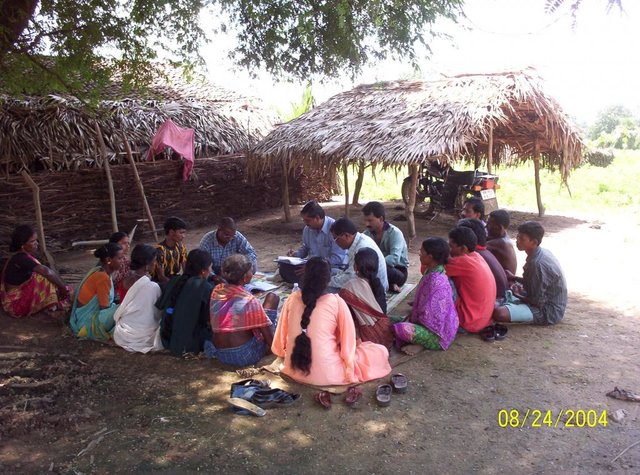
This technology has mainly to be applied on 5 Ha.of private waste land of poor farmers to increase production. This technology focuses on life fencing, planting of trees for both timber and food varieties, land development, water availability and green manuring. Three line bamboo plantation has been done by laying method at all along the boundary line. Agave also planted at boundary line to give additional protection. Then proper compartmentation has been done keeping intact the total area of individual land holders. Here 'V' ditches has been provided accross the slope of total land. Some fruit and fodder, forest trees were planted all along the bunds and inside the field. The density of tree plantation at crop field is less. So as to facilitate crop cultivation. Gullies has also been arrested by construction of gully control structures. One waterhole has been excavated for life saving irrigation. To manage field waste and to get green manure three compost pits also established.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: After several meeting and interaction with village people, this technology has been established. All the land users where technology is applied were fully engaged for every construction work. So as to have a clear understaing of each small intervention. As this technology uses locally available materials, its maintenance by land users become easy.
Natural / human environment: Here Soil & Water Conservation has been given importance, hence more vegetative cover has been noticed in and around technology area. Increase of soil fertility has also been noticed. Complete barren land conveted in to crop land. So the technology has positive impact on the environment undoubtedly.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
อินเดีย
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Orissa
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Orissa
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
If the Technology is evenly spread over an area, specify area covered (in km2):
0.05
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- < 0.1 ตร.กม.(10 เฮกตาร์)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.05 km2.
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
Project SWC Specialist utilizing the earlier experience in the project and other area.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ใช่

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชยืนต้นที่ไม่มีเนื้อไม้
- การปลูกไม้ยืนต้น ไม้พุ่ม
Perennial (non-woody) cropping - Specify crops:
- agave / sisal

ป่า/พื้นที่ทำไม้
- ป่า/พื้นที่ทำไม้
Tree plantation, afforestation: Specify origin and composition of species:
- การปลูกพืชพันธุ์ท้องถิ่นชนิดเดียว
Type of tree:
- Bamboo bamboo

ที่ดินที่ไม่ให้ผลผลิต
ระบุ:
Wastelands, deserts, glaciers, swamps, recreation areas, etc
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Due to slope and lack of vegetation cover, majority top soil were lost and many gullies also formed as a result there was no scope for cultivation.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): The soil was hard, no fertility, land is slopy. So there was no scope for any kind of cultivation in the same patch of land.
Constraints of wastelands / deserts / glaciers / swamps: Slope, Soil loss
Number of growing seasons per year: 1
Longest growing period in days: 150 Longest growing period from month to month: Jun - Oct
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- มาตรการปลูกพืชขวางความลาดชัน (cross-slope measure)
- การเก็บเกี่ยวน้ำ
- การจัดการด้านชลประทาน (รวมถึงการลำเลียงส่งน้ำ การระบายน้ำ)
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main measures: structural measures
Secondary measures: agronomic measures, vegetative measures
Type of agronomic measures: manure / compost / residues
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour, aligned: -graded strips *<sup>3</sup>, aligned: -against wind
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน
- Wg (Gully erosion): การกัดกร่อนแบบร่องธารหรือการทำให้เกิดร่องน้ำเซาะ

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cn (Fertility decline): ความอุดมสมบูรณ์และปริมาณอินทรียวัตถุในดินถูกทำให้ลดลงไป (ไม่ได้เกิดจากสาเหตุการกัดกร่อน)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Main causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (agricultural causes - Coordination of traditional method of agricultural practices like along the slope, use of long term local varieity of seeds etc.), poverty / wealth (lack of captial)
Secondary causes of degradation: education, access to knowledge and support services (lack of knowledge), Erosion problem, Common social practices
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ฟื้นฟูบำบัดที่ดินที่เสื่อมโทรมลงอย่างมาก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
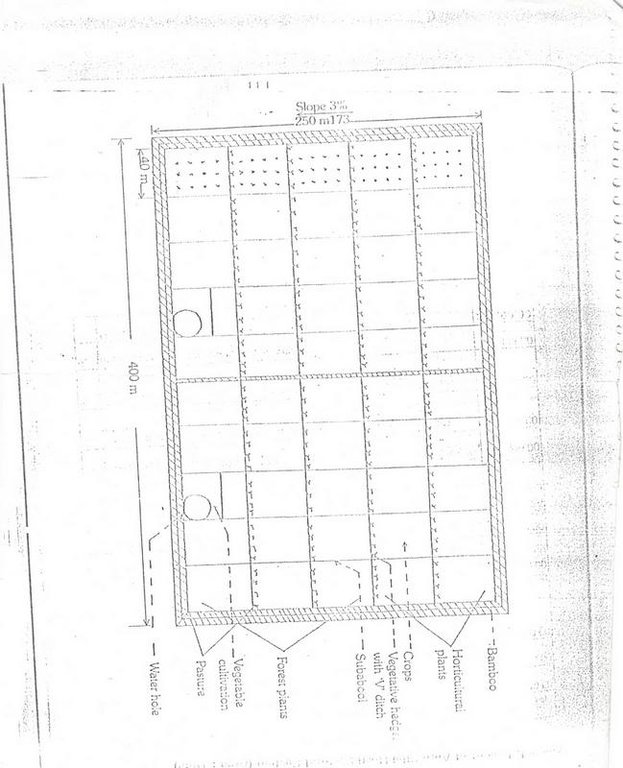
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
Diagram showing different soil conservation measures
Location: Maliguda. Koraput/Orissa/India
Date: 15/3/2005
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope length, increase of surface roughness, increase in soil fertility
Agronomic measure: Green Fencing
Material/ species: Bamboo, Agave
Remarks: Two type of Bamboo and Agave provided all round the technology area
Manure / compost / residues
Remarks: 3 compost pits has been established.
Agronomic measure: Tillage with country plough
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): 15000
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.25
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.25
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.3
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.3
Aligned: -graded strips
Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs, O : other
Number of plants per (ha): 114
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 9.15
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 9.15
Aligned: -against wind
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 1
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.33
Trees/ shrubs species: Bamboo, Agave (Sisal)
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Mango and Cashew
Other species: Teak, S.Glauca, Subabul
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 4.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 2.00%
Wall/ barrier
Spacing between structures (m): 6
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.3
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.25
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.7
Structural measure: Pits
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 25
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.9
Structural measure: 'V'Ditch with bund
Vertical interval between structures (m): 20
Spacing between structures (m): 15
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 500
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1.5
Construction material (earth): Bund constructed with earth
Construction material (other): Barries established with bamboo along the boundary for wind break as well as fence.
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 4%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 2%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
ผู้เขียน:
Parida S.K, Koraput,Orissa, In
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
Rupees
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
0.45
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
0.88
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Collection of matured bamboo and laying 9" below earth all along boundary in 3 rows | May |
| 2. | Collection of vertiver strips, trees from local nursery | July |
| 3. | Planting grasses, trees | July to Aug |
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 313.0 | 313.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Animal traction | ha | 1.0 | 7.72 | 7.72 | |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 39.22 | 39.22 | |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 99.0 | 99.0 | |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Biocides | ha | 1.0 | 12.33 | 12.33 | |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Compost/manure | ha | 1.0 | 32.0 | 32.0 | |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Others | ha | 1.0 | 193.33 | 193.33 | |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Stone | ha | 1.0 | 13.0 | 13.0 | |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Earth | ha | 1.0 | 55.55 | 55.55 | |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Pitcher | ha | 1.0 | 13.55 | 13.55 | |
| อื่น ๆ | Compost pit | ha | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 783.7 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 1741.56 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Duration of establishment phase: 48 month(s)
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Tillage | Jan to June / Twice |
| 2. | Line showing | July / Once |
| 3. | Weeding | Sept / Once |
| 4. | Fertilizer Application | Sept to Oct / Once |
| 5. | Harvesting | Nov / Once |
| 6. | Manuring, weeding and hoeing | September / |
| 7. | Catchpit, pitcher irrigation | November / |
| 8. | Spraying with plant protection materials | December / |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Convert of degraded fellow private land to a cultivable land on adopting new low cost technology in a 5 Ha. Compact patch. The following benefits -
(1) Slope of the land reduced.
(2) Land protected from severe soil erosion.
(3) Increase the moisture region of the soil.
(4) Soil fertility/ standy increased farmers achieved the minimum common needs (basic) common needy product from the technology i.e food, fuel and fodder etc.
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
(1) High slope:- Slope reduced Nos. of structure adopted. Labour engagement are expose of sub-surface soil used Nos. of planting materials.
(2) Diference:- The planting materials are not locally available and transported from 20 K.Ms distance (Bamboo, Vertiver, Mango, Cashew)
(3) Comunication was not up to SWC spot during the establishment period.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งชุ่มชื้น
Eastern Ghat High Land
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
Landforms: Hill slopes (ranked 1), ridges (ranked 2) and valley floors (ranked 3)
Slopes on average: Moderate (land Slope having undulated topography)
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ต่ำ (<1%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil texture: Medium (ranked 1, sandy loam to silty clay loam) and coarse/light
Soil fertility: Low (ranked 1) and medium (ranked 2)
Topsoil organic matter: Low (loss of top soils due to heavy run off, ranked 1)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Medium (soil varies from loam to silly clay loam, ranked 2)
Soil water storage capacity: Low
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- 10-50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- จน
- พอมีพอกิน
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
24% of the land users are rich and own 30% of the land.
45% of the land users are average wealthy and own 56% of the land (30% of house hold comes in standard wealth.).
31% of the land users are poor and own 14% of the land (70% of house hold comes below average).
Off-farm income specification: Through various training, interaction with specialist, they acquire more knowledge about other small business like Goatery, Poultry, Pisciculture, Beekeeping, Floriculture and also marketing facility and utilizing these knowledge their off-farm income increase.
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
การผลิตพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
คุณภาพพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
การผลิตไม้
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Finding market and getting better price f or product
ความเหลื่อมล้ำทางเศรษฐกิจ
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
สถาบันของชุมชน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Formation of UG/ SHG
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Imparting teaching to nearby village people on erosion, loss of top soil and timely aprehension at field
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
50
หลังจาก SLM:
40
การระบายน้ำส่วนเกิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Safe disposal of water.
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Adopting soil conservation activities
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Practising cropping
การสูญเสียดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
46
หลังจาก SLM:
20
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
ความเร็วของลม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Planting of bamboo at boundary
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยาอื่น ๆ
Soil fertility
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
On decomposition of straw
Biodiversity
Seed quality
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Better procurement of good quality of seeds
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
การไหลของน้ำคงที่และสม่ำเสมอในช่วงฤดูแล้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Stream flow remains up to February
น้ำท่วมพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
No flooding seen
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
26
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
6 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
20 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: survey results
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Some land users adopted the technology partially. As the technology has different measures, some took field bunds with local grasses, some did tree plantation. Some are planning to plant bamboo in their plot boundary.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| Low cost technology |
|
Early adoptbility by the farmers How can they be sustained / enhanced? Over all it is a best technology with proper management by the farmers |
| Combination of production gain from bamboo and crop, less use of chemical fertilizer as green manure is available localy. |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
|
Low cost and simple tech nology. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Proper understanding by land user for technology |
| Materials are used for the technology available locally |
|
Due to increase of income migration is reduced How can they be sustained / enhanced? Proper adoption of technology |
|
Reduction of runoff and soil loss and increase of soil fertility and soil moisture regime has been increase How can they be sustained / enhanced? Adopting proper cropping pattern. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Ownerships of land and additional taxation there on after implementation of technology. | Clear understanding by competant authority ( By revenue people) |
| Fruit trees died | Beneficiaries planted Cashew instead of fruit trees. |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Clear understanding of the technology. | Regular meeting with local representatives. |
| Availability of materials in the technology area. | Alternative available materials must be used in technology area. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Watershed Survey Report
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Director of Soil Conservation, Orissa, Bhubaneswar
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Plan and Estimate
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
-do-
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์

PARTICIPATORY APPROACH IN IDCWDP, DANIDA [อินเดีย]
Participatory approach for holistic and intigrated development of the defined area on watershed basis involving all level of stake holders.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Srikanta Kumar Parida
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล