Shelterbelts [อินเดีย]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Unknown User
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
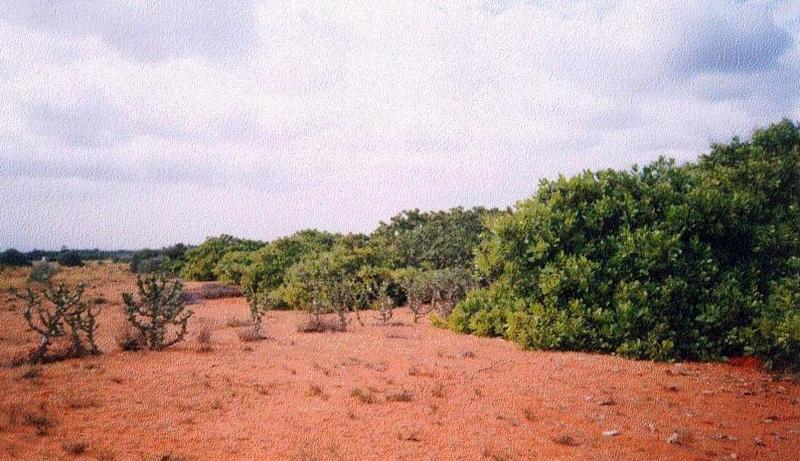
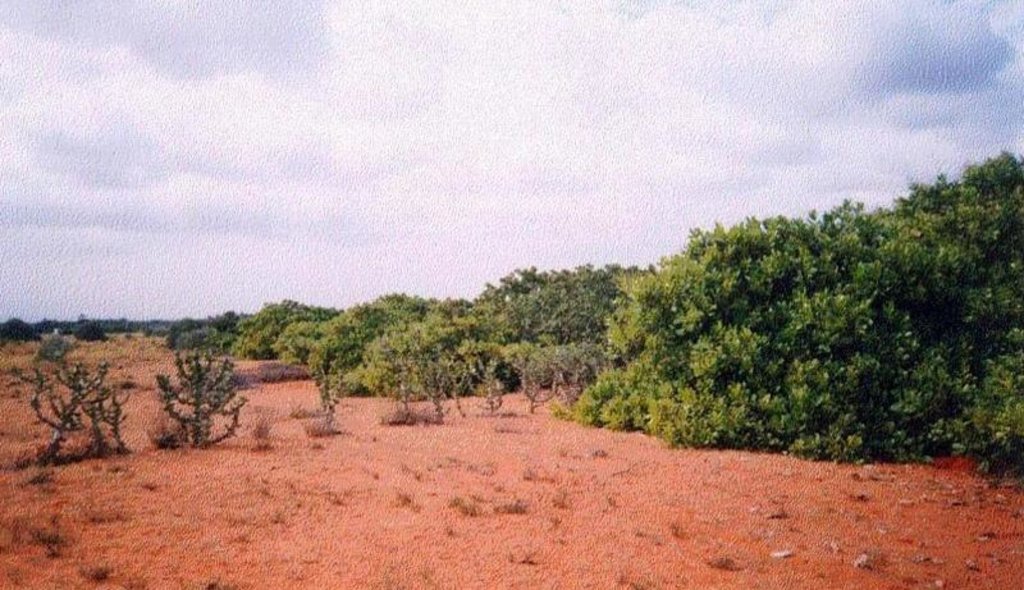
Line, Shelterbelts in Theri land
technologies_1473 - อินเดีย
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
Cultivation of tree belts across the direction of wind at appropriate intervals in the deposition zone, with a view to arrest wind erosion and facilitate stabilisation of dunes through interbelt development.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
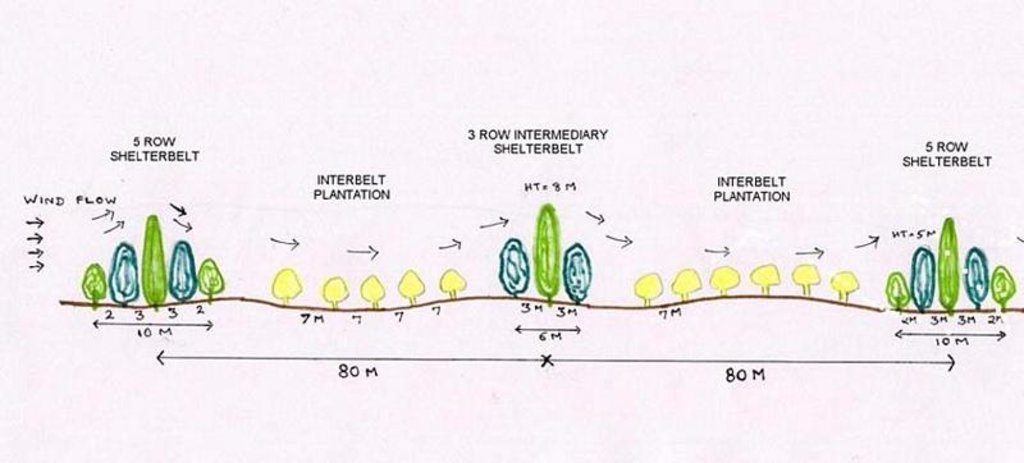
The technology comprises establishment of 5 row shelterbelts at 160 m intervals. 3 row intermediary shelterbelts are introduced in between existing shelterbelts at 80 m interval. Land owners are encouraged to cultivate tree crops in between the belts.
Purpose of the Technology: Shelterbelts are useful in reducing wind velocity, there by arresting shifting of sand dunes, deposition of sand on fields, habitation, wells, roads etc. Cultivation of area between tree belts is made possible leading to increase in productivity from these lands.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The shelterbelts comprise tree species of different heights planted in rows (5 and 3 row deep) in a straight line across the wind direction. Six month old seedlings are planted in pits of volume 1 cuft to 1.5 cuft, which are filled with tank silt. One borewell is provided for one km length for life saving irrigation.
Natural / human environment: The environment is arid and forms the deposition zone wherein sand lifted from the impact zone is deposited. Sand dunes cover the area.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
อินเดีย
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Tirunelveli district, Tamil nadu state
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 100 km2.
The technology was implemented in the sand dune belt locally known as 'theri', located between the western mountain range and east coast of south India. The technology was initially implemented by the Government of Tamil nadu state in 1978 till 1985. The Danida supported project implemented by the department of Agricultural Engineering began activities to strengthen existing shelter belts, introduce inter belts and mass plantation from 1991 till 1999. The technology was initially implemented in an area much wider than the their lands, but experience showed that the shelterbelts was not the best methodology for low wind agricultural areas, so a shift to agro forestry and mass planting occurred.
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
The Department of Agriculture Engineering implemented shelterbelts since 1958 in neighbouring Madurai district. The technology was introduced to Tirunelveli district by the department in 1978 wherein 5 row shelterbelts were established.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- อนุรักษ์ระบบนิเวศน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ใช่
Specify mixed land use (crops/ grazing/ trees):
- การปลูกพืชร่วมกับปศุสัตว์และการทำป่าไม้ (Agro-silvopastoralism)

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 100 Longest growing period from month to month: Oct - Dec

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์

ป่า/พื้นที่ทำไม้
- ป่า/พื้นที่ทำไม้
ผลิตภัณฑ์และบริการ:
- การป้องกันภัยธรรมชาติ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Crops cannot be cultivated due to sand deposition. Grass cover cannot develop due to shifting of dunes. Hence the area is neglected and degrades further. Only hardy species (ef. Palymra) and coarse grasses survive. Predominant land use is open grazing.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Land cannot be cultivated economically due to arid conditions, shifting dunes and open grazing.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Cultivation is practiced only in years of good rainfall. Single crop of pulse (black gram ) is taken.
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Water supply: Also mixed rainfed - irrigated (ranked 2)
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- แนวกันลมหรือแนวต้านลม
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยลม
- Ed (Deflation and deposition): การกัดกร่อนโดยลมและการทับถม
- Eo (Offsite degradation effect): ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main type of degradation addressed: Eo: offsite degradation effects
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Ed: deflation and deposition
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
Technical Drawing - Shelterbelt
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: reduction in wind speed
Secondary technical functions: improvement of ground cover, arresting movement of sand
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 2.00%
ผู้เขียน:
David Gandhi, India
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
Indian Rupee
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
48.85
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
1.00
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Nursery raising | May-Nov |
| 2. | Pitting | Oct-Nov |
| 3. | Filling of pits | Nov-Dec at plantation |
| 4. | Life watering | Nov-Dec at plantation |
| 5. | Periodic watering | weekly during 1st year, except monsoon |
| 6. | Provision of shade to saplings | at planting |
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Duration of establishment phase: 60 month(s)
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Watering | 2 & 3rd year after plantation /fortnightly, except monsoon |
| 2. | Casualty replacement | 2nd year /monsoon |
| 3. | Watch & ward | upto 5th year /full time watchman |
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
The above costs cover an establishment period of 5 years for 1 hectare (250 plants) of shelterbelt; year 1: pitting, planting, watering. Year 2 & 3: periodic watering, watch and ward, prunng, gap filling. Year 4 & 5: watch and ward, pruning. Of the total number of 391 mandays/ha. of shelterbelt, 288 mandays go towards periodic watering over the first 3 years. Watering of plants is essential due to the semi-arid climate and sandy soil. In addition, as supportive technology for provision of water, one borewell with handpump was established per kilometer of shelterbelt.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ระบุปริมาณน้ำฝนเฉลี่ยรายปี (ถ้ารู้) :หน่วย ม.ม.
559.00
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
30 years average
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
Since past few years, arid conditions prevail
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
Landforms: Plateau/plains (undulating terrain)
Slopes on average: Gentle (undulating)
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ต่ำ (<1%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil depth on average: Very deep (due to deposition by wind)
Soil texture: Coarse/light (sandy soil),
Soil fertility: Very low (low organic matter)
Topsoil organic matter: Low (low vegetative cover)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Good (permeability is high)
Soil water storage capacity: Very low (sandy soil, low organic matter)
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- > 50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- จน
- พอมีพอกิน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
38% of the land users are average wealthy (traders, labor).
42% of the land users are poor (small farmers, without water source).
20% of the land users are poor (small farmers, without water source).
Off-farm income specification: traders, employed in cashew processing plants, small industries, nearby towns, migration.
Level of mechanization: Manual work (in addition bullocks are used for ploughing)
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เข้าถึงได้แบบเปิด (ไม่ได้จัดระเบียบ)
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านลบอย่างมาก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านลบเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
5000 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Farmers are in favour of raising orchards to combat wind erosion and increase production in place of shelterbelts..
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Review Reports
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Chief Engineer, Agriculture Engineering Department, Anna Salai-439, Nandanam, Chennai-600035
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Project Implementation Plans, Project documents
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Programme Coordinator, WDCU, 11/1 Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi-110016.
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล