Odaltaal-10 Single Use Water System [เนปาล]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Jhuna Kattel
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Renate Fleiner
Tanki
technologies_5185 - เนปาล
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
วิทยากรหลัก
Water user:
Salami Kham Bahadur
N/A
เนปาล
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Prospects and challenges of water use systems as climate adaptive option for sustainable water management in Himalayan Regionชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Kathmandu University (KU) - เนปาล1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
This is a Single Use Water System implemented in order to preserve the water sources through their sustainable use.
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
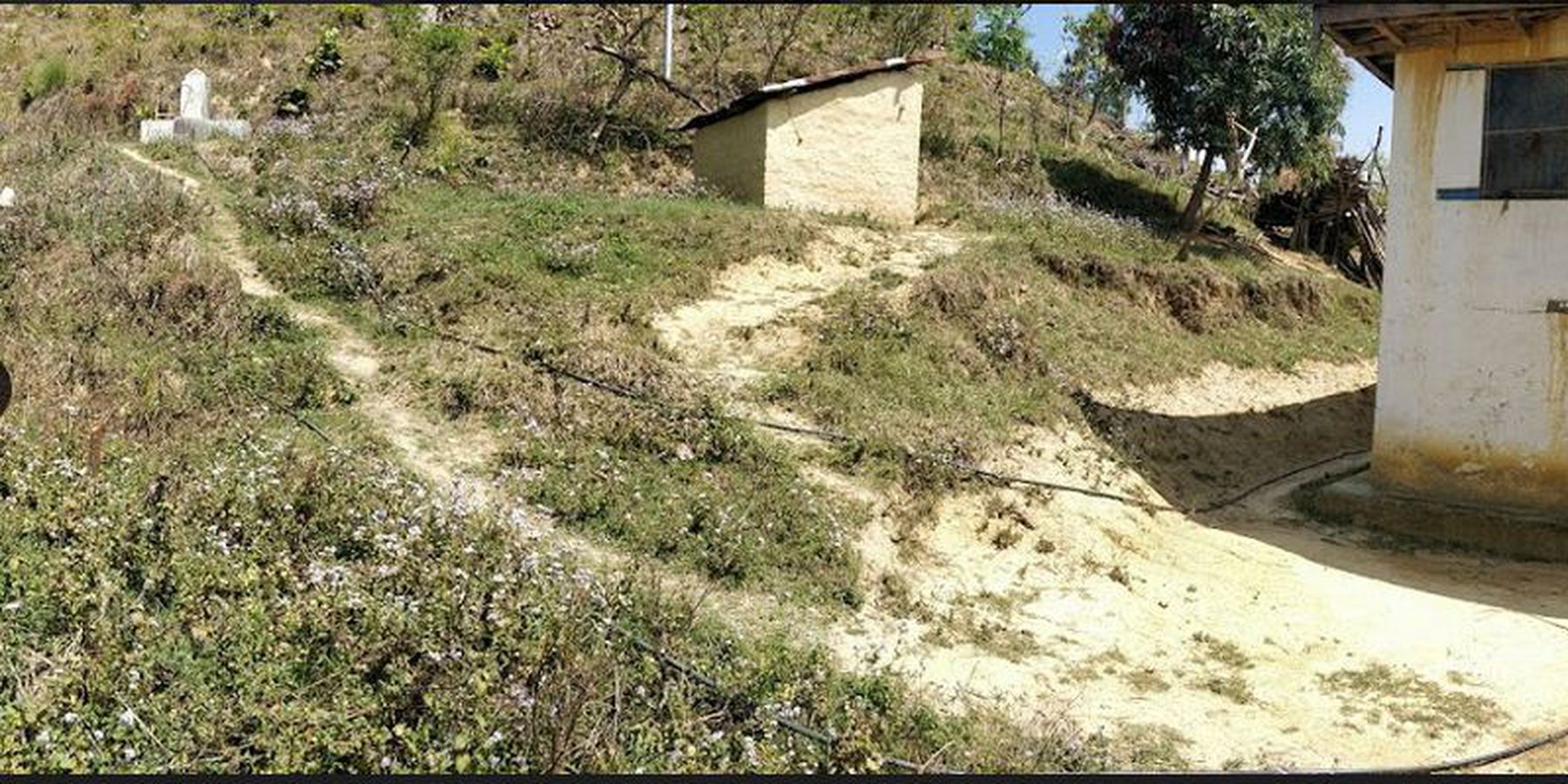
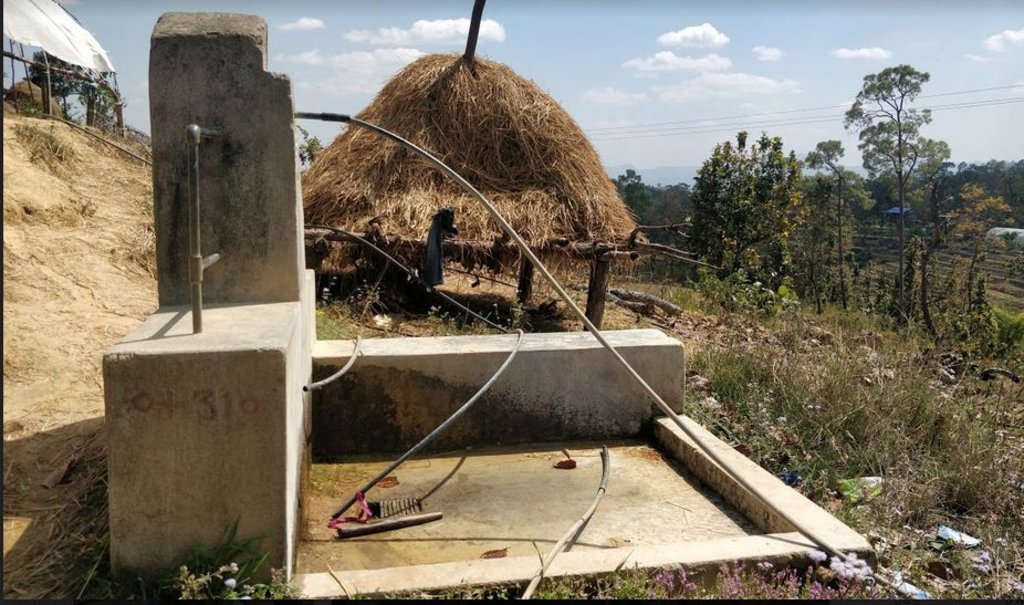
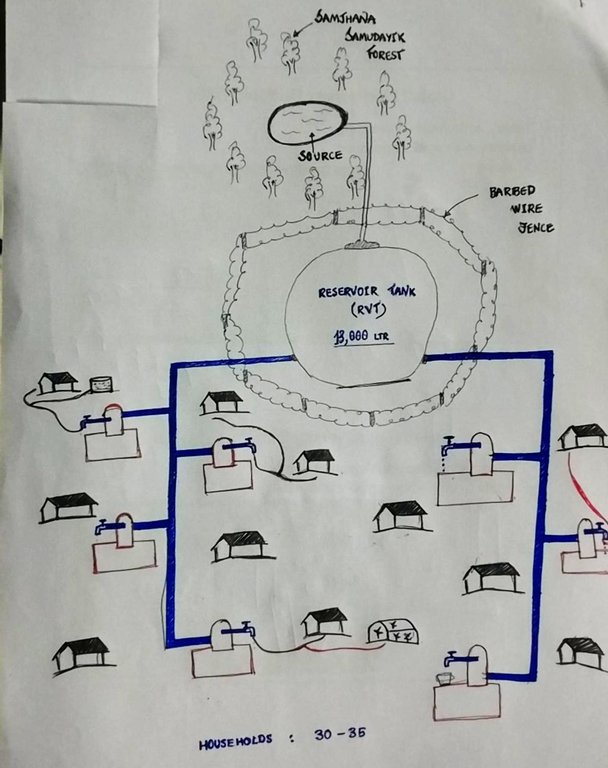
Water from source is collected in a reservoir tank ( RVT) of volume 13000 Ltr and then distributed to each household for Single Use. Traditionally, the system was constructed to serve a single purpose-drinking (hence the name "Single Use" water system). However, due to increasing demand and need to meet multiple uses, the water users are using the same water for different purposes like drinking, irrigation and other domestic uses.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
A Single Use Water System (SUWS) is the one in which the supplied water serves a single purpose. Traditionally, the system was constructed in order to meet the growing demand and serve a single purpose i.e. supply drinking water to households ( hence the name "Single Use" water systems). However, people's demands and needs increased and supplied water was then used for various purposes like for irrigation, animal husbandry, domestic chores like bathing, washing, etc.
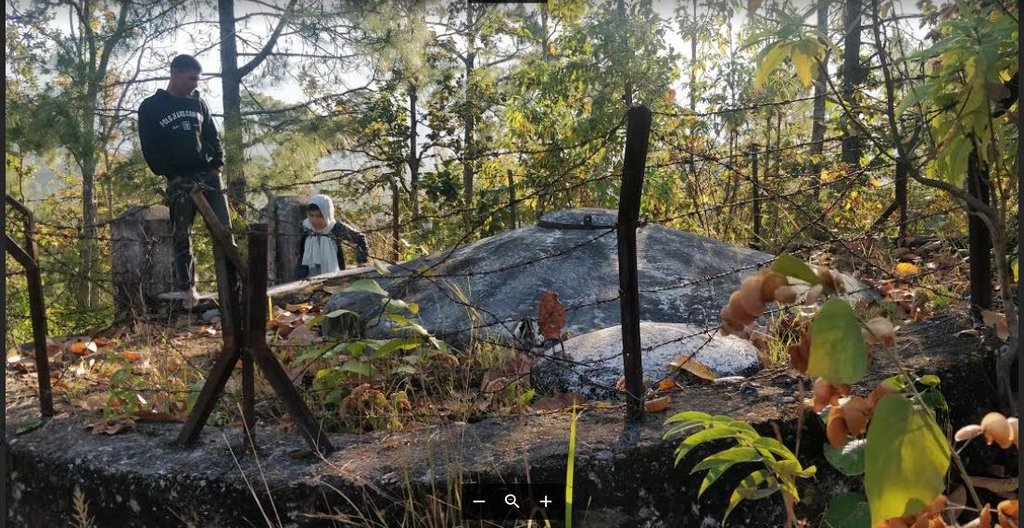
The technology is applied in a natural environment (community forest). The source of water is a natural source that lies in a community forest and hence, the availability is seasonal. The land where the source falls is owned by the government and the implementation of the technology was primarily assisted by the Village Development Committee (VDC). Its use rights falls under the water users. The main elements include a concrete Reservoir tank (RVT), pipeline and tap system or tap towers with faucets. The major functions of this technology are to store water and distribute to the 30-35 households and to ensure the preservation of natural water source through its sustainable use. Major activities are labor and construction activities for building the reservoir tank and laying down the pipeline. Maintenance work, if and when it is needed, is carried out with the help of the water users. No specific group or committee has been formed that looks onto the matters of discussion of the committee. No investment has been made by the local water users' group towards the construction of the technology. Benefits of the technology are the availability of clean drinking water at household level and the preservation of the natural source of water that ensures its perennial availability. Water users admire the overall improvement of their health status through the availability of clean drinking water.
They dislike the fact of water scarcity during dry seasons and the poor management of the system. The quantity of the water is adequate for most of the year. However, scarcity of water during the dry months (when the source dries out) is still eminent. Quality of water is good with low salinity and or iron and other elements but persistence of lime in the water remains.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
เนปาล
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Province 6, Karnali, Mid - Western Development Region
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Kunathari VDC -10, Odaltaal
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- 1-10 ตร.กม.
Is/are the technology site(s) located in a permanently protected area?
ใช่
ถ้าใช่ ระบุ:
Community Forest ( Samjhana Samudayik Ban)
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- 10-50 ปี
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- เป็นส่วนหนึ่งของระบบแบบดั้งเดิมที่ทำก้นอยู่ (> 50 ปี)
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
It is based on a traditional system, but improvised to construct a reservoir tank (RVT) and water supplied through a pipeline. The traditional system contained a reservoir pond dug up and water was supplied through feeding rubber and plastic pipes to the households with no faucets. This caused the water to flow through the pipes without stopping and there was loss of precious water due to excess drainage. The dug up pond caused sediments, dirt, insects and leaves to collect in the water, clogging the pipes and making water unsafe for drinking.
The construction of concrete RVT with lid ensured water stayed free from sediments and falling leaves. Construction of tap towers with taps and faucets ensured water was not wasted. The use of Poly-Vinyl Chloride (PVC) pipe with pipeline system was done to the traditional system of supply of water to households.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับตัวเข้ากับการเปลี่ยนแปลงภูมิอากาศของโลก สภาพภูมิอากาศที่รุนแรงและผลกระทบ
- drinking water purpose ( to improve water security at a household level)
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

ป่า/พื้นที่ทำไม้
- ป่ากึ่งธรรมชาติ / พื้นที่ทำไม้
(Semi-)natural forests/ woodlands: Specify management type:
- การตัดไม้ที่มีคัดเลือก (Selective felling)
Are the trees specified above deciduous or evergreen?
- evergreen
ผลิตภัณฑ์และบริการ:
- การอนุรักษ์ / ป้องกันธรรมชาติ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Samjhana Samudayik Ban ( Community Forest)
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
อื่นๆ (เช่น หลังจากน้ำท่วม):
- Natural Water Source
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Natural Spring water source inside Community Forest
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การเก็บเกี่ยวน้ำ
- การจัดการน้ำบาดาล
- water management ( for Drinking purpose) - Gravity Fed Single Line
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S5: เขื่อน ชั้นดินที่แน่นแข็งบ่อน้ำ
- S6: กำแพง สิ่งกีดขวาง รั้วไม้ รั้วต่างๆ
- S7: การกักเก็บน้ำ/การส่งลำเลียง/อุปกรณ์การชลประทาน
- S11: อื่น ๆ
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การเสื่อมโทรมของน้ำ
- Hs (Change in quantity of surface water): การเปลี่ยนแปลงปริมาณของน้ำที่ผิวดิน
- Hp (Decline of surface water quality): การลดลงของคุณภาพน้ำที่ผิวดิน
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ไม่สามารถใช้ได้
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The "intended" sole purpose of the technology was to serve a single purpose- to supply drinking water at a household level. Hence, no significant effect with regard to land degradation was intended to have been achieved; hence omitted.
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
Reservoir Tank (13,000 LTR in volume). Both the source and the RVT are located inside community forest ( Samjhana Samudayik Ban). The water then flows due to the effects of gravity onto the tap towers, wherein water is supplied for 30-35 households for Single Use. Even though single use (drinking) was considered in the construction of technology, people have been fulfilling various needs with the water supplied ( eg. Drinking, irrigation, and other domestic uses).
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อพื้นที่ที่ใช้เทคโนโลยี
ระบุขนาดและหน่วยพื้นที่:
10 Dhurs
If using a local area unit, indicate conversion factor to one hectare (e.g. 1 ha = 2.47 acres): 1 ha =:
1 ha= 590.70 dhurs
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
NPR
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
113.0
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
N/A
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Construction of Reservoir Tank | |
| 2. | Laying down the pipeline |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The SUWS system was contributed by the VDC but exact costs couldn't be recollected by the locals. Similarly, the locals vaguely remember the season of construction. As per some of the water users, the construction was started during summer, but could only be completed after winter season was over due to rains disturbing the work in between.
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Voluntary | |||||
| อุปกรณ์ | Construction of RVT | |||||
| อุปกรณ์ | Laying down pipeline |
If you are unable to break down the costs in the table above, give an estimation of the total costs of establishing the Technology:
1400.0
ถ้าผู้ใช้ที่ดินรับภาระน้อยกว่า 100% ของค่าใช้จ่าย ให้ระบุว่าใครเป็นผู้รับผิดชอบส่วนที่เหลือ:
Village Development Committee contributed 100% of costs, pipeline contributed by a NGO ( RRN), DFID helped with other miscellaneous costs and Newasanstha helping with other running costs.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Since exact estimation and/or recollection of the costs of construction of the technology was not possible; an estimation was made based upon the then prices of materials, pipes and labor costs- which estimated to be roughly 70 USD.
It has to be kept in mind that the 70 USD that was used was almost 50 years ago. Keeping in line with the inflation rates, it could be worth more than 15-20 times of the original cost ( >1400 USD).
Hence, to make it easier to compare with the construction VS maintenance costs, the figures have been rounded off to today's value as 1400 USD.
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Laying down pipeline ( by RRN) | Once (2056 B.S,) during winter |
| 2. | Operation and maintenance costs (borne by a NGO- DFID) | Once (2071 B.S.) during summer |
| 3. | Changing of pipes ( borne by NGO- Newasanstha and the locals) | 6-7 times ( during summer, winter and during rains) |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The running and maintenance costs borne by various non-governmental organizations and the local community as and when required.
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Voluntary Labour contribution by locals | 100.0 | ||||
| อุปกรณ์ | Changing of PVC Pipes | 25.0 |
If you are unable to break down the costs in the table above, give an estimation of the total costs of maintaining the Technology:
700.0
ถ้าผู้ใช้ที่ดินรับภาระน้อยกว่า 100% ของค่าใช้จ่าย ให้ระบุว่าใครเป็นผู้รับผิดชอบส่วนที่เหลือ:
Non-Governmental organizations like DFID, NewaSanstha and Village Development Committee contributed from time to time
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The exact costs couldn't be calculated. But as per the locals, the costs of changing the PVC pipes 6 times came to around 700 USD.
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
The construction materials, pipelines were the ones which costed the most.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
Total annual rainfall of the region was around 1609 mm; however no literature could give an idea on the annual "average" rainfall. Thus, estimated rainfall was mentioned.
ระบุชื่อของสถานีตรวดวัดอากาศที่ใช้อ้างอิงคือ:
Meteorological Forecasting Division, Nepal ( www.mfd.gov.np)
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งชุ่มชื้น
The climate is overall humid with monsoon consisting of 2-3 months ( June - August) and dry and arid conditions during the winter seasons.
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ละเอียด/หนัก (ดินเหนียว)
เนื้อดินล่าง (> 20 ซ.ม.ต่ำจากผิวดิน):
- ละเอียด/หนัก (ดินเหนียว)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
<5 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ปานกลาง
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ดี
Water quality refers to:
both ground and surface water
ความเค็มของน้ำเป็นปัญหาหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
กำลังเกิดน้ำท่วมในพื้นที่หรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- สูง
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งที่อยู่:
- ต่ำ
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน:
- กึ่งเร่ร่อน
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- เพื่อการยังชีพ (หาเลี้ยงตนเอง)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- 10-50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- จน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- กลุ่ม/ชุมชน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
เพศ:
- หญิง
- ชาย
อายุของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
- เด็ก
- ผู้เยาว์
- วัยกลางคน
- ผู้สูงอายุ
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Most of the community are literate ( finished upto classes 4/5 ) . The ratio of male: female is almost equal. Most of the users are middle-aged ( 40-50 yrs age-group) . The ethnicity consists of Thakuri, Dalits and Janajatis. Total land holding of the water users is around 20 ropanis. ( 1 hectare = 19.65 ropanis)
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
around 10 Dhurs of land is occupied by the technology. (1 hectare = 590.70 dhurs)
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รัฐ
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
Are land use rights based on a traditional legal system?
ไม่ใช่
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The water source is owned by the state / government. The access to water is open ; however during the time of crisis, its use is limited to each household.
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The access to all these services is limited as the locals have to traverse a distance of almost 30 minutes to bazaar area / marketplace. The road infrastructure is good.
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
การผลิตพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
คุณภาพป่า /พื้นที่ทำไม้
การเสี่ยงต่อความล้มเหลวในการผลิต
ความหลากหลายของผลิตภัณฑ์
พื้นที่สำหรับการผลิต
ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
การมีน้ำดื่มไว้ให้ใช้
คุณภาพน้ำดื่ม
การมีน้ำไว้ให้ปศุสัตว์
คุณภาพน้ำสำหรับปศุสัตว์
การมีน้ำไว้ให้สำหรับการชลประทาน
คุณภาพน้ำสำหรับการชลประทาน
ความต้องการน้ำจากการชลประทาน
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งผลิตรายได้
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
สถานการณ์ด้านสุขภาพ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Prior to the adoption of the technology, typhoid, jaundice, diarrhea and dysentery used to be a problem during the summer and rainy seasons. However, after the adoption of technology, the number of cases of such illnesses have drastically decreased and overall health status of the people greatly improved due to availability of clean drinking water.
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
ผลกระทบจากภัยแล้ง
Specify assessment of on-site impacts (measurements):
The "intended" sole purpose of the technology was to serve a single purpose- to supply drinking water at a household level. Hence, no significant effect with regard to other ecological impacts have been achieved; hence omitted.
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
น้ำที่ใช้ประโยชน์ได้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Water can be made available to distant places with the connection of a PVC pipe to the faucet in SUWS tap towers. Thus, more people are being benefitted from the technology.
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | increase or decrease | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ไม่ค่อยดี | |
| ฝนประจำปี | ลดลง | ไม่ค่อยดี |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ปานกลาง |
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Estimated maintenance and running costs could not be exactly calculated, but weighing down the pros with the costs; the benefits outweigh the costs.
6.6 การปรับตัว
เทคโนโลยีได้รับการปรับเปลี่ยนเมื่อเร็วๆนี้ เพื่อให้ปรับตัวเข้ากับสภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| Availability of clean source of drinking water is ensured. |
| Need to travel long distances to fetch water not prevalent due the the availability of taps with drinking water at household levels. |
| Water being used for various purposes like drinking, irrigation, domestic purposes, etc. |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| Water scarcity during arid and dry winters decreased if not stopped overall. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Water not available all year-round | By construction of another reservoir tank (RVT) |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Pipeline severely damaged due to lime | Lime treatment and changing of pipes to more resistant ones ( GI ) pipes instead of feeble PVC ones used |
| No specific committee / group set up to discuss the problems | Setting up water users' committee and donating a small sum per household every month that goes onto a fund, that can be later used to address various problems that may arise in the future. |
| Water being supplied for a single use only | upgrading the technology to Multiple Use Water Systems (MUWS) in place of Single-Use Water Systems (SUWS) could address the multiple uses of water users. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
> 10
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
> 1
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
15/06/2019
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล