Farmer Managed Natural Regeneration(FMNR) [กานา]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Joshua Adombire
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Tintuug lebge tii
technologies_6599 - กานา
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
วิทยากรหลัก
World Vision Regreening africa Project staff:
Adombire Joshua
World Vision
กานา
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Reversing land degradation in Africa by scaling-up Evergreen Agriculture (Regreening Africa)ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Not applicable (Not applicable) - สหรัฐอเมริกา1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The technology has empirically proven to have no adverse effects on land and any other agrarian venture
1.5 Reference to Questionnaire(s) on SLM Approaches (documented using WOCAT)

FMNR implementation approach [เคนยา]
After consultations with local stakeholders, experts (from NEMA, ICRAF, KFS, Wildlife Kenya) and Homabay County Government representatives the FMNR approach is being introduced by World Vision through a public funded project. The aim of the approach is to promote FMNR and sustainable land and natural resource management through disseminating the …
- ผู้รวบรวม: Thomas Kalytta
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
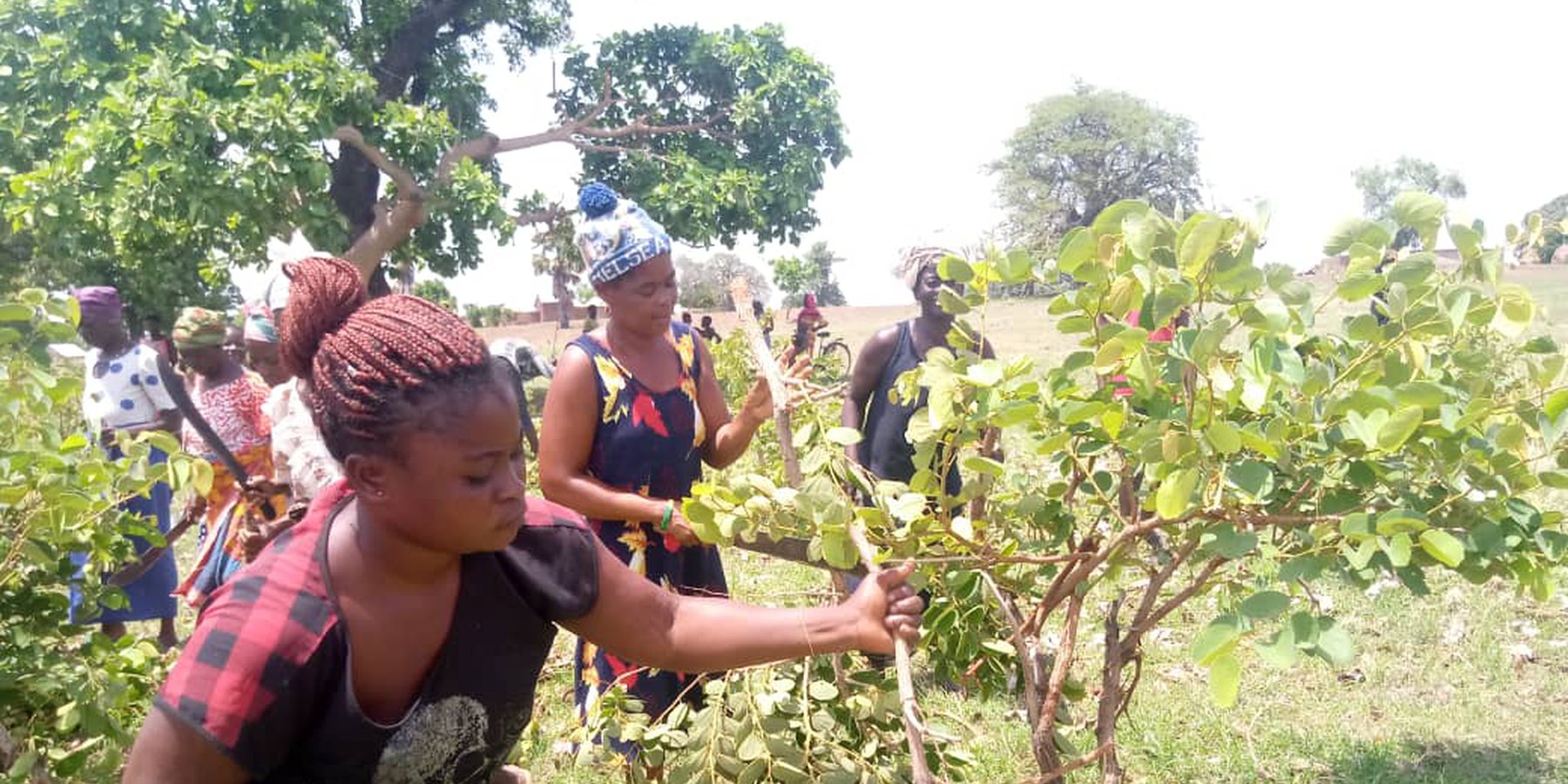
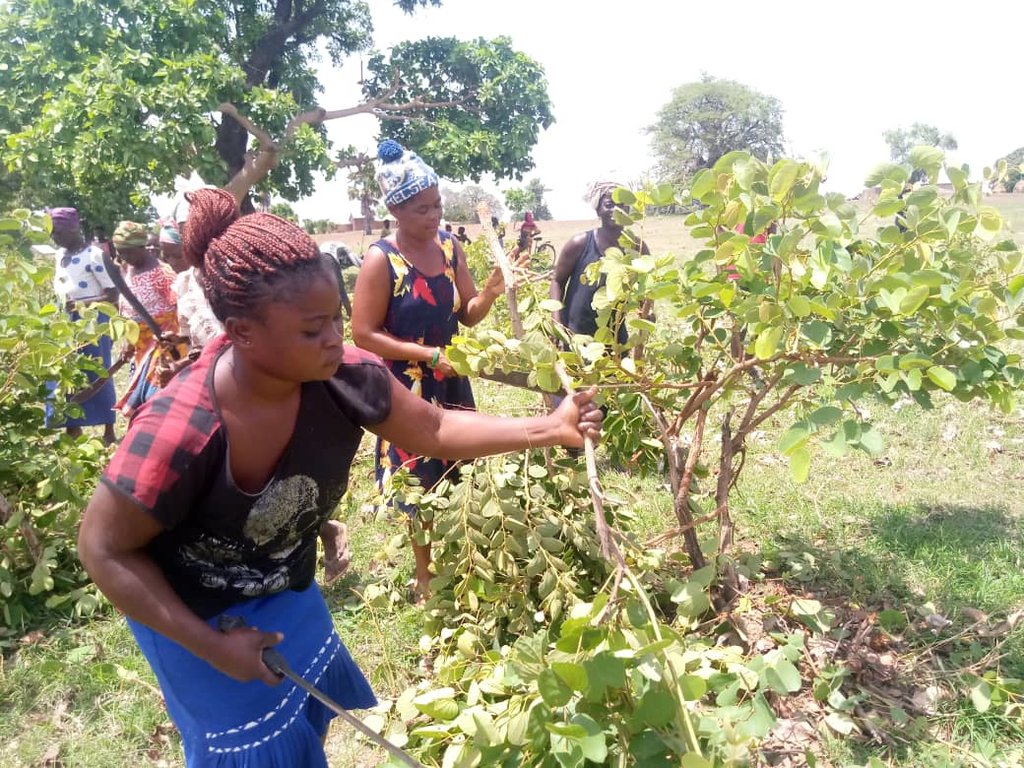
Farmer Managed Natural Regeneration (FMNR) comprises a set of practices used by farmers to encourage the growth of native trees on agricultural land by systematically allowing regeneration and managing trees and shrubs from tree stumps, roots and seeds.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
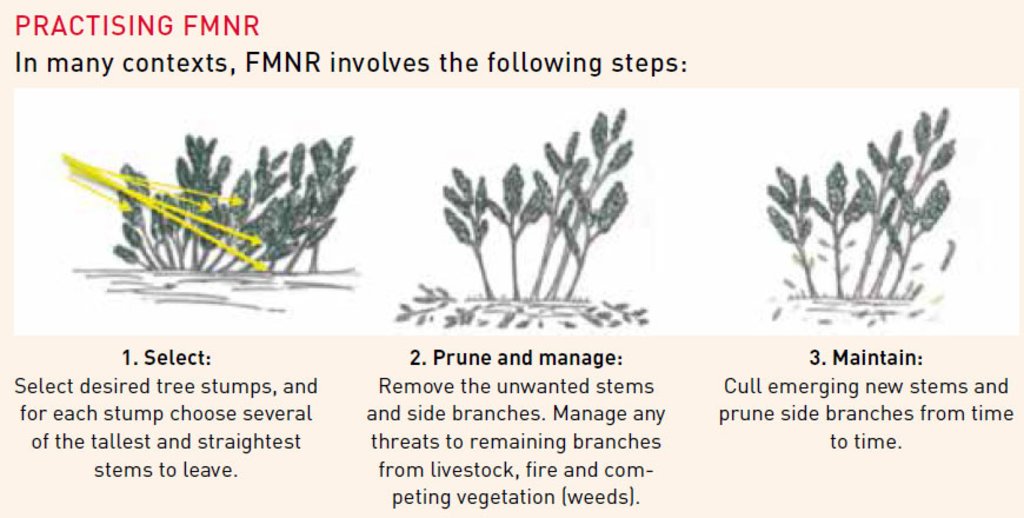
Farmer managed natural regeneration (FMNR) is an agroforestry practice that involves the deliberate protection and management of naturally regenerating woody vegetation by farmers on agricultural land. On farmland, selected trees are trimmed and pruned to manage their growth while promoting optimal growing conditions for annual crops (such as access to water and sunlight). Naturally it is a prerequisite that there should be evidence of sprouts from stumps or roots. FMNR is practiced through - but not limited to - the following:
1. Survey of the farm noting how many and what species of trees are present; In our project impact communities, the commonest indigenous tree species are Vitellaria paradoxa, Parkia biglobosa, Adansonia digitata, Piliostigma thonningii, Combretum spp, Diospyros mespiliformis, Lanea macrocarpa, Faidherbia albida, Acacia spp etc
2. Select the stumps of the desired species for regeneration; and
3. Select the best five or so stems and cull unwanted ones.
FMNR can restore degraded farmlands, pastures and forests by increasing the quantity and quality of woody vegetation, by increasing biodiversity and by improving soil structure and fertility through leaf litter and nutrient cycling. It has been reported in Senegal and Ghana in 2011 and 2012 that households practicing FMNR were less vulnerable to extreme weather shocks such as drought and damaging rain and windstorm. Conventional approaches to reversing desertification, such as tree planting, rarely spread beyond the project boundary once external funding is withdrawn. By comparison, FMNR is cheap, rapid, locally led and implemented. It uses local skills and resources – the poorest farmers can learn by observation and teach their neighbors. This technique is popular with land users because it is a low-cost and rapid sustainable land restoration technique. A well-established FMNR is succeeded by Farmer Managed Agroforestry (FMA) where farmers are cultivating annual crops as well are conserving indigenous tree species on the arable lands. Farmers go step ahead to do enrichment planting of preferred trees species such as Mangifera indica, Anacardium occidentale, Luceaena leucocephala etc.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบายภาพ:
Farmers are always excited to learn the technique since it is easy to do irrespective of the physique of the person.
2.4 วีดีโอของเทคโนโลยี
ความคิดเห็น/อธิบายสั้นๆ:
https://1drv.ms/v/s!AszYv0MhwVNji1-Kuo6kZRifcMzj?e=CMPcE0
วันที่:
17/12/2022
สถานที่:
Bawku West district
ชื่อผู้ถ่ายวีดีโอ:
Joshua Adombire
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
กานา
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Upper East
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Widnaba Community in Bawku West district
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- ใช้ ณ จุดที่เฉพาะเจาะจงหรือเน้นไปยังบริเวณพื้นที่ขนาดเล็ก
Is/are the technology site(s) located in a permanently protected area?
ไม่ใช่
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ระบุปีที่ใช้:
2017
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ด้วยการริเริ่มของผู้ใช้ที่ดินเอง
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
World Vision Regreening Africa Project
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- อนุรักษ์ระบบนิเวศน์
- รักษาสภาพหรือปรับปรุงความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านสังคมที่เป็นประโยชน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ใช่
Specify mixed land use (crops/ grazing/ trees):
- วนเกษตร (Agroforestry)

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
- การปลูกพืชยืนต้นที่ไม่มีเนื้อไม้
- การปลูกไม้ยืนต้น ไม้พุ่ม
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- cereals - maize
- cereals - millet
- cereals - rice (upland)
- legumes and pulses - beans
Annual cropping system:
Maize/sorghum/millet intercropped with legume
Tree and shrub cropping - Specify crops:
- cashew
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
Is intercropping practiced?
ใช่
If yes, specify which crops are intercropped:
Cashew -legumes, cashew- cereals, Teak- cereals, Mango- cereals etc
Is crop rotation practiced?
ใช่
ถ้าใช่ ระบุ:
Cereals and legumes,

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
Extensive grazing:
- กึ่งโนแมนดิซึ่มหรือแพสโตแรลลิซึ่ม (Semi-nomadism/pastoralism)
- Free range grazing
Animal type:
- cattle - dairy and beef (e.g. zebu)
- goats
- sheep
- Donkey
Is integrated crop-livestock management practiced?
ใช่
ถ้าใช่ ระบุ:
Farm residues are feed to animals and the dropping are used as manure for soil improvement. The animals are also used for farm work and other domestic works such as fetching water as in the case of donkeys
ผลิตภัณฑ์และบริการ:
- manure as fertilizer/ energy production
Species:
cattle - dairy and beef (e.g. zebu)

ป่า/พื้นที่ทำไม้
- ป่า/พื้นที่ทำไม้
- Community forests
Tree plantation, afforestation: Specify origin and composition of species:
- การปลูกหลายพันธุ์รวมกัน
Type of tree plantation, afforestation:
- tropical dry forest plantation
Type of tree:
- Acacia species
- Balanites aegyptiaca
- Tectona species
Are the trees specified above deciduous or evergreen?
- deciduous
ผลิตภัณฑ์และบริการ:
- ไม้ซุง
- ไม้ที่นำมาทำเป็นเชื้อเพลิง
- ผลไม้และถั่ว
- การแทะเล็มหญ้า / การเก็บกินหญ้า
- การป้องกันภัยธรรมชาติ
- Medicinal
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
N/A
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
- No (Continue with question 3.4)
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Some farmers dig out wells for vegetable farming in some communities
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การจัดการป่าธรรมชาติและกึ่งธรรมชาติ
- การจัดการสวนป่า
- การปลูกป่าร่วมกับพืช
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A1: พืช/สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
- A2: อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ความอุดมสมบูรณ์ในดิน
- A3: การรักษาหน้าดิน
A3: Differentiate tillage systems:
A 3.2: Reduced tillage (> 30% soil cover)

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V2: หญ้าและไม้ยืนต้น

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S1: คันดิน
- S6: กำแพง สิ่งกีดขวาง รั้วไม้ รั้วต่างๆ

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยการจัดการ
- M4: การเปลี่ยนแปลงช่วงเวลาให้เหมาะแก่การทำกิจกรรม
- M5: การควบคุมหรือการเปลี่ยนแปลงขององค์ประกอบของชนิดพันธุ์

มาตรการอื่น ๆ
ระบุ:
Mulching
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยลม
- Et (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบน

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cn (Fertility decline): ความอุดมสมบูรณ์และปริมาณอินทรียวัตถุในดินถูกทำให้ลดลงไป (ไม่ได้เกิดจากสาเหตุการกัดกร่อน)

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านกายภาพ
- Pc (Compaction): การอัดแน่น

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านชีวภาพ
- Bc (Reduction of vegetation cover): การลดลงของจำนวนพืชที่ปกคลุมดิน
- Bh (Loss of habitat): การสูญเสียแหล่งที่อยู่
- Bl (Loss of soil life): การสูญเสียสิ่งมีชีวิตในดิน
- Bp (Increase of pests/diseases): การเพิ่มขึ้นของศัตรูพืชและโรคพืช

การเสื่อมโทรมของน้ำ
- Ha (Aridification): การเกิดความแห้งแล้ง
- Hs (Change in quantity of surface water): การเปลี่ยนแปลงปริมาณของน้ำที่ผิวดิน

อื่น ๆ
ระบุ:
Acidification of water bodies
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ฟื้นฟูบำบัดที่ดินที่เสื่อมโทรมลงอย่างมาก
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
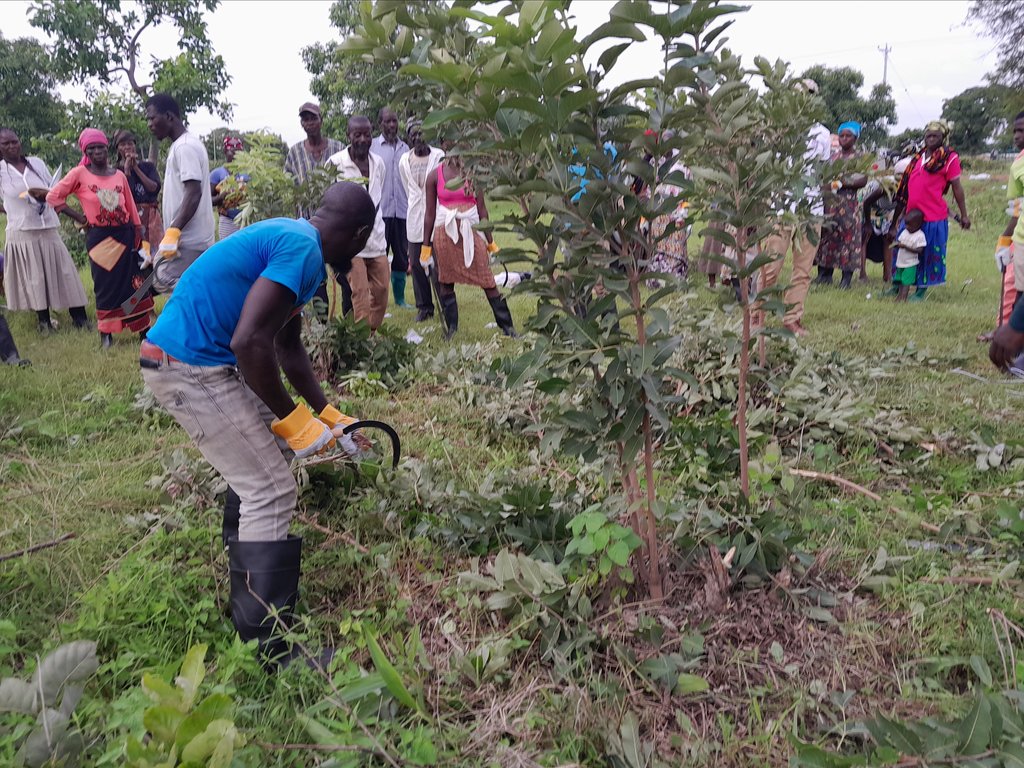
Where there are so many stands, depending on the species, some are culled leaving two to five stands of shrubs or stands. For edible fruit trees, it is recommended a single stem is left to facilitate quicker growth and fruiting.
When pruning, the cutting tool must be very sharp and cutting down upwards but not downwards to prevent tearing of the bark.
Stems must not be prune of side twigs to the apex but halfway up is recommended to give the plant more stability and opportunity for adequate photosynthesis
ผู้เขียน:
Van Schoubroeck, Frank (2018). Integrating trees in farming systems in Baringo County, Kenya reduced variability of food and fodder production.
วันที่:
17/12/2022
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อพื้นที่ที่ใช้เทคโนโลยี
ระบุขนาดและหน่วยพื้นที่:
10 acres
If using a local area unit, indicate conversion factor to one hectare (e.g. 1 ha = 2.47 acres): 1 ha =:
1 hectare= 2.5 acres
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
Cedis
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
13.9493
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
N/A
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Community entry | Any time except nights |
| 2. | Community mobilization | Any time except nights |
| 3. | Community sensitization | Any time except nights |
| 4. | Communities' selection of volunteers to be trained | Any time except nights |
| 5. | Training of volunteers on pruning and tree management | Any time except nights |
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Cutlass | piece | 40.0 | 33.0 | 1320.0 | |
| แรงงาน | Welligtoon boot | pair | 40.0 | 50.0 | 2000.0 | |
| แรงงาน | Communal labour | person | 40.0 | 30.0 | 1200.0 | |
| แรงงาน | Pruning knives | piece | 40.0 | 24.0 | 960.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Hand gloves | pair | 40.0 | 16.0 | 640.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Sickles | piece | 40.0 | 28.0 | 1120.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | N/A | |||||
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Natural shrubs | |||||
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | N/A | |||||
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | N/A | |||||
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 7240.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 519.02 | |||||
ถ้าผู้ใช้ที่ดินรับภาระน้อยกว่า 100% ของค่าใช้จ่าย ให้ระบุว่าใครเป็นผู้รับผิดชอบส่วนที่เหลือ:
The cost is covered by the projects
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Pruning of shrubs | Biweekly |
| 2. | Creation of fire belts | Every six months |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | N/A | |||||
| แรงงาน | Communal | person | 40.0 | 30.0 | 1200.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | N/A | |||||
| อุปกรณ์ | Cutlasses | piece | 40.0 | 33.0 | 1320.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Wellington boots | pair | 40.0 | 50.0 | 2000.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Sickles | piece | 40.0 | 28.0 | 1120.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Handgloves | pair | 40.0 | 16.0 | 640.0 | |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Pruning knives | piece | 40.0 | 24.0 | 960.0 | |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | N/A | |||||
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | N/A | |||||
| อื่น ๆ | N/A | |||||
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 7240.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 519.02 | |||||
ถ้าผู้ใช้ที่ดินรับภาระน้อยกว่า 100% ของค่าใช้จ่าย ให้ระบุว่าใครเป็นผู้รับผิดชอบส่วนที่เหลือ:
N/A
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
It must be noted that the cost of maintenance is bored totally by the community members after the project set up the intervention. Community members in consultation with their leaders procure their own working tools and plan their work schedules while project staff conduct periodic monitoring visits to provide technical backstopping.
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Increase in fuel prices and government tax affects cost of sickles, cutlasses, Wellington boots, pruning knives, food and snacks and T-shirts in the markets
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ระบุปริมาณน้ำฝนเฉลี่ยรายปี (ถ้ารู้) :หน่วย ม.ม.
956.00
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
The area experience unimodal rainfall that lasts 4-6 months in a year
ระบุชื่อของสถานีตรวดวัดอากาศที่ใช้อ้างอิงคือ:
Ghana Meteorological Agency
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งชุ่มชื้น
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- ไม่เกี่ยวข้อง
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
The area is dominated by low lying areas with high water tables. These areas are usually used for rice cultivation and dry season gardening
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
เนื้อดินล่าง (> 20 ซ.ม.ต่ำจากผิวดิน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
<5 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ดี
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ดี
Water quality refers to:
ground water
ความเค็มของน้ำเป็นปัญหาหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
กำลังเกิดน้ำท่วมในพื้นที่หรือไม่:
ใช่
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ปานกลาง
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งที่อยู่:
- ปานกลาง
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน:
- อยู่กับที่
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- 10-50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- ยากจนมาก
- จน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
- กลุ่ม/ชุมชน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
- การใช้กำลังจากสัตว์
เพศ:
- หญิง
- ชาย
อายุของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
- ผู้เยาว์
- วัยกลางคน
- ผู้สูงอายุ
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดกลาง
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- เป็นแบบชุมชนหรือหมู่บ้าน
- รายบุคคล ไม่ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เช่า
- รายบุคคล
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
- รายบุคคล
Are land use rights based on a traditional legal system?
ใช่
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
land is either bequeathed or leased out to for use
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
200kg of grains per acre
หลังจาก SLM:
200-400 kg of grain per acre
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
FMNR together with appropriate land preparation and improved agronomic practices promoted by the project have resulted in increased soil productivity
คุณภาพพืชผล
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
N/A
หลังจาก SLM:
N/A
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Interventions such as post-harvest loss management trainings facilitated by the project have resulted in increased quality of farm produce.
การผลิตพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
Scarce
หลังจาก SLM:
Available
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Through enrichment planting of browse tree species such as Leucaena, Albizia, there's availability of fodder for animals
คุณภาพพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
Scarce
หลังจาก SLM:
Available
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
There are Faidherbia, Lecaena, Albizia as protein and vitamin source for ruminants in the communities
การผลิตสัตว์
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
Few (about 1 ruminants)
หลังจาก SLM:
2-3 ruminants per household
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The project supported vulnerable house households with at least two she- goats each to keep for their well -being
การผลิตไม้
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
N/A
หลังจาก SLM:
N/A
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Prunings serve as readily available firewood. Some bigger branches are also pruned for use. Introduction of fast-growing tree species such as Tectona grandis enables farmer easily harvest wood
คุณภาพป่า /พื้นที่ทำไม้
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
Maximum 1
หลังจาก SLM:
At least 2
การผลิตของจากป่าทุกชนิดยกเว้นไม้
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
N/A
หลังจาก SLM:
N/A
การเสี่ยงต่อความล้มเหลวในการผลิต
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
FMNR on farms create micro-climate which helps in preventing total crop failure.
ความหลากหลายของผลิตภัณฑ์
พื้นที่สำหรับการผลิต
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
0.5 acre
หลังจาก SLM:
1 acre
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The project supports vulnerable families with improved maize and cowpea seeds in the cropping seasons to farm at least an acre of land
การจัดการที่ดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
N/A
หลังจาก SLM:
N/A
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Through trainings on appropriate land preparations, good agronomic practices etc there has been improvement in land management techniques.
การผลิตพลังงาน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
N/A
หลังจาก SLM:
N/A
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
With the introduction of energy efficient cooking stoves, less fuel wood is used to generate more long-lasting heat for cooking and other domestic uses
ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
การมีน้ำดื่มไว้ให้ใช้
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
N/A
หลังจาก SLM:
N/A
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Water bodies experience less siltation and also last longer before drying up than before the technology
คุณภาพน้ำดื่ม
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
N/A
หลังจาก SLM:
N/A
การมีน้ำไว้ให้ปศุสัตว์
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
N/A
หลังจาก SLM:
N/A
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
There's availability of clean surface water for livestock for especially loner duration of the dry season
คุณภาพน้ำสำหรับปศุสัตว์
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
N/A
หลังจาก SLM:
N/A
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Surface water bodies are less contaminated by debris from the environment dure to sequestration by trees
การมีน้ำไว้ให้สำหรับการชลประทาน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
N/A
หลังจาก SLM:
N/A
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
There's availability of more surface water bodies for irrigation purposes
คุณภาพน้ำสำหรับการชลประทาน
ความต้องการน้ำจากการชลประทาน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
N/A
หลังจาก SLM:
N/A
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
There's less surface water contamination
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ค่าใช่จ่ายของปัจจัยการผลิตทางการเกษตร
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
N/A
หลังจาก SLM:
N/A
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Little or no expenditure on soil fertility improvement fertilizers
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
N/A
หลังจาก SLM:
N/A
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Less inputs with resultant increased yields result in increased farmers income
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งผลิตรายได้
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
1
หลังจาก SLM:
2
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Farmers can now rear livestock in addition to crops for diverse income sources
ความเหลื่อมล้ำทางเศรษฐกิจ
ภาระงาน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
N/A
หลังจาก SLM:
N/A
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
There's some form of release on workload as less time and distance is made in collecting fuelwood.
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
ความมั่นคงด้านอาหาร / พึ่งตนเองได้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Increased in productivity for the peasant farmers ensures food security and some sort of self-sufficiency as some of the produce could be sold to meet other family needs.
สถานการณ์ด้านสุขภาพ
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
N/A
หลังจาก SLM:
N/A
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Food availability, access and utilization leads to improved nutrition and ultimately improvement in health conditions for the farmers.
การใช้ที่ดิน / สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
โอกาสทางวัฒนธรรม
โอกาสทางด้านสันทนาการ
สถาบันของชุมชน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The technology facilitates community to put in place structures towards environmental governance
สถาบันแห่งชาติ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The technology is gradually creeping into the government environmental protection and farming policies.
การบรรเทาความขัดแย้ง
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
N/A
หลังจาก SLM:
N/A
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Formation of community committees to spearhead land restoration approaches have reduce conflicts in communities.
สถานการณ์ของกลุ่มด้อยโอกาส ทางด้านสังคมและเศรษฐกิจ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The disadvantage in the communities have been supported with seeds and livestock for their welfare
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
ปริมาณน้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
There's minimal runoff due to increase in tree population on the environment
คุณภาพน้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
There's less of acid rains due to carbon sequestration by trees in the atmosphere
การเก็บเกี่ยวหรือการกักเก็บน้ำ
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
การระบายน้ำส่วนเกิน
การระเหย
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Increased in soil organic Carbon (SOC) build up and leaf litter serves as mulch and retains soil moisture for longer period.
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Increased in tree density, SOC protects soil from adversaries
การสูญเสียดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
N/A
หลังจาก SLM:
N/A
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
There less soil loss as soil erosion and other harmful environmental agents are checked
การสะสมของดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
N/A
หลังจาก SLM:
N/A
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
SOC builds up the topsoil layer of the soil
การเกิดแผ่นแข็งที่ผิวดิน /การเกิดชั้นดาน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
N/A
หลังจาก SLM:
N/A
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
There's less soil sealing as a result of appropriate land preparation and good agronomic practices the technology promotes .
การอัดแน่นของดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
There's less soil sealing as a result of appropriate land preparation the technology promotes.
การหมุนเวียนและการเติมของธาตุอาหาร
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Improved
ความเค็ม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The technology promotes less use of NPK fertilizers thereby reducing soil salinity
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ต่ำกว่าดินชั้น C
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
N/A
หลังจาก SLM:
N/A
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Leaf litter increases soil organic matter content in the soil
ความเป็นกรด
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
N/A
หลังจาก SLM:
N/A
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
There is sequestration of acid forming gases by trees thereby reducing acidity
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
การปกคลุมด้วยพืช
มวลชีวภาพ/เหนือดินชั้น C
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืช
พืชพันธุ์ต่างถิ่นที่รุกล้ำเข้ามา
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
There's reduction in invasive alien species as they are culled in FMNR technology
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของสัตว์
ชนิดพันธุ์ที่ให้ประโยชน์
ความหลากหลายของสัตว์
การจัดการศัตรูพืชและโรคพืช
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
ผลกระทบจากน้ำท่วม
ดินถล่ม/ ซากต่าง ๆ ที่ถูกพัดพามา
ผลกระทบจากภัยแล้ง
ผลกระทบของพายุไซโคลน พายุฝน
การปล่อยคาร์บอนและก๊าซเรือนกระจก
ความเสี่ยงจากไฟ
ความเร็วของลม
ภูมิอากาศจุลภาค
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
น้ำที่ใช้ประโยชน์ได้
การไหลของน้ำคงที่และสม่ำเสมอในช่วงฤดูแล้ง
น้ำท่วมพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
การทับถมของดินตะกอนพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
การเกิดมลพิษในน้ำบาดาลหรือแม่น้ำ
ความสามารถต้านทานการเปลี่ยนแปลง / ความสามารถในการคัดกรอง
ตะกอนที่ถูกพัดพามาโดยลม
ความเสียหายต่อพื้นที่เพาะปลูกของเพื่อนบ้าน
ความเสียหายต่อโครงสร้างพื้นฐานของรัฐหรือของเอกชน
ผลกระทบของก๊าซเรือนกระจก
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | increase or decrease | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ปานกลาง | |
| อุณหภูมิตามฤดูกาล | ฤดูแล้ง | เพิ่มขึ้น | ปานกลาง |
| ฝนประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดีมาก | |
| ฝนตามฤดู | ฤดูฝน | เพิ่มขึ้น | ปานกลาง |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุเขตร้อน | ปานกลาง |
| พายุหมุนนอกเขตร้อน | ไม่ทราบ |
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ดีมาก |
| พายุฝนฟ้าคะนองประจำท้องถิ่น | ดีมาก |
| พายุลูกเห็บประจำท้องถิ่น | ไม่ทราบ |
| พายุหิมะประจำท้องถิ่น | ไม่ทราบ |
| พายุทรายหรือพายุฝุ่นประจำท้องถิ่น | ไม่ทราบ |
| พายุลมประจำท้องถิ่น | ดีมาก |
| พายุทอร์นาโดประจำท้องถิ่น | ไม่ทราบ |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| คลื่นความร้อน | ดีมาก |
| คลื่นความหนาว | ดีมาก |
| สภาพอากาศฤดูหนาวที่รุนแรง | ไม่ทราบ |
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ปานกลาง |
| ไฟป่า | ปานกลาง |
| ไฟบนบก | ปานกลาง |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมตามปกติ (แม่น้ำ) | ปานกลาง |
| น้ำท่วมฉับพลัน | ปานกลาง |
| น้ำขึ้นจากพายุหรือน้ำท่วมชายฝั่ง | ไม่ทราบ |
| ดินถล่ม | ไม่ทราบ |
| หิมะถล่ม | ไม่ทราบ |
ภัยพิบัติทางชีวภาพ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| โรคระบาด | ปานกลาง |
| การบุกรุกของแมลง / หนอน | ปานกลาง |
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- > 50%
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
0ver 100 households
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 51-90%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
These spontaneous adopters used their own locally tools in practices the technology on their own arable lands due to the anticipated benefits of the technology
6.6 การปรับตัว
เทคโนโลยีได้รับการปรับเปลี่ยนเมื่อเร็วๆนี้ เพื่อให้ปรับตัวเข้ากับสภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| It is easy to adopt and adapt |
| It has no negative effects on agriculture |
| It is the appropriate approach to resorting biodiversity in communities |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| The technology is low cost, very effective and every community is endowed with the natural resources to practice it |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| It requires entire community by-in for a start-up | Communities are better sensitized and educated on the technology |
| Difficulty in getting tools and materials for pruning | Projects support with cutlasses, knives, sickles, safety gears to work |
| Indiscriminate cutting and wildfires retard the regeneration of trees | Community fire stewards and extensive sensitizations on wildfires and bye- laws on environmental management are being enforced |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Practitioners at times depend so much on projects to support them sustain the technology on communal lands | More training on sustainability after projects |
| Burning of farmlands deprives arable lands of shrubs and saplings to practice the technology | Intensification of trainings on appropriate land preparation technologies. |
| Invasive species such as Leucaena, teak etc taking over community forests | Culling out of invasive species in community forests |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
400
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
20
- การสัมภาษณ์ผู้เชี่ยวชาญด้าน SLM หรือผู้ชำนาญ
15
- การเก็บรวบรวมมาจากรายงานและเอกสารที่มีอยู่
10
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
4.Diagne, M., 2012, "Evaluation Finale du Projet Beysatol", World Vision Senegal.The social, environmental and economic benefits of Farmer Managed Natural Regeneration: R Francis, P Weston, J Birch - World Vision Australia, 2015 - worldvision.org, Assessing social equity in farmer-managed natural regeneration (FMNR) interventions: findings from ghana M Kandel, G Agaba, RS Alare, T Addoah… - Ecological …, 2021 - er.uwpress.org
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Google Scholar
7.3 Links to relevant online information
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Farmer-managed natural regeneration. (2022, November 4).
URL:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Farmer-managed_natural_regeneration
7.4 General comments
The Questionnaire needs to be treated as a research work with the relevant experts to populate the data
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์

FMNR implementation approach [เคนยา]
After consultations with local stakeholders, experts (from NEMA, ICRAF, KFS, Wildlife Kenya) and Homabay County Government representatives the FMNR approach is being introduced by World Vision through a public funded project. The aim of the approach is to promote FMNR and sustainable land and natural resource management through disseminating the …
- ผู้รวบรวม: Thomas Kalytta
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล