Zero Tillage [智利]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Carlos Ruiz
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger
approaches_2655 - 智利
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与方法评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
SLM专业人员:
有助于对方法进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Instituto de Investigaciones Agropecuarias (INIA) (Instituto de Investigaciones Agropecuarias (INIA)) - 智利有助于对方法进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Asociación para la Diversificación y el Desarrollo Agricultural Comunal (ADDAC) - 尼加拉瓜1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM方法的描述
2.1 该方法的简要说明
Zero tillage approch was developed to protect the soil of de rainfall
2.2 该方法的详细说明
该方法的详细说明:
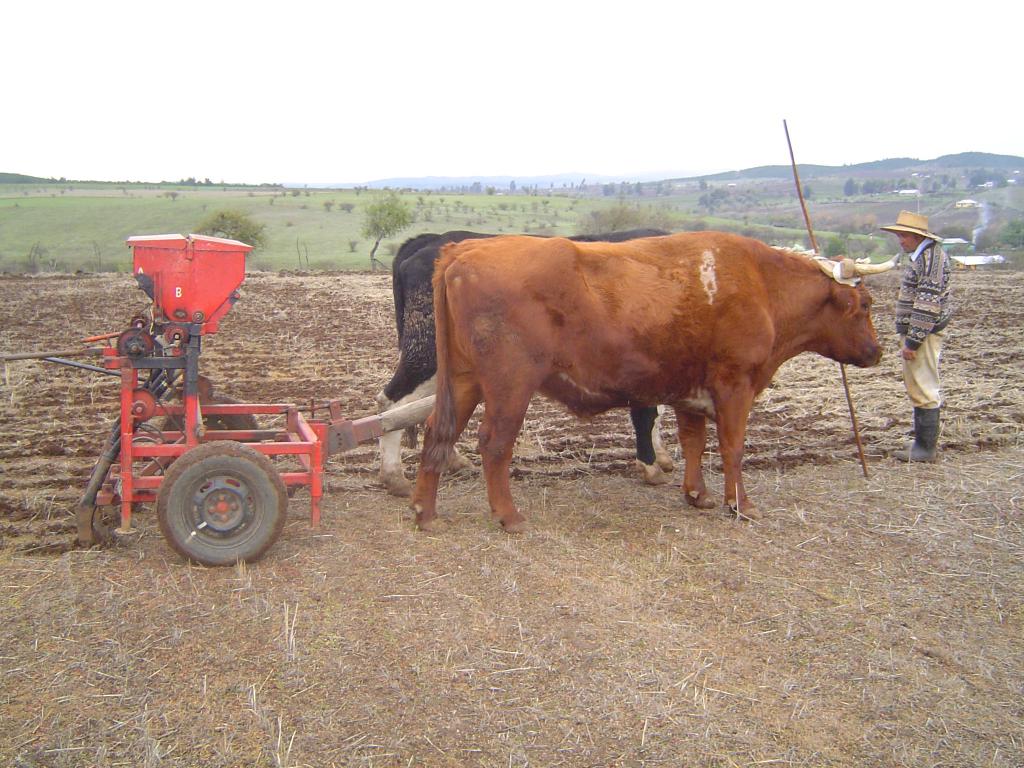
Methods: Zero tillage is realized with a crop rotation cereal-pastures, with elimination of traditional fire practices and fallow, supported with organic manure, zero tillage practice (horse drawn tillage and with machinery).
2.3 该方法的照片
2.5 采用该方法的国家/地区/地点
国家:
智利
区域/州/省:
Chilán, Chile
Map
×2.6 该方法的开始和终止日期
终止年份(若不再采用该方法):
2009
2.8 该方法的主要目的/目标
The Approach focused mainly on other activities than SLM (Zero tillage, dry and semi-dry land)
To apply conservation tillage for agricultural development.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: Social conflict and low knowledge in agricultural machinary.
2.9 推动或妨碍实施本办法所适用的技术的条件
社会/文化/宗教规范和价值观
- 阻碍
Traditions
Treatment through the SLM Approach:
法律框架(土地使用权、土地和水使用权)
- 阻碍
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights moderately hindered the approach implementation The research was successfull but with difficult in the applicatio
了解SLM,获得技术支持
- 阻碍
Lack of knowledge in agricultural machinery
Treatment through the SLM Approach:
3. 相关利益相关者的参与和角色
3.1 该方法涉及的利益相关者及其职责
- 当地土地使用者/当地社区
Cultural differences. Ussually women work at home although women participated in planning decissions
- NGO
- 国家政府(规划者、决策者)
- 国际组织
如果涉及多个利益相关者,请注明领导机构:
Was conisedered the integration and consideration of the gender.
3.2 当地土地使用者/当地社区参与该方法的不同阶段
| 当地土地使用者/当地社区的参与 | 指定参与人员并描述活动 | |
|---|---|---|
| 启动/动机 | 互动 | |
| 计划 | 互动 | |
| 实施 | 互动 | |
| 监测/评估 | 互动 | |
| Research | 互动 |
3.4 有关SLM技术选择的决策
具体说明谁有权决定选择要实施的技术:
- 主要是SLM专家,咨询土地使用者之后
解释:
From the interaction between japanesse experience and chilean expertise
4. 技术支持、能力建设和知识管理
4.1 能力建设/培训
是否为土地使用者/其他利益相关者提供培训?:
是
培训形式:
- 课程
涵盖的主题:
25 chilean professionals were trainning in Japan (short courses of 1 month).
4.2 咨询服务
土地使用者有权使用咨询服务吗?:
是
指明是否提供了咨询服务:
- 在土地使用者的土地上
- 在固定中心
说明/注释:
Name of method used for advisory service: In situ demonstration and trainning; Key elements: Demonstration, Farmer visit
Advisory service is quite adequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities; Chilean agricultural politics give to the farmers big part of the responsability, after a powerfull support from the government.
4.3 机构强化(组织发展)
是否通过这种方法建立或加强了机构?:
- 是,适度
具体说明机构的强化或建立程度:
- 本地
4.4 监测和评估
监测和评估是该方法的一部分吗?:
是
注释:
technical aspects were monitored through observations
socio-cultural aspects were monitored through observations
economic / production aspects were monitored through observations
There were many changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: Technical recommendation were improve (cultives and machine)
4.5 研究
研究是该方法的一部分吗?
是
提供进一步的细节,并指出是谁做的研究:
The institutions were mainly focused on physical soil structure, increasing yield and water conservation
Research was carried out both on station and on-farm
5. 融资和外部物质支持
5.1 该方法中SLM组成部分的年度预算
如果不知道准确的年度预算,请给出一个范围:
- > 1,000,000
注释(例如主要的资助来源/主要捐助者):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: international (tillage machine): 25.0%; government (incentive): 25.0%; local community / land user(s) (land and working): 50.0%
5.2 为土地使用者提供财政/物质支援
土地使用者是否获得实施该技术的财政/物质支持?:
是
5.3 对特定投入的补贴(包括劳动力)
- 农业
| 具体说明哪些投入得到了补贴 | 程度如何 | 对补贴做出具体说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 种子 | 部分融资 | |
如果土地使用者的劳动力是一项重要的投入,那么是不是:
- 自愿
注释:
Active participation of farmers.
5.4 信用
是否根据SLM活动的方法给予信用值?:
否
6. 影响分析和结论性陈述
6.1 方法的影响
该方法是否帮助土地使用者实施和维护SLM技术?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
Improvement the soil infiltration and mitigation soil erosion
该方法是否改善了阻碍SLM技术实施的土地使用权/用户权问题?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
Social problems The problem is likely to be overcome in the near future. Farmers prefer personal solution.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
It was observed that the adoption of the technology depend from the market (prices)
6.2 土地使用者实施SLM的主要动机
- 减少工作量
- 支付/补贴
- 加入运动/项目/团体/网络
6.3 方法活动的可持续性
土地使用者能否维持通过该方法实施的措施(无外部支持的情况下)?:
- 不确定
6.4 该方法的长处/优点
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| technology behaviour (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: it depends) |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| productives (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: financial support from the government) |
| economic (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: insumes (uncertainty costs).) |
6.5 该方法的弱点/缺点以及克服它们的方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Machinary and fertilizers | High costs |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Machinary and fertilizers | High costs |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 方法/信息来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与土地使用者的访谈
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块