2.1 该方法的简要说明
Regulations and financial grants for reduction of pollution and promotion of the cultural landscape.
2.2 该方法的详细说明
该方法的详细说明:
Aims / objectives: The Regional Environmental Program (RMP) is a part of the Regional Rural Development Program provided by County Governors, in this case the County Governors of Østfold and Akershus. The programs differ somewhat between counties and the one for Østfold is used as an example here. The program aims to target environmental efforts in the agricultural sector, mainly focusing on
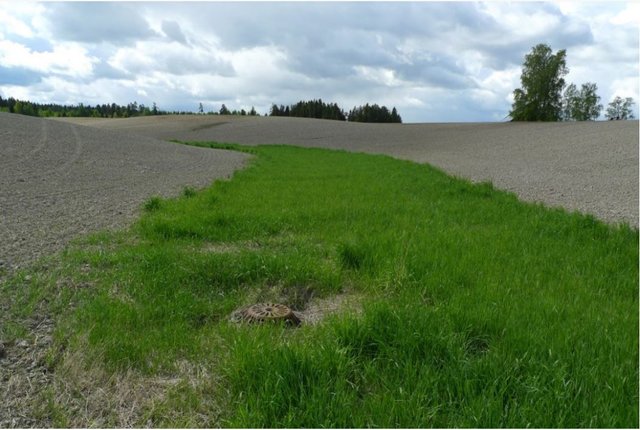
agricultural runoff, reduced usage of pesticides, cultural landscapes, biological diversity, cultural monuments and environments, outdoor recreation and availability. Measures related to reduction of runoff from agricultural land to waterbodies has resent years been given the highest priority, and the greatest part of the financial grants. Improvement of soil structure to maintain soil functions and prevention of soil loss and nutrient leaching, are some of the main goals of the approach.
Methods: Management plans and local regulations for different catchments are implemented through the Regional Environmental Program. Funds to finance measures are provided from both this program and other sources, such as the Grant Scheme for Special Agricultural Environmental Measures (SMIL). The latter is allocated by the County Governor and managed by local municipalities. In order to receive production subsidies the land users have to carry out the regulation measures. In areas of
prioritized watercourses the soil tillage regulations are stricter, and the financial support higher. Around especially vulnerable waterbodies the measures are compulsory. Agricultural areas are classified by their susceptibility to water erosion (four erosion risk classes), with different soil management requirements. High erosion risk classes normally provide higher grant rates.
Stages of implementation: The Regional Environmental Program was first introduced in 2005, followed by a rollover in 2009. It
was at the agricultural settlement in 2012 decided to continue the program in the same path as settled in 2004/2005, with improvements from the evaluation in 2007/2008 and 2011. The County Governor continues the ongoing work of targeting the economical funds to measures of high environmental benefit. The Regional Environmental Program is also influenced by guidelines from the National Environmental Program of 2013-2016. Random controls are carried out and falsely reported measures lead to reduction and repayment of production grants.
Role of stakeholders: The farmers are mainly conducting the measures by changing their land use practices, but the Regional
Environmental Program is developed in collaboration between municipalities, the county, the Farmers’ Organization, industry, and the County Governor. The measures are revised annually, mainly based on inputs from the Farmers’ Organization and the municipality. Other measures are included by the Regional Environmental Program than shown in the QT (Grass Covered Riparian Buffer Strips and Reduced Tillage), but these were evaluated to be less relevant for the prevention of soil loss.
Other important information: Other measures are included by the Regional Environmental Program than shown in the QT (Grass Covered Riparian Buffer Strips and Reduced Tillage), but these were evaluated to be less relevant for the prevention of soil loss.
For more information: http://www.fylkesmannen.no/en/Ostfold/Agriculture-and-food/Environmental-measures/Tilskudd-til-regionale-miljotiltak-RMP-2014/ (In Norwegian only)
Regional regulations: https://lovdata.no/dokument/JB/forskrift/2011-06-01-716?q=morsa
2.3 该方法的照片
2.5 采用该方法的国家/地区/地点
2.6 该方法的开始和终止日期
2.7 方法的类型
2.8 该方法的主要目的/目标
The Approach focused on SLM only
Target the environmental initiatives and provide increased visibility.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: Agricultural runoff and erosion, usage of pesticides, degradation of cultural landscapes, loss of biological diversity, degradation of cultural monuments and environments, decreased availability to outdoor recreational areas.
2.9 推动或妨碍实施本办法所适用的技术的条件
财务资源和服务的可用性/可得性
Measures may lead to income loss for land users.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Financial grants.
法律框架(土地使用权、土地和水使用权)
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights hindered a little the approach implementation Not all land users implemented the technologies.
工作量、人力资源可用性
The workload may increase with land use changes and implementation of erosion risk classes and regulations.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Higher financial grants for high risk areas.