Vegetated Fanya juu [埃塞俄比亚]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Unknown User
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger
Ye Masa Erken (Amharic)
technologies_1074 - 埃塞俄比亚
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
SLM专业人员:
Fikadu
0465553936
SNNPR, Omo Sheleko Agricultural and Rural Development Office
Mudula
埃塞俄比亚
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
SNNPR Bureau of Agriculture - 埃塞俄比亚1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
30/05/2011
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.5 请参阅有关SLM方法的问卷

Incentive based CCPPA [埃塞俄比亚]
The participation of the communities in the planning implementation and evaluation of SWC activities and provided with food for work as an insentive to encourage participation.
- 编制者: Daniel Danano
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
A terrace constructed along the contour with the embankment above the basin to prevent/control or reduce runoff.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
The technology is integrated with cutoff drain, stablized by grass and trees and also integrated with some agronomic measures such as inter cropping, crop rotation and green manuring.
Purpose of the Technology: It aims at controlling runoff velocity and soil erosion, changes the slope inclination, recharge ground water, conserve soil moisture and increase the productivity per unit of land.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: It is done or maintained on self-help bases. When the basin is filled up with sediment or it is damaged by over flowing of runoff, repair work is undertaken.
Natural / human environment: It is environmentaly sound, conducive and accepted by the communit
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
埃塞俄比亚
区域/州/省:
NNNPR/Kembata Tembaro Zone
有关地点的进一步说明:
Omo Sheleko woreda
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
from expriences in other countries and also other woredas in the country.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
- 多年一作(非木材)
主要农作物(经济作物及粮食作物):
Major cash crop annual cropping: Teff, wheat
Major food crop annual cropping: sorghum, maize
Major cash crop perennial (non-woody) cropping: Coffee
Major food crop perennial (non-woody) cropping: Fruit trees
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Low soil fertility, land degradation, decline in productivity.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Productivity has highly declined, high amounts of inputs required to improve the soil fertility.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Teff - Maize - Beans - Sweet potato
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 240 Longest growing period from month to month: Mar - Oct Second longest growing period in days: 180 Second longest growing period from month to month: Jun - Dec
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 横坡措施
3.5 技术传播
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 15.18 m2.
The technology is integrated with different biological measures such as bund stablized by grass, legumes and tree species and supplimented with cutoff drain.
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
注释:
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation, rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
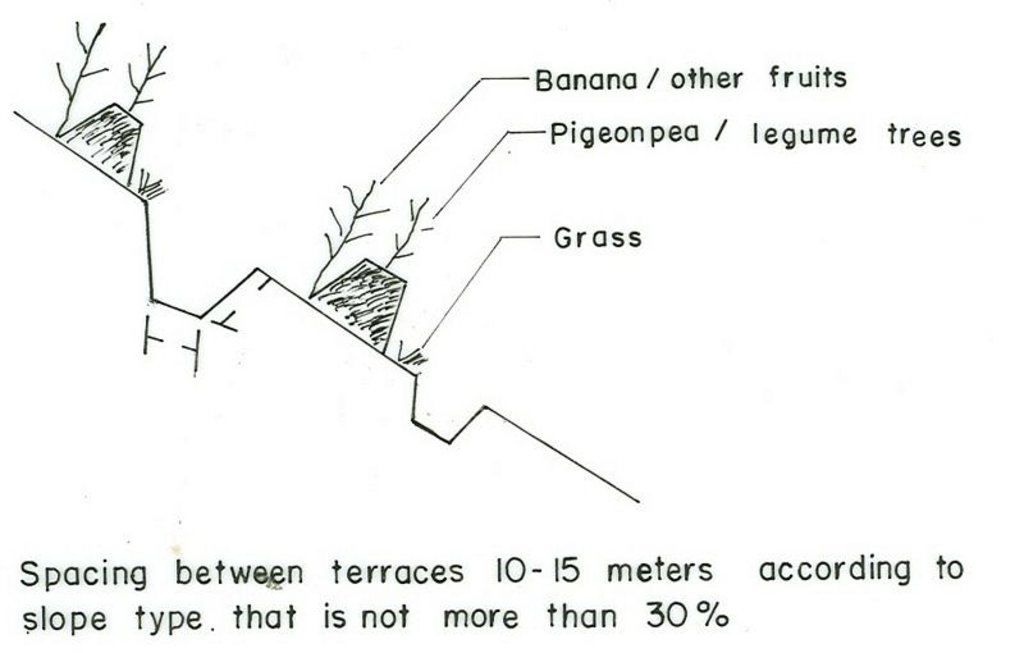
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
SNNPR
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap
Secondary technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, water harvesting / increase water supply
Early planting
Material/ species: maize, teff
Remarks: broad casting, row planting
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: maize with beans
Quantity/ density: 25kg/ha
Remarks: row planting
Agronomic measure: sweet potato
Quantity/ density: 55000
Legume inter-planting
Remarks: row planting
Contour tillage
Remarks: furrow formation
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: G : grass
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1m
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 7m
In blocks
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, F : fruit trees / shrubs
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 33
Trees/ shrubs species: sesbania, Shinus molle
Fruit trees / shrubs species: mango, avocado, papaya
Perennial crops species: coffee
Grass species: elephant grass, phalaris
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 8.00%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 0.00%
Diversion ditch/ drainage
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.75
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.5
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 300
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.75
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1.2
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 300
Bund/ bank: level
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1-1.5
Spacing between structures (m): 10-20
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 100
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.6
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1.2m
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 100
Construction material (earth): At the time of ditch construction, the excavated soil is used to make the embankment.
Construction material (stone): Stones are used for ditch pavement
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 20%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 0%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Other type of management: change of management / intensity level
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Birr
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
8.6
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
0.70
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Collecting of planting materials (seeds) | 植物性的 | during rainy season |
| 2. | Planting on bunds | 植物性的 | during rainy season |
| 3. | Cultivation | 植物性的 | during rainy season |
| 4. | Fencing | 植物性的 | during rainy season |
| 5. | Survey | 结构性的 | dry season |
| 6. | Layout | 结构性的 | dry season |
| 7. | Constructing the terrace | 结构性的 | dry season |
| 8. | Stablization of terrace | 结构性的 | rain season |
| 9. | control grazing | 管理 |
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 140.0 | 140.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Person days | ha | 1.0 | 29.0 | 29.0 | |
| 设备 | Animal traction | ha | 1.0 | 101.0 | 101.0 | |
| 设备 | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 47.0 | 47.0 | |
| 植物材料 | Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 24.0 | 24.0 | |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Fertilizer | ha | 1.0 | 55.0 | 55.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 396.0 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Land preparation | 农业学的 | before and onset of rains / each cropping season |
| 2. | Planting/Sowing | 农业学的 | during rains / each cropping season |
| 3. | Weeding | 农业学的 | during rains / each cropping season |
| 4. | Harvesting | 农业学的 | dry season / each cropping season |
| 5. | Replanting | 植物性的 | rainy season /as needed |
| 6. | Replanting | 结构性的 | rainy season/annual |
| 7. | Sediment removal | 结构性的 | offset of rain/annual |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 14.0 | 14.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Person days | ha | 1.0 | 29.0 | 29.0 | |
| 设备 | Animal traction | ha | 1.0 | 101.0 | 101.0 | |
| 植物材料 | Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 24.0 | 24.0 | |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Fertilizer | ha | 1.0 | 55.0 | 55.0 | |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 223.0 | |||||
注释:
Machinery/ tools: Shovel and hoe
The cost estimation is made for 1 km length bund in a hectare of land planted with maize.
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Labour cost increases or decreases per hectare of land depending on land form, type and depth of the soil. Cost of construction with increase in slope.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
900-1400 mm, in good years rains up to 1440 mm are received, quite good enough for perennial crops such as Enset, coffee and fruit trees.
农业气候带
- 潮湿的
- 半湿润
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Altitudinal zone: 1501-2000 m a.s.l. ( over 70% falls in this category, ranked 1), 2000-2500 m a.s.l. (ranked 2) and 1001-1500 m a.s.l. as well as 2501-3000 m a.s.l. (both ranked 3)
Landforms: Ridges (ranked 2) and mountain slopes as well as valley floors (both ranked 3)
Slopes on average: Hilly (soils have better fertility, ranked 1), rolling (ranked 2) and moderate (ranked 3)
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil depth on average: Moderately deep (most of the soils (60%) have moderately deep soils, ranked 1), deep (25 % SWC area, ranked 2) and shallow (soils on steep slopes (15%), ranked 3)
Soil fertility: Low (continuous cropping-long period cultivation, ranked 1), very low (shallow soils, ranked 2) and medium (ranked 3)
Topsoil organic matter: Low (no crop yield with out fertilizers applied, ranked 1), medium (ranked 2) and high (flat slopes and around harvested, ranked 3)
Soil water storage capacity: High (ranked 1), very high (ranked 2) and medium (ranked 3)
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
- 混合(生计/商业
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 非常贫瘠
- 贫瘠
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 畜力牵引
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
20% of the land users are average wealthy and own 40% of the land (own few livestock).
45% of the land users are poor and own 25% of the land (have small land holding).
35% of the land users are poor and own 35% of the land (no/too little land, no property).
Off-farm income specification: Most of the people in the area are engaged in agricultural activities and only few people are engaged on off-farm activities.
Level of mechanization: Animal traction (most of the land users, ranked 1) and manual work (few land useres, ranked 2)
Market oriantation cropland: Subsistence (The produce is only enough for family consumption)
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
注释:
Land holding is very small and it is 0.50 ha per household
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
饲料生产
注释/具体说明:
the bund is planted with grasses and legume trees
饲料质量
注释/具体说明:
the bund is planted with grasses and legume trees
木材生产
生产区域
土地管理
收入和成本
农业收入
社会文化影响
SLM/土地退化知识
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
SLM之前的数量:
65
SLM之后的数量:
20
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
SLM之前的数量:
20
SLM之后的数量:
1
其它生态影响
Soil fertility
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
旱季稳定可靠的水流
下游洪水
下游淤积
地下水/河流污染
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 10-50%
注释:
75% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
25% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: SWC intervention is an activity that aims at controlling erosion, improving soil moisture and productivity per unit area of land.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Controls erosion How can they be sustained / enhanced? use of multipurpose plant species for bund stablization. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Effective in controlling erosion How can they be sustained / enhanced? quality and technical standard should be kept. |
|
Fast to develop to bench terrace How can they be sustained / enhanced? require continuous maintainance |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| harbour rodents | provision of pesticides |
| labour intensive | provision of hand tools and incentives |
| no short time impact | introduce multipurpose planting material |
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Incentive based CCPPA [埃塞俄比亚]
The participation of the communities in the planning implementation and evaluation of SWC activities and provided with food for work as an insentive to encourage participation.
- 编制者: Daniel Danano
模块
无模块