Water harvest [肯尼亚]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Kithinji Mutunga
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff
Kunasa maji ya muua yanuyobubugika na kuyuelekeza shambani kwa uzakshaji-Alex R.Adual RSCU/SIDA1996
technologies_1097 - 肯尼亚
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
SLM专业人员:
Mutisya Peter Maithya
Daleo's office P.O.Box 42 Makueni Kenya
肯尼亚
SLM专业人员:
Ndengele Michael
Daleo's office P.O.Box 42 Makueni Kenya
肯尼亚
SLM专业人员:
Nguluu Lucas Makau
Daleo's office P.O.Box 42 Makueni Kenya
肯尼亚
SLM专业人员:
SLM专业人员:
SLM专业人员:
Adunal Alex R.
RELMA/SIDA
Lcraf house P.O.Box 63403 Nairobi, Kenya
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Ministry of Agriculture and Livestock Development of Kenya (MoA) - 肯尼亚1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
21/04/2003
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Water harvest for agricultural production in Asals
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
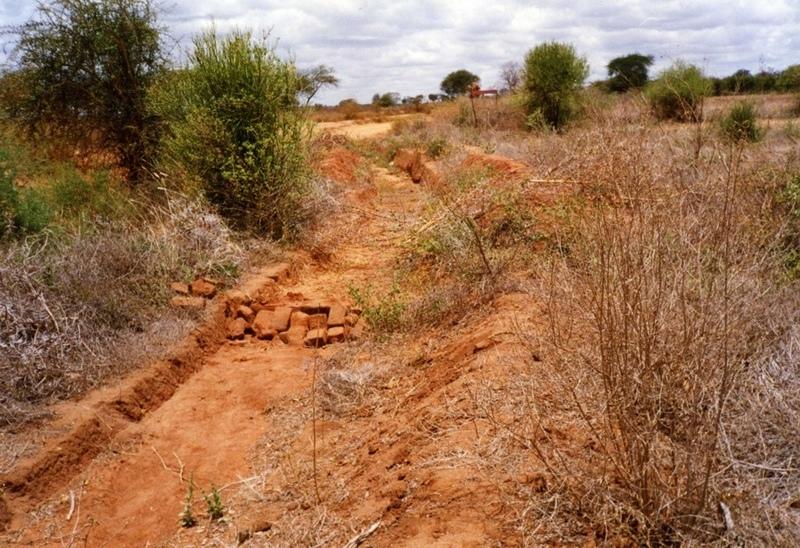
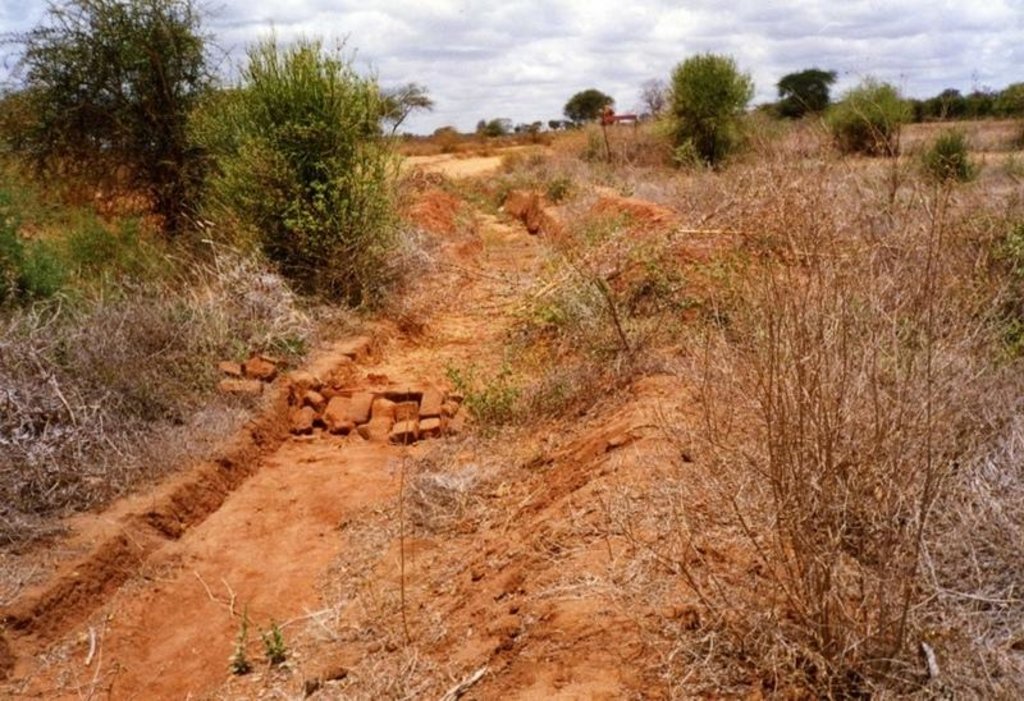
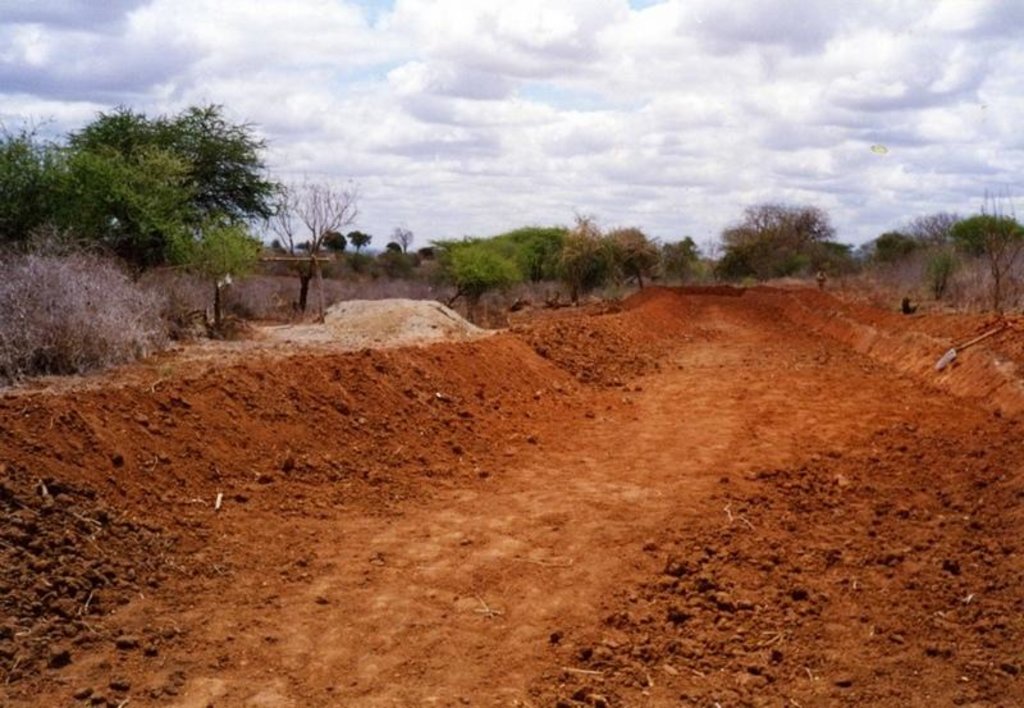
Water harvest enhances extra moisture and reduces risk of crop failure. It can either be external or internal. The activities also reduce runoff/overland flow and soil loss.
Manure and fertilizer improve soil water holding capacity and soil properties.
Appropriate tillage for improvement of infiltration rate of the soil.
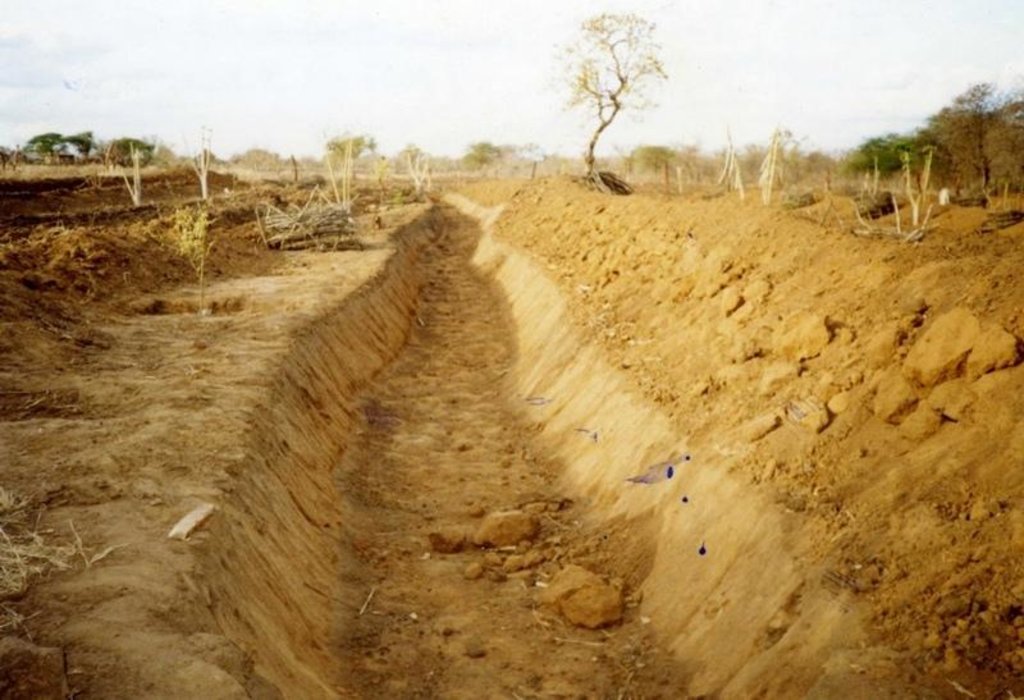
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
肯尼亚
区域/州/省:
Eastern
有关地点的进一步说明:
KiMuiki, Kitise, Mburo, Kwa Kauisi
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
ministry of agriculture and rural development, soil and water conservation branch Nairobi, Kenya
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
主要农作物(经济作物及粮食作物):
Major food crop: Maize
Other: C.peas

混合(作物/放牧/树木),包括农林
- 农林牧业
主要产品/服务:
Major cash crop CT: fruits
Selective felling of (semi-) natural forests for fuelwood purpose
Clear felling of (semi-)natural forests for agricultural production
Forest also for fruits and nuts
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Topsoil losses, creation of hardban, soil surface crusting and fertility decline are major problems in areas without SWC.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Yield decline and poor quality produce are problems in areas without SWC.
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: mixed land use type
Mixed: (eg agro-pastoralism, silvo-pastoralism): practiced by few
Other grazingland: semi-intensive grazing: semi-intensive grazing
Grazingland comments: Area closure can not be substituted, stall feeding materials not available. The family leader owns the stock but could fail to meet family needs if the system is not commercialized.
Selective felling of (semi-) natural forests: fuelwood purpose
Clear felling of (semi-)natural forests: for agricultural production
Problems / comments regarding forest use: Some uncontrolled grazing/browsing rather critical tp forest establoshment. Gapping can last long due to rainfall long intervals
Forest products and services: fuelwood, fruits and nuts
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: maize as major crop, followed by tubbers and legumes.
Type of grazing system comments: Area closure can not be substituted, stall feeding materials not available. The family leader owns the stock but could fail to meet family needs if the system is not commercialized.
Constraints of astructure network (roads, railways, pipe lines, power lines): roadside runoff enhances runoff Farming. Isolated trees preserved by traders in Mkt-centres
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 106 Longest growing period from month to month: Mar - Jun Second longest growing period in days: 71 Second longest growing period from month to month: Oct - Dec
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 集水
3.5 技术传播
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 45 m2.
Target-area 485 km^2 inhabited by 6550 farm families and population dynamic 46075.
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施

植物措施
- V2:草和多年生草本植物

结构措施
- S3:分级沟渠、渠道、水道
注释:
Main measures: structural measures
Secondary measures: agronomic measures, vegetative measures
Type of agronomic measures: relay cropping, manure / compost / residues, breaking compacted topsoil
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour, scattered / dispersed, in blocks
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)

物理性土壤退化
- Pk:熟化和结壳
- Pi:覆土
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Pk: sealing and crusting
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
注释:
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation, rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
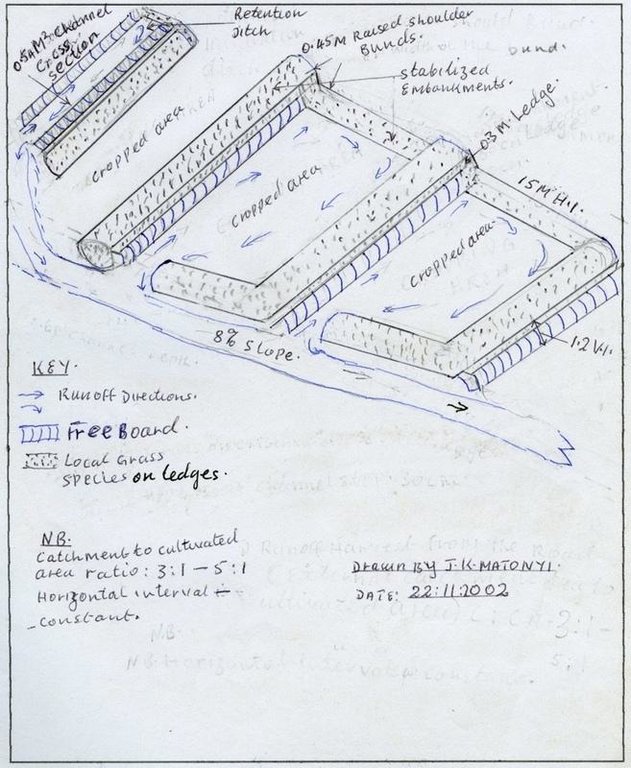
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
technical drawing catchment to cultural area ratio: 3:1 - 5:1 Horizontal interval constant
Makueni district
Date: 22.11.2002
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Main technical functions: water harvesting / increase water supply
Secondary technical functions: increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase in soil fertility
Relay cropping
Material/ species: improved mango trees
Quantity/ density: 124
Remarks: 9 m^2
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: FYM/compost
Quantity/ density: 12.5 t/ha
Breaking compacted topsoil
Remarks: appropriate tillage
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: G : grass
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1.2
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.6x0.3
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 15
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1.5
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 40
In blocks
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 124
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 9
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 9x9
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 9
Trees/ shrubs species: Cacia scamea, Accacia albida
Fruit trees / shrubs species: mango, citrus, pawpaw
Grass species: ceuchrus cuharis, erayroster superba
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 8.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 0.00%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 0.20%
Retention/infiltration ditch/pit, sediment/sand trap
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1.2
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.2
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 100
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.45
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1.5
Terrace: bench level
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1.2
Spacing between structures (m): 15
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 100
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.45
Construction material (earth): earth moving for SWC embankment construction
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 8%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 0.2%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Change of land use type: stock holding capacity of land
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
1.92
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | grass planting on embankments | 植物性的 | after onset of rain |
| 2. | fruits seedling transplanting | 植物性的 | october rain |
| 3. | dispersed tree seedlings transplanting | 植物性的 | october rain |
| 4. | retention/infiltration ditches | 结构性的 | after crop harvest |
| 5. | Bench terraces | 结构性的 | after crop harvest |
| 6. | external water harvest channels | 结构性的 | before raining season |
| 7. | structure stabilization | 结构性的 | onset of rain |
| 8. | manure/fertilizer application | 结构性的 | after crop harvest |
| 9. | Bush clearing | 管理 | after grazing |
| 10. | reseeding/grass planting in bare parches | 管理 | dry season |
| 11. | fodder establishment | 管理 | rainy season |
| 12. | removal of unwanted shrubs | 管理 | following rotational sequence |
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 296.0 | 296.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Machine use | ha | 1.0 | 32.5 | 32.5 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Animal traction | ha | 1.0 | 72.3 | 72.3 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 385.0 | 385.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 76.3 | 76.3 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seedligs | ha | 1.0 | 79.5 | 79.5 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Fertilizer | ha | 1.0 | 58.0 | 58.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Biocides | ha | 1.0 | 47.4 | 47.4 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Compost/manure | ha | 1.0 | 78.0 | 78.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Stone | ha | 1.0 | 244.0 | 244.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 1369.0 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 36 month(s)
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | tillaging | 农业学的 | before rain / annually |
| 2. | tillaging | 农业学的 | on set / seasonally |
| 3. | manure application | 农业学的 | dry season / annually |
| 4. | grass cutting and gapping | 植物性的 | onset of rain /twice per season |
| 5. | prunning and trimming | 植物性的 | after every harvest /annual |
| 6. | pollading and copsing | 植物性的 | when intended /after several years |
| 7. | retention/infiltration | 结构性的 | before onset of rain/seasonally |
| 8. | ditch cleaning | 结构性的 | before onset of rain/anually |
| 9. | Bench terraces repairing | 结构性的 | before onset of rain/when necessary |
| 10. | Water channel cleaning/repairing | 结构性的 | dry period/seasonally |
| 11. | grass cutting for stall feedinf | 管理 | rainy season / at maturity stage |
| 12. | gapping | 管理 | rainy season / seasonally |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 98.0 | 98.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Animal traction | ha | 1.0 | 72.3 | 72.3 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 67.3 | 67.3 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 55.7 | 55.7 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Fertilizer | ha | 1.0 | 44.2 | 44.2 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Biocides | ha | 1.0 | 21.5 | 21.5 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Earth | ha | 1.0 | 244.0 | 244.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 603.0 | |||||
注释:
Machinery/ tools: oxplough, oxcart, hoe, sprayer, shovel, wheelbarrow
The above costs were calculated in cost per qm
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Factors affecting the costs include hard ground at SWC peak period, labour, slope, catchment area, channel size and source of income
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
350.00
农业气候带
- 半干旱
- 干旱
semi-arid: LGP-70-180
arid: LGP-60-120
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Altitudinal zone: about 1000 m a.s.l. average
Landforms: Footslopes 8-16% slope and valley floors 2-8% slope
Slopes on average: Moderate = 6.5 % and rolling = 12 %
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil depth on average: shallow = 35 cm average and moderately deep = 65 cm average
Soil texture: Coarse/light = degradable/erodable and medium is common in the division
Soil fertility is medium in newly opened lands but fertility depletes quickly and is therefore also low.
Topsoil organic matter is medium on newly opened land and low after several years of cultivation.
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium with regular improvement, but there is also top soil crusting and therefore drainage becomes poor,
Soil water storage capacity is low during long duration of rainfall intervals and medium (effectiveness not realistic).
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
- 平均水平
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 畜力牵引
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
20% of the land users are rich and own 20% of the land (prestige).
35% of the land users are average wealthy and own 30% of the land (improved living standard).
25% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land (for subsistance).
Off-farm income specification: Most of youth seek for off-farm employment. Others due to lack of employment engage on trading as small holders.
Level of mechanization: Around 75 % use animal traction and manual labour is especially used for weeding
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
注释:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: Also 0.5-1 ha
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,未命名
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
Extra output 50%
生产区域
注释/具体说明:
given area reduced by 14%
收入和成本
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
Extra income 27.5%
工作量
注释/具体说明:
requires high labour costs
社会文化影响
社区机构
注释/具体说明:
in capacity building
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
to land user
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
SLM之前的数量:
32
SLM之后的数量:
14
多余水的排放
注释/具体说明:
risking occasion
土壤
土壤水分
注释/具体说明:
external WH.
土壤流失
SLM之前的数量:
20
SLM之后的数量:
10
注释/具体说明:
WH combination
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
旱季稳定可靠的水流
注释/具体说明:
irrigation potential reduced
下游洪水
注释/具体说明:
rainfall runoff trapped
下游淤积
注释/具体说明:
silt retained on cropland
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
非常积极
6.5 技术采用
- 1-10%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
630 household covered an area of 9%
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 90-100%
注释:
630 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Pressure on daily personal needs. No other sources of income yet the rainfall is not reliable in ASALS.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
induces the technique of implementation How can they be sustained / enhanced? land users be aquidance with the technology and its importance. |
|
land users acquires more grass for stall feeding. How can they be sustained / enhanced? introduction of intensive grazing system. |
|
reduces floods of heavy storms downsteram. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Proper tillage to curb soil crusting and hardban. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
water harvest increases farm production and reduces risks of crop failure. How can they be sustained / enhanced? To stabilize SWC structure embankments, desilt channels and retention ditches. |
|
Improvement in infiltration rate and moisture holding capacity. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Use of manure, organic matter, inorganic fertlizer and appropriate tillage. |
|
Reduces soil, fertility, runoff and overland flow losses How can they be sustained / enhanced? Maximum adaptability of the SWC technology to ustain high production level. |
|
Enhanced vegetative cover for moisture retention. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Intercropping, mulching and repairing where needed. |
|
Reduces erosion by wind and other land degradation. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Appropriate stocking rate andd replanting trees and grass. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| consumes a lot of time to implement the technology | the land user awareness of the importance of the activity. |
| Technology area resists a direct grazing | to mitiate stall feeding |
| the technology design is beyond the farmers knowledge. | continuous interaction with SWC specialists. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Land area reduced by SWC structures constructed. | Use of certified seeds, manure and fertilizer. |
| soil fertility is interfered with. | more manure and organic matter use. |
| High labour cost requirement to implement the technology. | Introduced source of smooth loan and policy for ASALS. |
| Risk of water logging where soil drainage is unaimable. | acquired knowledge of different soil types and applicable technology and system. |
| cost-benefit return can last long to be realized. | to maintain record for both, implementing cost and income from the given area (SWC area) |
7. 参考和链接
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
SWC manual for Kenya by D:B: Thomas. 1997.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Mard Kenya, free
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
SWC technology Dev. in ASAL by Kithinji Mutunga
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
SWC branch, free
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
SC in Kenya, Carl G.Wenner. 1984.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Aici, free
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
ony superb DXE-180 video
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Mard Kenya, free
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
The sun will still rise
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Mard Kenya, free
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Run off a friend or a foe
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Mard Kenya, free
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块