Water harvest [เคนยา]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Kithinji Mutunga
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: David Streiff
Kunasa maji ya muua yanuyobubugika na kuyuelekeza shambani kwa uzakshaji-Alex R.Adual RSCU/SIDA1996
technologies_1097 - เคนยา
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
วิทยากรหลัก
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Mutisya Peter Maithya
Daleo's office P.O.Box 42 Makueni Kenya
เคนยา
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Ndengele Michael
Daleo's office P.O.Box 42 Makueni Kenya
เคนยา
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Nguluu Lucas Makau
Daleo's office P.O.Box 42 Makueni Kenya
เคนยา
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Adunal Alex R.
RELMA/SIDA
Lcraf house P.O.Box 63403 Nairobi, Kenya
ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Ministry of Agriculture, Livestock and Fisheries (MoA) - เคนยา1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
21/04/2003
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
Water harvest for agricultural production in Asals
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
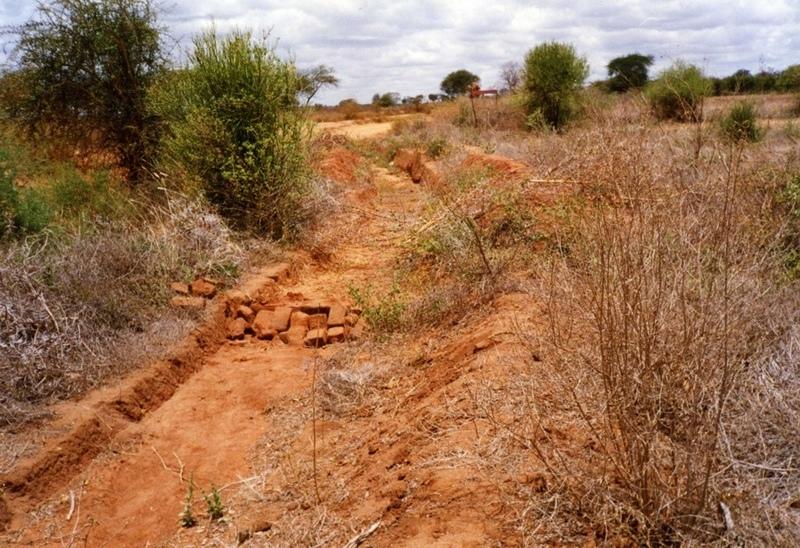
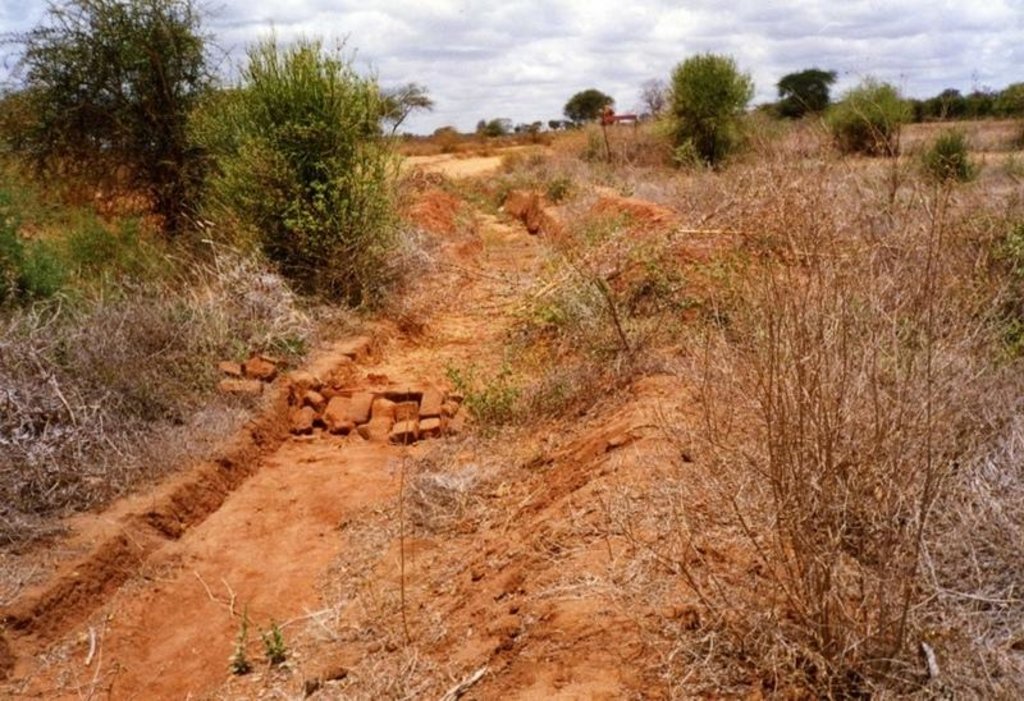
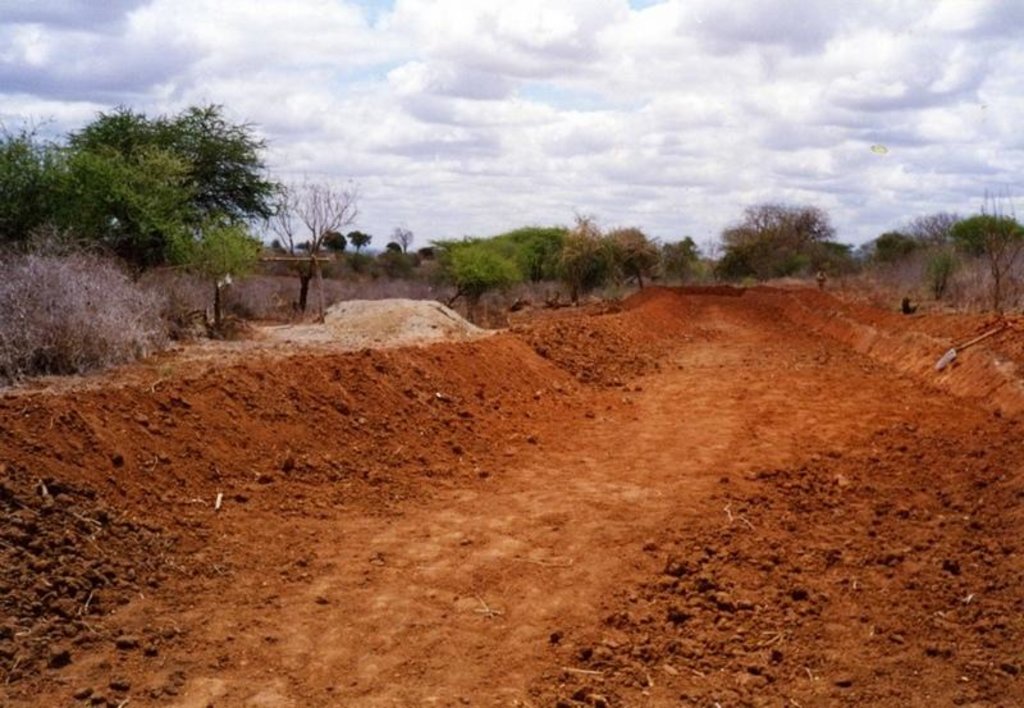
Water harvest enhances extra moisture and reduces risk of crop failure. It can either be external or internal. The activities also reduce runoff/overland flow and soil loss.
Manure and fertilizer improve soil water holding capacity and soil properties.
Appropriate tillage for improvement of infiltration rate of the soil.
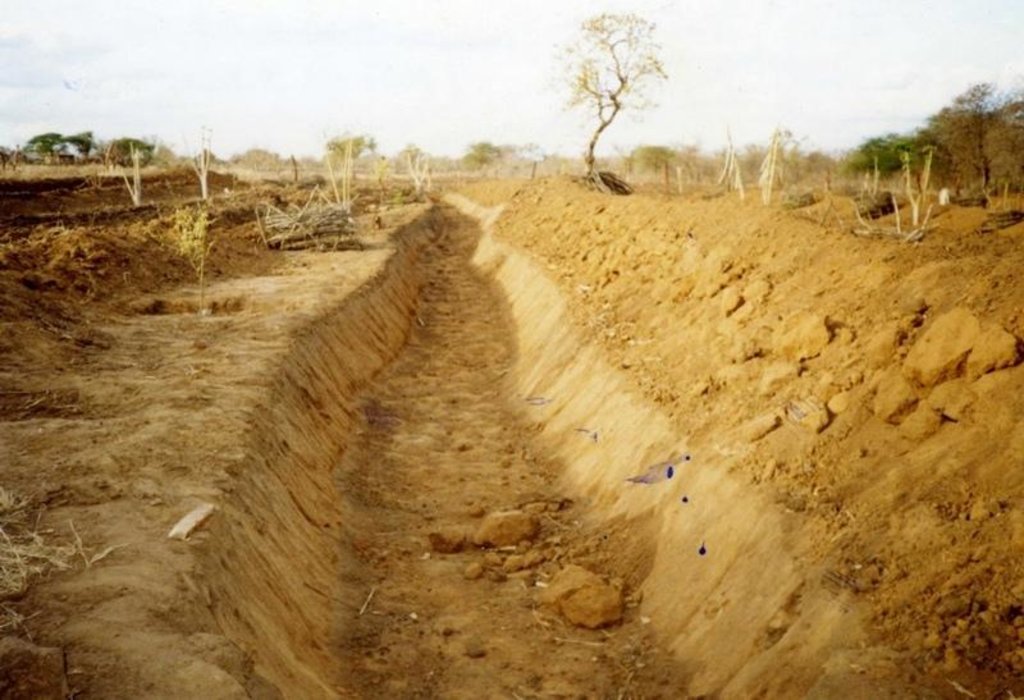
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
เคนยา
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Eastern
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
KiMuiki, Kitise, Mburo, Kwa Kauisi
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
ministry of agriculture and rural development, soil and water conservation branch Nairobi, Kenya
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
พืชหลัก (พืชเศรษฐกิจและพืชอาหาร):
Major food crop: Maize
Other: C.peas

การใช้ที่ดินแบบผสมผสาน (รวมถึงวนเกษตร)
- การปลูกพืชร่วมกับปศุสัตว์และการทำป่าไม้ (Agro-silvopastoralism)
ผลิตภัณฑ์หลักหรือบริการ:
Major cash crop CT: fruits
Selective felling of (semi-) natural forests for fuelwood purpose
Clear felling of (semi-)natural forests for agricultural production
Forest also for fruits and nuts
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Topsoil losses, creation of hardban, soil surface crusting and fertility decline are major problems in areas without SWC.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Yield decline and poor quality produce are problems in areas without SWC.
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: mixed land use type
Mixed: (eg agro-pastoralism, silvo-pastoralism): practiced by few
Other grazingland: semi-intensive grazing: semi-intensive grazing
Grazingland comments: Area closure can not be substituted, stall feeding materials not available. The family leader owns the stock but could fail to meet family needs if the system is not commercialized.
Selective felling of (semi-) natural forests: fuelwood purpose
Clear felling of (semi-)natural forests: for agricultural production
Problems / comments regarding forest use: Some uncontrolled grazing/browsing rather critical tp forest establoshment. Gapping can last long due to rainfall long intervals
Forest products and services: fuelwood, fruits and nuts
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: maize as major crop, followed by tubbers and legumes.
Type of grazing system comments: Area closure can not be substituted, stall feeding materials not available. The family leader owns the stock but could fail to meet family needs if the system is not commercialized.
Constraints of astructure network (roads, railways, pipe lines, power lines): roadside runoff enhances runoff Farming. Isolated trees preserved by traders in Mkt-centres
3.3 ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการใช้ที่ดิน
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 2
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 106 Longest growing period from month to month: Mar - Jun Second longest growing period in days: 71 Second longest growing period from month to month: Oct - Dec
3.4 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การเก็บเกี่ยวน้ำ
3.5 กระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 45 m2.
Target-area 485 km^2 inhabited by 6550 farm families and population dynamic 46075.
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V2: หญ้าและไม้ยืนต้น

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S3: Graded ditches, channels, waterways
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main measures: structural measures
Secondary measures: agronomic measures, vegetative measures
Type of agronomic measures: relay cropping, manure / compost / residues, breaking compacted topsoil
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour, scattered / dispersed, in blocks
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cn (Fertility decline): ความอุดมสมบูรณ์และปริมาณอินทรียวัตถุในดินถูกทำให้ลดลงไป (ไม่ได้เกิดจากสาเหตุการกัดกร่อน)

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านกายภาพ
- Pk (Slaking and crusting): การอุดตันของช่องว่างในดินหรือรูพรุน
- Pi (Soil sealing)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main type of degradation addressed: Pk: sealing and crusting
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation, rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
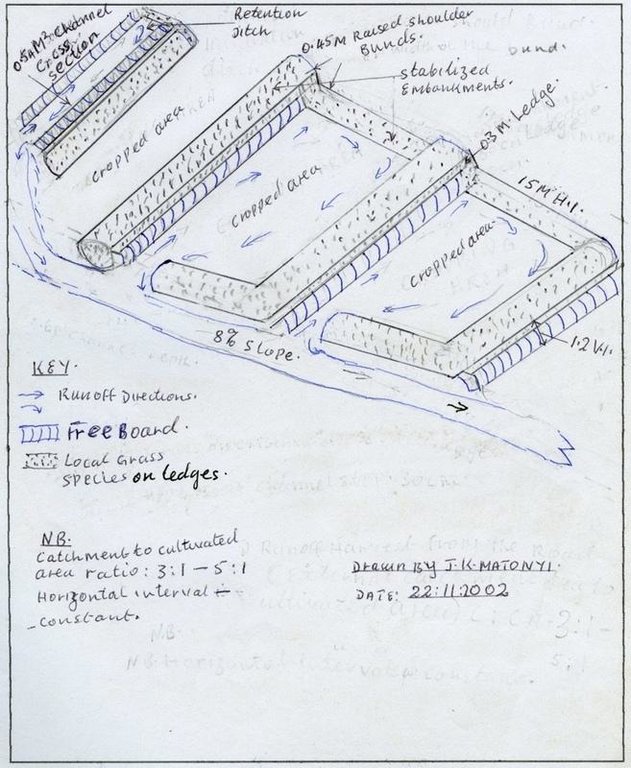
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
4.2 ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิคและการอธิบายแบบแปลนทางเทคนิค
technical drawing catchment to cultural area ratio: 3:1 - 5:1 Horizontal interval constant
Makueni district
Date: 22.11.2002
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Main technical functions: water harvesting / increase water supply
Secondary technical functions: increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase in soil fertility
Relay cropping
Material/ species: improved mango trees
Quantity/ density: 124
Remarks: 9 m^2
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: FYM/compost
Quantity/ density: 12.5 t/ha
Breaking compacted topsoil
Remarks: appropriate tillage
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: G : grass
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1.2
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.6x0.3
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 15
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1.5
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 40
In blocks
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 124
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 9
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 9x9
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 9
Trees/ shrubs species: Cacia scamea, Accacia albida
Fruit trees / shrubs species: mango, citrus, pawpaw
Grass species: ceuchrus cuharis, erayroster superba
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 8.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 0.00%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 0.20%
Retention/infiltration ditch/pit, sediment/sand trap
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1.2
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.2
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 100
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.45
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1.5
Terrace: bench level
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1.2
Spacing between structures (m): 15
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 100
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.45
Construction material (earth): earth moving for SWC embankment construction
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 8%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 0.2%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Change of land use type: stock holding capacity of land
4.3 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ระบุสกุลเงินที่ใช้คำนวณค่าใช้จ่าย:
- ดอลลาร์สหรัฐ
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
1.92
4.4 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงเวลาดำเนินการ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | grass planting on embankments | ด้วยวิธีพืช | after onset of rain |
| 2. | fruits seedling transplanting | ด้วยวิธีพืช | october rain |
| 3. | dispersed tree seedlings transplanting | ด้วยวิธีพืช | october rain |
| 4. | retention/infiltration ditches | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | after crop harvest |
| 5. | Bench terraces | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | after crop harvest |
| 6. | external water harvest channels | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | before raining season |
| 7. | structure stabilization | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | onset of rain |
| 8. | manure/fertilizer application | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | after crop harvest |
| 9. | Bush clearing | ด้วยการจัดการ | after grazing |
| 10. | reseeding/grass planting in bare parches | ด้วยการจัดการ | dry season |
| 11. | fodder establishment | ด้วยการจัดการ | rainy season |
| 12. | removal of unwanted shrubs | ด้วยการจัดการ | following rotational sequence |
4.5 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 296.0 | 296.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Machine use | ha | 1.0 | 32.5 | 32.5 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Animal traction | ha | 1.0 | 72.3 | 72.3 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 385.0 | 385.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 76.3 | 76.3 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Seedligs | ha | 1.0 | 79.5 | 79.5 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Fertilizer | ha | 1.0 | 58.0 | 58.0 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Biocides | ha | 1.0 | 47.4 | 47.4 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Compost/manure | ha | 1.0 | 78.0 | 78.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Stone | ha | 1.0 | 244.0 | 244.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 1369.0 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Duration of establishment phase: 36 month(s)
4.6 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | tillaging | จัดการพืช | before rain / annually |
| 2. | tillaging | จัดการพืช | on set / seasonally |
| 3. | manure application | จัดการพืช | dry season / annually |
| 4. | grass cutting and gapping | ด้วยวิธีพืช | onset of rain /twice per season |
| 5. | prunning and trimming | ด้วยวิธีพืช | after every harvest /annual |
| 6. | pollading and copsing | ด้วยวิธีพืช | when intended /after several years |
| 7. | retention/infiltration | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | before onset of rain/seasonally |
| 8. | ditch cleaning | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | before onset of rain/anually |
| 9. | Bench terraces repairing | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | before onset of rain/when necessary |
| 10. | Water channel cleaning/repairing | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | dry period/seasonally |
| 11. | grass cutting for stall feedinf | ด้วยการจัดการ | rainy season / at maturity stage |
| 12. | gapping | ด้วยการจัดการ | rainy season / seasonally |
4.7 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 98.0 | 98.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Animal traction | ha | 1.0 | 72.3 | 72.3 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 67.3 | 67.3 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 55.7 | 55.7 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Fertilizer | ha | 1.0 | 44.2 | 44.2 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Biocides | ha | 1.0 | 21.5 | 21.5 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Earth | ha | 1.0 | 244.0 | 244.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 603.0 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Machinery/ tools: oxplough, oxcart, hoe, sprayer, shovel, wheelbarrow
The above costs were calculated in cost per qm
4.8 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Factors affecting the costs include hard ground at SWC peak period, labour, slope, catchment area, channel size and source of income
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ระบุปริมาณน้ำฝนเฉลี่ยรายปี (ถ้ารู้) :หน่วย ม.ม.
350.00
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
- แห้งแล้ง
semi-arid: LGP-70-180
arid: LGP-60-120
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
Altitudinal zone: about 1000 m a.s.l. average
Landforms: Footslopes 8-16% slope and valley floors 2-8% slope
Slopes on average: Moderate = 6.5 % and rolling = 12 %
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
- ต่ำ (<1%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil depth on average: shallow = 35 cm average and moderately deep = 65 cm average
Soil texture: Coarse/light = degradable/erodable and medium is common in the division
Soil fertility is medium in newly opened lands but fertility depletes quickly and is therefore also low.
Topsoil organic matter is medium on newly opened land and low after several years of cultivation.
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium with regular improvement, but there is also top soil crusting and therefore drainage becomes poor,
Soil water storage capacity is low during long duration of rainfall intervals and medium (effectiveness not realistic).
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- ผสม (การเลี้ยงชีพ/ทำการค้า)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- 10-50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- จน
- พอมีพอกิน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
- การใช้กำลังจากสัตว์
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
20% of the land users are rich and own 20% of the land (prestige).
35% of the land users are average wealthy and own 30% of the land (improved living standard).
25% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land (for subsistance).
Off-farm income specification: Most of youth seek for off-farm employment. Others due to lack of employment engage on trading as small holders.
Level of mechanization: Around 75 % use animal traction and manual labour is especially used for weeding
5.7 พื้นที่เฉลี่ยของที่ดินที่เป็นเจ้าของหรือเช่าโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: Also 0.5-1 ha
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ไม่ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
- รายบุคคล ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Extra output 50%
พื้นที่สำหรับการผลิต
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
given area reduced by 14%
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Extra income 27.5%
ภาระงาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
requires high labour costs
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
สถาบันของชุมชน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
in capacity building
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
to land user
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
32
หลังจาก SLM:
14
การระบายน้ำส่วนเกิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
risking occasion
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
external WH.
การสูญเสียดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
20
หลังจาก SLM:
10
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
WH combination
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
การไหลของน้ำคงที่และสม่ำเสมอในช่วงฤดูแล้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
irrigation potential reduced
น้ำท่วมพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
rainfall runoff trapped
การทับถมของดินตะกอนพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
silt retained on cropland
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- 1-10%
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
630 household covered an area of 9%
จากทั้งหมดที่ได้รับเทคโนโลยีเข้ามามีจำนวนเท่าใดที่ทำแบบทันที โดยไม่ได้รับการจูงใจด้านวัสดุหรือการเงินใด ๆ:
- 90-100%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
630 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Pressure on daily personal needs. No other sources of income yet the rainfall is not reliable in ASALS.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
|
induces the technique of implementation How can they be sustained / enhanced? land users be aquidance with the technology and its importance. |
|
land users acquires more grass for stall feeding. How can they be sustained / enhanced? introduction of intensive grazing system. |
|
reduces floods of heavy storms downsteram. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Proper tillage to curb soil crusting and hardban. |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
|
water harvest increases farm production and reduces risks of crop failure. How can they be sustained / enhanced? To stabilize SWC structure embankments, desilt channels and retention ditches. |
|
Improvement in infiltration rate and moisture holding capacity. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Use of manure, organic matter, inorganic fertlizer and appropriate tillage. |
|
Reduces soil, fertility, runoff and overland flow losses How can they be sustained / enhanced? Maximum adaptability of the SWC technology to ustain high production level. |
|
Enhanced vegetative cover for moisture retention. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Intercropping, mulching and repairing where needed. |
|
Reduces erosion by wind and other land degradation. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Appropriate stocking rate andd replanting trees and grass. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| consumes a lot of time to implement the technology | the land user awareness of the importance of the activity. |
| Technology area resists a direct grazing | to mitiate stall feeding |
| the technology design is beyond the farmers knowledge. | continuous interaction with SWC specialists. |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Land area reduced by SWC structures constructed. | Use of certified seeds, manure and fertilizer. |
| soil fertility is interfered with. | more manure and organic matter use. |
| High labour cost requirement to implement the technology. | Introduced source of smooth loan and policy for ASALS. |
| Risk of water logging where soil drainage is unaimable. | acquired knowledge of different soil types and applicable technology and system. |
| cost-benefit return can last long to be realized. | to maintain record for both, implementing cost and income from the given area (SWC area) |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
SWC manual for Kenya by D:B: Thomas. 1997.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Mard Kenya, free
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
SWC technology Dev. in ASAL by Kithinji Mutunga
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
SWC branch, free
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
SC in Kenya, Carl G.Wenner. 1984.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Aici, free
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
ony superb DXE-180 video
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Mard Kenya, free
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
The sun will still rise
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Mard Kenya, free
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Run off a friend or a foe
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Mard Kenya, free
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล