Natural riparian vegetation to sustain a stable riverbank at Naro Moru River [肯尼亚]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Manuel Fischer
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1569 - 肯尼亚
- Natural riparian vegetation to sustain a stable riverbank at Naro Moru River: March 30, 2017 (inactive)
- Natural riparian vegetation to sustain a stable riverbank at Naro Moru River: March 30, 2017 (inactive)
- Natural riparian vegetation to sustain a stable riverbank at Naro Moru River: May 8, 2019 (public)
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
土地使用者:
Ngunjiri Simon
肯尼亚
1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Riverbank erosion and biodiversity decline in the riparian area can be overcome by leaving the natural vegetation undisturbed.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
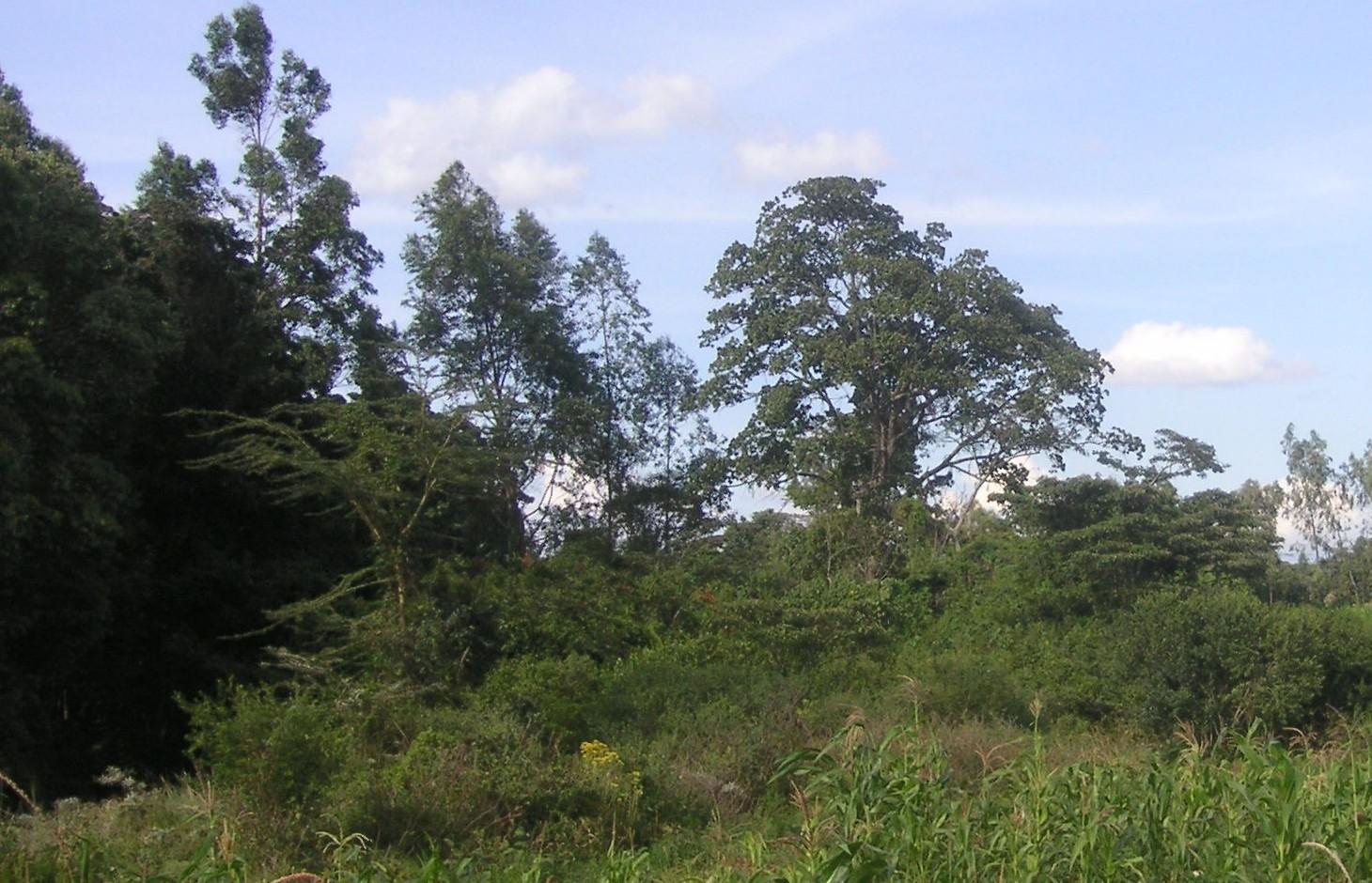
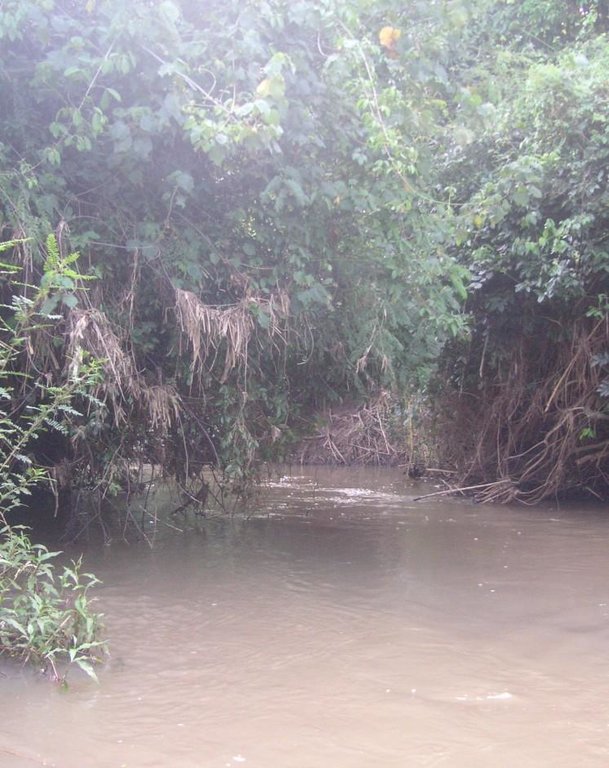
The studied land plot is situated in the semi-arid savannah zone of the Naro Moru sub-catchment at the foot of Mt. Kenya. A small-scale farmer leaves the riparian vegetation undisturbed, which enables the growth of dense bushes. On the one hand, the riparian vegetation contributes to prevent land loss caused by riverbank erosion, on the other hand it is a habitat for the special riparian fauna and flora.
Purpose of the Technology: Despite semi-arid conditions, there is a high probability of flooding. Heavy rainfalls on upper slopes of Mt. Kenya lead to flood events in the semi-arid areas of Naro Moru River. These events have a destructive effect on the riverbanks, which have become instable by human induced activities such as overgrazing and deforestation. The instable riparian soils are eroded easily. The farmers lose their precious land and the water is polluted.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: A good way to overcome the riverbank degradation triggered by high runoff is a passive approach: simply leaving the riparian area undisturbed by human interference. Trees, bushes and grasses stabilize even steep riverbanks with their invading roots. As a result, almost no erosion takes place and infiltration is enhanced during rain events. The riparian microclimate, which is characterized by cooler temperatures during the day and slightly warmer temperatures during the night, is very special compared to the surrounding semi-arid zones. Also water availability is much higher than in the surroundings. Thus, this habitat offers a high biodiversity.
Natural / human environment: The plot is situated on a plateau at the western side of Mt. Kenya. There is not the same amount of precipitation as at the foot slopes of Mt. Kenya. However, the area still benefits from the runoff that is generated on the mountain. Precipitation in the so-called savannah zone ranges from 600mm to 900mm per year. Due to the high evaporation, rain-fed agriculture is only partly possible. Therefore most land users depend on irrigation using river water.
During the last decades, the region has experienced a still continuing population growth which increases population pressure in the area and removal and use of the vegetation along the rivers. The good accessibility and the moderate tourism allow even off-farm income-generation.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
肯尼亚
区域/州/省:
Kenya/Central Province
有关地点的进一步说明:
Naro Moru
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- < 0.1 平方千米(10 公顷)
注释:
The riparian area is very small, thus the whole plot of the farmer is indicated.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 10-50年前
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过土地使用者的创新
注释(项目类型等):
The farmer has not touched the land since 20 years.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 保持/提高生物多样性
- 降低灾害风险
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

森林/林地
产品和服务:
- 自然保持/保护
- 自然灾害防护
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): In not treated areas, land users have to fight serious riverbank erosion. Due to steep riverbanks, stabilisation is very tricky.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Deforested riverbanks are very difficult to control, land loss is a consequence.
Other type of forest: Protected riparian forest
Problems / comments regarding forest use: The forest is left as protected forest because it stabilizes the riverbank.
Forest products and services: nature conservation / protection, protection against natural hazards
Number of growing seasons per year: 2
Longest growing period in days: 60 Longest growing period from month to month: april to may Second longest growing period in days: 60 Second longest growing period from month to month: october to november
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 区域封闭(停止使用,支持恢复)
- 地表水管理(泉、河、湖、海)
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

管理措施
- M5:物种组成的控制/变化
注释:
Main measures: management measures
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wr:河岸侵蚀

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
- Bh:栖息地丧失
- Bq:数量/生物量减少

水质恶化
- Hg:地下水/含水层水位的变化
- Hp:地表水水质下降
- Hw:湿地缓冲能力下降
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wr: riverbank erosion, Hp: decline of surface water quality
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover, Bh: loss of habitats, Bq: quantity / biomass decline, Hg: change in groundwater / aquifer level, Hw: reduction of the buffering capacity of wetland areas
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, overgrazing, floods
Secondary causes of degradation: Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts), population pressure, poverty / wealth
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
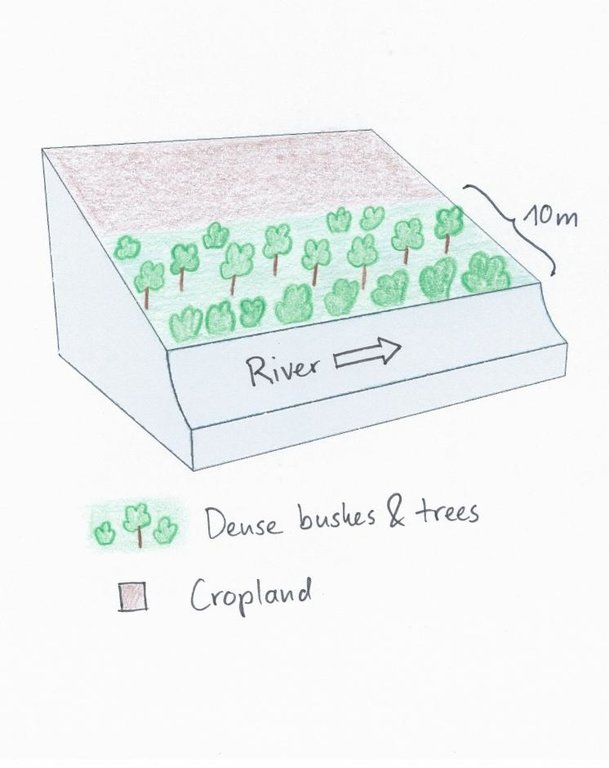
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
The land user noticed the riverbank erosion problems neighbours had after clearing of the riparian vegetation. This led to the protective approach of natural trees and bushes. Adjacent to the riparian area, crops are cultivated.
Location: Naro Moru. Nyeri / Central Province
Date: 28.12.2013
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase of infiltration, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Secondary technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase of surface roughness, increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater
Control / change of species composition: In the protected area only indigenous tress, bushes and grasses should be present. Especially indigenous trees do not need much water and allow more water to infiltrate into the soil.
作者:
Manuel Fischer
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术单元
指定单位:
Riparian area
指定单位面积(如相关):
60 m
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Kenyan Shilling
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
90.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
2.70
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | No activities were needed |
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Control of species composition and destruction of invading plants | during rainy season |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Control of species composition and destruction of invading plants | Persons/day | 2.0 | 3.0 | 6.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 6.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 0.07 | |||||
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半干旱
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Altitudinal zone: 1800 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage / infiltration is poor - medium
Soil water storage capacity is low but with mulching it changes to medium
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
< 5米
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Ground water table: Just along the river, deeper ground water level 50-100m
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Off-farm income specification: The farmer has no off-farm income.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,未命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
- 社区(有组织)
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
木材生产
注释/具体说明:
Before the establishment of the technology, the farmer used to prune the trees. He does not do that anymore.
社会文化影响
SLM/土地退化知识
aesthetics
Livelihood and human well-being
注释/具体说明:
Erosion knowledge was improved
生态影响
水循环/径流
水量
水质
地下水位/含水层
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
生物多样性:植被、动物
植物多样性
有益物种
栖息地多样性
减少气候和灾害风险
干旱影响
其它生态影响
Riverbank erosion
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
水资源可用性
旱季稳定可靠的水流
下游淤积
地下水/河流污染
缓冲/过滤能力
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 好 |
| 局地风暴 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
稍微积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
稍微积极
注释:
There are no establishment costs, that is why the short-term returns ares neutral. After some years, the benefits develop as long-term returns
6.5 技术采用
- 单例/实验
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 11-50%
注释:
20% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: There are some farmers who are very convinced. The number of farmers adopting the technology is growing slowly.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
There are no problems with riverbank erosion. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Keep the vegetation cover and do not perform too many activities in the riparian zone. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
The technology creates a habitat for the very specific riparian fauna and flora and this boosts biodiversity. How can they be sustained / enhanced? By enlarging the riparian zone. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| There is no productive use of this technology, therefore it is difficult to convince other farmers to adopt this technology. | Slight use of the riparian brings already good returns of fodder and fuelwood and still allows good protection. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块