Irrigation of uplands through Hydraulic Flange Pump [阿富汗]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Aqila Haidery
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Alexandra Gavilano, David Streiff, Joana Eichenberger
Aabyari zamin hai boland Aaba thawasut Pump_e_Aabi_Charkhdar
technologies_1731 - 阿富汗
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
SLM专业人员:
SLM专业人员:
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
HELVETAS (Swiss Intercooperation)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
People in Need (PIN) (People in Need (PIN)) - 阿富汗1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Technology for lifting water to uplands: hydraulic flange pump, reservoir and pipe scheme.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
This technology is documented by the Sustainable Land Management Project, implemented by HELVETAS Swiss Intercooperation and funded by the Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (SDC), with close support and cooperation of People in Need.
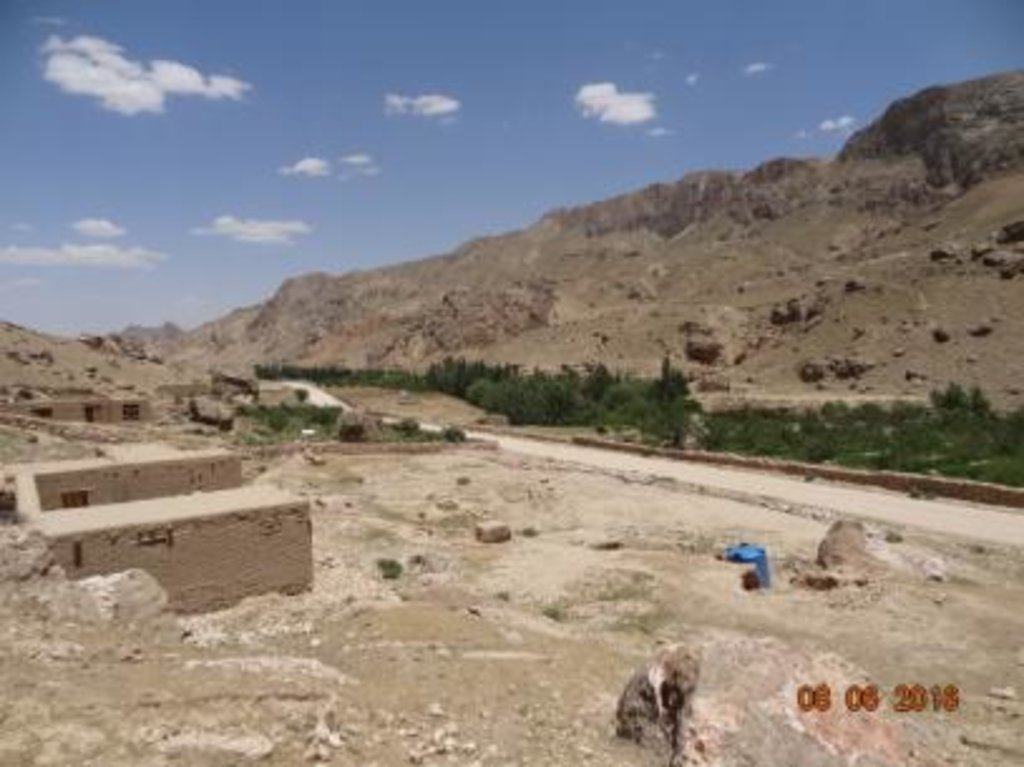
Samangan, Khuram wa Sarbagh district, Klor-e-Bala village is situated in a mountainous region where the greatest limiting factor to agricultural production is water. Arable lands are located far away from water sources. Lack of technology to exploit these lands prohibits villagers to cultivate their land to make a livelihood. Therefore, families are compelled to leave their village during summer.
Purpose of the Technology: To address this problem, People in Need (PIN), with financial support from GIZ and the Czech Embassy (CzDA) introduced irrigation through hydraulic flange pump. The hydraulic flange pump provides water to 30 orchards of Klor-e-Bala village, drinking water to the 43 village households, the mosque and the school of 500 students.
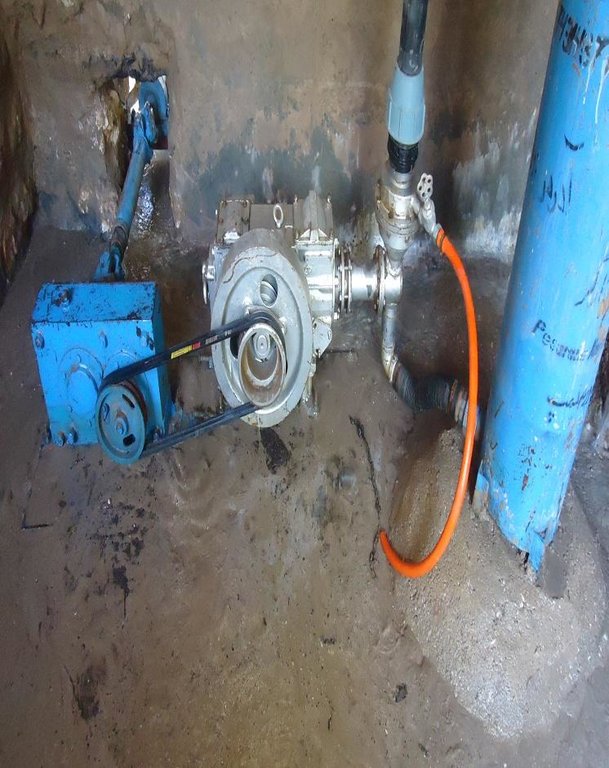
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The main water source which starts and runs the hydraulic flange pump is the Khuwaja Hayat spring. The spring water arrives to the hydraulic flange pump from 1.8 meter height on a 12 percent slope in 200 meters distance from the water source. The water flow passes through the intake and moves towards the water wheel which starts/runs the hydraulic flange pump. The water is then pumped through three pipes of one inch to the reservoir. The hydraulic flange pump has the capacity of lifting water up to 250 meters.
The reservoir’s storage capacity is 25,600 liters of water with the dimensions as follows: 4.9 meter length; 2.9 m width; and 1.8 m height. It has two outlets: a spill way fitted with three pipes of one inch at the top of the reservoir and two outlets fitted with two pipes of three inches at the bottom. The lower outlet leads water to the orchards by diverting water after 40 meters into two pipes which are 1,000 meters long. Each orchard is connected to one of these two pipes by a T-connector and the water flows into a tin water tank with the capacity of 1,000 liters for each orchard. The two pipes are extended as far as the school which is located near the orchards and has been equipped with a 2000 liters tin water tank.
The hydraulic flange pump is made locally in Taloqan city, Takhar province of Afghanistan in the Baradaran-e- Kargar workshop. The pump costs 140,000 Afghani/ 2,200 US$, including installment. The estimated cost of the construction of the reservoir and the pump’s room including the hydraulic flange pump is 19,000 US$. The pipe scheme of the project was installed by the Community Development Council (CDC) with technical support from PIN’s engineering team. Community members contributed 10 percent of the costs as labor. As Klor-e-Bala village is situated in flood prone area and flooding is a common occurrence, PIN, with funding from the GIZ, constructed in 2015 two protection walls, 45 m and 55 m in length, on both sides of the river, to minimize erosion and protect the pump’s intake from floods. The protection walls were built through cash for work programme, but community members provided 10 percent contribution through labor and by providing stones for construction. The total estimated cost of the hydraulic flange pump, reservoir and pipe scheme technology amounted to 37,000 US$.
Furthermore, in order to maintain the technology, a caretaker, who lives close to the pump’s room has been appointed. The caretaker was trained by the technician who installed the hydraulic flange pump and has voluntarily taken the responsibility of maintenance activities; changing the oil and cleaning of the hydraulic flange pump's room and changing of the pipes in case of need. The owners of the orchards have to cover for all maintenance costs and the chairman of the Community Development Council (CDC) has the responsibility of managing the money for maintenance and other recurrent activities.
The flange pump technology contributed to the economic growth of the community members by increasing the orchards’ yields. Currently, the hydraulic flange pump irrigates 12 jireb/2.4 ha (30*800m2) orchards of apple, apricot, almond, pear and cherry trees. In addition to the orchards, alfalfa, potato, vegetables and other crops are as well cultivated on these lands. Furthermore, the pump supports the community members to settle year-round in their villages and prevents from their seasonal displacement. Moreover, the flange pump enables the provision of drinking water to the whole community and the school.
Natural / human environment: Samangan is one of the northern provinces of Afghanistan. Wheat, melons, pistachio,
almonds, potatoes, onions and caraway are important crops and Karakul sheep
and goats the main livestock for meat, dairy, and wool production. Rugs are the
main handicraft of this area. Khuram-wa-Sarbagh district in Samangan has two growing
seasons, the longest of which is 150 days from February to June and the second is 90
days from June to September. The average rainfall is below 500mm and the climate semi-arid.
The community members have limited access to off farm employment, market, energy,
financial services, roads and transportation and moderate access to health and education.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
阿富汗
区域/州/省:
Samangan
有关地点的进一步说明:
Khuram-wa-Sarbagh district, Klor_e_Bala village
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 1-10 平方千米
注释:
The technology area which is considered here is the distance from the water area where the machine exists to the reservoir and reservoir to the orchard and crop land.
2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- access to water
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是
具体说明混合土地使用(作物/放牧/树木):
- 农林业

农田
- 一年一作
- 乔木与灌木的种植
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 150; Longest growing period from month to month: February - June; Second longest growing period in days: 90; Second longest growing period from month to month: June - September

牧场
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Lack of safe drinking and irrigation water which makes agricultural activities difficult.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Lack of cultivation due to the scarcity of water. High workloads and small incomes.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Mixed: Mf: Agroforestry
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 是(请在技术实施前填写以下有关土地利用的问题)

水道、水体、湿地
- 排水管道、水道
- 池塘、大坝
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 天然和半天然森林管理
- 农业林学
- 灌溉管理(包括供水、排水)
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

结构措施
- S5:大坝、集水斗、水池
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
- Bq:数量/生物量减少
注释:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Bq: quantity / biomass decline
Main causes of degradation: disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff), droughts, education, access to knowledge and support services
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
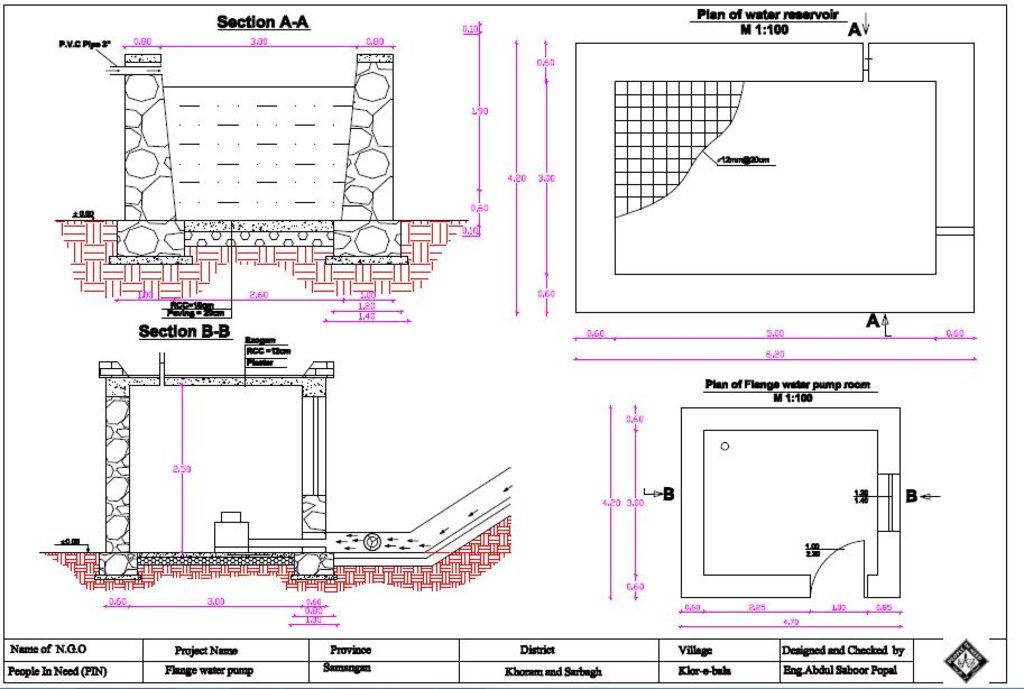
A detailed technical drawing of the hydraulic flange pump and the reservoir, Klor-e-Bala village, Khuram-wa-Sarbagh district, Samangan province.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), water harvesting / increase water supply, water spreading
作者:
Eng. Saboor Popal, People In Need (PIN)
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
7.00
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Excavation of the foundation | |
| 2. | Construction activities,Stone masonry foundation and wall: | |
| 3. | a:P.C.C concrete foundationb:R.C.C concretec:Iron shattering for walls, roof and floord:External and internal pointing | |
| 4. | a:Plasteringb:Steel barsc:Door and window | |
| 5. | Pipe scheme:a:Pipesb:Water tanksc:other equipmentd:Skilled and unskilled labor | |
| 6. | Procurement of the Hydraulic flange pump |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Excavation of the foundation | square meters | 50.0 | 2.88 | 144.0 | 10.0 |
| 劳动力 | Excavation of the foundation | cubic meters | 161.0 | 2.4037 | 387.0 | 10.0 |
| 劳动力 | Skilled and unskilled labor | persons/day | 343.0 | 9.47521 | 3250.0 | 10.0 |
| 设备 | Water tanks | pieces | 39.0 | 98.615384 | 3846.0 | 10.0 |
| 设备 | Pipes | meter | 2900.0 | 2.9241379 | 8480.0 | 10.0 |
| 设备 | Other equipment | all | 1.0 | 2424.0 | 2424.0 | 10.0 |
| 设备 | Procurement of the Hydraulic flange pump | pieces | 1.0 | 2200.0 | 2200.0 | 10.0 |
| 施工材料 | Concrete foundation | cubic meters | 12.23 | 96.64758 | 1182.0 | 10.0 |
| 施工材料 | Concrete | cubic meters | 8.4 | 114.0476 | 958.0 | 10.0 |
| 施工材料 | Iron shattering for walls, roof and floor | cubic meters | 110.0 | 4.86363 | 535.0 | 10.0 |
| 施工材料 | External and internal pointing | square meters | 226.0 | 2.85398 | 645.0 | 10.0 |
| 施工材料 | Plastering | square meters | 32.0 | 5.9375 | 190.0 | 10.0 |
| 施工材料 | Steel bars | square meters | 364.4 | 1.21844 | 444.0 | 10.0 |
| 施工材料 | Door and window | square meters | 3.98 | 28.8944 | 115.0 | 10.0 |
| 施工材料 | Stones | square meters | 244.0 | 50.0 | 12200.0 | 10.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 37000.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 37000.0 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 7 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Changing of the pipes | Once a year |
| 2. | Cleaning of the flange pump room | Six times a year |
| 3. | Changing of the hydraulic flange pump oil |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Changing of the pipes | persons/day | 1.0 | 7.0 | 7.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Cleaning of the flange pump room | persons/day | 1.0 | 7.0 | 7.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Changing of the hydraulic flange pump oil | persons/day | 1.0 | 7.0 | 7.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Pipes | meter | 20.0 | 0.65 | 13.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Oil | times/year | 4.0 | 4.5 | 18.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 52.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 52.0 | |||||
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Labor, stone and equipment are the main fundamental factors which need high initial investments.
After a couple of years pipes may need to be changed.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半干旱
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is low
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
中等
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
栖息地多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 游牧的
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
个人或集体:
- 团体/社区
性别:
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly disadvantaged land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Constructional activities which are done outside of the houses and compounds are mainly applied by men in Afghanistan.
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
100% of the land users are poor.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 社区/村庄
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
饲料生产
饲料质量
产品多样性
生产区域
土地管理
水资源可用性和质量
饮用水的可用性
家畜用水的可用性
家畜用水的质量
灌溉用水的可用性
灌溉用水的质量
收入和成本
农业投入费用
农业收入
收入来源的多样性
工作量
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
健康状况
SLM/土地退化知识
冲突缓解
注释/具体说明:
In case the owner of the first orchard do not obey the water use right
livelihood and human well-being
注释/具体说明:
The pump improved households’ economy through increasing agricultural yieIds and by decreasing the need for a generator pump. It has as well reduced the workload of the community members
生态影响
水循环/径流
水的回收/收集
蒸发
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤结壳/密封
土壤压实
盐度
生物多样性:植被、动物
植物多样性
动物多样性
减少气候和灾害风险
洪水影响
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
水资源可用性
注释/具体说明:
It has decreased the water flow only in the place where the hydraulic flange pump is installed.
旱季稳定可靠的水流
地下水/河流污染
缓冲/过滤能力
对邻近农田的破坏
对公共/私人基础设施的破坏
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 | |
| 年降雨量 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 未知 |
| 局地风暴 | 不好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 山洪暴发 | 不好 |
其他与气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
| 其它(具体说明) | 该技术是如何应对的? |
|---|---|
| length of growing period | 好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
非常消极
长期回报:
稍微积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
- 11-50%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
98 households covering 50 percent of the stated area
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
注释:
98 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: Due to high expenses of the implementation of the technology, it has not been applied without any external support.
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The technology is of a high cost and needs external support to be established.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Application of the technology has reduced the workload for the families. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Greater awareness on water management can be created by training/workshop for the water users. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
The technology has supported the community members economically by increasing agricultural yields. Moreover, it contributes to reduce the costs of water during the summer season. How can they be sustained / enhanced? The land users should try to plant local and native trees and cultivate the crops which are adapted to the land.Community members should actively participate in maintenance activities. |
|
Provides safe drinking water to the 43 households and the school at low cost. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Pipe scheme and cover of the reservoir, should be cleaned regularly. If any leakages occurs in the pipes or reservoir, they should be sealed. Water taps and water tanks should be properly maintained. |
|
This technology has been applied in a low slope/latitude where the water flows with a very low speed and the application of other technologies was difficult. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Protect from sedimentation. |
|
The hydraulic flange pump is produced locally. Procurement and installment of the pump contributes therefore to local economic growth and private sector development. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Link the company to the other potential buyers. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Social conflicts can occur during the distribution of water | The water in keeper/maintainer can be introduced by CDCs for the distribution of water. |
| Electricity cannot be produced by applying this technology. The slope and latitude of the location where the flange pump is installed is too small. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
|
It is difficult to apply the technology without any external and financial support. |
Locally available materials should be used to reduce costs. |
| High level of technical knowledge is required for the establishment of the technology. | The technical knowledge should be transferred to the extension workers or local people to provide technical support in the future. |
|
This technology needs regular maintenance and the reservoir has to be properly cleaned after heavy rainfalls. |
The CDC should monitor maintenance activities by the caretaker as well as manage funds for maintenance costs. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块