Brush Layering [莱索托]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Matoka Moshoeshoe
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Rima Mekdaschi Studer, William Critchley
Brush packs
technologies_4594 - 莱索托
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
SLM专业人员:
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Decision Support for Mainstreaming and Scaling out Sustainable Land Management (GEF-FAO / DS-SLM)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Integrated Catchment Management Project (Integrated Catchment Management Project) - 莱索托1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
注释:
This technology is environmentally sustainable
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷

Enhancement of existing SLM technologies into demonstration sites [塔吉克斯坦]
Enhancement of existing self developed SLM technologies into demonstration sites.
- 编制者: Habib Kamolidinov
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
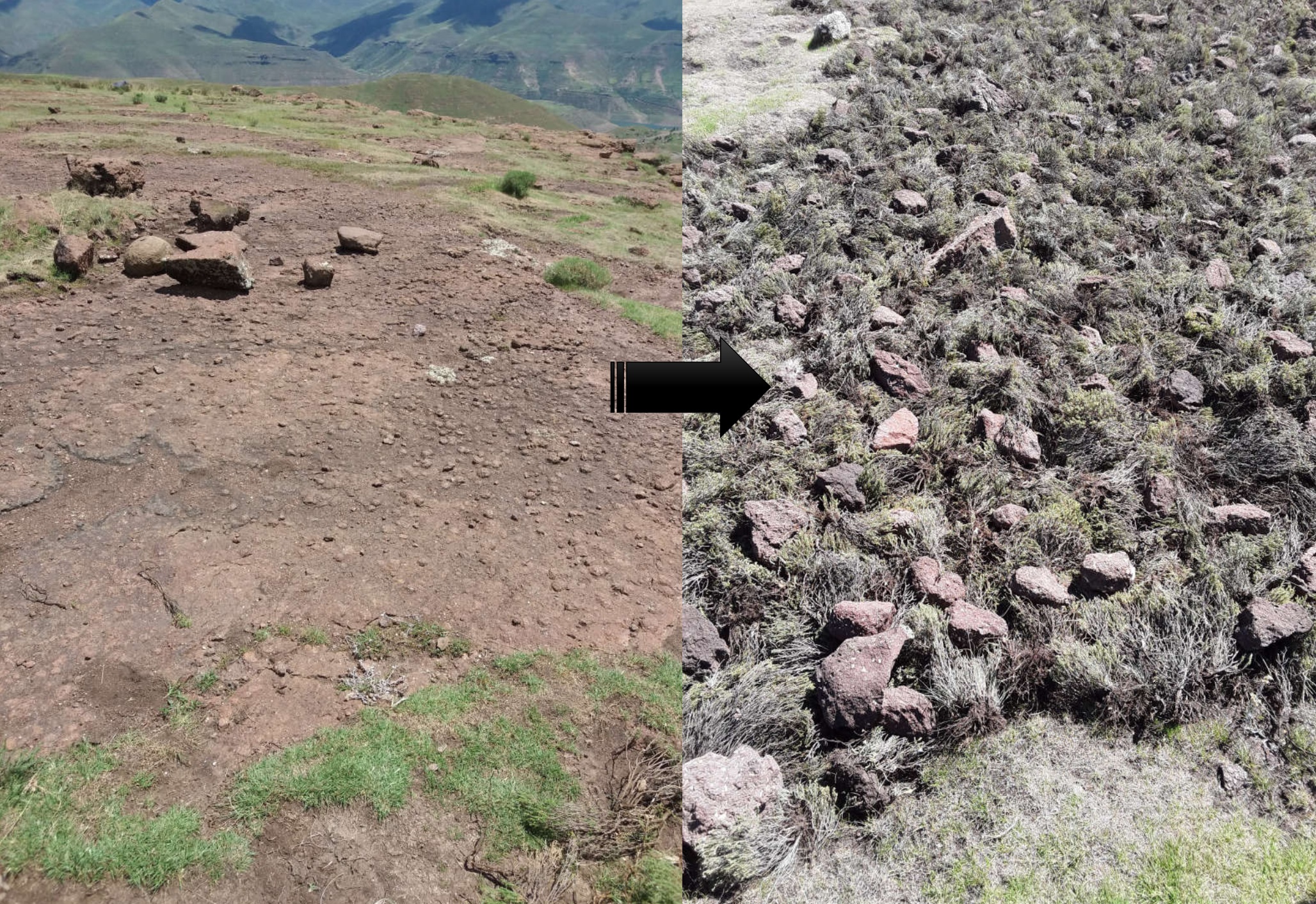
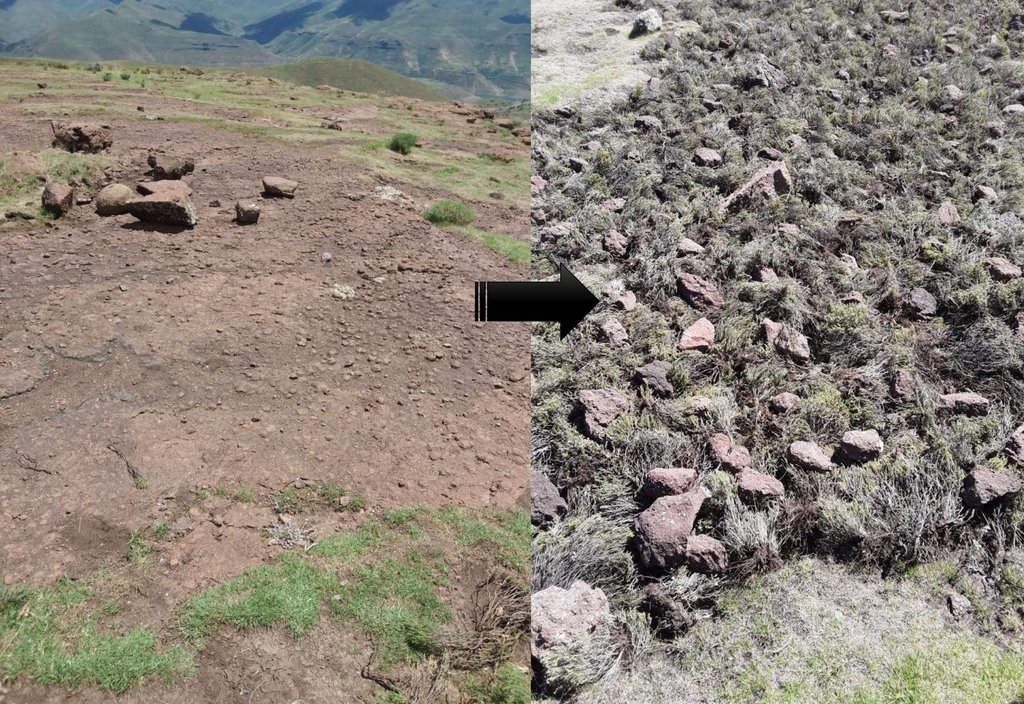
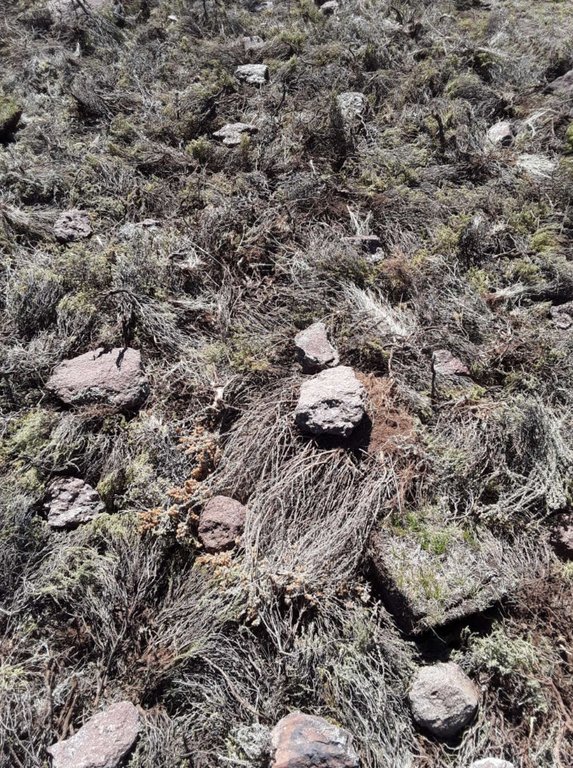
The technology requires removal of invaders as resources for layering. The technology enhances accumulation of silt and moisture storage in dry-lands due to increased organic matter content in the soil from the brush.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
DESCRIPTION OF TECHNOLOGY
1. It is applied on bare lands
2. Flowering stages of invaders should be taken into consideration before layering
3. functions; silt trap, moisture retention, as a factor of soil formation and medium for plant growth
4. Locally available materials such as invasive species
5. Improves land cover, land productivity and soil organic carbon
6. To land users, the technology is easy to implement and it has higher chances of reclaiming the marginal land. However, most of invasive species are used as source of fuel by the rural communities for cooking and heating in households. Many rural communities do not have electricity, gas or firewood as a source of fuel. Whenever people come across a heap of these invasive species, they vandalize it.
2.3 技术照片
2.4 技术视频
注释、简短说明:
N/A
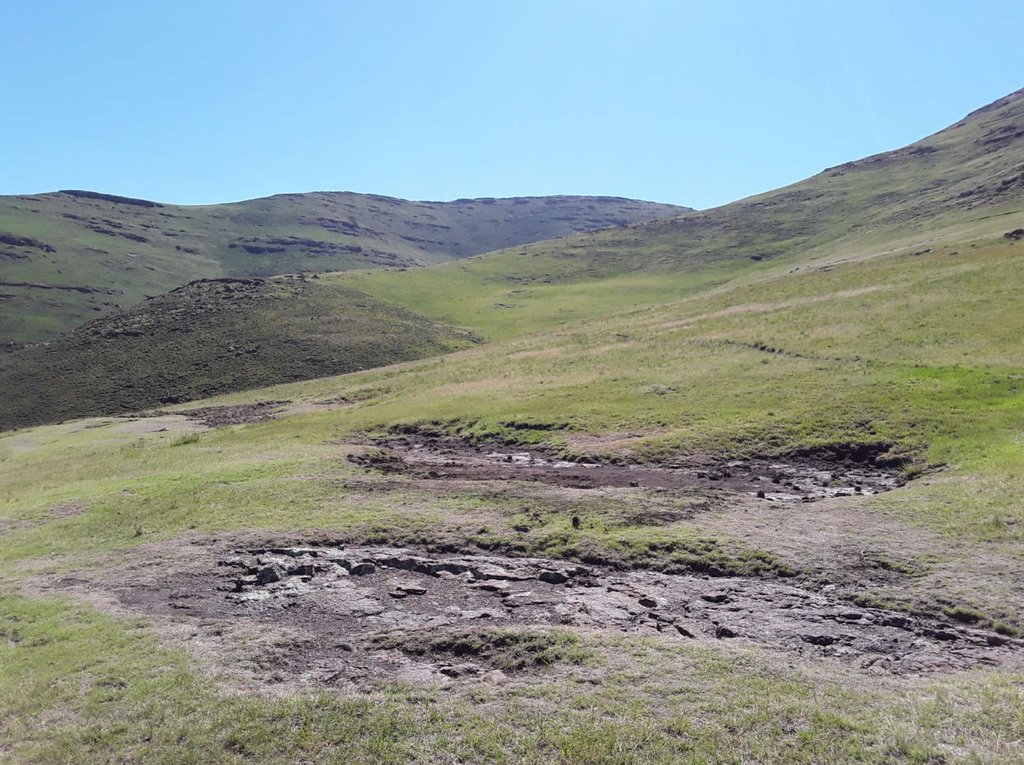
位置:
N/A
摄影师的名字:
N/A
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
莱索托
区域/州/省:
Leribe District
有关地点的进一步说明:
Lesotho highlands
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
技术现场是否位于永久保护区?:
否
注释:
all forms of biodiversity were reclaimed since the implementation of the technology
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2019
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
The technology was advocated to the community during scaling out of DS-SLM project
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 保护生态系统
- 结合其他技术保护流域/下游区域
- 保持/提高生物多样性
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
否

牧场
粗放式放牧:
- 半游牧畜牧业
集约放牧/饲料生产:
- 改良牧场
动物类型:
- 牛 - 非奶牛牛肉
是否实行作物与牲畜的综合管理?:
是
如果是,请具体说明:
Maize, peas and wheat
产品和服务:
- 肉类
- 交通工具/役畜
品种:
牛 - 非乳制品工作
注释:
more than 80% of the area is range-land. The area forms part of the upper catchment for the Katse dam (LHDA)
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 否(继续问题3.4)
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
注释:
The technology is implemented on the range-land
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 农畜综合管理
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V2:草和多年生草本植物
- V4:更换或清除外来/入侵物种

管理措施
- M5:物种组成的控制/变化
注释:
The technology improves acreage and range-land health
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

土壤风蚀
- Et:表土流失

物理性土壤退化
- Pk:熟化和结壳
- Pi:覆土

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
- Bh:栖息地丧失
- Bq:数量/生物量减少
- Bl:土壤寿命损失

水质恶化
- Hp:地表水水质下降
注释:
Improves land cover quality and productivity
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
注释:
It is very effective as a means to control land degradation - LDN indicators; Land cover, Land productivity and Soil organic carbon can be achieved through this technology
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
There is no criteria on how to construct the brush packs, the brush/invaders are uprooted from somewhere, whether within the same area or transported from another area, what is important is that any bare land within the catchment is applied this technology. The brush is simply placed on any area that has no vegetative cover, and stones are put on top of the brush so as to avoid being blown away by the wind. There is no specific design for this technology. As a result, there cannot be any technical drawing for this technology.
作者:
Koetlisi Koetlisi
日期:
20/02/2019
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
0.25ha
如果使用本地面积单位,注明转换系数为1公顷(例如1公顷=2.47英亩):1公顷=:
N/A
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
4.6
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | public gathering | Any |
| 2. | brush control | before flowering |
| 3. | brush layering | Any |
注释:
The brush is uprooted then put as it is onto the bare soil, the rest is done is done by insects and micro-organisms
It is important to consider flowering season of invaders in order to avoid anthropogenic dispersal of seeds
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | person-days | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | |
| 设备 | muttock | piece | 1.0 | 16.0 | 16.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 21.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 21.0 | |||||
如果您无法分解上表中的成本,请估算建立该技术所需要的总成本。:
21.0
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
Government
注释:
This technology is free, nothing is procured in order to implement it. The communities alone do implement by themselves.
With or without government funds, the activity can still be implemented
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | N/A | N/A |
注释:
One way to maintain this technology is re-layering where the first attempt was not successful.
Periodic visits required in order to check re-growth of invaders as well as expected species
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | N/A | N/A |
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
Government
注释:
The activity requires minimal effort and less funds to be performed although the yields are very high
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
The technology is a free one, anybody even a layman does implement it. Herders at cattle post do implement it. There are no costs incurred to implement it.
The implementation as well as maintenance are least cost effective
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
1200.00
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Lesotho highlands receive generally very good rains
注明所考虑的参考气象站名称:
Bokong
农业气候带
- 半干旱
Lesotho is generally on temperate zones
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
It is easily implemented on gently to moderate slopes
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Detailed soil depth, type and texture map could be found on https;//lesis.gov.ls
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
< 5米
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
水质请参考::
地下水和地表水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Water quality is attributed to good range-land management as the erosion is minimal as well as parent rock
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 高
栖息地多样性:
- 高
关于生物多样性的注释和进一步规范:
Most areas still have good biodiversity especially where range-lands are rested
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 半游牧的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
- 团体/社区
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 畜力牵引
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 中年人
- 老年人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
The land users are very cooperative together with their local authorities in land management activities
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
注释:
The technology is yet to be up-scaled as this was just a demonstration site
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 社区/村庄
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
- 社区(有组织)
用水权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
- 社区(有组织)
土地使用权是否基于传统的法律制度?:
是
注释:
In Lesotho, land is communally owned therefore, all land users have access to the communal land, no user rights are given, that is why there is common pool resources challenges. communities manage their resources by laying down regulations and bylaws.
Lesotho land tenure system supports communal ownership of land
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
注释:
Unlike most highlands in Lesotho, this area is most privileged due to Lesotho Highlands Development Authority interventions
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
土地管理
SLM之前的数量:
Degraded land
SLM之后的数量:
Restoration significant
注释/具体说明:
Layering restores bare areas
社会文化影响
SLM/土地退化知识
SLM之前的数量:
Poor
SLM之后的数量:
Increased
生态影响
土壤
土壤水分
SLM之前的数量:
Wilting point
SLM之后的数量:
Field capacity
注释/具体说明:
Moisture content not measured
土壤覆盖层
SLM之前的数量:
NDVI 0.1
SLM之后的数量:
NDVI 0.5
注释/具体说明:
Not measured but estimated from landsat
土壤有机物/地下C
SLM之前的数量:
1%
SLM之后的数量:
1.01%
注释/具体说明:
Might improve with
生物多样性:植被、动物
植被覆盖
SLM之前的数量:
NDVI 0.1
SLM之后的数量:
NDVI 0.5
注释/具体说明:
This technology has improved vegetation cover where it has been applied.
减少气候和灾害风险
干旱影响
SLM之前的数量:
wilting point
SLM之后的数量:
prolonged field capacity
注释/具体说明:
Brush works more or less like mulch.
对现场影响的评估(测量)进行具体说明:
vegetation, water resources, soil quality and properties, livelihoods as well as land use assessments were done
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
水资源可用性
SLM之前的数量:
Ground water not recharged
SLM之后的数量:
Ground water mostly recharged
注释/具体说明:
Several seasonal water sources enhanced
对场外影响(测量)的评估进行具体说明:
vegetation, water resources, soil quality and properties, livelihoods as well as land use assessments were done
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| Snow cover in some areas in the highlands | 未知 |
注释:
Lesotho highlands receive much snow in winter and they are very cold and dry
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
中性/平衡
注释:
according to land users, the technology is easy to implement
6.5 技术采用
- 1-10%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
40
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
注释:
Livestock owners found the technology very easy to implement as against those who did not own any livestock
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| It requires no inputs |
| It needs less equipment |
| It does not need periodic monitoring and evaluation |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| It can be demonstrated to a lot of people at the same time |
| It is less time consuming |
| It can be implemented without government funds |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Locally available material liable to vandalism | intensive extension |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| community participation | extension service enforcement |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
45
- 与土地使用者的访谈
15
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
19/02/2019
注释:
The community members who owned livestock found the technology more relevant than those who did not own any livestock. This is because this technology improves rangelands more than any other resource. Lesotho rangelands are characterised by presence of invaders and absence of vegetation cover due to poor management of rangelands
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
N/A
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
N/A
7.3 链接到网络上的相关信息
标题/说明:
N/A
URL:
N/A
7.4 一般注释
Most information on this technology has been deduced from various studies and also learned through attendance of various land-scape management fora and excursions
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Enhancement of existing SLM technologies into demonstration sites [塔吉克斯坦]
Enhancement of existing self developed SLM technologies into demonstration sites.
- 编制者: Habib Kamolidinov
模块
无模块