Project of check-dam for land [الصين]
- تاريخ الإنشاء:
- تحديث:
- جامع المعلومات: Fei WANG
- المحرر: –
- المُراجع: David Streiff
淤地坝工程
approaches_2450 - الصين
عرض الأقسام
توسيع الكل طي الكل1. معلومات عامة
1.2 تفاصيل الاتصال بالأشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات والمؤسسات المعنية بتقييم وتوثيق النهج
اسم المؤسسة (المؤسسات) التي سهلت توثيق/تقييم النهج (إذا كان ذلك على صلة)
Northwest A&F University (NWAFU) - الصين1.3 الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT
يوافق جامع المعلومات والشخص (لاشخاص) الرئيسي لمصدر المعلومات على الشروط المتعلقة باستخدام البيانات الموثقة من خلال WOCAT:
نعم
1.4 المراجع الخاصة باستبيان(استبيانات) تقنيات الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي

Check dam for land [الصين]
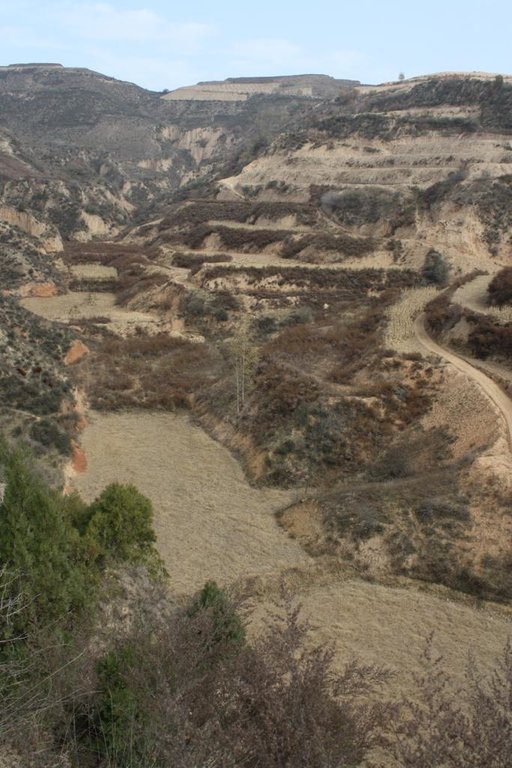
Check dam for land is a structural SLM practice that is constructed in the valley of a watershed in order to slow down the runoff and increase sedimentation. After this, the land quality of the controlling area will increase because soil and water conditions in this place are improved.
- جامع المعلومات: Fei WANG
2. وصف نهج الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
2.1 وصف موجز للنهج
Approach of check dam for land is a kind of soil and water conservation activity to reduce the sediment discharge and improve the agricultural condition through building a dam across the valley in order to silt the sediment from upstream untill it convert to land with few soil erosion and flash floods.
2.2 وصف تفصيلي للنهج
وصف تفصيلي للنهج:
Aims / objectives: The aims of this approach are to reduce sediment discharge of the rivers and to create cropland in the valley. A wall across the valley is built to hold up the muddy flash flood and to slow down the runoff and to silt the sediment. The water in the check dam could be used as waterbody or discharge as clear water. The local farmers and governments want to improve the agricultural condition in the valley near to village and select the check dam for land.
Methods: Normally the farmers and the local experts judge the feasibility of the technology firstly and then apply the support of local government. The construction should be finished by group (village) with labour input combining with finicial support outside.
Stages of implementation: The first stage to implenment this technology is to call on the local farmers with benefits show of such technologies. Then, an application should be submitted to local gevernment. After getting the support, the construction begin.
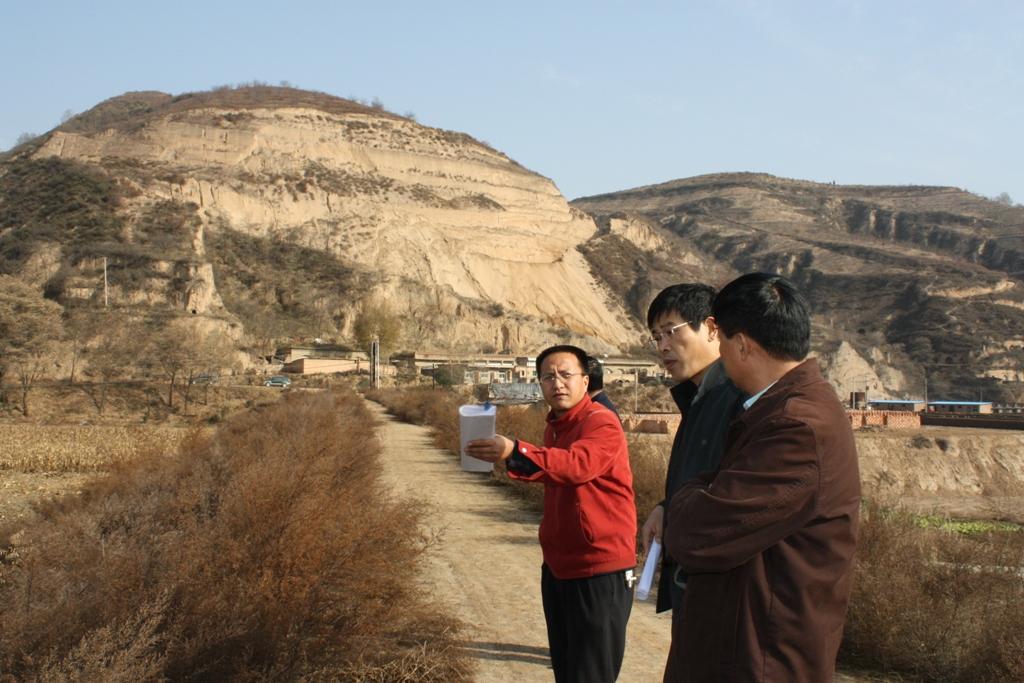
Role of stakeholders: The local farmers, experts and local government are main participants in this approach.
2.3 صور عن النهج
2.5 البلد/المنطقة/المواقع التي تم تطبيق النهج فيها
البلد:
الصين
المنطقة/الولاية/المحافظة:
Shaanxi Province
مزيد من التفاصيل حول الموقع:
Baota County, Yan'an City
التعليقات:
The total area with different measures is almost 2000 km2 . Yanhe River is a first class branch of Yellow River, China. The average channel slope is 3.26‰, and the area of whole basin is 7,687 km2. It is situated in the semi-arid North Temperate Zone with an average annual precipitation varying from 500 to 550 mm, and an average annual air temperature ranging from 8.5 to 11.4℃. It is in hilly gull
Map
×2.6 تواريخ بدء وإنهاء تنفيذ النهج
أشر إلى سنة البدء:
18
سنة الإنهاء (إذا لم يعد النهج مطبقًا):
16
2.7 نوع النهج
- قائم على مشروع/برنامج
2.8 الغايات/الأهداف الرئيسية للنهج
The Approach focused mainly on SLM with other activities (Structural practices; crop land; reduction of sediment load downstream)
1. it reduces the sediment load of the downstream or main river. 2. it improves the agricultural condition through the gain of new cropland in the valleys; 3. it reduces the soil erosion of gullies by down-cutting erosion; 4. it to reduces the gravity erosion or collapse of slopes because the land would increase the stability of slopes. 5. it designs the check dam well and search funds in order to construct the check dam.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: The problems include: lack of flat areas for crop production, high soil erosion on the slopes, poverty induced by low production, requirement of sediment control , lack of cash, and so on.
2.9 الظروف التي تمكن أو تعيق تنفيذ التقنية/التقنيات المطبقة بموجب النهج
توفر/الوصول إلى الموارد والخدمات المالية
- معيق
the input for a check dam is high for small households and villages
Treatment through the SLM Approach: financial support from outside such as local or central governemnt, or the management organization of water basin.
الإطار القانوني (حيازة الأراضي، وحقوق استخدام الأراضي والمياه)
- تمكين/تمكيني
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights greatly helped the approach implementation: The approach has many advantages for the different stakeholders. The existing land ownship, land user rights and water rights could help the approach implementation.
المعرفة حول الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي، والوصول إلى الدعم الفني
- معيق
A huge flood would destroy the dam
Treatment through the SLM Approach: To improve the quality which is depending on calculation of the possibility of flood and during extrem storms the control area of the dam.
3. المشاركة وأدوار الأطراف المعنية
3.1 أصحاب المصلحة المعنيون بالنهج وأدوارهم
- مستخدمو الأراضي المحليون/المجتمعات المحلية
Some check dams were implemented by villagers, before
The land area of local farmers is very small, and the decision at the village level should be decided by the group.
- متخصصون في الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي / مستشارون زراعيون
The geologist designs the site of engineering, the hydyologist designs the ability of dam according the strom records and landform of the basin; the civil engineers design the number of engineers.
They can evaluate the properity of check dam for land and design it
- الحكومة المحلية
The departments with certification to implement
They decide the planning of soil and water conservation.
- الحكومة الوطنية (المخططون، صانعو القرار)
By politicians / leaders
3.2 انخراط مستخدمي الأراضي المحليين/المجتمعات المحلية في المراحل المختلفة للنهج
| انخراط مستخدمي الأراضي المحليين/المجتمعات المحلية | حدد من شارك وصف الأنشطة | |
|---|---|---|
| المبادرة/التحفيز | التعبئة الذاتية | the local farmers and village head involved normally. They could build the check dam before but they submit the proposal for the building now. |
| التخطيط | الدعم الخارجي | the experts in hydrology, soil erosion, landform involved. They survey, calculate and design the check dam. |
| التنفيذ | تفاعلي | |
| الرصد/التقييم | غير موجود | |
| Research | غير موجود |
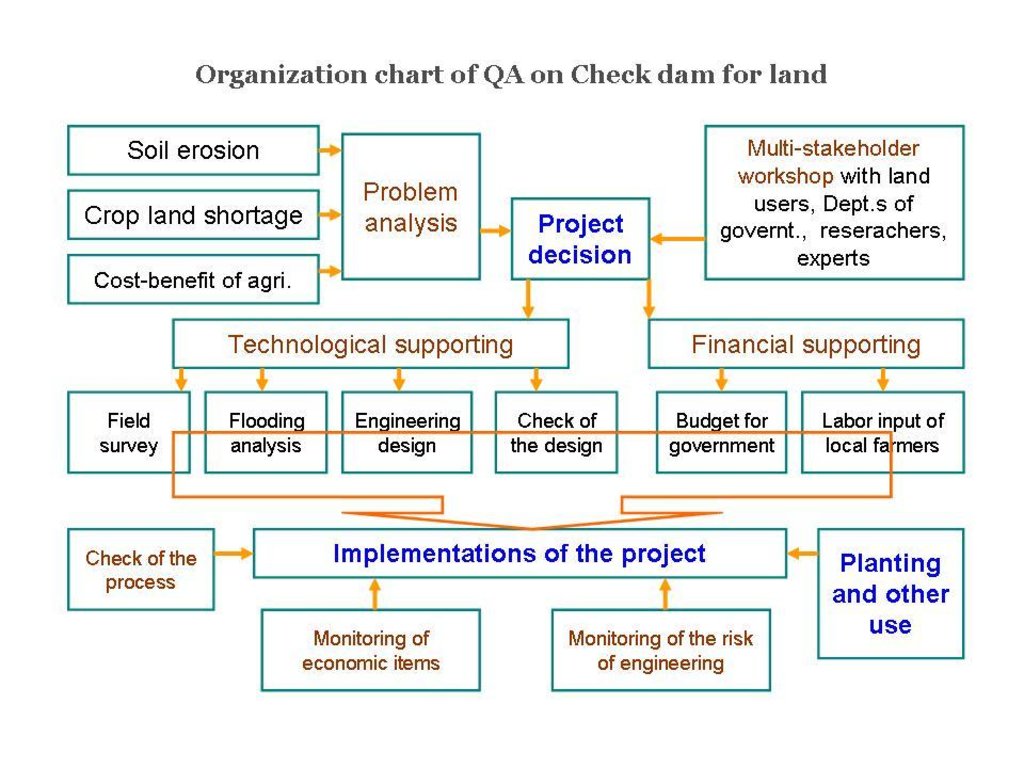
3.3 مخطط التدفق (إذا كان متاحًا)
3.4 اتخاذ القرار بشأن اختيار تقنية/تقنيات الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
حدد من الذي قرر اختيار التقنية/التقنيات التي سيتم تنفيذها:
- السياسيون / القادة
اشرح:
the high input is mainly from the government. Specialist also play a very important role in decision making.
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by mainly by SLM specialists with consultation of land users. the specialists are the conductor according the natural condition and the requirement of the land users.
4. الدعم الفني وبناء القدرات وإدارة المعرفة
4.1 بناء القدرات/التدريب
هل تم تقديم التدريب لمستخدمي الأراضي / الأطراف المعنيين الآخرين؟:
نعم
حدد من تم تدريبه:
- مستخدمو الأراضي
- موظفون ميدانيون/ مستشارون
شكل التدريب:
- مناطق العرض
- اجتماعات عامة
4.2 خدمة استشارية
هل يملك مستخدمو الأراضي وصولا إلى خدمة استشارية؟:
نعم
حدد ما إذا كانت الخدمة الاستشارية متوفرة:
- في حقول مستخدمي الأراضي
- في مراكز دائمة
وصف/تعليقات:
Consultation and Discussion; Key elements: Determine and classify the questions and problems of the project, Analysis the problems and discussion it wth the relative experts, Explain the whole condition of the project to the participants; it is not so difficult in the Loess Plateau because the local farmers are familiar with the check dam for land more or less.
Advisory service is quite adequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities; the technology is not new in the Yan River Basin
4.3 تعزيز المؤسسات (التطوير التنظيمي)
هل تم إنشاء أو تعزيز مؤسسات من خلال هذا النهج؟:
- نعم، قليلا
حدد المستوى (المستويات) التي تم فيها تعزيز أو إنشاء المؤسسات:
- محلي
حدد نوع الدعم:
- بناء القدرات/التدريب
اعط مزيدا من التفاصيل:
To show the benefits and process of construction for local farmers.
4.4 الرصد والتقييم
هل يشكل الرصد والتقييم جزءا من النهج؟:
نعم
التعليقات:
technical aspects were regular monitored by project staff through measurements; indicators: Professional is necessary in measure and design.
economic / production aspects were regular monitored by project staff, land users through observations; indicators: To know the benefit of project
economic / production aspects were regular monitored by project staff through measurements; indicators: To monitor sometime.
no. of land users involved aspects were regular monitored by government through measurements; indicators: To know how many people participating
management of Approach aspects were regular monitored by government through measurements; indicators: To manage the whole project
There were few changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: the safety of the dam should be checked after flood season in order that the check dam management can be adapted to changing risks.
There were several changes in the Technology as a result of monitoring and evaluation: the sediment from slopes decreased recently, the drainage channel changed to lower level since the stage of designing.
4.5 البحوث
هل كانت البحوث جزءًا من النهج؟:
نعم
حدد المواضيع:
- الاقتصاد / التسويق
- علم الايكولوجيا
- تكنولوجيا
أعط تفاصيل إضافية وأشر إلى من قام بالبحوث:
The experts should know the important parameters of the technology for improved designing. The researchers also need to judge and evaluate the permission and support of the project based on the econonic and ecological impacts.
Research was carried out both on station and on-farm
5. التمويل والدعم المادي الخارجي
5.1 الميزانية السنوية لمكون الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي في النهج المذكور
إذا لم تكن الميزانية السنوية الدقيقة معروفة، قم بالإشارة إلى نطاقها:
- < 2000
التعليقات (على سبيل المثال المصادر الرئيسية للتمويل/الجهات المانحة الرئيسية):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: government (the input is mainly from government): 90.0%; local community / land user(s) (labour work input): 10.0%
5.2 الدعم المالي/المادي المقدم لمستخدمي الأراضي
هل حصل مستخدمو الأراضي على دعم مالي/ مادي لتنفيذ التقنية/ التقنيات؟:
نعم
إذا كانت الإجابة بنعم، حدد نوع (أنواع) الدعم والشروط والمزودين:
by state
5.3 إعانات لمدخلات محددة (بما في ذلك العمالة)
- معدات
| حدد المدخلات التي تم دعمها | إلى أي مدى | حدد الإعانات |
|---|---|---|
| الآلات | ممول بالكامل | by government |
- بناء
| حدد المدخلات التي تم دعمها | إلى أي مدى | حدد الإعانات |
|---|---|---|
| حجر | ممول بالكامل | loess around the site of the dam |
التعليقات:
The labor input is necessary and some time they can get money from government or other families have no time to participate the construction.
The tools of farmers is very simple.
5.4 الائتمان
هل تم توفير ائتمان في إطار نهج أنشطة الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي؟:
كلا
6. تحليل الأثر والتصريحات الختامية
6.1 آثار النهج
هل ساعد النهج مستخدمي الأراضي على تنفيذ وصيانة تقنيات الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
1. the land in the valley is prone to incision by flash flood, the check dam could prevent the erosion; 2. crop land is very useful for the local farmers because of its good condition of soil properities, the local farmers paid more attention to protect this land;3. the ability of production is hig
هل ساهم النهج في تمكين الفئات المحرومة اجتماعيا واقتصاديا؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
agricultural condition improved so that the yield, income and spare time increases. There are no special changes on gender, age and ethnicity induced by this approach.
هل أدى النهج إلى تحسن في مسائل حيازة الأراضي / حقوق المستخدمين التي أعاقت تنفيذ تقنيات الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي؟:
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
The problem is unlikely to be overcome in the near future. The approach has been approved that the ability of anti-flooding is high. The possible extream storm is out of the consideration till now.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
the Ministry of Water Resources of China developed a project for check dam engineering land based on its the integrated functions. The local government and land users (local farmers) also try to find financial support for this project.
Did the Approach lead to improved livelihoods / human well-being?
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
Stable and high yield, and the relative labor input, of check-dam land could improve livihoods and human well-being; 2. In general cropland land is limited in such an area
Did the Approach help to alleviate poverty?
- لا
- نعم، قليلا
- نعم، باعتدال
- نعم، إلى حد كبير
Stable and high yield, and the relative labor input, of check-dam land could improve livihoods and human well-being; 2. In general cropland land is limited in such an area
6.2 المحفز الرئيسي لقيام مستخدمي الأراضي بتنفيذ الإدارة المستدامة للأراضي
- زيادة الإنتاج
the yield of the check dam land is stable and high
- انخفاض عبء العمل
the labour work less when getting the same food
- well-being and livelihoods improvement
the output of labour is higher
6.3 استدامة أنشطة النهج
هل يمكن لمستخدمي الأراضي المحافظة على استدامة ما تم تنفيذه من خلال النهج (بدون دعم خارجي)؟:
- غير مؤكد
إذا كان الجواب لا أو غير متأكد، حدد ذلك وعلق عليه:
the finicial support of local farmers is limited that makes it impossible to continue, but if the economic condition improved, they might build the check dam for cropland reclamation by themselves.
6.4 نقاط قوة/مزايا النهج
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر مستخدمي الأراضي |
|---|
| Could get the finicial from government (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Continue to support the construction at the suitable place) |
| To create 'good' land for themselves (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Share the land fairly) |
| نقاط القوة/ المزايا/ الفرص من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات |
|---|
| Make more people know its benefits (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Show the integrated impacts of project ) |
| Professional design (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: To improve the quanlity of project through field survey and calculation. ) |
| to organize the local farmers working together (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Plan and make the local farmers to know they can share fairly within the local farmers. ) |
6.5 نقاط الضعف/ العيوب في المنهج وطرق التغلب عليها
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر مستخدم الأراضي | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| very few, sometimes the are is temporary flooded | drainage of the flash water on time |
| نقاط الضعف/ المساوىء/ المخاطر من وجهة نظر جامع المعلومات أو غيره من الاشخاص الرئيسيين لمصدر المعلومات | كيف يمكن التغلب عليها؟ |
|---|---|
| change of landform | can not be overcome |
| The farmer does not plan to build check dam for land with their own invest | New approach is necessary for some farmers or small farmer group to implenment project themselves |
7. المراجع والروابط
7.1 طرق جمع/مصادر المعلومات
- زيارات ميدانية، مسوحات ميدانية
7.2 المراجع للمنشورات المتاحة
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Experiment and Practice of Check Dam Land, Zheng Baoming, Wang Xiao, Tianyonghong, Shangguomei, Mu Zhenlian. 2004
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
Yellow River Conservancy Press【YRCP】
العنوان، المؤلف، السنة، النظام القياسي الدولي لترقيم الكتب ISBN:
Effect of soil-retaining dams on flood and sediment reduction in middle reaches of Yellow River. Ran Dachuan, Luo Quanhua, Liu Bin, Wang Hong. 2004
متاح من أين؟كم التكلفة؟:
JOURNAL OF HYDRAULIC ENGINEERING ,2004, (5)
7.3 روابط للمعلومات ذات الصلة المتوفرة على الإنترنت
العنوان/الوصف:
Regional Impact of Human Activities on Soil and Water Losses. Wang Fei. PhD thesis, 2004
عنوان الرابط URL:
http://epub.cnki.net/grid2008/detail.aspx?DBName=CDFD2004&FileName=2004124106.nh
الروابط والوحدات المواضيعية
توسيع الكل طي الكلالروابط

Check dam for land [الصين]
Check dam for land is a structural SLM practice that is constructed in the valley of a watershed in order to slow down the runoff and increase sedimentation. After this, the land quality of the controlling area will increase because soil and water conditions in this place are improved.
- جامع المعلومات: Fei WANG
الوحدات المواضيعية
لا يوجد وحدات مواضيعية