Conventional (contour-line and ploughing) tillage [Hungary]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Ádám Kertész
- Editor: –
- Reviewers: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Hagyományos (szintvonalas és szántásos) müvelés (Hungarian)
technologies_1081 - Hungary
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
SLM specialist:
SLM specialist:
Csepinszky Béla
Geographical Research Institute, Hungarian Academy of Sciences
Hungary
Name of project which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Soil and water protection (EU-SOWAP)Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Geographical Research Institute, Hungarian Academy of Sciences (MTA CSFK) - Hungary1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Yes
1.5 Reference to Questionnaire(s) on SLM Approaches (documented using WOCAT)
Conventional (contour-line and ploughing) tillage [Hungary]
Conventional (contour-line and ploughing) tillage
- Compiler: Adam Kertesz
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
Conventional (contour-line and ploughing) tillage
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
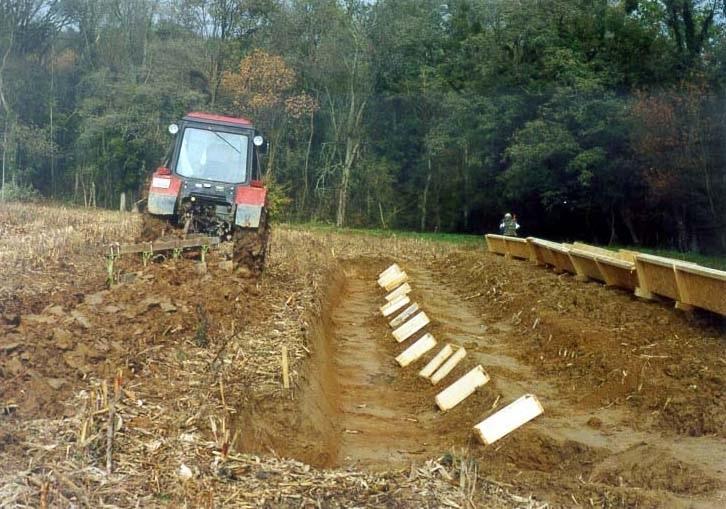
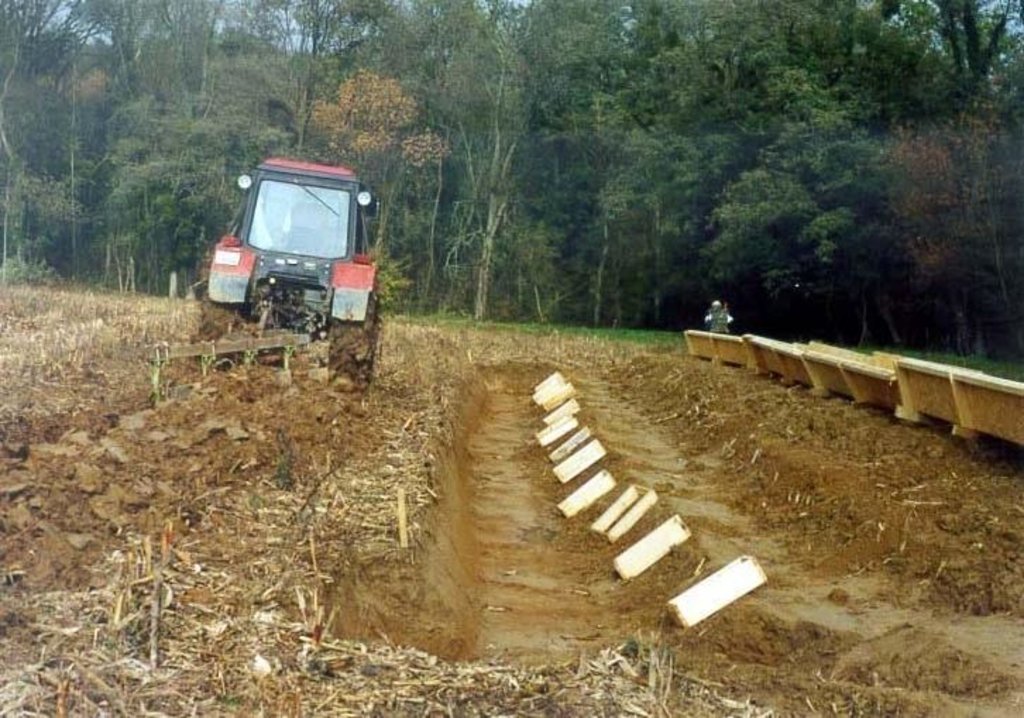
The basis of the technology is the annual autumn ploughing. The ploughing and all other cultivation is carried out parallel to the contour lines. This way the erosion can be significantly decreased. The rotational cultivation aims at the reduction of the areal and fluvial erosion, at the repulsion of the weeds and at the attainment of the ideal state of the seedbed at the time of sowing. It is applicable anywhere bellow a certain slope angle. The only restriction is the excessively thin parcel structure.
Special education and investment are not required, it can be realised by the available instruments.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Hungary
Region/ State/ Province:
Zala county
Further specification of location:
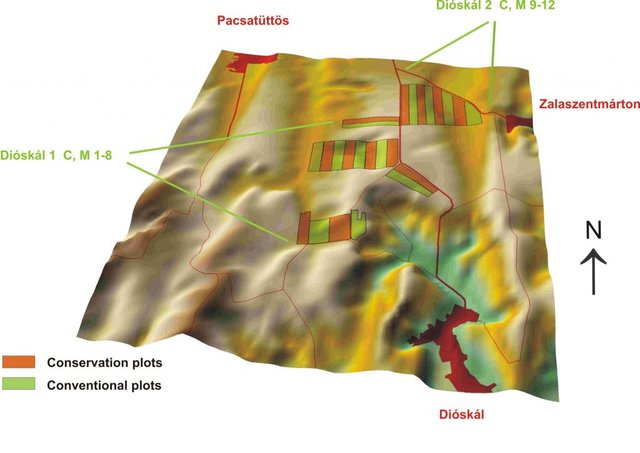
Zala county, Zala hills, Zala
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- evenly spread over an area
If the Technology is evenly spread over an area, specify area covered (in km2):
0.1963
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- 0.1-1 km2
Comments:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.1963 km2.
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- more than 50 years ago (traditional)
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- as part of a traditional system (> 50 years)
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- reduce, prevent, restore land degradation
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Cropland
- Annual cropping
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- cereals - maize
- cereals - wheat (winter)
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 1
Specify:
Longest growing period in days: 185; Longest growing period from month to month: Apr - Oct
Is crop rotation practiced?
Yes
If yes, specify:
Relay cropping: wheat, maize
Comments:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Fine loess soil with significant soil degradation, soil compaction due to inconvenient land use
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): EU and government rules, problems of the subsidy system, sales and marketing concerns
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: maize, winter wheat, maize…
3.4 Water supply
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- rainfed
3.5 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- rotational systems (crop rotation, fallows, shifting cultivation)
- minimal soil disturbance
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

agronomic measures
- A1: Vegetation/ soil cover
- A3: Soil surface treatment
Comments:
Type of agronomic measures: relay cropping, mineral (inorganic) fertilizers, soil conditioners (lime, gypsum), rotations / fallows, contour tillage
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wt: loss of topsoil/ surface erosion
- Wg: gully erosion/ gullying
- Wm: mass movements/ landslides

physical soil deterioration
- Pc: compaction
Comments:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wm: mass movements / landslides, Pc: compaction
Main causes of degradation: reorganization of the ownerships, land subdivision
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- reduce land degradation
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
Technical specifications (related to technical drawing):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, increase of infiltration
Relay cropping
Material/ species: wheat, maize
Quantity/ density: 5-6t/ha, 9
Rotations / fallows
Material/ species: wheat, maize
4.2 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
other/ national currency (specify):
Hungarian Forint
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
195.8
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
25.50
4.5 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | ploughing | autumn / annualy |
4.6 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
Comments:
Machinery/ tools: plough, disc, roller, drill, tractor, sprayer, harvester
4.7 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
compacted soil surface> chiselling (loosening); steep slops>more fuel; nutrient supply>expensive inorganic fertilizers
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Specify average annual rainfall (if known), in mm:
650.00
Agro-climatic zone
- sub-humid
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Comments and further specifications on topography:
Altitudinal zone: ~ 200 m
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Topsoil organic matter:
- medium (1-3%)
If available, attach full soil description or specify the available information, e.g. soil type, soil PH/ acidity, Cation Exchange Capacity, nitrogen, salinity etc.
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage / infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is medium and sometimes high
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Market orientation of production system:
- commercial/ market
Relative level of wealth:
- average
- rich
Level of mechanization:
- mechanized/ motorized
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: negative
Off-farm income specification: no off-farm income
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Comments:
Also 100-500 ha and 500-1,000 ha
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- individual, titled
Land use rights:
- individual
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
crop production
Income and costs
farm income
Socio-cultural impacts
SLM/ land degradation knowledge
Ecological impacts
Soil
soil loss
Other ecological impacts
soil fertility
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
downstream flooding
downstream siltation
groundwater/ river pollution
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
slightly positive
Long-term returns:
positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
slightly positive
Long-term returns:
positive
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- single cases/ experimental
If available, quantify (no. of households and/ or area covered):
1 household
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 91-100%
Comments:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: survey results
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| production increase |
| no investment necessary |
| decreased soil erosion |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| decreased soil erosion |
| production increase |
| no investment necessary |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks

Conventional (contour-line and ploughing) tillage [Hungary]
Conventional (contour-line and ploughing) tillage
- Compiler: Adam Kertesz
Modules
No modules