Piggery-Banana-Coffee technology [ອູເຈນດາ]
- ການສ້າງ:
- ປັບປູງ:
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: Tonny Kyambadde
- ບັນນາທິການ: Beatrice Nabukenya, Michael Mulindwa, Kyagaba Prossy, Annika Reimann
- ຜູ້ທົບທວນຄືນ: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
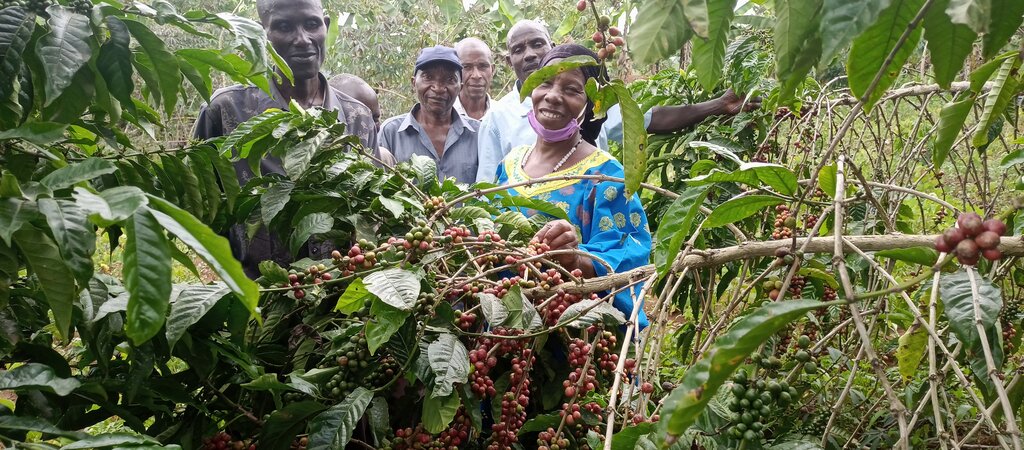
Obusa bwe mbizzi kumwanyi ne bitooke
technologies_5914 - ອູເຈນດາ
ເບິ່ງພາກສ່ວນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດ1. ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປ
1.2 ຂໍ້ມູນ ການຕິດຕໍ່ພົວພັນ ຂອງບຸກຄົນທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ແລະ ສະຖາບັນ ທີ່ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນການປະເມີນເອກກະສານ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
co-compiler:
Kyagaba Prossy
Caritas MADDO
ອູເຈນດາ
co-compiler:
co-compiler:
ຊື່ໂຄງການ ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ/ປະເມີນ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
Euregio-East Africa Livelihood Improvement Programme (EEALIP)ຊື່ສະຖາບັນ (ຫຼາຍສະຖາບັນ) ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ / ປະເມີນ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
Caritas Masaka Diocesan Development Organisation (Caritas MADDO) - ອູເຈນດາ1.3 ເງື່ອນໄຂ ກ່ຽວກັບ ການນໍາໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນເອກະສານ ທີ່ສ້າງຂື້ນ ໂດຍຜ່ານ ອົງການພາບລວມຂອງໂລກ ທາງດ້ານແນວທາງ ແລະ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການອານຸລັກ ທໍາມະຊາດ (WOCAT)
ຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ແລະ ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ ທີ່ໃຫ້ຂໍ້ມູນ (ຫຼາຍ) ຍິນຍອມ ຕາມເງື່ອນໄຂ ໃນການນຳໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນ ເພື່ອສ້າງເປັນເອກກະສານຂອງ WOCAT:
ແມ່ນ
1.4 ແຈ້ງການວ່າ ດ້ວຍຄວາມຍືນຍົງຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ດັ່ງກ່າວໄດ້ອະທິບາຍ ເຖິງບັນຫາ ກ່ຽວກັບ ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນບໍ? ຖ້າບໍ່ດັ່ງນັ້ນ ມັນບໍ່ສາມາດ ຢັ້ງຢືນໄດ້ວ່າ ເປັນເຕັກໂນໂລຊີ ໃນການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ? :
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The technology under documentation is practically proven for its efficiency and effectiveness in conserving land and improving productivity.
1.5 ແບບສອບຖາມທີ່ອ້າງອີງເຖີງແນວທາງ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ (ໄດ້ເຮັດເປັນເອກະສານທີ່ໃຊ້ WOCAT)

MADDO SLM approach [ອູເຈນດາ]
This integrated soil fertility management approach aims at identifying and promoting practices in land management that can increase soil fertility, reduce land degradation and improve production. Under this specific example, organic manure from a piggery was applied to banana and coffee plantations.
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: Tonny Kyambadde
2. ການອະທິບາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
2.1 ຄໍາອະທິບາຍສັ້ນຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການກຳໜົດຄວາມໝາຍ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
The "Piggery-Banana-Coffee" sustainable land management technology is a proven practice that significantly improves soil fertility and productivity in an integrated farming system for smallholder farmers in Uganda.
2.2 ການອະທິບາຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການພັນລະນາ:
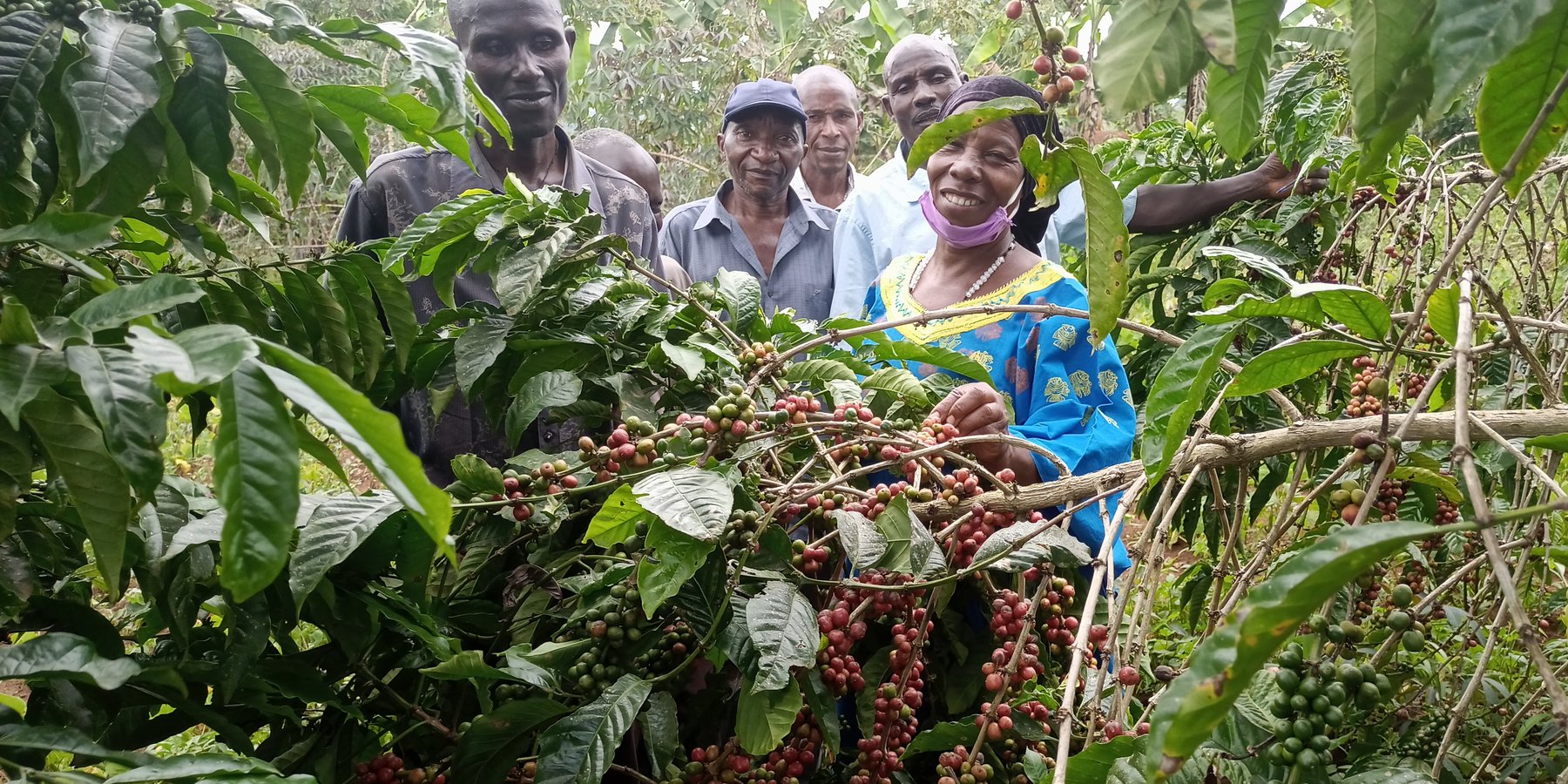
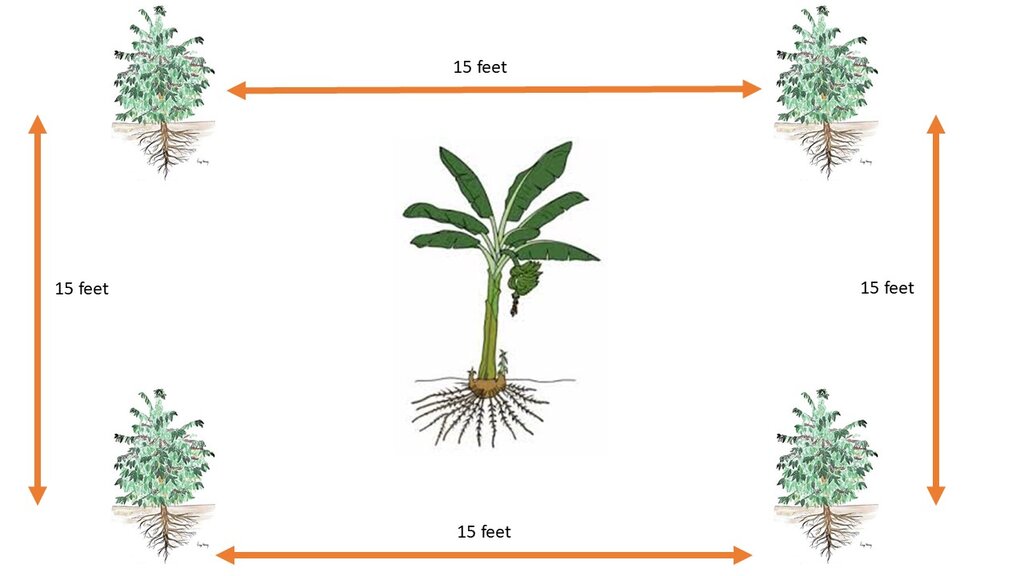
The “piggery-banana-coffee” SLM technology has been widely practiced by smallholders in Bukumansimbi District, Central Uganda for many years. The technology is proven due to its manifold functions and benefits, including increased productivity and improved soil biodiversity leading to better food security with organic, healthy produce. It simultaneously contributes to environmental protection. The technology has been applied for many years in Bukumansimbi but it needed a promotion by the implementer Caritas MADDO for wider adaption by the community.
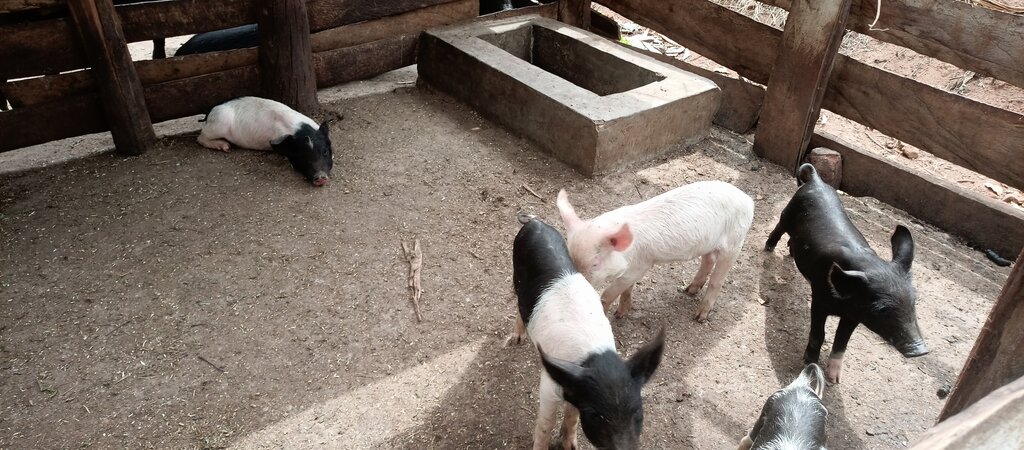
The technology can be applied in a natural environmental setting with no controlled conditions. Taking a case of one acre (0.4 ha) of land the farmer will need 450 coffee seedlings and 150 banana suckers to establish an integrated banana-coffee plantation. Then there is a requirement for 10 pigs to supply enough manure (urine and dung) to maintain the fertility of the soil in the plantation. Bananas provide shade to the coffee and reduce the impact of wind and soil erosion. Manure from the piggery is applied to the mixed plantation. Manure application increases soil biodiversity and improves both the physical and chemical properties of the soil, including soil structure, aeration, and moisture retention. Integrating piggery components into the system requires shed construction, purchase of piglets, feeding costs, treatment, and vaccinations. The pigsty occupies a space of 50 ft by 25 ft (approx. 15 m x 7.5 m). Each enterprise is complementary to the other: manure from pigs goes to the coffee and banana plantation and in return the banana peelings as well as the household food leftovers are served as important food resources for the pigs.
The land users under the pilot project acknowledge the significance of the technology because of its ability to sustain production and the other benefits listen above. However, swine fever disease is one of the limiting factors to the technology, as the pigs are prone to its outbreak. Moreover, some farmers report the high feeding costs for the pigs’ maintenance - particularly in the dry season (when there are few weeds that can be supplemented to the diet of the pigs).
2.3 ຮູບພາບຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
2.5 ປະເທດ / ເຂດ / ສະຖານທີ່ບ່ອນທີ່ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຮັບການນໍາໃຊ້ ແລະ ທີ່ຖືກປົກຄຸມດ້ວຍການປະເມີນຜົນ
ປະເທດ:
ອູເຈນດາ
ພາກພື້ນ / ລັດ / ແຂວງ:
Central region
ຂໍ້ມູນເພີ່ມເຕີມຂອງສະຖານທີ່:
Bigasa Sub County in Bukomansimbi District
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ການແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
- ແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍຢ່າງໄວວາໃນພື້ນທີ່
ຖ້າຫາກບໍ່ຮູ້ເນື້ອທີ່ທີ່ແນ່ນອນ, ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເນື້ອທີ່ໂດຍປະມານ ທີ່ໃກ້ຄຽງ:
- 0.1-1 ກມ 2
ສ່ວນຫຼາຍສະຖານທີ່ຕັ້ງຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແມ່ນ ຢູ່ໃນເຂດພື້ນທີ່ສະຫງວນບໍ?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
Map
×2.6 ວັນທີໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸປີ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ:
2017
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າ ບໍ່ຮູ້ຈັກ ປີທີ່ຊັດເຈນ ແມ່ນໃຫ້ປະມານ ວັນທີເອົາ:
- ຕໍ່າກວ່າ 10 ປີ ຜ່ານມາ (ມາເຖິງປະຈຸບັນ)
2.7 ການນໍາສະເໜີ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຖືກຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດຄືແນວໃດ?
- ເປັນສ່ວນໜື່ງຂອງລະບົບພື້ນເມືອງ (>50 ປີ)
- ໂດຍຜ່ານໂຄງການ / ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອຈາກພາຍນອກ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ (ປະເພດ ໂຄງການ ແລະ ອື່ນໆ):
The "piggery-banana-coffee” SLM technology has been practiced as a traditional system in the area for more than 50 years, however the project rebooted the technology and its adoption under the EEALIP project starting in 2017.
3. ການໃຈ້ແຍກ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໃນການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
3.1 ຈຸດປະສົງຫຼັກ (ຫຼາຍ) ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- ປັບປຸງ ການຜະລິດ
- ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ, ປ້ອງກັນ, ຟື້ນຟູ ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
- ການອະນຸລັກ ລະບົບນິເວດ
- ປົກປັກຮັກສາ / ການປັບປຸງຊີວະນາໆພັນ
- ສ້າງຜົນກະທົບ ທາງເສດຖະກິດ ທີ່ເປັນປະໂຫຍດ
3.2 ປະເພດການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃນປະຈຸບັນ() ທີ່ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຖືກນໍາໃຊ້
ການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ປະສົມພາຍໃນພື້ນທີ່ດຽວກັນ:
ແມ່ນ
ລະບຸການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນແບບປະສົມ (ຜົນລະປູກ / ທົ່ງຫຍ້າລ້ຽງສັດ / ຕົ້ນໄມ້):
- ກະສິກໍາ-ປ່າໄມ້ ແບບປະສົມປະສານ

ດິນທີ່ປູກພືດ
- ພືດຢືນຕົ້ນ (ບໍ່ແມ່ນໄມ້)
ການປູກພືດຢືນຕົ້ນ(ບໍ່ແມ່ນໄມ້ໄມ້ຢືນຕົ້ນ) - ໃຫ້ລະບຸປະເພດພືດ:
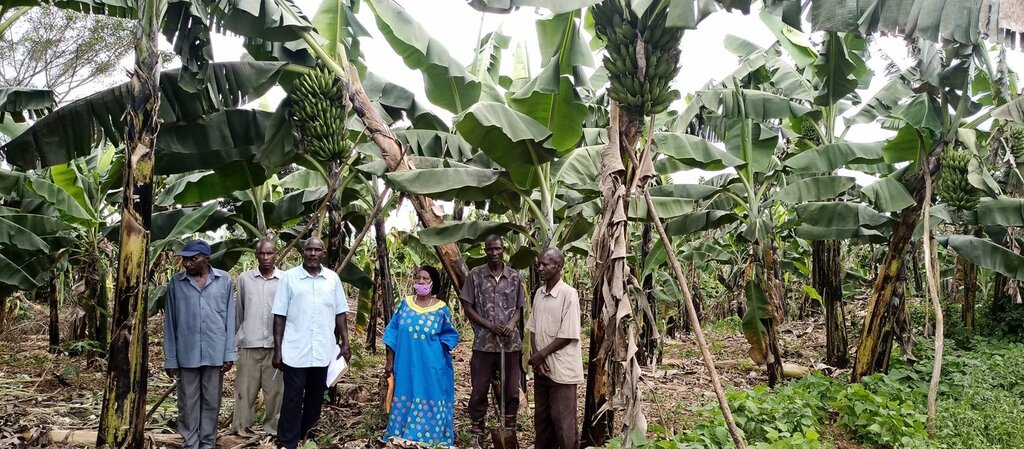
- ກ້ວຍ/ກວ້ຍຂຽວ/ໄຍຕົ້ນກ້ວຍ
- Coffee
ຈໍານວນ ລະດູການ ປູກໃນປີໜຶ່ງ:
- 2
ລະບຸ ຊະນິດ:
For banana the harvest is continuous through the year whiles as coffee has two harvesting seasons
ມີການເຝືກປູກພືດແບບສັບຫວ່າງບໍ່?
ແມ່ນ
ຖ້າມີ, ໃຫ້ລະບຸວ່າປູກພືດຊະນິດໃດທີ່ປູກສັບຫວ່າງ:
Banana and coffee are intercropped
ມີການເຝືກປູກພືດແບບໝູນວຽນບໍ່?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ

ປ່າໄມ້ / ປ່າ
- ການປູກຕົ້ນໄມ້, ການປູກປ່າ
ການປູກຕົ້ນໄມ້, ປູກປ່າ: ລະບຸ ຕົ້ນກຳເນີດ ແລະ ອົງປະກອບ ຂອງສາຍພັນ:
- ແນວພັນປະສົມ
- Ficus natalensis (mutuba in luganda) tree
ຕົ້ນໄມ້ທີ່ຖືກລະບຸຢູ່ຂ້າງເທິງ ເປັນປ່າຜັດປ່ຽນໃບ ຫລື ປ່າດົງດິບ?
- ປ່າດົງດິບ
ຜົນຜະລິດ ແລະ ການບໍລິການ:
- ເຄື່ອງປ່າຂອງດົງ
- ໄມ້ຟືນ
- ຜະລິດຕະພັນ ປ່າໄມ້ອື່ນໆ
- ທົ່ງຫຍ້າ
- ການອະນຸລັກທໍາມະຊາດ / ການປ້ອງກັນ
- ນັນທະນາການ / ການທ່ອງທ່ຽວ
- ປ້ອງກັນ ການຄຸກຄາມ ທາງທໍາມະຊາດ
- Backcloth

ທິດທາງໄຫຼຂອງນໍ້າ, ນໍ້າ, ດິນທາມ
- ໜອງ, ດິນທາມ
ຜະລິດຕະພັນຫຼັກ / ບໍລິການ:
Swamp is nearby for water supply
3.3 ການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ມີການປ່ຽນແປງຍ້ອນການຈັດຕັ້ງທົດລອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແມ່ນບໍ່?
ການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ມີການປ່ຽນແປງຍ້ອນການຈັດຕັ້ງທົດລອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແມ່ນບໍ່?
- ແມ່ນ (ກະລຸນາຕື່ມໃສ່ ຄຳຖາມຂ້າງລຸ່ມນີ້ກ່ຽວກັບການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ກ່ອນການທົດລອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ)
ການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ປະສົມພາຍໃນພື້ນທີ່ດຽວກັນ:
ແມ່ນ
ລະບຸການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນແບບປະສົມ (ຜົນລະປູກ / ທົ່ງຫຍ້າລ້ຽງສັດ / ຕົ້ນໄມ້):
- ປ່າໄມ້-ທົ່ງຫຍ້າ

ດິນທີ່ປູກພືດ
- ພືດຢືນຕົ້ນ (ບໍ່ແມ່ນໄມ້)
ການປູກພືດຢືນຕົ້ນ(ບໍ່ແມ່ນໄມ້ໄມ້ຢືນຕົ້ນ) - ໃຫ້ລະບຸປະເພດພືດ:
- ກ້ວຍ/ກວ້ຍຂຽວ/ໄຍຕົ້ນກ້ວຍ
- coffee
ມີການເຝືກປູກພືດແບບສັບຫວ່າງບໍ່?
ແມ່ນ
ຖ້າມີ, ໃຫ້ລະບຸວ່າປູກພືດຊະນິດໃດທີ່ປູກສັບຫວ່າງ:
Banana and coffee are intercropped
ມີການເຝືກປູກພືດແບບໝູນວຽນບໍ່?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ

ປ່າໄມ້ / ປ່າ
- ການປູກຕົ້ນໄມ້, ການປູກປ່າ
ການປູກຕົ້ນໄມ້, ປູກປ່າ: ລະບຸ ຕົ້ນກຳເນີດ ແລະ ອົງປະກອບ ຂອງສາຍພັນ:
- ແນວພັນປະສົມ
- Ficus natalensis (mutuba in luganda) tree
ຕົ້ນໄມ້ທີ່ຖືກລະບຸຢູ່ຂ້າງເທິງ ເປັນປ່າຜັດປ່ຽນໃບ ຫລື ປ່າດົງດິບ?
- ປ່າດົງດິບ
ຜົນຜະລິດ ແລະ ການບໍລິການ:
- ເຄື່ອງປ່າຂອງດົງ
- ໄມ້ຟືນ
- ຜະລິດຕະພັນ ປ່າໄມ້ອື່ນໆ
- ທົ່ງຫຍ້າ
- ການອະນຸລັກທໍາມະຊາດ / ການປ້ອງກັນ
- ນັນທະນາການ / ການທ່ອງທ່ຽວ
- ປ້ອງກັນ ການຄຸກຄາມ ທາງທໍາມະຊາດ

ທິດທາງໄຫຼຂອງນໍ້າ, ນໍ້າ, ດິນທາມ
- ໜອງ, ດິນທາມ
ຜະລິດຕະພັນຫຼັກ / ບໍລິການ:
Swamp is nearby for water supply
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Pigs are kept on zero grazing. There are not allowed to roam in the bananas or coffee farm.
3.4 ການສະໜອງນ້ຳ
ການສະໜອງນໍ້າ ໃນພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
- ນໍ້າຝົນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The land is mulched with dry grass and banana materials to conserve rainfed water from evaporation.
3.5 ການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ຢູ່ໃນກຸ່ມການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
- ກະສິກໍາ-ປ່າໄມ້ ແບບປະສົມປະສານ
- ການຄຸ້ມຄອງພືດ ແລະ ລ້ຽງສັດ ແບບປະສົມປະສານ
- ການຈັດການອຸດົມສົມບູນ ຂອງດິນປະສົມປະສານ
3.6 ມາດຕະການ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ ປະກອບດ້ວຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ມາດຕະການ ທາງການກະສິກໍາ
- A1: ພືດ / ການປົກຫຸ້ມຂອງດິນ
- A2: ອິນຊີວັດຖຸ ຫຼື ຄວາມອຸດົມສົມບູນໃນດິນ
- A3: ການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາຊັ້ນໜ້າດິນ
- A7: ອື່ນໆ
A3: ລະບົບການໄຖແຕກຕ່າງກັນ:
A 3.2: Reduced tillage (> 30% soil cover)

ມາດຕະການ ທາງດ້ານພືດພັນ
- V1: ເປັນໄມ້ຢືນຕົ້ນ ແລະ ການປົກຫຸ້ມຂອງໄມ້ພຸ່ມ
- V2: ຫຍ້າ ແລະ ພືດສະໝູນໄພທີ່ເປັນໄມ້ຢືນຕົ້ນ
- V3: ການຈັດການປູກພືດ

ມາດຕະການໂຄງສ້າງ
- S1: ພັກຄັນໃດ
- S9: ແນວບັງພືດ ແລະ ສັດລ້ຽງ
3.7 ປະເພດດິນເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຫຼັກທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ດິນເຊາະເຈື່ອນ ໂດຍນໍ້າ
- Wt: ການສູນເສຍຊັ້ນໜ້າດິນ / ການເຊາະເຈື່ອນຜິວໜ້າດິນ
- Wo: ຜົນກະທົບ ຂອງການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຕໍ່ພື້ນທີ່ພາຍນອກ

ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຂອງດິນ ທາງເຄມີ
- Cp: ດິນເປັນມົນລະພິດ

ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ທາງຊີວະພາບ
- Bq: ປະລິມານ / ອິນຊີວັດຖຸຫຼຸດລົງ
- Bs: ຄຸນນະພາບ / ການອັດແໜ້ນ ຂອງສາຍພັນຫຼຸດລົງ
- Bl: ການສູນເສຍ ຈຸລິນຊີໃນດິນ
- Bp: ສັດຕູພືດ ແລະ ພະຍາດເພີ່ມຂື້ນ, ສູນເສຍນັກລ່າ ແມງໄມ້ທີ່ໃຊ້ປາບສັດຕູພືດ ແລະ ພະຍາດຂອງພືດ

ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຂອງນໍ້າ
- Hq: ຄຸນນະພາບ ຂອງນ້ຳໃຕ້ດິນຫຼຸດລົງ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The technology is promoting better quality of groundwater on two grounds. Firstly, by applying the organic manure of the pigs on the coffee and banana farm instead of chemical fertilizers no pollution of the waterbodies is given. Secondly, the pigs are confined in their pigs sty and thus due not have the opportunity to go to the water bodies and pollute the water with urine or dung.
3.8 ການປ້ອງກັນ, ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ, ຫຼືການຟື້ນຟູຂອງການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເປົ້າໝາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ພົວພັນ ກັບຄວາມເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ:
- ປ້ອງກັນການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
- ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The major purpose for this technology is to prevent soil degradation and improve soil fertility.
4. ຂໍ້ກໍາໜົດ, ກິດຈະກໍາການປະຕິບັດ, ວັດຖຸດິບ, ແລະຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
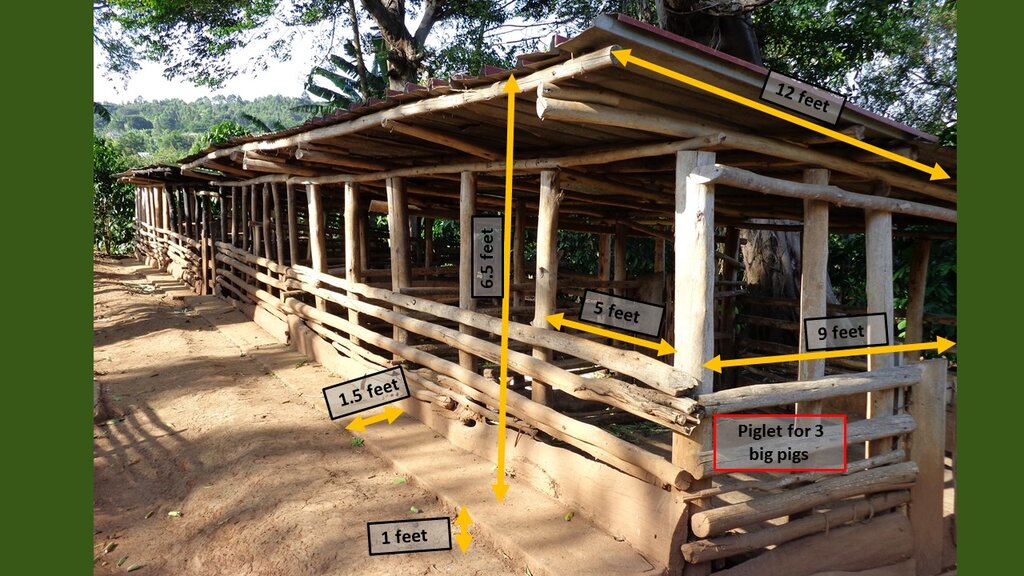
4.1 ເຕັກນິກ ໃນການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງເຕັກນິກ (ທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ ກັບການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດ ທາງດ້ານເຕັກນີກ):
Technical specifications of the pig sty construction
ຜູ້ຂຽນ:
Kyambadde, Tonny
ວັນທີ:
19/04/2021
ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງເຕັກນິກ (ທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ ກັບການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດ ທາງດ້ານເຕັກນີກ):
Technical specifications of the coffee and banana integration
ຜູ້ຂຽນ:
Kyambadde, Tonny
ວັນທີ:
13/07/2023
4.2 ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປກ່ຽວກັບການຄິດໄລ່ປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າໃນການຜະລິດ ແລະ ມູນຄ່າອື່ນໆ
ລະບຸ ວິທີການ ຄຳໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ແລະ ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າ ທີ່ໄດ້ຄິດໄລ່:
- ຕໍ່ພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸຫົວໜ່ວຍ ຂະໜາດ ແລະ ເນື້ອທີ່:
one hectare
ສະກຸນເງິນອື່ນໆ / ປະເທດອື່ນໆ (ລະບຸ):
Uganda Shilling
ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ, ໃຫ້ລະບຸອັດຕາແລກປ່ຽນຈາກ USD ເປັນສະກຸນເງິນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ (ເຊັ່ນ: 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
3750.0
ລະບຸ ຄ່າຈ້າງ ຄ່າແຮງງານສະເລ່ຍ ຕໍ່ ວັນ:
no labour was hired
4.3 ການສ້າງຕັ້ງກິດຈະກໍາ
| ກິດຈະກໍາ | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Land clearing and preparation | once a year |
| 2. | Hole digging | once |
| 3. | Coffee and banana planting | once |
| 4. | Pig sty (house) construction | once |
| 5. | Purchase of pigs | once |
4.4 ຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ປັດໄຈຂາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນໃນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ
ຖ້າທ່ານບໍ່ສາມາດ ໄຈ້ແຍກຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍໃນຕາຕະລາງຂ້າງເທິງ, ໃຫ້ຄາດຄະເນຂອງຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍທັງຫມົດ ຂອງການສ້າງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
5300000.0
ຖ້າຫາກຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ນຳໃຊ້ມູນຄ່າຕ່ຳກວ່າ 100% ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ແມ່ນໃຜເປັນຜູ້ຊ່ວຍ ໃນລາຍຈ່າຍທີ່ເຫຼືອ:
The Euregio project contributed two pigs and some starter coffee seedlings and banana suckers (roughly 35 % of total establishment costs were catered by the project).
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
These costs include the clearing of the land and prior establishment of the coffee and banana plantation. The majority of the costs are attributed to the purchase of pigs and the construction of the pig sty (roughly 3 million UGX).
4.5 ບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ / ແຜນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ກິດຈະກໍາ
| ກິດຈະກໍາ | ໄລຍະເວລາ / ຄວາມຖີ່ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Weeding and garden clearing | Twice a seaon |
| 2. | Manure application | At the onset of rain season |
| 3. | Feeding and watering of pigs | On daily basis |
| 4. | Treatment and deworming of pigs | On monthly basis |
| 5. | Mulching of the garden | Once a year or more |
| 6. | Contour digging | once a year |
| 7. | Pruning of coffee and banana plantation | For banana its done twice a season and for coffee its done every after harvesting season. |
| 8. | Maintenance of piggery sty | once a year |
4.6 ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ແລະ ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນສໍາລັບການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາກິດຈະກໍາ / ແຜນປະຕິບັດ (ຕໍ່ປີ)
ຖ້າທ່ານບໍ່ສາມາດ ໄຈ້ແຍກຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍໃນຕາຕະລາງຂ້າງເທິງ, ໃຫ້ຄາດຄະເນຂອງຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍທັງຫມົດ ຂອງການບຳລຸງຮັກສາ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
500000.0
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Estimation of 500,000 UGX per year. Most costs are for the treatment for the pigs and the maintenance of the pigsty. The rest is covered by family labour.
4.7 ປັດໄຈ ທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
ໃຫ້ອະທິບາຍ ປັດໃຈ ທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ຕົ້ນທຶນ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ:
Most costs are connected to the piggery in particular the maintenance of the pigs. Animal diseases and the resulting costs for the treatments are unplanned expenses.
5. ສະພາບແວດລ້ອມທໍາມະຊາດ ແລະ ມະນຸດ
5.1 ອາກາດ
ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນປະຈໍາປີ
- < 250 ມີລິແມັດ
- 251-500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 501-750 ມີລິແມັດ
- 751-1,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,001-1,500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,501-2,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 2,001-3,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 3,001-4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- > 4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸສະເລ່ຍ ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນຕົກປະຈໍາປີ ເປັນມິນລິແມັດ (ຖ້າຫາກຮູ້ຈັກ):
1200.00
ຂໍ້ມູນສະເພາະ / ຄວາມເຫັນກ່ຽວກັບ ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນ:
The rainfall pattern is bimodal, having two seasons. The two dry spell seasons are between January - March and between June to August, with the winter seasons between March to May and September to December.
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ຊື່ສະຖານີ ອຸຕຸນິຍົມ ເພື່ອເປັນຂໍ້ມູນອ້າງອີງ:
Uganda metrological authority
ເຂດສະພາບອາກາດກະສິກໍາ
- ເຄີ່ງຄວາມຊຸ່ມ
The average maximum temperature doesn't exceed 30 degrees Celcius and the minimum temperature is not below 10 degrees Celcius with almost equal length of the day and night through out the year.
The humidity level is relatively low through out the area.
5.2 ພູມິປະເທດ
ຄ່າສະເລ່ຍ ຄວາມຄ້ອຍຊັນ:
- ພື້ນທີ່ຮາບພຽງ (0-2%)
- ອ່ອນ (3-5 %)
- ປານກາງ (6-10 %)
- ມ້ວນ (11-15 %)
- ເນີນ(16-30%)
- ໍຊັນ (31-60%)
- ຊັນຫຼາຍ (>60%)
ຮູບແບບຂອງດິນ:
- ພູພຽງ / ທົ່ງພຽງ
- ສັນພູ
- ເປີ້ນພູ
- ເນີນພູ
- ຕີນພູ
- ຮ່ອມພູ
ເຂດລະດັບສູງ:
- 0-100 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 101-500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- > 4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
5.3 ດິນ
ຄວາມເລິກ ຂອງດິນສະເລ່ຍ:
- ຕື້ນຫຼາຍ (0-20 ຊັງຕີແມັດ)
- ຕື້ນ (21-50 ຊຕມ)
- ເລີກປານກາງ (51-80 ຊຕມ)
- ເລິກ (81-120 ຊມ)
- ເລິກຫຼາຍ (> 120 cm)
ເນື້ອດິນ (ໜ້າດິນ):
- ປານກາງ (ດິນໜຽວ, ດິນໂຄນ)
ເນື້ອດິນ (ເລິກຈາກໜ້າດິນ ລົງໄປຫຼາຍກວ່າ 20 ຊັງຕິແມັດ):
- ປານກາງ (ດິນໜຽວ, ດິນໂຄນ)
ຊັ້ນອິນຊີວັດຖຸ ເທິງໜ້າດິນ:
- ປານກາງ (1-3 %)
ຖ້າເປັນໄປໄດ້ ແມ່ນໃຫ້ຕິດຄັດ ການພັນລະນາດິນ ຫຼື ຂໍ້ມູນສະເພາະຂອງດິນ, ຕົວຢ່າງ, ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ປະເພດຂອງດິນ, ຄ່າຄວາມເປັນກົດ / ເປັນດ່າງຂອງດິນ, ສານອາຫານ, ດິນເຄັມ ແລະ ອື່ນໆ.
The soils ranging from red laterite, sandy loam and loam.
Soils are generally ferrallisol characterized by red colored sandy clay loams and sandy loams, but relatively productive.
5.4 ມີນໍ້າ ແລະ ຄຸນນະພາບ
ລະດັບ ນໍ້າໃຕ້ດິນ:
5-50 ແມັດ
ການມີນໍ້າ ເທິງໜ້າດິນ:
ປານກາງ
ຄຸນນະພາບນໍ້າ (ບໍ່ມີການບໍາບັດ):
ບໍ່ມີນໍ້າດື່ມ (ຮຽກຮ້ອງໃຫ້ມີການບຳບັດນ້ຳ)
ຄຸນນະພາບນ້ຳ ໝາຍເຖີງ:
ທັງນ້ຳໃຕ້ດິນ ແລະ ນ້ຳໜ້າດິນ
ມີບັນຫາ ກ່ຽວກັບນໍ້າເຄັມບໍ່?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
ເກີດມີນໍ້າຖ້ວມ ໃນພື້ນທີ່ບໍ່?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ ແລະ ຂໍ້ກໍານົດ ເພີ່ມເຕີມ ກ່ຽວກັບ ຄຸນນະພາບ ແລະ ປະລິມານ ຂອງນ້ຳ:
Major source of water supply is swamp and readily available all the time in both seasons dry and rain season
5.5 ຊີວະນາໆພັນ
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ທາງສາຍພັນ:
- ສູງ
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ທາງດ້ານ ທີ່ຢູ່ອາໃສ ຂອງສິ່ງທີ່ມີຊີວິດ:
- ປານກາງ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ ແລະ ລັກສະນະສະເພາະ ເພີ່ມເຕີມກ່ຽວກັບ ຊີວະນາໆພັນ:
No official statistics available, but Banana plantations usually have higher diversity with up to 15 species of other crops within.
5.6 ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຢູ່ປະຈຳ ຫຼື ເຄື່ອນຍ້າຍຕະຫຼອດ:
- ບໍ່ເຄື່ອນໄຫວ
ລະບົບ ການຕະຫຼາດ ແລະ ຜົນຜະລິດ:
- ປະສົມປົນເປ( ກຸ້ມຕົນເອງ/ເປັນສິນຄ້າ)
- ການຄ້າ / ຕະຫຼາດ
ລາຍຮັບ ທີ່ບໍ່ໄດ້ມາຈາກ ການຜະລິດ ກະສິກໍາ:
- ໜ້ອຍກ່ວາ 10 % ຂອງລາຍຮັບທັງໝົດ
ລະດັບຄວາມຮັ່ງມີ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
ບຸກຄົນ ຫຼື ກຸ່ມ:
- ກຸ່ມ / ຊຸມຊົນ
ລະດັບ ການຫັນເປັນກົນຈັກ:
- ການໃຊ້ແຮງງານຄົນ
ເພດ:
- ຜູ້ຍິງ
- ຜູ້ຊາຍ
ອາຍຸ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
- ຊາວໜຸ່ມ
- ໄວກາງຄົນ
- ຜູ້ສູງອາຍຸ
5.7 ເນື້ອທີ່ສະເລ່ຍຂອງດິນ ທີ່ຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ເຮັດເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- <0.5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 0.5-1 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1-2 ເຮັກຕາ
- 2-5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 5-15 ເຮັກຕາ
- 15-50 ເຮັກຕາ
- 50-100 ເຮັກຕາ
- 100-500 ເຮັກຕາ
- 500-1,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1,000-10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- > 10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
ຖືໄດ້ວ່າ ເປັນຂະໜາດນ້ອຍ, ກາງ ຫຼື ໃຫຍ່ (ອີງຕາມເງື່ອນໄຂ ສະພາບຄວາມເປັນຈິງ ຂອງທ້ອງຖີ່ນ)? :
- ຂະໜາດນ້ອຍ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
In Central Uganda 1-2 ha is considered small scale. It might be different in other regions of Uganda.
5.8 ເຈົ້າຂອງທີ່ດິນ, ສິດໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ, ແລະ ສິດທິການນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ
ເຈົ້າຂອງດິນ:
- ບຸກຄົນ, ບໍ່ມີຕໍາແໜ່ງ
- ບຸກຄົນ, ທີ່ມີຕໍາແໜ່ງ
ສິດທິ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
- ບຸກຄົນ
ສິດທິ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ:
- ເປີດກວ້າງ (ບໍ່ມີການຈັດຕັ້ງ)
ສິດນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ແມ່ນ ອີງໃສ່ລະບົບກົດໝາຍແບບດັ້ງເດີມບໍ?
ແມ່ນ
5.9 ການເຂົ້າເຖິງການບໍລິການ ແລະ ພື້ນຖານໂຄງລ່າງ
ສຸຂະພາບ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການສຶກສາ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ດ້ານວິຊາການ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການຈ້າງງານ (ຕົວຢ່າງ, ການເຮັດກິດຈະກໍາອື່ນ ທີ່ບໍ່ແມ່ນ ການຜະລິດກະສິກໍາ):
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ຕະຫຼາດ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ພະລັງງານ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ຖະໜົນຫົນທາງ ແລະ ການຂົນສົ່ງ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການດື່ມນໍ້າ ແລະ ສຸຂາພິບານ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການບໍລິການ ທາງດ້ານການເງິນ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
6. ຜົນກະທົບ ແລະ ລາຍງານສະຫຼຸບ
6.1 ການສະແດງຜົນກະທົບ ພາຍໃນພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງເສດຖະກິດສັງຄົມ
ການຜະລິດ
ການຜະລິດພືດ
ປະລິມານ ກ່ອນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
1
ປະລີມານ ຫຼັງການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
3
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Significant improvement in coffee production was noticed jumping from an average yield increase of 300kg to 700kg of coffee harvest in one acre per season. Size of banana bunches with an average increase in weight from from 12kg to 30kg.
ຄຸນນະພາບຂອງພືດ
ປະລິມານ ກ່ອນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
0
ປະລີມານ ຫຼັງການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
2
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Coffee beans improved a lot in terms of size and quality, with over 70% coffee beans harvested in the category of screen 18 (super beans). The banana size and its fingers improved in size, and the taste of banana food greatly improve with a pleasant aroma, softer on eating and cooks faster compared to previously produced bananas.
ຜົນຜະລິດຂອງສັດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
The production of pigs increased substantially in a time period of a year. The participating farmers started with 3 pigs at the beginning and reached an increase of pigs to an average 15 pigs after a year (2 breeding cycles per pig per year).
ການຈັດການຄຸ້ມຄອງທີ່ດິນ
ປະລິມານ ກ່ອນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
-2
ປະລີມານ ຫຼັງການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
3
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
The farming system employed by the farmers previously before introduction of the technology was not sustainable. Resources were being continuously depleted by crop practices employed without replacement of what is lost from the soil during harvest. integration of piggery into the system improved soil fertility with manure composted from piggery wastes. Besides boosting soil fertility, biodiversity on the farm improved as well (the soil organisms, new plant species emerged, insect species among others) the green biomass and overall soil health improved.
ລາຍໄດ້ ແລະ ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
ລາຍຮັບ ຈາກການຜະລີດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
The average farm income before the technology was very little and did not support the family's basic home needs. With the introduction of the technology, the household income improved from an average of monthly 45.000 UGX to 150.000 UGX. However, it is important to note that this is not a fixed monthly income and is depending on the harvest season. Thus, there are peak income phases followed by low seasons.
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ຂອງແຫຼ່ງລາຍຮັບ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
More income sources were established through the three enterprises (coffee, banana and piggery).
ຜົນກະທົບດ້ານວັດທະນາທໍາສັງຄົມ
ການຄໍ້າປະກັນ ສະບຽງອາຫານ / ກຸ້ມຢູ່ກຸ້ມກິນ
ປະລິມານ ກ່ອນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
0
ປະລີມານ ຫຼັງການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
2
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
With improved soil fertility resulting in bigger sizes of banana bunches, improved food security was achieved. The increased income from coffee and piggery ensured availability of alternative food supply though their sale.
ສະພາບທາງດ້ານສຸຂະພາບ
ປະລິມານ ກ່ອນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
-1
ປະລີມານ ຫຼັງການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
2
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
There was less exposure to agriculture chemical by farmers and the entire community at large which poses health threat to the people and cause environment damage. the quality of food produced was free from any chemical residues emanating from synthetic fertilizers.
ຄວາມຮູ້ກ່ຽວກັບ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ / ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Through the technology farmers were able to learn how important it is to use organic sources of fertilizer and its benefits to the environment and soil health. MADDO facilitated roughly 15 different training sessions for the participating farmer group targeting the soil and water conservation practices.
ສະຖານະການຂອງສັງຄົມ ແລະ ກຸ່ມດ້ອຍໂອກາດທາງເສດຖະກິດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
The situation of women (average between 40-55 years old) was improved through the technology by giving them access and knowledge to this pilot project. The mobilization and right selection of participants were crucial for the improvement.
ຜົນກະທົບຕໍ່ລະບົບນິເວດ
ດິນ
ຄວາມຊຸ່ມຂອງດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Higher retention of soil moisture
ອິນຊີວັດຖຸໃນດິນ / ຢູ່ລຸ່ມຊັ້ນດິນ C
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Better composition of soil nutrients with increased population of soil organisms (micro and macro)
ຊີວະນານາພັນ: ສັດ, ພືດ
ມວນຊີວະພາບ / ຢູ່ເທິງຊັ້ນດິນ C
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ທາງດ້ານທີ່ຢູ່ອາໃສ ຂອງສິ່ງທີ່ມີຊີວິດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Organic manure provided a conducive environment for multiplication and survival of living organisms
ລະບຸ ການປະເມີນຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ສະຖານທີ່ (ການວັດແທກ):
All the impacts are based on estimations. Thereby, assessments by farmers have been added with observations from the staff to get a clear understanding of the impacts.
6.2 ຜົນກະທົບທາງອ້ອມ ຈາກການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
Pollution of water
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
The usage of organic manure instead of chemical fertilizers reduced the pollution of downstream water from fields
ກໍານົດ ການປະເມີນ ຜົນກະທົບທາງນອກ (ການວັດແທກ):
This impact is based on estimation by the project staff as well as some observations from participants.
6.3 ການປ້ອງກັນ ແລະ ຄວາມບອບບາງ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢິ ໃນການປ່ຽນແປງສະພາບດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ແລະ ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງກັບອາກາດທີ່ມີການປ່ຽນແປງທີ່ຮຸນແຮງ / ໄພພິບັດທາງທໍາມະຊາດ (ຮັບຮູ້ໄດ້ໂດຍຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ)
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The technology was piloted in a 3-year program and climate-related consequences cannot be measured yet.
6.4 ການວິເຄາະຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ຜົນປະໂຫຍດ
ຈະເຮັດປະໂຫຍດເພື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍກັບສິ່ງກໍ່ສ້າງ (ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ) ໄດ້ແນວໃດ?
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກຫຼາຍ
ຈະໄດ້ຮັບຜົນປະໂຫຍດເມື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບ / ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍໃນການບຳລຸງຮັກສາທີເ່ກີດຂື້ນອິກ (ຈາກທັດສະນະຄະຕິຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ) ໄດ້ແນວໃດ?
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກເລັກນ້ອຍ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
After the establishment of the technology, the returns from coffee are attained in period of two years, for banana returns observed in less than one year and for piggery profits attained in period of less than two years.
6.5 ການປັບຕົວຮັບເອົາເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- 11-50%
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າມີ, ປະລິມານ (ຈໍານວນຂອງຄົວເຮືອນ / ເນື້ອທີ່ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ):
Mainstreaming of the technology was promoted through copying from the participants and also due to the promotion by the district field staff. The technology has been in existence for years and that is why a high adoption can be observed.
ທັງໝົດນັ້ນ ແມ່ນໃຜ ໄດ້ປັບຕົວເຂົ້າ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ, ມີຈັກຄົນ ທີ່ສາມາດເຮັດເອງໄດ້, ຕົວຢ່າງ, ປາດສະຈາກ ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ທາງດ້ານອຸປະກອນ / ການຈ່າຍເປັນເງິນ?
- 51-90%
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The technology is commonly used in the area. However, those who were not part of the program take short-cuts or do not have such high positive progress as the others.
6.6 ການປັບຕົວ
ໄດ້ມີການດັດປັບ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເພື່ອໃຫ້ແທດເໝາະກັບເງື່ອນໄຂ ການປ່ຽນແປງບໍ?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
6.7 ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ |
|---|
| Contributes positively to the soil fertility. |
| Improves the food security and household income |
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຈຸດດີ / ໂອກາດ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ |
|---|
| Farmers were able to local available resources for this technology. |
| It improved the soil health and contributed to environmental conservation. |
6.8 ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແລະ ວິທີການແກ້ໄຂບັນຫາ
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງໃນມຸມມອງຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| Diseases that affect the piggery (swine fewer). | No mitigation (vaccination) available. |
| The vet officers are not always available for vaccinations or treatments for the pigs. Moreover, there are quite expensive. | Farmers group together to lobby for the service. |
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ/ຂໍ້ບົກຜ່ອງ/ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| Follow up on the management practices for the piggery were time consuming. | Establishment of community-based trainers (CBT) that take over |
7. ເອກະສານອ້າງອີງ ແລະ ການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
7.1 ວິທີການ / ແຫຼ່ງຂໍ້ມູນ
- ການສໍາພາດ ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
About 30 participants
- ສໍາພາດ ຊ່ຽວຊານ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
Interview with two experts from the district (agriculture officer and production officer).
- ການລວບລວມ ບົດລາຍງານ ແລະ ເອກະສານ ອື່ນໆ ທີ່ມີຢູ່ແລ້ວ
The following sources was used:
Ministry of Agriculture, Animal Industry and Fisheries (2014): Uganda Training Materials for Coffee Production. Trainer's Guide. First Edition.
ເມື່ອໃດທີ່ໄດ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ (ຢູ່ພາກສະໜາມ)?
26/05/2021
7.2 ເອກກະສານອ້າງອີງທີ່ເປັນບົດລາຍງານ
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Benefits of sustainable land management, UNCCD
ມີຢູ່ໃສ?ມູນຄ່າເທົ່າໃດ?
https://catalogue.unccd.int/838_Benefits_of_SLM_eng.pdf
7.3 ເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ກັບຂໍ້ມູນທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງໂດຍກົງ
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
Sustainable Agriculture in Africa,
URL:
https://wedocs.unep.org/bitstream/handle/20.500.11822/34621/RSRSA.pdf?sequence=3&isAllowed=y
ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ ແລະ ເນື້ອໃນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່

MADDO SLM approach [ອູເຈນດາ]
This integrated soil fertility management approach aims at identifying and promoting practices in land management that can increase soil fertility, reduce land degradation and improve production. Under this specific example, organic manure from a piggery was applied to banana and coffee plantations.
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: Tonny Kyambadde
ເນື້ອໃນ
ບໍ່ມີເນື້ອໃນ