Stone Check Walls and Check Dams for Soil and Water Conservation [Энэтхэг]
- Шинийг нээх:
- Шинэчлэх:
- Эмхэтгэгч: Jaclyn Bandy
- Хянан тохиолдуулагч: –
- Хянагч: Hanspeter Liniger
technologies_5210 - Энэтхэг
Бүлгүүдийг үзэх
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаах1. Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
1.2 Технологийг үнэлэх, баримтжуулах ажилд хамаарах мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүс, байгууллагуудын холбоо барих мэдээлэл
Мэдээлэл өгсөн хүн (с)
Газар ашиглагч:
Jagdamba Joshi
Nakina Village
Энэтхэг
Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн төслийн нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Onsite and Offsite Benefits of SLMТехнологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
ICIMOD International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) - НепалТехнологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
G.B. Pant Institute of Himalayan Einvironment & Development (G.B. Pant Institute of Himalayan Einvironment & Development) - Энэтхэг1.3 ВОКАТ-аар баримтжуулсан өгөгдлийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцөл
Эмхэтгэгч болон гол мэдээлэгч хүн(хүмүүс) WOCAT аргачлалаар баримтжуулсан мэдээллийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцлийг хүлээн зөвшөөрсөн:
Тийм
1.4 Технологи тогтвортой гэдгийг баталгаажуулах
Энэ технологийг газрын доройтлыг бууруулж, газрын тогтвортой менежментийг хангахад тохиромжтой гэж үзэж болох уу?
Үгүй
1.5 ГТМ Арга барилын Асуулга (ууд) руу хандах (ВОКАТ ашиглан баримтжуулсан)

Community Forest Management in the Nakina Van Panchayat [Энэтхэг]
Van Panchayats or village forest councils are a impressive example of grassroots community management of natural resources, where a specific administrative unit is locally elected by community members who are responsible for the management of activities related to the forest.
- Эмхэтгэгч: Jaclyn Bandy
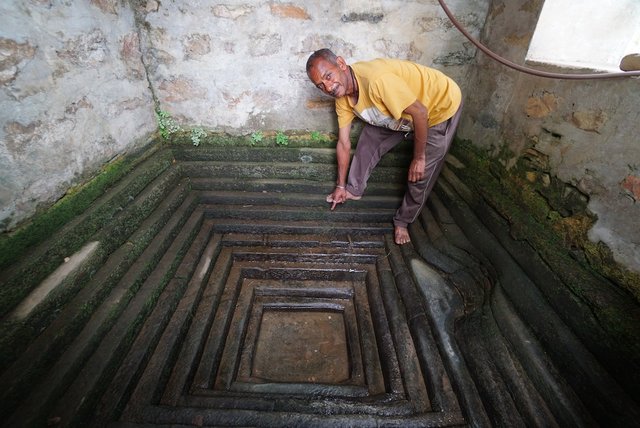

Naula Management and Conservation [Энэтхэг]
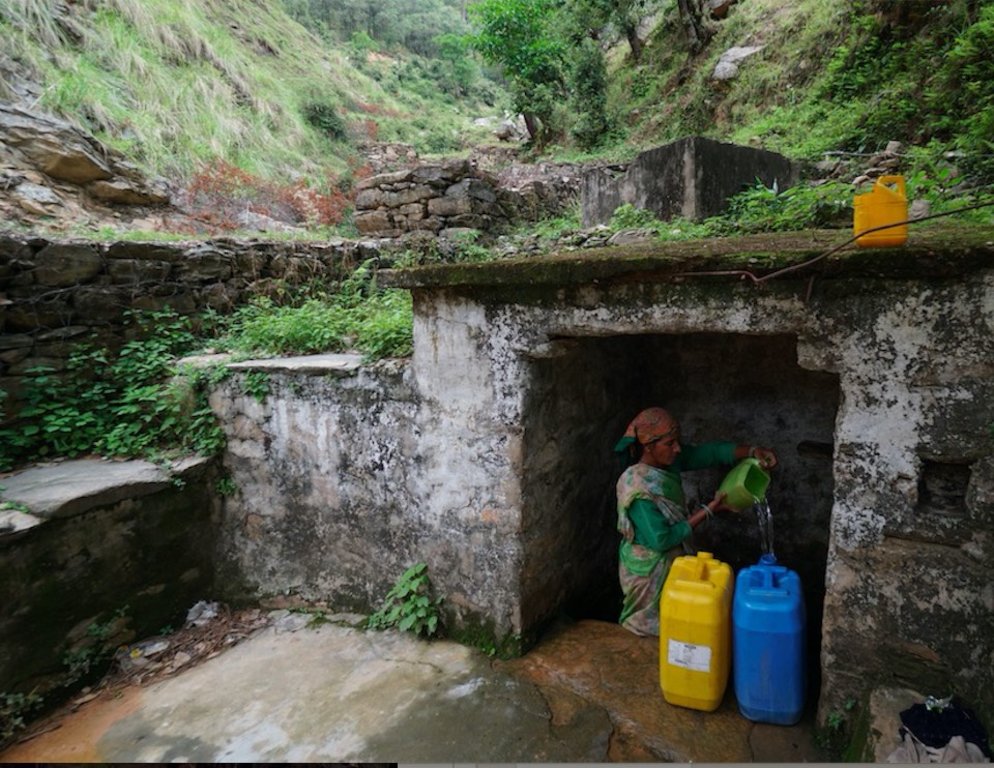
Naulas are shallow, four-sided stepped wells designed to collect water from subterranean seepages or springs and are used to meet domestic water needs by the local communities. Naula management and conservation encompasses a range of activities that preserve their structure and function.
- Эмхэтгэгч: Jaclyn Bandy
2. ГТМ Технологийн тодорхойлолт
2.1 Технологийн товч тодорхойлолт
Технологийн тодорхойлолт:
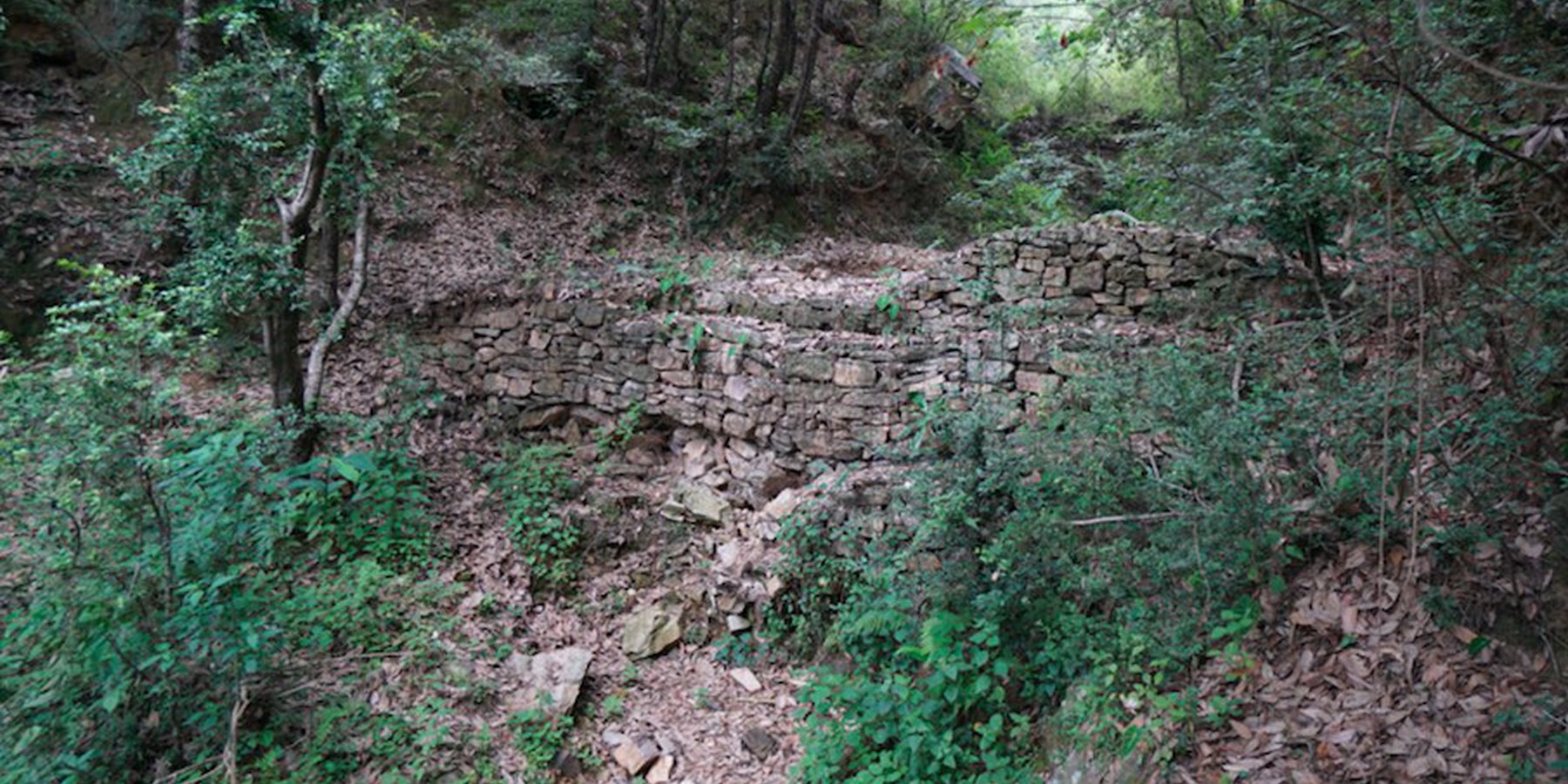
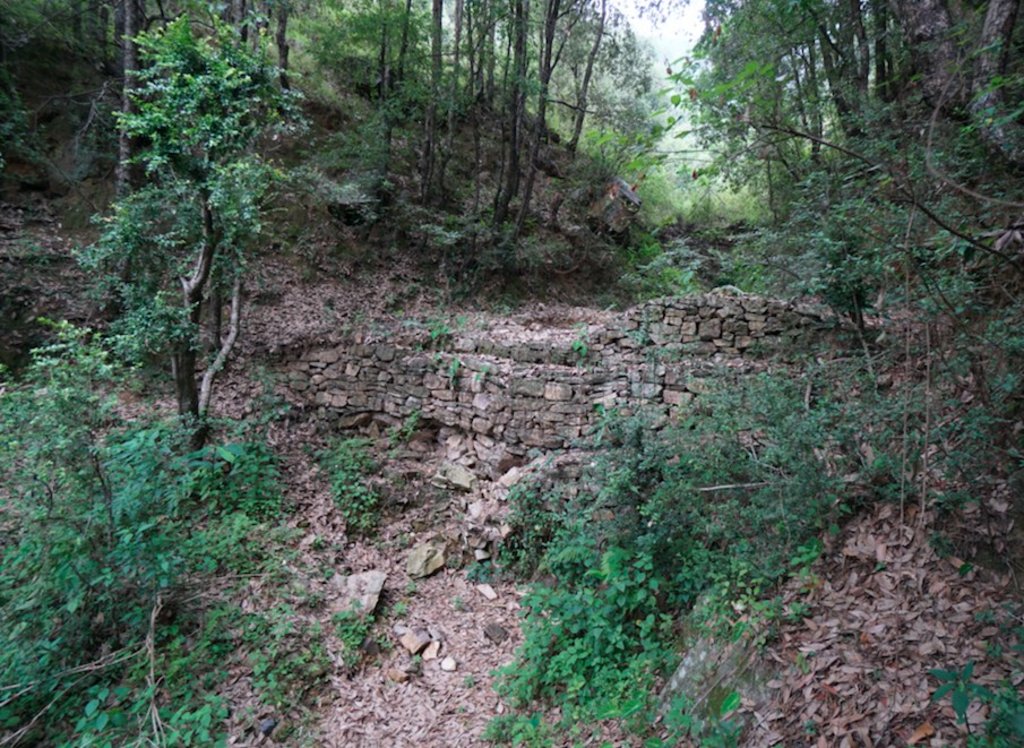
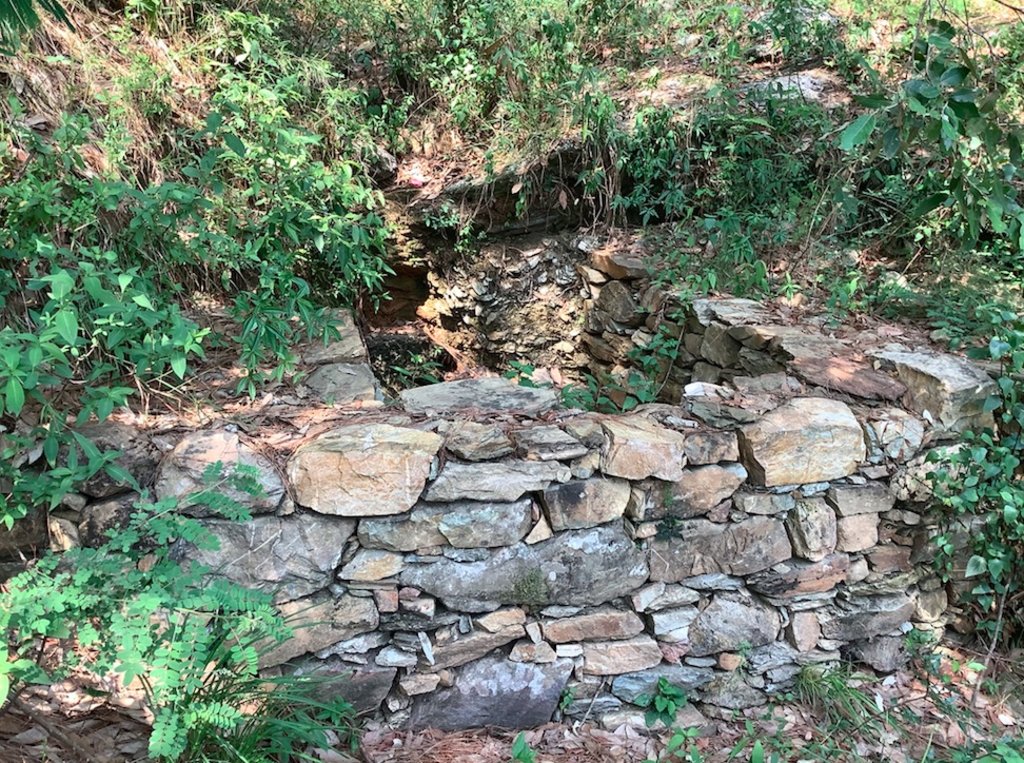
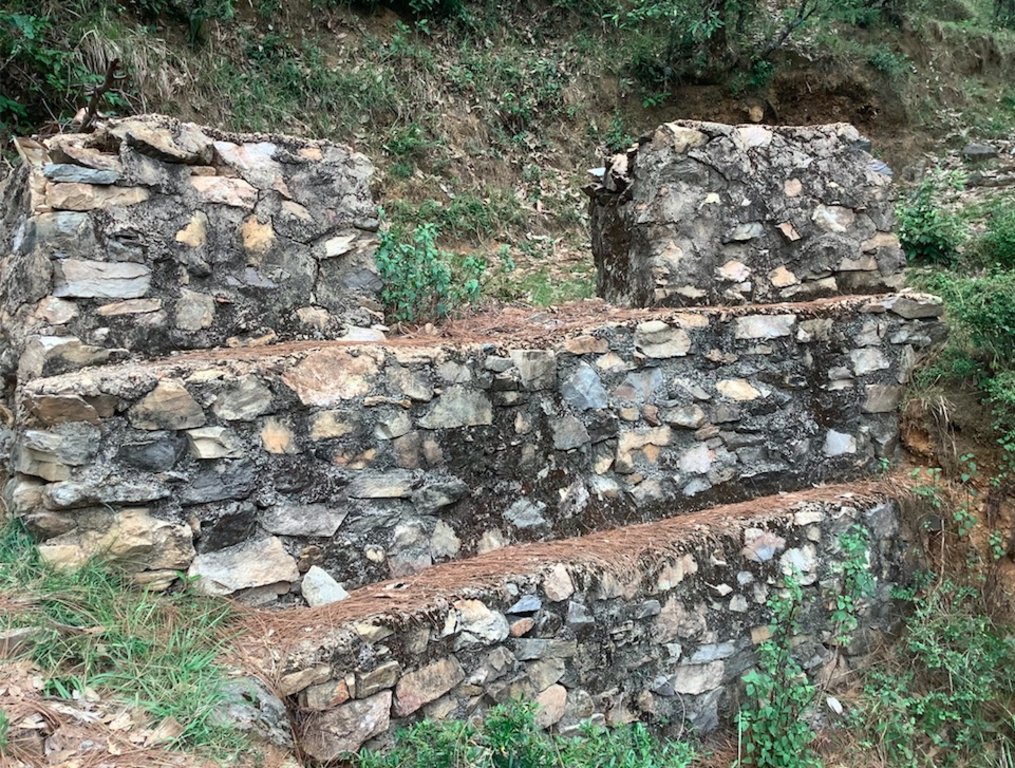
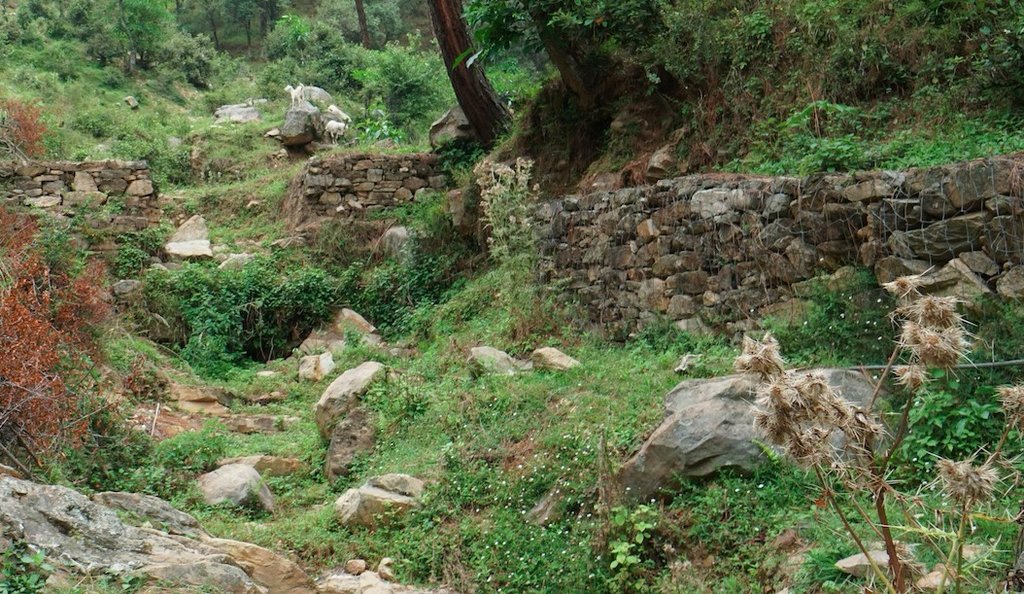
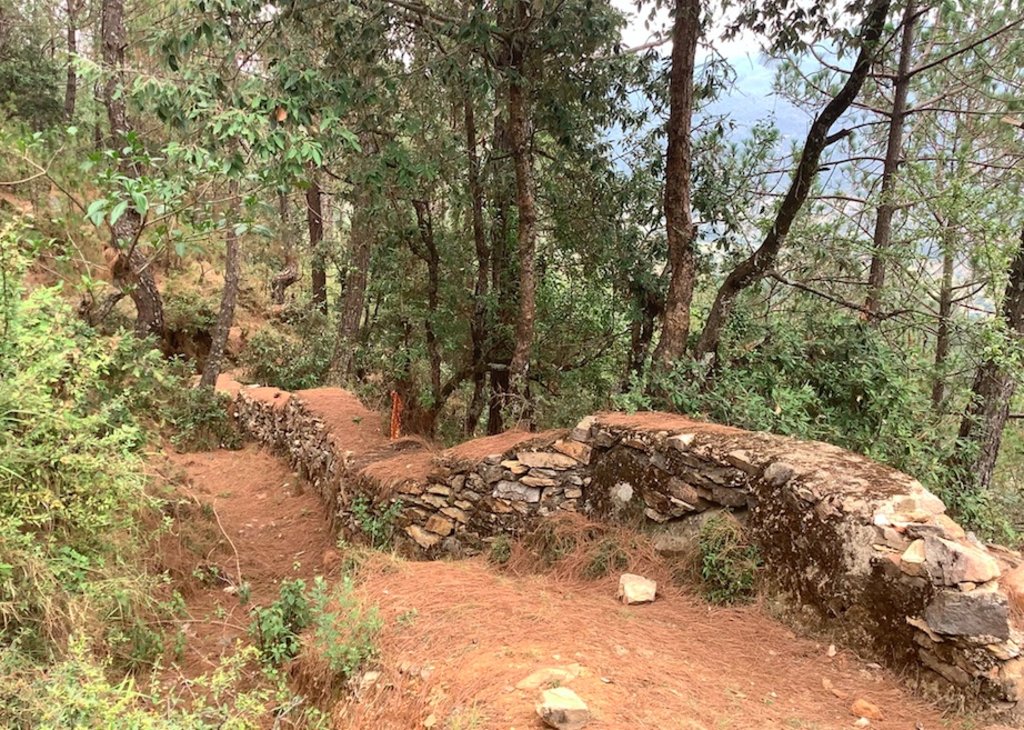
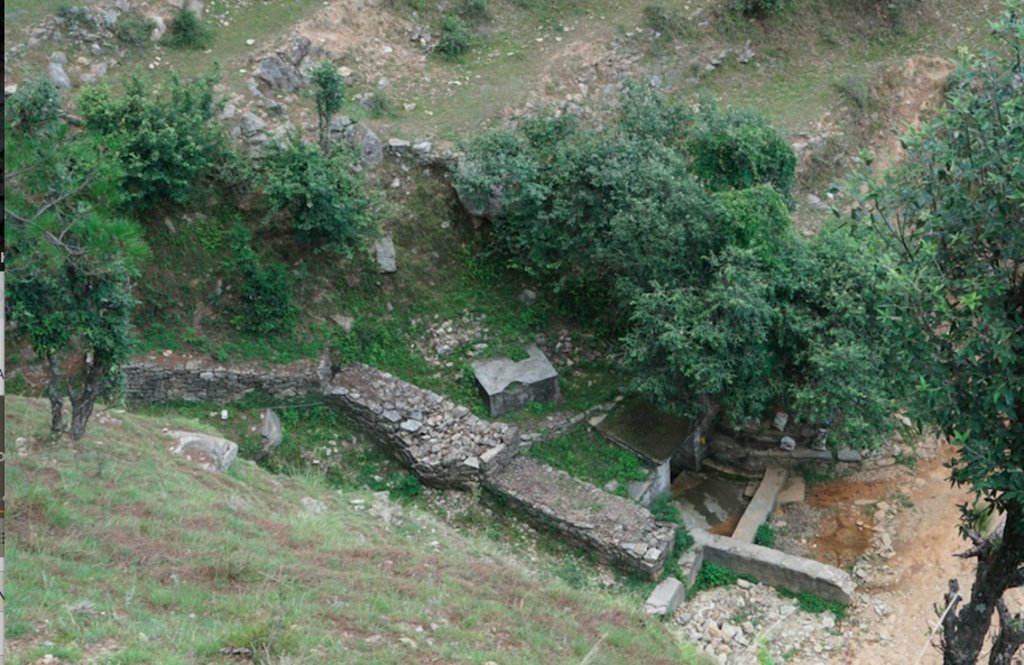
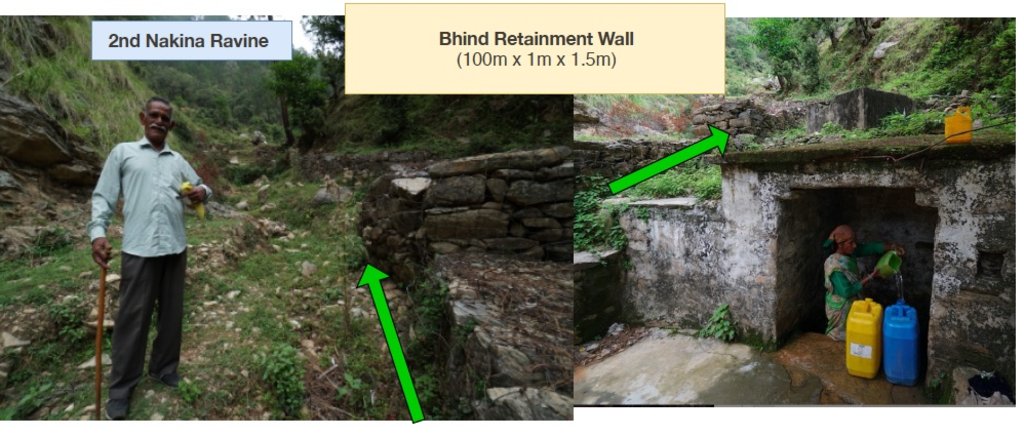
Stone Check Dams/Walls, Retainment Walls, and a Water Diversion Wall has been constructed in Nakina Village and Nakina Community Forest to help protect their settlements, agriculture land, forest land, and preserve the hilly landscape. These structures serve to reduce the runoff velocity (lowering the rate of erosion and gullying in steep slope channels) and increase infiltration for groundwater recharge.
2.2 Технологийн дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт
Тодорхойлолт:
1. The technology is found in both natural and human environments (forest and settlement areas)
2. Main Characteristics: A check dam or check wall is constructed in a loose or active gully or a rill (shallow channel) that threatens to enlarge, or anywhere on a slope where there is a danger of scour from running water. The structures lower the velocity of flow. In Nakina porous check walls, check dams, and retainment walls were made out of stone gathered from the surrounding area. A porous check dam releases a portion of flow through the structure, decreases the head of flow over the spillway, and decreases the dynamic and hydrostatic forces against the check dam. Porous check dams are simple and more economical for construction.
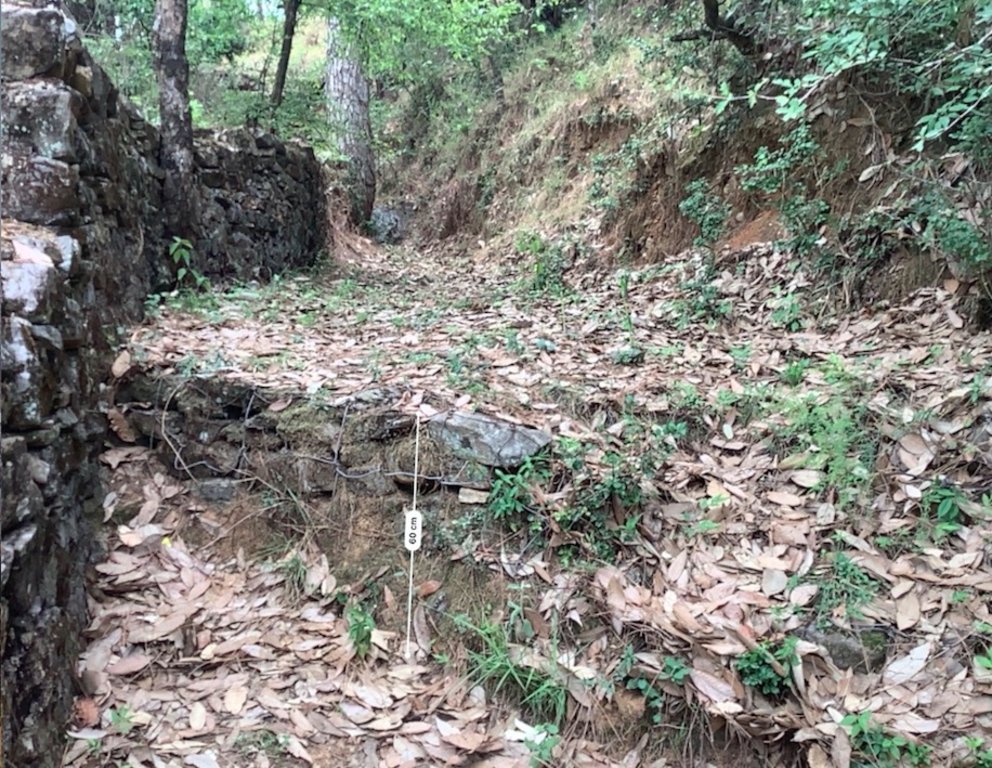
Once stones are collected they are cut into suitable sizes and surfaces ( "dressing" of stones). The site where the technology is to be constructed is then cleared and, for check dams, the sides are sloped 1:1 (this simply refers to the ratio of the rise and run of the slope, so 1:1 means you'll have a 45 degree slope for your excavation). This is also known as the angle of repose, where the granular material of the embankment will be stable and not slump from its own weight. The base of the dam should be around 70 cm thick if it is 1 meter high. The bed of gully is excavated for foundation and dry stones are packed from that level.
3. Purposes/functions: Interrupts the flow of water and flattens the gradient of a channel, thereby reducing the velocity and inducing infiltration rather than eroding the channel. These structures not only slow flow velocity but also to distribute flows across vegetation. Despite some sedimentation resulting behind the dam, small cracks and porous spaces in the holes of the stones allow some sediment to flow through and the finer particles fill the gaps and strengthen the structure. Check dams can also be designed to create small reservoirs.
4. Major activities include identifying the appropriate site of installation, collection of construction materials, technical planning of the structure dimensions and design, manual labor, and maintenance.
5. Benefits/impacts: These structures decelerate runoff and accelerates groundwater recharging by storing water and facilitating infiltration of water into the soil
6. Like/Dislike:
Advantages
•Inexpensive and relatively easy to install given local building materials and labor availability
•Reduce velocity, prevent gully erosion and cause a high proportion of the sediment load in runoff to settle out, preventing downstream damage
•When carefully located and designed, check dams can remain as permanent installations with very minor regrading
Disadvantages
•Many of these structures have a temporary nature, and need to reconstructed or removed after significant damage
•Removal or reconstruction may be a significant cost depending on the size and design
•May kill grass linings in channels if the water level remains high after rainstorms or if there is significant sedimentation.
•May create turbulence which erodes the channel banks.
•Clogging by organic material may be a problem and hinder the structure's function
2.3 Технологийн гэрэл зураг
2.5 Энэ үнэлгээнд хамрагдсан технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн улс орон/ бүс нутаг/ байршил
Улс:
Энэтхэг
Улс/аймаг/сум:
Uttarakhand
Байршлын дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт:
Nakina Village, Pithoragarh Bloc
Технологи өргөн дэлгэрсэн эсхийг тодорхойл:
- тодорхой газар хэрэгжсэн/ жижиг талбайд төвлөрсөн
Технологи(иуд) нэвтрүүлсэн талбай тусгай хамгаалалттай газар нутагт байрладаг уу?
Тийм
Хэрэв тийм бол, тодруулна уу:
5 check dams are located in the protected forest of Nakina. The other structures are located in the village settlement (the 5 check walls are within the ravine) or just above the Bhind Spring (Naula).
Map
×2.6 Хэрэгжсэн хугацаа
Байгуулсан тодорхой оныг мэдэхгүй бол баримжаа хугацааг тодорхойл:
- >50 жилийн өмнө (уламжлалт)
2.7 Технологийн танилцуулга
Технологийг хэрхэн нэвтрүүлснийг тодорхойл:
- Газар ашиглагчдын санаачилгаар
- Уламжлалт системийн хэсэг (> 50 жил)
- Гадны төсөл/хөтөлбөрийн дэмжлэгтэйгээр
Тайлбар (төслийн төрөл г.м.):
Check dams and other retainment structures are technologies that have been used for centuries. Some of the structures in the village are nearly +50 years old and have either been constructed with the help of the government (ravine check dams in settlement and above Bhind Naula) and others have been more recently constructed by the villagers themselves to support the forest landscape, specifically springshed recharge.
3. ГТМ технологийн ангилал
3.1 Технологийн үндсэн зорилго (ууд)
- газрын доройтлыг бууруулах, сэргийлэх, нөхөн сэргээх
- экосистемийг хамгаалах
- сав газрыг хамгаалах (усны эх/ голын адаг) - бусад технологитой хослуулах
- гамшгийн эрсдлийг бууруулах
- уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт/ экстрим байдал болон түүний нөлөөлөлд дасан зохицох
3.2 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын одоогийн газар ашиглалтын хэлбэр(үүд)

Байгалийн ой / модтой газар
- (Таримал) байгалийн ой/мод бүхий газар
(Сэргээсэн)байгалийн ой/тармаг ойд: Менежментийн төрлийг тодорхойлно уу:
- Сонгомол огтлол
(Сайжруулсан)байгалийн ойн төрөл:
- субтропикийн хуурай ойн ургамалжилт
- quercus leucotrichophora (Banj oak)
Дээр дурьдсан модны төрөл навч, шилмүүсээ гөвдөг үү эсвэл мөнх ногоон уу?
- навч, шилмүүсээ гөвдөг
Бүтээгдэхүүн ба үйлчилгээ:
- Мод бэлтгэл
- Түлшний мод
- Бэлчээрийн талбай/Хариулгатай бэлчээрлэлт
- Байгалийн нөөцийг хамгаалах

Суурьшил, дэд бүтэц
- Хот суурин, барилга
3.3 Технологи хэрэгжүүлснээр газар ашиглалтад өөрчлөлт гарсан уу?
Технологи хэрэгжүүлснээр газар ашиглалтад өөрчлөлт гарсан уу?
- Үгүй (3.4 руу шилжинэ үү)
3.4 Усан хангамж
Технологи хэрэгжүүлсэн газрын усан хангамж:
- Байгалийн усалгаатай
3.5 Технологи ГТМ-ийн аль бүлэгт хамаарах вэ
- Налуугийн арга хэмжээ
- Усны урсац зохицуулах болон салаалах
- гадаргын усны менежмент (булаг, гол, нуур, тэнгис гэх мэт)
3.6 Технологийг бүрдүүлэх ГТМ арга хэмжээ

Барилга байгууламжийн арга хэмжээ
- S3: Шаталсан суваг, шуудуу, голдирол
- S6: Хашаа, саад, явган хашлага, хашаа
3.7 Технологид харгалзах газрын доройтлын төрөл

хөрс усаар эвдрэх
- Wt: Хөрсний гадаргын угаагдал
- Wg: Гуу жалгын элэгдэл
- Wm: Хөрсний нуралт, шилжилт
- Wr: Голын эргийн эвдрэл
- Wo: Усны элэгдлийн дам нөлөө

хөрсний физик доройтол
- Ps: Хөрсний органик үе давхаргын алдрал, гадаргын суулт

биологийн доройтол
- Bc: Ургамлан нөмрөг багасах
- Bq: биомасс буурах

усны доройтол
- Hg: Гүний ус / уст үеийн усны түвшин өөрчлөгдөх
3.8 Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх, сааруулах ба нөхөн сэргээх
Газрын доройтолтой холбоотойгоор Технологи ямар зорилго тавьсан болохыг тодорхойл:
- газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх
- Газрын доройтлыг бууруулах
4. Техникийн нөхцөл, хэрэгжүүлсэн үйл ажиллагаа, материал ба зардал
4.1 Технологийн техник зураг
4.2 Материал болон зардалд хамаарах ерөнхий мэдээлэл
Үнэ өртөг, оруулсан хувь нэмрийг хэрхэн тооцсоныг тодорхойл:
- Технологийн нэгж тус бүр
Нэгжийг тодорхойл:
1. Small Check Dams 2. Large Check Walls 3. Water Diversion Wall 4. Bhind Check Walls/Retainment wall
Нэгжийн хэмжих нэгж (тохирох бол):
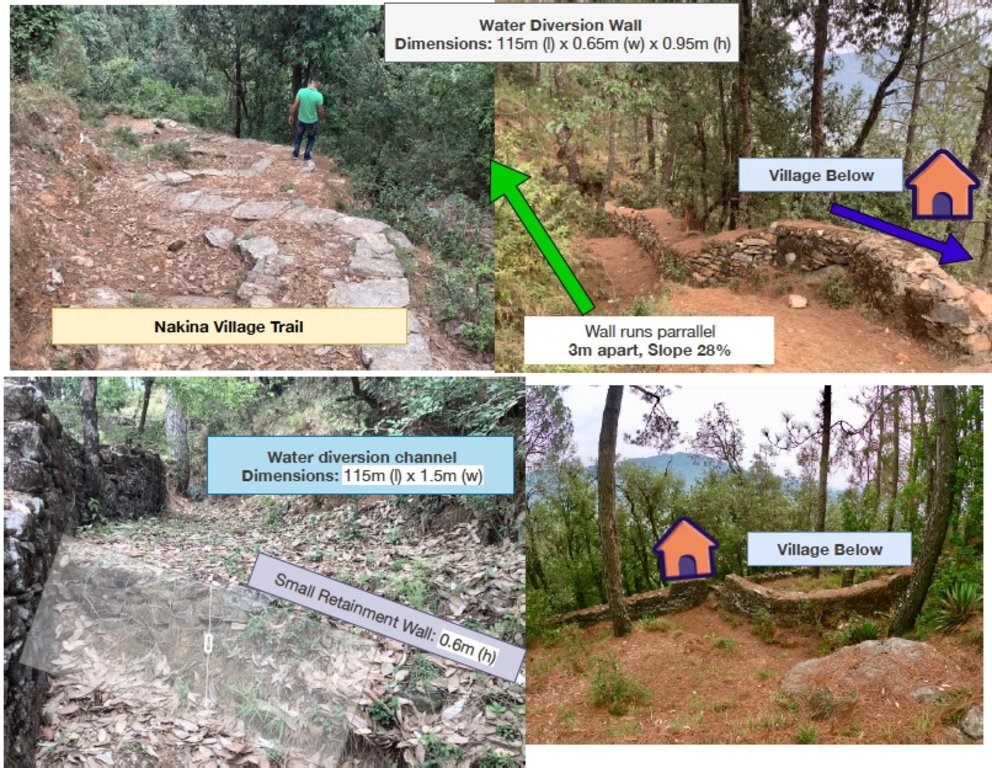
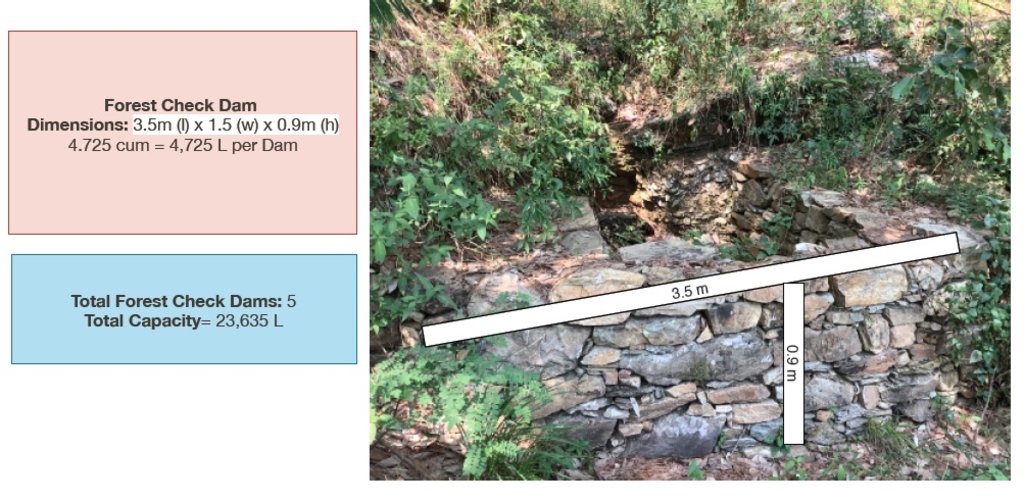
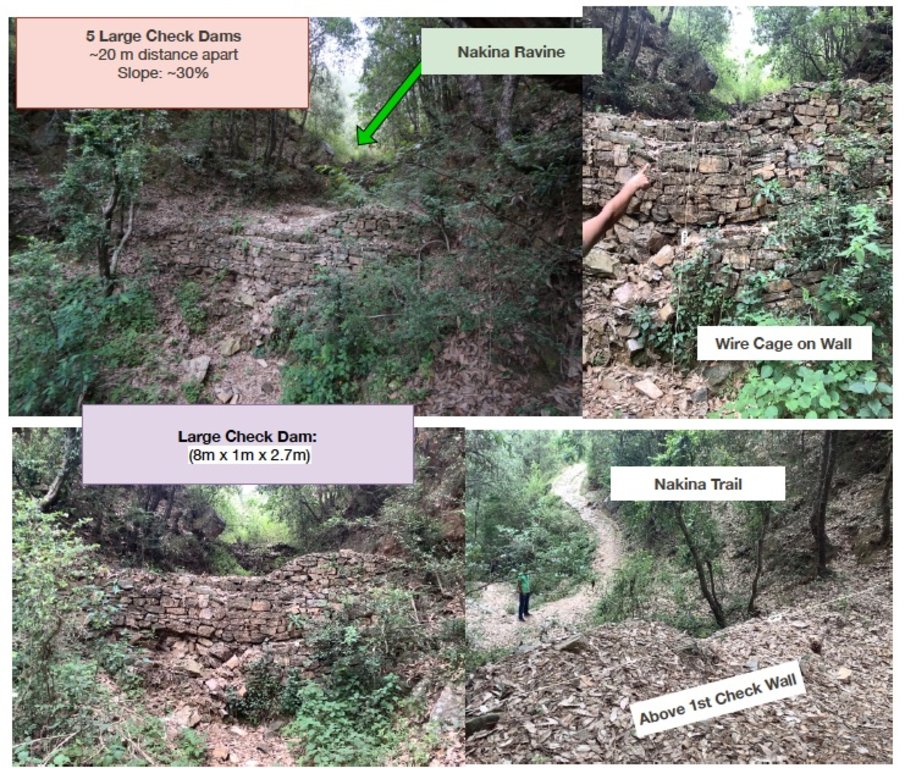
1. 5 units (3.5m x 1.5m x 0.9m) 2. 5 units (8m x 1m x 2.7m) 3. 1 unit (115m x 0.65 x 0.95m) 4. 1 unit (100m x 1m x 1.5m)
бусад/үндэсний мөнгөн нэгж (тодорхойл):
INR
Хэрэв боломжтой бол үндэсний валютын Америк доллартай харьцах харьцааг бичнэ үү (тухайлбал, 1 ам.дол. = 79,9 Бразил реал): 1 ам.дол. =:
70.0
Хөлсний ажилчны нэг өдрийн цалингийн хэмжээг тодорхойлно уу:
400 INR per head/day
4.3 Бий болгох үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа (улирал) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Nakina village built a long water diversion wall over +50 years ago that serves as a water channel, directing runoff away from settlements and towards the ravine | Pre-monsoon /dry season |
| 2. | Within the ravine/gully in Nakina Village, there is a series of 5 large check walls that were established with the help of the Forest Department | Pre-monsoon /dry season |
| 3. | There is a series of check walls/check dams in another gully that were established in 1952 above the Bhind Spring/Naula (on the opposite side of the village) to protect it and decrease runoff/further erosion | Pre-monsoon/dry season |
| 4. | In December 2017 the Nakina Van Panchayat (community forest council) decided to construct 5 new check dams within the Nakina Forest, which lie in the upper catchment area of the Bhind Spring | Pre-monsoon/dry season |
| 5. | For the establishment of all these structures, the community and technical assistants assessed the topography of the area, size of the gully, catchment area and runoff rate before establishing the check-dam. | Pre-monsoon/dry season |
| 6. | The sites were selected and prepared by removing debris and other unsuitable material which would interfere with proper placement of the check dam/wall materials. | Pre-monsoon/dry season |
4.4 Бий болгоход шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Large Water Diversion Wall | person-days | 60.0 | 400.0 | 24000.0 | 20.0 |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | 5 Large Check Walls | person-days | 50.0 | 400.0 | 20000.0 | 20.0 |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Bhind Spring Check Walls/Retainment Wall | person-days | 19.0 | 400.0 | 7600.0 | 50.0 |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | 5 Small Check Walls in Forest | person-days | 10.0 | 400.0 | 4000.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Crate Wire (15m x 2m x 2m) | Cum | 60.0 | 75.0 | 4500.0 | |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Pick | pieces | 15.0 | 300.0 | 4500.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Shovel | pieces | 20.0 | 500.0 | 10000.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | pharuwa (hoe) | pieces | 15.0 | 300.0 | 4500.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | khanti (digging bar) | pieces | 10.0 | 1500.0 | 15000.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | hammer (5kg) | pieces | 10.0 | 2000.0 | 20000.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | chino (chisel) | pieces | 10.0 | 500.0 | 5000.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | khukuri (knife) | pieces | 10.0 | 250.0 | 2500.0 | 100.0 |
| таримал материал | small hammer (0.5-1 kg) | pieces | 15.0 | 300.0 | 4500.0 | 100.0 |
| Барилгын материал | Rocks of various size and shape collected/excavated on site | |||||
| Барилгын материал | Small Check Walls in Forest (5) | cum | 23.625 | 200.0 | 4725.0 | 100.0 |
| Барилгын материал | Large Check Walls (5) | cum | 108.0 | 200.0 | 21600.0 | 20.0 |
| Барилгын материал | Large Water Diversion Wall (1) | cum | 71.0 | 200.0 | 14200.0 | 100.0 |
| Барилгын материал | Bhind Check Walls/Retainment Wall (5) | cum | 150.0 | 200.0 | 30000.0 | 50.0 |
| Бусад | Rocks of various size and shape collected/excavated on site | |||||
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг | 196625.0 | |||||
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 2808.93 | |||||
Хэрэв газар ашиглагч нийт зардлын 100% -иас бага хэсгийг төлсөн бол хэн голлох зардлыг гаргасан бэ:
Uttarakhand Forest Department (Government), JICA (Japan International Cooperation Agency)
Тайлбар:
Cost Estimate: 200 INR/cum
Example:
1. Small Check Dams: 5 units (3.5m x 1.5m x 0.9m) ----- 4.725 cum x 200 INR = 945 INR/unit
945 INR/unit x 5 units = 4,725 Rs
or...
(4.725 cum/unit x 5 unit = 23.625 total cum )
(23.625 total cum x 200 INR = 4,725 Rs.)
2. Large Check Walls: 5 units (8m x 1m x 2.7m) -----21.6 x 200 = 4320
4320 cum x 5 units = 21,600 Rs
3. Water Diversion Wall: 1 unit (115m x 0.65 x 0.95m) ------71 x 200= 14,200
14,200 X 1 unit= 14,200 Rs
3. Bhind Spring Check Walls/Retainment Wall: 1 unit (100m x 1m x 1.5m) = 150 total cum
150 x 200 INR = 30,000 INR Total
4.5 Арчилгаа/ урсгал үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа/ давтамж | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Inspection of the check dam for rock displacement and erosion around the ends of the dam after each significant rainfall event | Monsoon/ weekly |
| 2. | Sediment accumulation is removed if it reaches a depth of ½ the original dam height | Pre-monsoon/Monsoon |
| 3. | Sometimes check dams are removed when their useful life is completed | Annual inspections |
4.6 Арчилгаа/урсгал ажилд шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг (нэг жилд)
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Reconstruction of damaged check dams | person-days/unit | 10.0 | 400.0 | 4000.0 | 100.0 |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Removal of sediment | person-days/unit | 5.0 | 400.0 | 2000.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | pick | pieces | 3.0 | 70.0 | 210.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | shovel | pieces | 3.0 | 42.0 | 126.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | pharuwa (hoe) | pieces | 2.0 | 52.0 | 104.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | khanti (digging bar) | pieces | 2.0 | 30.0 | 60.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | hammer | pieces | 3.0 | 25.0 | 75.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | chino (chisel) | pieces | 2.0 | 75.0 | 150.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | khukuri (knife) | pieces | 2.0 | 22.0 | 44.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | small hammer (0.5-1kg) | pieces | 3.0 | 120.0 | 360.0 | 100.0 |
| Барилгын материал | Stones available at site locally | |||||
| Технологийн арчилгаа/урсгал үйл ажиллагаанд шаардагдах нийт үнэ өртөг | 7129.0 | |||||
| Технологи арчилах ба урсгал ажлын нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 101.84 | |||||
4.7 Зардалд нөлөөлж байгаа хамгийн чухал хүчин зүйл
Өртөг, зардалд нөлөөлөх гол хүчин зүйл:
Size of the check dam/check wall
Frequency and intensity of the damage to the structures
Labor availability
5. Байгаль ба нийгмийн нөхцөл
5.1 Уур амьсгал
Жилийн нийлбэр хур тундас
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1,000 мм
- 1,001-1,500 мм
- 1,501-2,000 мм
- 2,001-3,000 мм
- 3,001-4,000 мм
- > 4,000 мм
Жилийн дундаж хур тунадас (хэрэв мэдэгдэж байвал), мм:
1500.00
Хур тунадасны талаархи тодорхойлолт/ тайлбар:
Monsoon- mid-June to mid-September; July and August are the rainiest months and the temperature is warm and moist; between 70-85% of the annual precipitation occurs in the monsoon season
Seasons
a. Winter or Cold weather (mid Dec. - mid March)
b. Summer or hot weather (mid March - mid June)
c. Season of general rains (South - West monsoon season)
d. Season of retreating monsoon (mid September to mid November)
Холбогдох цаг уурын станцын нэр:
India Meteorological Department, Meteorological Centre Dehradun
Агро-уур амьсгалын бүс
- чийглэг
The overall climatic condition in the Pithoragarh district is governed by the southwest monsoon. It has a sub-tropical to temperate climate, with three pronounced seasons; summer, winter, and monsoon. The hilly terrain of the Himalayan region has snow cover and is cold during winter with snowfall normally occurring during the months of December to March.
Temperature- The temperature ranges from 0°C to 10°C in winter and from 8°C to 33°C in summer season. However, there is no meteorological observatory in the district. The account of the climate is based mainly on the records of the observations in the neighboring districts where similar meteorological conditions prevail. Variations in temperature are considerable from place to place and depend upon elevation as well as aspect. As the insolation is intense at high altitudes, in summer temperatures are considerably higher in the open than in the shade.
5.2 Гадаргын хэлбэр
Дундаж налуу:
- хавтгай (0-2 %)
- бага зэрэг налуу (3-5 %)
- дунд зэрэг налуу (6-10 % )
- хэвгий (11-15 %)
- налуу (16-30 %)
- их налуу (31-60 % )
- эгц налуу (>60 %)
Гадаргын хэлбэр:
- тэгш өндөрлөг / тал
- нуруу
- уулын энгэр
- дов толгод
- бэл
- хөндий
Өндрийн бүслүүр:
- 0-100 д.т.д. м.
- 101-500 д.т.д. м.
- 501-1,000 д.т.д м.
- 1,001-1,500 д.т.д м.
- 1,501-2,000 д.т.д м.
- 2,001-2,500 д.т.д. м.
- 2,501-3,000 д.т.д. м.
- 3,001-4,000 д.т.д м.
- > 4,000 д.т.д. м.
Технологи дараах асуудалд хандсан эсэхийг тодорхойл:
- хотгор нөхцөл
Гадаргын талаархи тодорхойлолт ба бусад тайлбар:
Altitude of evaluated sites: 1800-1990m
Average Slope: 25-+30%
5.3 Хөрс
Хөрсний дундаж зузаан:
- маш нимгэн (0-20 см)
- нимгэн (21-50 см)
- дунд зэрэг зузаан (51-80 см)
- зузаан (81-120 cм)
- маш зузаан (>120 cм)
Хөрсний бүтэц (өнгөн хөрс):
- бүдүүн/ хөнгөн (элсэрхэг)
- дундаж (элсэнцэр, шавранцар)
Хөрсний бүтэц (>20 см-ээс доош):
- дундаж (элсэнцэр, шавранцар)
Өнгөн хөрсөнд агуулагдах ялзмаг:
- дунд (1-3 % )
- бага (<1 % )
Боломжтой бол хөрсний бүрэн тодорхойлолт, боломжит мэдээллийг өгнө үү, жишээ нь хөрсний төрөл, хөрсний урвалын орчин/хүчиллэг байдал, катион солилцох чадавхи, азотын хэмжээ, давсжилт г.м.
Mountain/hill soils are a collective name given to various types of soils found under the following conditions :
-under sub-tropical, temperate and sub-alpine conditions
-under various forest types
Characteristics: very thin, fertile, and may be less than a centimeter deep on steep slopes; they are mixed with pebbles, shingles (a mass of small rounded pebbles), and gravels; they have a low-medium water holding capacity. Angular and subangular fragments of parent rock may be found mixed with the lower layers of the mountain and hill soils.
Texture: varies from loamy to sandy loam.
Soil Reaction: ranges from acidic to neutral (pH 4.6 to 6.5)
Organic Matter content: 1-5%
Ferrugenous red roils are found in this district and are well developed over Himalayan rocks (quartzite, biotite schist, amphibolite schist). They are free of carbonates and deficient in nitrogen, humus and phosphorus, light textured, porous, and friable (brittle/crumbly). The soil depth ranges from about 10cm-75 cm. These soils may be grouped into two on basis of morphology
1. Red earths- loose, friable topsoil rich in secondary concretions (hard, compact mass of matter formed by the precipitation of mineral cement within the spaces between particles, and is found in sedimentary rock or soil)
2. Red loam- argillaceous soils having a blocky structure (argillaceous minerals may appear silvery upon optical reflection and are minerals containing substantial amounts of clay-like components, e.g. argillaceous limestones are limestones consisting predominantly of calcium carbonate, but including 10-40% of clay minerals)
Brown soil: is found particularly under dense broadleaved temperate and sub-alpine forests. There occurs a thick layer of humus on the forest floor (made of decomposed leaves, branches, twigs) and the topsoil is extremely rich in humus
Podsolic Soil: soil that has developed in humid/temperate conditions usually under coniferous forests (e.g. deodar, blue pine, fir, spruce) over quartzite, granites, schists and gneiss.
Citation: Kumaun: The Land and the People, Sharad Singh Negi (1993)
5.4 Усны хүртээмж ба чанар
Гүний усны түвшин:
> 50 м
Гадаргын усны хүртээмж:
дунд зэрэг
Усны чанар (цэвэршүүлээгүй):
сайн чанарын ундны ус
Усны чанар гэж:
газрын доорхи ус
Усны давсжилтын асуудал бий юу?
Үгүй
Энэ газар үерт автдаг уу?
Үгүй
Усны чанар, нөөцийн талаархи тайлбар ба бусад тодорхойлолт:
Quantity: Water crisis has been a perennial problem in both the rural and urban areas of the Pithoragarh district
There is scarcity of safe drinking water of the villages in the study area. Hand pumps are often not functioning, pipe-water schemes are unreliable and the spring discharges have reduced during the dry season. Hand-pumped water often has a high iron content and bitter taste. Poor quality of groundwater in some of the naulas is mainly due to misuse and/or disuse of the structures.
A block-district groundwater resource estimation could not be carried out as the area is hilly (with slope >20%) and in major part aquifers are small, isolated bodies, and groundwater abstraction is done mainly through hand pumps and springs with small discharges.
However, we collected some physicochemical parameters that indicate the water (sourced from springs) is of good quality:
Water Quality Parameters of Springs:
pH: 6.29-8.18
Temp: 19.0-23.5 ºC
Electrical Conductivity: 109-504 µmsiemens
Total Dissolved Solids: 75-385 ppm
Other Parameters (from springs of nearby district, Champawat)
Electrical Conductivity: 127-222 µmsiemens
pH: 7.69-8.24
Calcium: 16-36 mg/l
Magnesium: 4.9-7.3 mg/l
Bicarbonate: 61-134 mg/l
Chloride: 5.3- 8.9 mg/l
Total Hardness as CaCO3: 70-110 mg/l
Source: Government of India Ministry of Water Resources, Central Ground Water Board, 2009 Groundwater Brochure of Champawat District (2009)
5.5 Биологийн олон янз байдал
Зүйлийн олон янз байдал:
- дунд зэрэг
Амьдрах орчны олон янз байдал:
- дунд зэрэг
Биологийн олон янз байдлын талаархи тайлбар ба бусад тодорхойлолт:
Uttarakhand has more than 7000 species of medicinal plants and 500 species of fauna. Floral diversity contributes 31% of total floral density of India. Fauna contributes just 1.58% of the total faunal density of the country. There are 119 endemic species of flowering plants in the state that exhibited 2.35% endemism and 35 faunal endemic species. Because it lies at the juncture of India, Nepal and the Tibeten Autononmous region, there often cases of poaching and smuggling of wildlife contrabands, including bear bile, musk pods and leopard skins through the borders. Yarsa Gumba Ophiocordyceps sinensis, commonly known as Caterpillar Fungus, is also illegally traded transboundary in the region, together with various plant species. Due to anthropogenic impacts, changes is soil quality, and climatic elements, the biodiversity of our study site is not as high as in other areas of the Pithoragarh district.
Citation: Sundriyal, M. & Sharma, B. (2016). Status of Biodiversity in Central Himalaya, Applied Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 4( 2), 37-43.
5.6 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчдын тухай мэдээлэл
Суурьшмал эсвэл нүүдлийн:
- Суурьшмал
Үйлдвэрлэлийн системийн зах зээлийн чиг баримжаа:
- амь зуух арга хэлбэрийн (өөрийгөө хангах)
- холимог (амьжиргаа ба худалдаанд)
Бусад эх үүсвэрээс олох орлого:
- Нийт орлогын 10-50 %
Чинээлэг байдлын түвшин:
- ядуу
Хувь хүн эсвэл бүлэг:
- бүлэг / олон нийтийн
Механикжилтын түвшин:
- гар ажил
Хүйс:
- эмэгтэй
- эрэгтэй
Газар ашиглагчийн нас:
- залуус
- дунд нас
- ахимаг нас
Газар ашиглагчдын бусад шинж чанарыг тодорхойл:
With recent development in Pithoragarh, an influx of funds coming from outside sources has caused a decline in the importance of agriculture production, which in now marginalized, based on female labour, and mainly conducted for subsistence with little surplus to sell. High caste men do not work in cultivation at all, and male tasks such as ploughing are performed by the Scheduled Caste.
Although most women are still cultivating, their work has lost economic importance. For most families, the produce does not cover the needs of the household and surplus must be bought from the market. Many of the terraces that were formerly fruit orchards (mainly citrus) have been completely abandoned. Farming is less intensive and landholdings are small and fragmented. The main crops are wheat, millet, and pulses, but yields are low as the land is not irrigated. Less livestock (cows, goats, buffalo) is kept because of the labor involved. Very little capital is returned to farming. Crops produced for the markets in the plains are replacing traditional crops to sustain the household.
With exposure to the“Modern” lifestyle, new values have also been accepted. Two children are the norm (the ideal being one son and one daughter, but at least one son in a must). Although access to education is quite good, it does not seem to result in working careers for women. The women, both young and old, spend their days with domestic and agriculture work. Several village persons stated that it would be best to educate their daughters so they could get a government job.
5.7 Газар ашиглагчийн технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын дундаж талбайн хэмжээ
- < 0.5 га
- 0.5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1,000 га
- 1,000-10,000 га
- > 10,000 га
Энэ талбай том, жижиг, дунд алинд хамаарах вэ (орон нутгийн нөхцөлд харгалзуулна уу)?
- бага-хэмжээний
5.8 Газар эзэмшил, газар ашиглах эрх, ус ашиглах эрх
Газар өмчлөл:
- нэгдлийн/ тосгон
Газар ашиглах эрх:
- нэгдлийн хэлбэрээр (зохион байгуулалттай)
Ус ашиглах эрх:
- нээлттэй хүртэх (зохион байгуулалтгүй)
- нэгдлийн хэлбэрээр (зохион байгуулалттай)
Газар ашиглах эрх нь уламжлалт эрхзүйн тогтолцоонд суурилсан уу?
Тийм
Тодорхойлно уу:
Under the Kumaun Panchayat forest rules of 1931 (amended in 1976): A Van Panchayat, (community forest council), can be formed out of non-private land within the settlement boundaries of a village. Accordingly, all villagers are members of the VP upon their approval by a Sub-Divisional Magistrate under the state Revenue Department. The members are collectively referred to as the general body, which selects the management committee members through a democratic process.
Тайлбар:
5-9 elected members assume control and regulation of forest resources. They additionally raise funds and mobilize the village to protect and support sustainable land use.
5.9 Дэд бүтэц, үйлчилгээний хүртээмж
эрүүл мэнд:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
боловсрол:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
техник зөвлөгөө:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт (жишээ нь, ХАА-аас өөр):
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
зах зээл:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
эрчим хүчний хангамж:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
зам тээвэр:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
усан хангамж ба ариутгал:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
санхүүгийн үйлчилгээ:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
Тайлбар:
The situation of infrastructure is difficult and inconsistent in the hill regions because of the terrain. The major infrastructural issues are drinking water and irrigation facilities, electricity, transportation and communication facilities and social infrastructure (housing and education). As for financial services, only the State Bank of India (SBI) is active in the hill regions where it is trying to achieve the objective of 100% financial inclusion. Some villages mentioned buying into into agricultural insurance in the past, however this was a temporary enterprise and they were never compensated after extreme climatic events that occurred and damaged over 70% of their crop.
Though infrastructure and education has generally improved over the years, institutional and marketing networks in the region aimed at supporting hill-farmers are lacking.
6. Үр нөлөө ба дүгнэлт
6.1 Технологийн талбайд үзүүлсэн нөлөө
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн үр нөлөө
Үйлдвэрлэл
ойн чанар
газрын менежмент
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
The check dams helped deter the damage from runoff to their settlements and conserved the forest trail that is commonly used to access the areas where fodder/grass collection is permitted.
Нийгэм-соёлын үр нөлөө
ГТМ/ газрын доройтлын мэдлэг
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
People have seen the benefits of constructing these structures, and they continue to participate in maintaining and building more check dams to reduce erosion and increase groundwater recharge.
Экологийн үр нөлөө
Усны эргэлт/ илүүдэл
усны хэмжээ
ус хураах / цуглуулах
гадаргын урсац
усны урсац
гүний усны түвшин / уст давхарга
ууршилт
Хөрс
хөрсний чийг
хөрсөн бүрхэвч
хөрс алдагдах
хөрс хуримтлагдах
хөрс хагарах/ хагсах
хөрс нягтрах
шимт бодисын эргэлт/ сэргэлт
Биологийн олон янз байдал: ургамал, амьтан
Ургамалын бүрхэвч
газрын дээрхи / доорхи карбон
Уур амьсгал болон гамшгийн эрсдлийг бууруулах
хөрсний гулсалт/ чулуун нуранги
гангийн нөлөө
циклон, бороо, шуурганы нөлөө
түймрийн эрсдэл
бичил уур амьсгал
6.2 Технологийн талбайн гадна үзүүлсэн үр нөлөө
Усны хүртээмж
хуурай улиралд ашиглах найдвартай, тогтвортой урсац
голын адагт лаг шавар хуримтлагдах
буферлэх / шүүлтүүрийн багтаамж
хөрш зэргэлдээ газарт учирах хохирол
нийтийн/хувийн хэвшлийн дэд бүтцэд учрах хохирол
6.3 Технологийн уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт, цаг агаарын гамшигт үзэгдэлд өртөх байдал ба эмзэг байдал (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)
Уур амьсгалын аажим өөрчлөлт
Уур амьсгалын аажим өөрчлөлт
| Улирал | Өсөх эсвэл буурах | Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| жилийн дундаж температур | Өсөлт | сайн | |
| бусад аажим уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт | Irregular rainfall | Өсөлт | сайн |
Уур амьсгалаас хамаарах аюул (гамшиг)
Цаг уурын гамшигт үзэгдэл
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| орон нутгийн аадар бороо | сайн |
Уур амьсгалын гамшиг
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| ган гачиг | сайн |
| ойн түймэр | сайн |
Усзүйн гамшиг
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| шар усны үер | сайн |
| хөрсний гулсалт | дунд зэрэг |
Тайлбар:
Some check dams and check walls are more durable than others. Depending on the site specific conditions, some do very well after incidences such as after an extreme rainstorm. However this depends on the design/structural soundness, the level of maintenance, and overall hydrological impact. For example, the large check walls in the ravine of Nakina have required immense reconstruction and have required significant effort to maintain, as they receive a huge amount of flow during monsoon each year. The size and slope of the gully are impactful determinants for how sensitive/enduring the structure is.
6.4 Өртөг ба ашгийн шинжилгээ
Бий болгох зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
маш эерэг
Арчилгаа/урсгал зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Тайлбар:
Although maintenance can be troublesome and require lots of manual labor for repair, the long term benefits and avoided damage from monsoon runoff outweigh the costs/effort.
6.5 Технологи нэвтрүүлэлт
- > 50%
Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн хүмүүсээс хэд нь өөрийн хүчээр технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн бэ, өөрөөр хэлбэл гадны тусламж дэмжлэг авалгүйгээр?
- 11-50%
Тайлбар:
In many cases, collective action is encountered at all stages for these technologies, from planning and construction, to demolition of temporary check-dams without any technical or financial backing from the state.
6.6 Дасан зохицох
Бий болсон өөрчлөлтөд зохицуулан технологийг өөрчилсөн үү?
Үгүй
6.7 Технологийн давуу тал/боломжууд
| Газар ашиглагчдын тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
| Decrease velocity of runoff and erosive processes to the landscape |
| Support recharge of groundwater/springshed recharge |
| Increase water availability for surrounding vegetation |
| Well constructed check dams function as permanent installations and require little maintenance |
| The technology is relatively inexpensive and easy to install |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
| Views aligned with the land-user |
| There is potential for the village to construct more check dams and use the water for storage/irrigation purposes |
6.8 Технологийн дутагдалтай/сул тал/аюул болон тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах арга зам
| Газар ашиглагч нарын тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| Removal and reconstruction can be costly for some types of check dams | Give thorough attention to the criteria for the site selection to avoid the need for removal; stress the need for maintenance and structure check ups. |
| There can be turbulence downstream, causing erosion of the channel banks. | Vegetative interventions can support these structures, so trees or shrubs can be planted around and in the spaces between check dams to further decrease runoff velocity, increase infiltration, and act as a shock absorber. |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| Aligned with the land user | The government should consider providing appropriate incentives for constructing and managing check-dams, which enable more efficient use of water and also generate the positive externality of recharging ground water in surrounding areas. |
| Check dam construction, if not done by skilled labour, can fail. These situations often arise and become noticeable to the land users when check-dams located upstream are damaged and there is a rapid flow of water to check-dams located downstream. | Special maintenance can be performed by designated people to monitor the status of check dams upstream |
| The large check dams have consistent issues and appear to require more reconstruction. These structures are located downstream and must bear more pressure. The reason for their damage could be inconsistency in repairing existing damage before monsoon. Construction cost is then increased, as additional cost is incurred in removing the accumulated silt and arranging new boulders. | The land users should organize themselves more formally for check dam reconstruction is this area. Collectively generating the necessary capital and labor needed for timely reconstruction may be required from external sources like the Forest Department or JICA organization. |
7. Ном зүй ба холбоосууд
7.1 Мэдээлэл цуглуулсан арга/эх үүсвэр
- Хээрийн уулзалт, судалгаа
4
- Газар ашиглагчтай хийсэн ярилцлага
2
Мэдээллийг хэзээ (газар дээр нь) цуглуулсан бэ?
26/06/2019
7.2 Ном, хэвлэлийн ишлэл
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Evaluation of the effect of porous check dam location on fine sediment retention (a case study), A. M. Hassanli, A. Esmaeli Nameghi, S. Beecham, 2007.
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
DOI 10.1007/s10661-008-0318-2
7.3 Холбогдох мэдээллийн интернет холбоос
Гарчиг/ тодорхойлолт:
Mainstreaming Slope Stability Management
URL:
http://www.research4cap.org/Library/ScottWilson-LaoPDR-2009-Slopes+Theme8.5+6+Retaining+Wall+Design+PPT+E-SEACAP21-v111220.pdf
Гарчиг/ тодорхойлолт:
Policy Brief: Spring Revival through Sustainable Land Management (SLM) in the Himalayan Foothills: Uttarakhand, North India. Author: Liniger HP, Bandy J, Year: 2020
URL:
https://www.wocat.net/en/projects-and-countries/projects/onsite-and-offsite-benefits-sustainable-land-management/india
Гарчиг/ тодорхойлолт:
Video: SLM for Himalayan Spring Revival. Author: Liniger HP, Bandy J, Year: 2020
URL:
https://vimeo.com/429988881
Холбоос ба модулууд
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаахХолбоосууд

Community Forest Management in the Nakina Van Panchayat [Энэтхэг]
Van Panchayats or village forest councils are a impressive example of grassroots community management of natural resources, where a specific administrative unit is locally elected by community members who are responsible for the management of activities related to the forest.
- Эмхэтгэгч: Jaclyn Bandy

Naula Management and Conservation [Энэтхэг]
Naulas are shallow, four-sided stepped wells designed to collect water from subterranean seepages or springs and are used to meet domestic water needs by the local communities. Naula management and conservation encompasses a range of activities that preserve their structure and function.
- Эмхэтгэгч: Jaclyn Bandy
Модулууд
Модуль байхгүй байна