Gully plug [Йордан]
- Шинийг нээх:
- Шинэчлэх:
- Эмхэтгэгч: Mira Haddad
- Хянан тохиолдуулагч: –
- Хянагчид: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
السدات
technologies_5862 - Йордан
Бүлгүүдийг үзэх
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаах1. Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
1.2 Технологийг үнэлэх, баримтжуулах ажилд хамаарах мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүс, байгууллагуудын холбоо барих мэдээлэл
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
Strohmeier Stefan
International Center of Agriculture Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA)
Йордан
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
Evett Steve
USDA Agricultural Research Service
Америк
Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA) - Ливан1.3 ВОКАТ-аар баримтжуулсан өгөгдлийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцөл
Эмхэтгэгч болон гол мэдээлэгч хүн(хүмүүс) WOCAT аргачлалаар баримтжуулсан мэдээллийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцлийг хүлээн зөвшөөрсөн:
Тийм
1.4 Технологи тогтвортой гэдгийг баталгаажуулах
Энэ технологийг газрын доройтлыг бууруулж, газрын тогтвортой менежментийг хангахад тохиромжтой гэж үзэж болох уу?
Үгүй
2. ГТМ Технологийн тодорхойлолт
2.1 Технологийн товч тодорхойлолт
Технологийн тодорхойлолт:
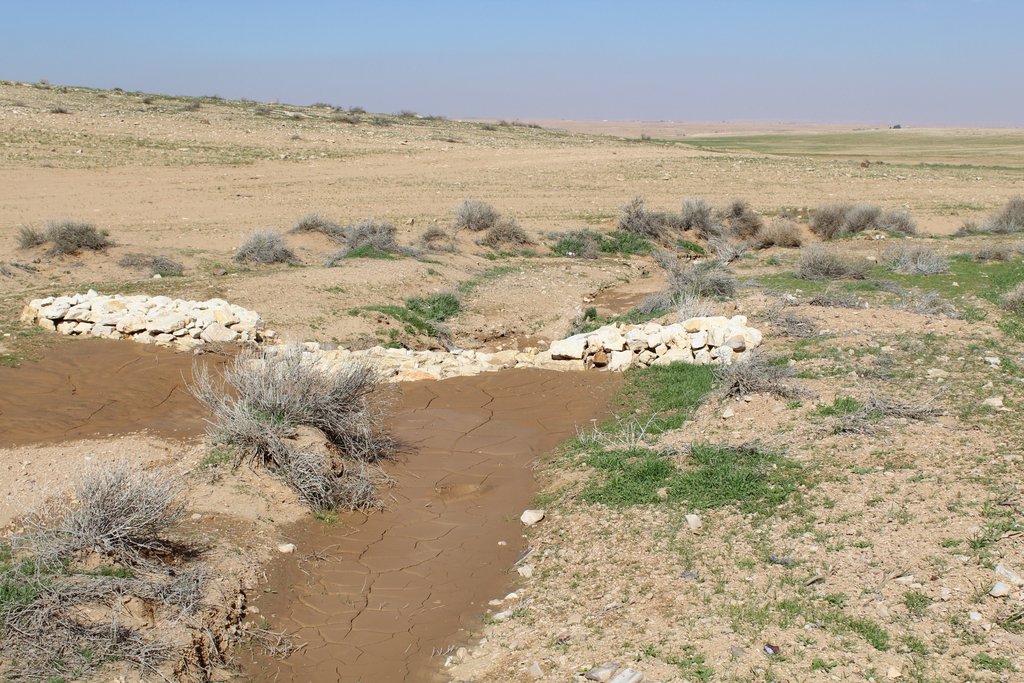
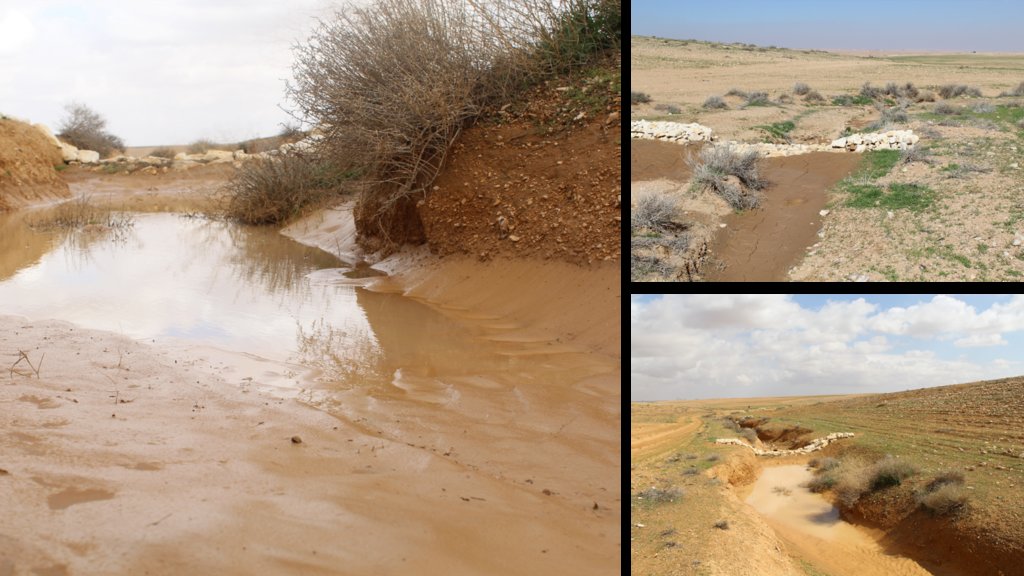
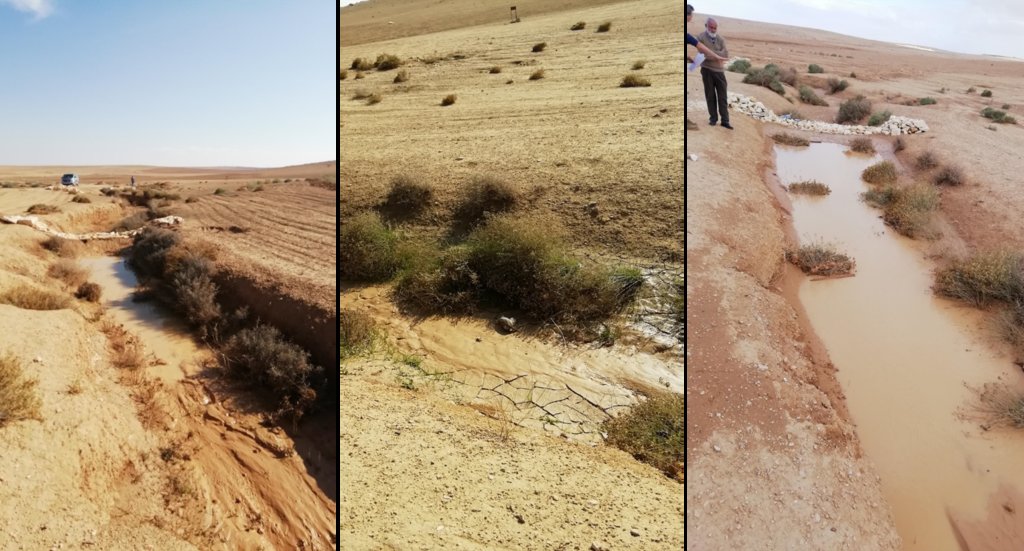
Gully plugs aim at rehabilitating active gullies in dryland watersheds, which are prone to erosion through concentrated surface runoff. Multiple gullies plugged in succession dissipate runoff energy, foster local water retention and infiltration, encourage sedimentation, assist in the stabilization of gully bed and side banks, and stimulate revegetation of flow paths; the channel measures must be combined with proper SLM in the catchments upstream.
2.2 Технологийн дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт
Тодорхойлолт:
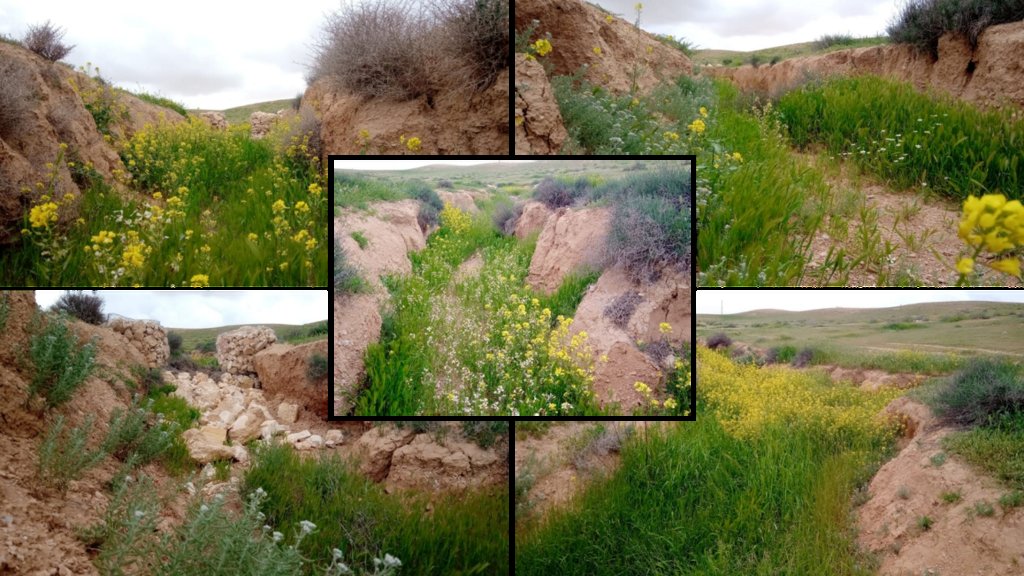
Characteristics: Multiple gully plugs positioned sequentially within a gully system interrupt concentrated surface runoff and reduce its erosive power. The plugs are each made of multiple cobbles/stones mostly ranging between 10 and 30 cm diameter and constructed to ensure a stable structure. The plugs started at the head of the gully (upstream) and ranges from 1.5 - 3.7 m in width with an average of 2.5 m. For heavily eroded and very unstable sections, gabions can be used also. The structures are around 1.0 to 1.5-m high, anchored into the sidewalls, and around 0.20 to 0.35 m deep into the gully bed, built up to around 1/3 to max. 1/2 of the gully depth - ensuring the concentrated flow stays within the channel and does not overflow the side banks. The top of the plug is U-shaped, with the sides built higher than the centre. Upslope, the plugs are packed with soil to trap sediments (stopping it flowing through the structure), and downslope the plugs have an apron to dissipate the energy of overflowing water, into a micro stilling basin. The downslope side of the gully plug is sloped rather than vertical. The large stones add roughness to the slope, creating a rough spillway that dissipates erosive energy. In the direction of gully flow, several gully plugs are placed such that the upper gully apron is set at approximately the height of the following downstream gully crest.
Environment: The technology is used in a watershed close to Al Majeddyeh village, located in the Middle Badia zone, approximately 30 km south-east of Amman. The climate is arid and warm (Palmer, 2013). The average annual rainfall is around 130 mm. The natural environment is labelled as steppe, “BSh” in the köppen classification. The human environment is characterized by agropastoralists. They are semi-nomadic and live in villages around the watershed, for example, Al Majeddyeh village.
Purpose: The measure interrupts the concentrated flow, reduces velocity, and dissipates energy. Multiple structures along the gully decrease the erosive power of runoff, retaining a fraction of the runoff, inducing sedimentation (upstream of the plug), thus protecting the gully bed from further deep-scouring, and strengthening the gully side banks, especially when this is linked with re-vegetation. Over time, the establishing vegetation (roots and surface cover) stabilizes the soil and protects it from concentrated flow erosion. To be effective, gully plug emplacement requires SLM in upland areas. These measures then jointly mitigate peak runoff generation and accordingly reduce downstream flooding.
Major activities: Upland SLM is essential. In the specific watershed rehabilitation context, upland SLM was achieved through micro water harvesting and re-vegetation through native shrubs (the “VALLERANI” method). Gully morphology assessment is required for gully plug design, and positioning and earthwork excavation is necessary for foundation preparation in the gully bed and wall anchors. Proper layering of various size stones and shaping of gully plugs is necessary as is the addition of a packed soil pack upstream of the stone structure, to semi-seal the surface and to pond water. Then gully walls are revegetated through native seedlings: these benefit from the water ponding upstream prior to sedimentation upstream of the gully and enhanced soil water storage in the sediments once the gully is filled.
Benefits: Stops ongoing land degradation and gully deepening, and achieves a certain degree of rehabilitation; retains a fraction of runoff water and sediments in the watershed – water mainly infiltrates and provides moisture to the gully vegetation; gully vegetation serves various purposes including livestock fodder, reduction of flow velocities in the gully, and retention of further sediment.
Land user's opinion: Land users benefit from the vegetation (e.g. fruit trees can potentially be out-planted), as well as ponded water for livestock; however, the technology is labor-intensive, and therefore costly, and landowners (at the local target site) require incentives to carry out the work.
2.3 Технологийн гэрэл зураг
2.5 Энэ үнэлгээнд хамрагдсан технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн улс орон/ бүс нутаг/ байршил
Улс:
Йордан
Улс/аймаг/сум:
Amman governorate/Al Jizza/Al Majeddyeh village
Технологи өргөн дэлгэрсэн эсхийг тодорхойл:
- тодорхой газар хэрэгжсэн/ жижиг талбайд төвлөрсөн
Технологи(иуд) нэвтрүүлсэн талбай тусгай хамгаалалттай газар нутагт байрладаг уу?
Үгүй
Map
×2.6 Хэрэгжсэн хугацаа
Хэрэгжүүлсэн он:
2017
2.7 Технологийн танилцуулга
Технологийг хэрхэн нэвтрүүлснийг тодорхойл:
- Туршилт/судалгааны үр дүн
- Гадны төсөл/хөтөлбөрийн дэмжлэгтэйгээр
3. ГТМ технологийн ангилал
3.1 Технологийн үндсэн зорилго (ууд)
- газрын доройтлыг бууруулах, сэргийлэх, нөхөн сэргээх
- биологийн төрөл зүйлийг хамгаалах / сайжруулах
- гамшгийн эрсдлийг бууруулах
3.2 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын одоогийн газар ашиглалтын хэлбэр(үүд)
Нэг газр нутгийн хэмжээнд хэрэгжих холимог газар ашиглалт:
Тийм
Газар ашиглалтын холимог тогтолцоог (тарилан/бэлчээр/ой мод) тодорхойл:
- Агро-бэлчээр (тарилан-мал аж ахуйн хослуулсан тогтолцоог хамруулан ойлгоно)

Бэлчээрийн газар
Бэлчээрийн мал аж ахуй:
- Хагас нүүдлийн бэлчээрийн аж ахуй

Усан зам, усан сан, ус намгархаг газар
- Усны зайлуулах шугам, усан зам
Гол бүтээгдэхүүн/ үйлчилгээ:
To convey and drain: Wd
3.3 Технологи хэрэгжүүлснээр газар ашиглалтад өөрчлөлт гарсан уу?
Технологи хэрэгжүүлснээр газар ашиглалтад өөрчлөлт гарсан уу?
- Тийм (Технологи хэрэгжүүлэхээс өмнөх үеийн газар ашиглалтын талаархи асуулгыг бөглөнө үү)
Нэг газр нутгийн хэмжээнд хэрэгжих холимог газар ашиглалт:
Үгүй

Бэлчээрийн газар
Бэлчээрийн мал аж ахуй:
- Нүүдлийн мал аж ахуй
- Хагас нүүдлийн бэлчээрийн аж ахуй
Амьтдын төрөл зүйл:
- ямаа
- хонь
Тариалан-мал аж ахуйн нэгдсэн менежмент хэрэгждэг үү?
Үгүй
Бүтээгдэхүүн ба үйлчилгээ:
- мах
3.4 Усан хангамж
Технологи хэрэгжүүлсэн газрын усан хангамж:
- Байгалийн усалгаатай
Тайлбар:
The measure mitigates the effect of surface runoff in concentrated flow areas - as a consequence of heavy rainfall events
3.5 Технологи ГТМ-ийн аль бүлэгт хамаарах вэ
- хөрс/ ургамлын бүрхэвч сайжруулах
- хөрсийг бага гүнд боловсруулах
- Налуугийн арга хэмжээ
- water harvesting; surface water management (spring, river, lakes, sea, riparian zone, riverbanks, seashore, lakeshore, spring shed); ecosystem-based disaster risk reduction
3.6 Технологийг бүрдүүлэх ГТМ арга хэмжээ

Ургамлын арга хэмжээ
- V2: Өвс ба олон наст өвслөг ургамал

Барилга байгууламжийн арга хэмжээ
- S6: Хашаа, саад, явган хашлага, хашаа

бусад арга хэмжээ
Тодорхойлно уу:
Specify tillage system: no tillage
Specify residue management: grazed and retained
3.7 Технологид харгалзах газрын доройтлын төрөл

хөрс усаар эвдрэх
- Wg: Гуу жалгын элэгдэл
- Wo: Усны элэгдлийн дам нөлөө

хөрсний физик доройтол
- Pk: Гадарга дээр хагсах, хагарах
- Pu: Бусад үйл ажиллагааны улмаас био-бүтээмжит функц алдагдах

усны доройтол
- Hs: Гадаргын усны хэмжээ багасах
- Hw: Ус намгархаг газрын буферлэх буюу хаах чадвар багасах
3.8 Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх, сааруулах ба нөхөн сэргээх
Газрын доройтолтой холбоотойгоор Технологи ямар зорилго тавьсан болохыг тодорхойл:
- Газрын доройтлыг бууруулах
- Хүчтэй доройтсон газрыг нөхөн сэргээх/ сайжруулах
4. Техникийн нөхцөл, хэрэгжүүлсэн үйл ажиллагаа, материал ба зардал
4.1 Технологийн техник зураг
Техник тодорхойлолт (техник зургийн тайлбар):
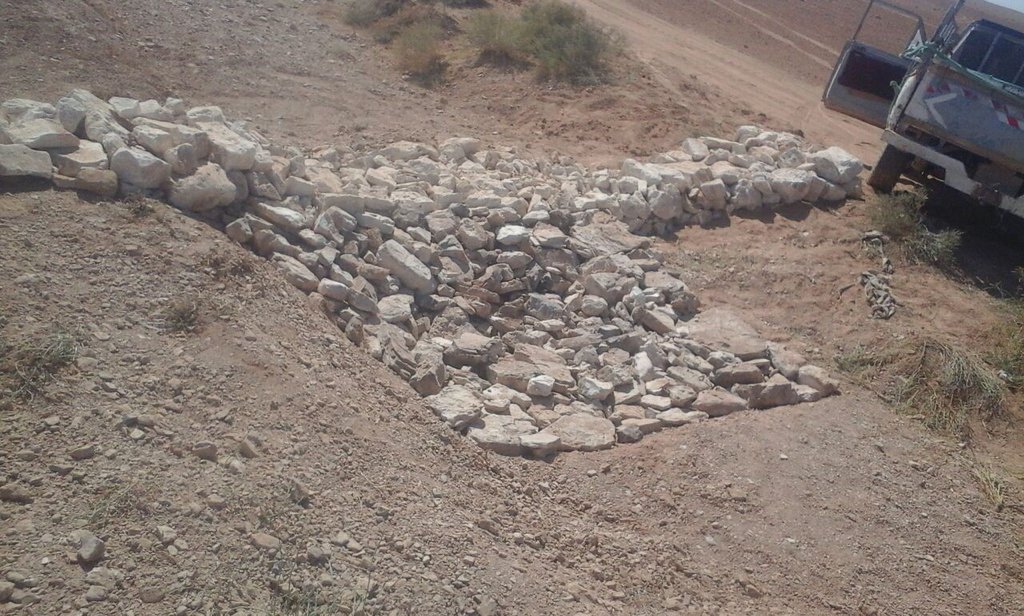
Emplacement in gully morphological system and watershed context: Determine the downstream starting point for the gully plugs and then extend upstream. The basic design is to keep the structure height maximum half the gully depth regardless of structure type. The spacing between structures is set as a gully depth function, structure crest height above the gully bed, and slope of the gully bed between structures. Additionally, the structure's final location will be shifted either upstream or downstream of the calculated gully bed level to place the structure in a more stable point if required. Following this methodology ensures variable spacing between structures to cope with both slope and depth of gully to ensure the sediment filling in between these structures occurs. In the case of distinct gully morphology and side banks that are very unstable, gabion structures can also be used/instead of a single stone pack.
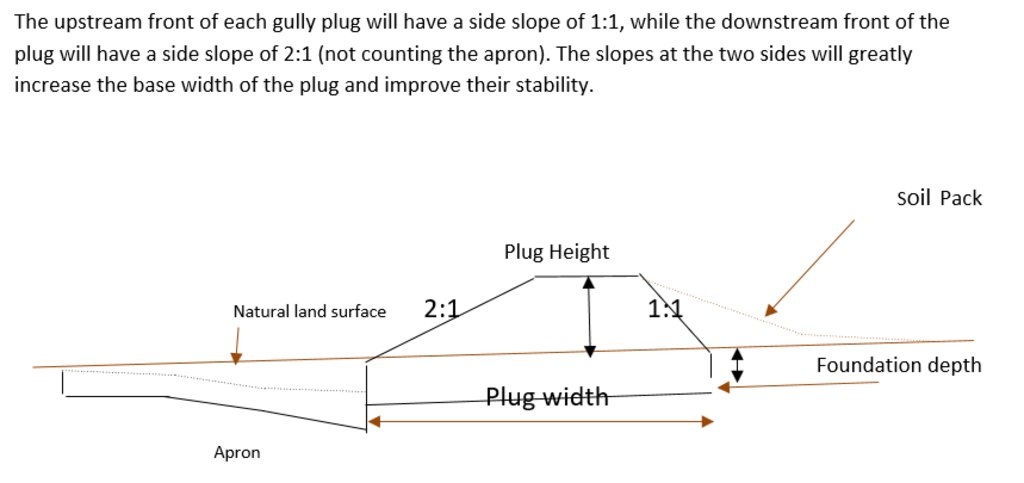
Design of the Structure: Gully plugs must be anchored strong enough to resist water flow and prevent bypass from the side banks. A foundation is also required for all structures, depending on their dimensions and the bed's nature. At the specific site, the foundation depth for the planned structures ranges between 0.2 to 0.35 meters. The anchoring of gully plugs ranges between 1 and 1.5 meters. This depends on the existing condition of the banks at each structure location. Gully plugs have a downstream apron with a length of around 3 to 4 times the height of structures. The apron starts from below the bottom level of the foundation and gradually level halfway down. All gully plugs were designed to have a height maximum of 0.5 the depth of the gully. So each structure will pass water flow downward but keeping it inside the gully. Gabion structures have a sort of spillway from the top but at the same time protecting the banks. The configuration slightly differs from the normal stone structure, but the idea is to protect the sides and a spillway in the middle. The upstream front of each gully plug has a side slope of 1:1, while the downstream front of the plug has a side slope of 2:1 (not counting the apron). The slopes at the two sides greatly increase the base width of the plug and improve their stability. The gully plugs are provided with an amount of soil resulting from the foundation to form a triangle of soil fill against the structure at the upstream side; this improves the function of the gully plugin holding more water and trapping sediments. On the other side of each structure, the downstream side's slope is meant to tackle the overflow of water along the drop to safely return to the gully bed level without causing additional erosion. The rock-filled apron catches the flow and acts to dissipate erosive energy.
Зохиогч:
Steve Evett
Он, сар, өдөр:
15/08/2017
4.2 Материал болон зардалд хамаарах ерөнхий мэдээлэл
Үнэ өртөг, оруулсан хувь нэмрийг хэрхэн тооцсоныг тодорхойл:
- Технологийн нэгж тус бүр
Нэгжийг тодорхойл:
Gully plug
Үнэ өртөгийг тооцоход ашигласан мөнгөн нэгж:
- Ам.доллар
4.3 Бий болгох үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа (улирал) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Implement upland watershed SLM (reference VALLERANI) | |
| 2. | Gully system/morphological assessment | |
| 3. | Determine plug design and implementation in the watershed | |
| 4. | Excavation earthworks for anchors and foundation | At least 2 months prior rainy season onset |
| 5. | Stone made construction of gully plugs (occasionally with gabions) | At least 1 month prior rainy season onset |
| 6. | Soil pack at upstream front | At least 1 month prior rainy season onset |
| 7. | Revegetation of gully side banks | At the onset of the rainy season |
Тайлбар:
Gully plugs require proper SLM in the uplands. Revegetation of gully side banks is optional – depending on the recovery potential of the area.
4.4 Бий болгоход шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Field technician (design and oversight) | Labour Day (LD) per structure | 0.2 | 50.0 | 10.0 | |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Workers (excavation/earthworks) | LD | 4.0 | 35.0 | 140.0 | |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Workers (stone layering/construction) | LD | 4.0 | 35.0 | 140.0 | |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Worker (out-planting of seedlings) | LD | 1.0 | 35.0 | 35.0 | |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Shovel, Pickaxe, buckets, ruler | Lump sum | 1.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | |
| таримал материал | Seedlings | per item | 10.0 | 0.5 | 5.0 | |
| Барилгын материал | Stones | m3 | 4.0 | 10.0 | 40.0 | |
| Бусад | Logistics (seedling transport, local stone transport) | lump sum | 1.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | |
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг | 390.0 | |||||
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 390.0 | |||||
Хэрэв газар ашиглагч нийт зардлын 100% -иас бага хэсгийг төлсөн бол хэн голлох зардлыг гаргасан бэ:
International research for the development project.
Тайлбар:
Design is tailored for implementation through local workers (rural agro-pastoral community) and local materials. The engagement of local community workers as part of the specific project; if a professional contractor is hired costs can be significantly reduced.
4.5 Арчилгаа/ урсгал үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа/ давтамж | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Inspect damage/status | After severe storms and runoff events |
| 2. | Maintain/repair/improve | After inspection |
Тайлбар:
If optimally designed and connected with proper upland SLM the gully plug technology would not require maintenance; the measure induces nature-based (vegetation) protection of vulnerable gully zones over time.
4.6 Арчилгаа/урсгал ажилд шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг (нэг жилд)
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Expert (investigation) | LD | 0.1 | 50.0 | 5.0 | |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | LD | 0.5 | 35.0 | 17.5 | ||
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | LD | 1.0 | 35.0 | 35.0 | ||
| Барилгын материал | stones | m3 | 0.5 | 10.0 | 5.0 | |
| Технологийн арчилгаа/урсгал үйл ажиллагаанд шаардагдах нийт үнэ өртөг | 62.5 | |||||
| Технологи арчилах ба урсгал ажлын нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 62.5 | |||||
Хэрэв газар ашиглагч нийт зардлын 100% -иас бага хэсгийг төлсөн бол хэн голлох зардлыг гаргасан бэ:
It is 100% covered by the research project
Тайлбар:
Maintenance might be needed in case of improper implementation and/or extreme event occurrence. Maintenance should be minimal - mostly after initial 1-2 rainy seasons. Thereafter, revegetated and rehabilitated gully system – and most importantly, the rehabilitated uplands - would take on hydrological buffering functions and withstand the erosive force of surface runoff.
4.7 Зардалд нөлөөлж байгаа хамгийн чухал хүчин зүйл
Өртөг, зардалд нөлөөлөх гол хүчин зүйл:
The most distinct cost factor is labor – which is especially significant when using local (community) labor; some technical training is required.
5. Байгаль ба нийгмийн нөхцөл
5.1 Уур амьсгал
Жилийн нийлбэр хур тундас
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1,000 мм
- 1,001-1,500 мм
- 1,501-2,000 мм
- 2,001-3,000 мм
- 3,001-4,000 мм
- > 4,000 мм
Жилийн дундаж хур тунадас (хэрэв мэдэгдэж байвал), мм:
130.00
Хур тунадасны талаархи тодорхойлолт/ тайлбар:
Jordan has a rainy season from September to May – but locally, the effective rainy season sets on later (November or December) and lasts until April.
Холбогдох цаг уурын станцын нэр:
Queen Alia international airport reference station reports long term average annual rainfall of about 150 mm A rainfall tipping bucket installed in the site in 2016.
Агро-уур амьсгалын бүс
- хуурай
5.2 Гадаргын хэлбэр
Дундаж налуу:
- хавтгай (0-2 %)
- бага зэрэг налуу (3-5 %)
- дунд зэрэг налуу (6-10 % )
- хэвгий (11-15 %)
- налуу (16-30 %)
- их налуу (31-60 % )
- эгц налуу (>60 %)
Гадаргын хэлбэр:
- тэгш өндөрлөг / тал
- нуруу
- уулын энгэр
- дов толгод
- бэл
- хөндий
Өндрийн бүслүүр:
- 0-100 д.т.д. м.
- 101-500 д.т.д. м.
- 501-1,000 д.т.д м.
- 1,001-1,500 д.т.д м.
- 1,501-2,000 д.т.д м.
- 2,001-2,500 д.т.д. м.
- 2,501-3,000 д.т.д. м.
- 3,001-4,000 д.т.д м.
- > 4,000 д.т.д. м.
Технологи дараах асуудалд хандсан эсэхийг тодорхойл:
- хотгор нөхцөл
Гадаргын талаархи тодорхойлолт ба бусад тайлбар:
Gully slope is 3.4% on average.
5.3 Хөрс
Хөрсний дундаж зузаан:
- маш нимгэн (0-20 см)
- нимгэн (21-50 см)
- дунд зэрэг зузаан (51-80 см)
- зузаан (81-120 cм)
- маш зузаан (>120 cм)
Хөрсний бүтэц (өнгөн хөрс):
- дундаж (элсэнцэр, шавранцар)
- нарийн /хүнд (шаварлаг)
Хөрсний бүтэц (>20 см-ээс доош):
- дундаж (элсэнцэр, шавранцар)
- нарийн /хүнд (шаварлаг)
Өнгөн хөрсөнд агуулагдах ялзмаг:
- бага (<1 % )
Боломжтой бол хөрсний бүрэн тодорхойлолт, боломжит мэдээллийг өгнө үү, жишээ нь хөрсний төрөл, хөрсний урвалын орчин/хүчиллэг байдал, катион солилцох чадавхи, азотын хэмжээ, давсжилт г.м.
Soil depth is varying throughout the gully areas. At some points (mostly upstream) the gully bed reaches the bedrock
5.4 Усны хүртээмж ба чанар
Гүний усны түвшин:
> 50 м
Гадаргын усны хүртээмж:
дунд зэрэг
Усны чанар (цэвэршүүлээгүй):
зөвхөн газар тариалангийн зориулалтаар ашиглах (усалгаа)
Усны чанар гэж:
гадаргын ус
Усны давсжилтын асуудал бий юу?
Үгүй
Энэ газар үерт автдаг уу?
Тийм
Тогтмол байдал:
байнга
5.5 Биологийн олон янз байдал
Зүйлийн олон янз байдал:
- Их
Амьдрах орчны олон янз байдал:
- дунд зэрэг
Биологийн олон янз байдлын талаархи тайлбар ба бусад тодорхойлолт:
Gully plugs with out-planted vegetation create micro-climates; after recruitment and emergence of seed material, biodiversity increases.
5.6 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчдын тухай мэдээлэл
Суурьшмал эсвэл нүүдлийн:
- Суурьшмал
- Хагас-нүүдэлийн
Бусад эх үүсвэрээс олох орлого:
- Нийт орлогын 10 %-иас доош
Чинээлэг байдлын түвшин:
- нэн ядуу
- ядуу
Хувь хүн эсвэл бүлэг:
- Хувь хүн / өрх
- бүлэг / олон нийтийн
Механикжилтын түвшин:
- гар ажил
Хүйс:
- эрэгтэй
Газар ашиглагчийн нас:
- залуус
- дунд нас
5.7 Газар ашиглагчийн технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын дундаж талбайн хэмжээ
- < 0.5 га
- 0.5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1,000 га
- 1,000-10,000 га
- > 10,000 га
Энэ талбай том, жижиг, дунд алинд хамаарах вэ (орон нутгийн нөхцөлд харгалзуулна уу)?
- том-хэмжээний
Тайлбар:
The entire watershed area affected by gully plugs is 160 hectares.
The total constructed plugs are 55.
5.8 Газар эзэмшил, газар ашиглах эрх, ус ашиглах эрх
Газар өмчлөл:
- хувь хүн, өмчийн гэрчилгээтэй
Газар ашиглах эрх:
- хувь хүн
Газар ашиглах эрх нь уламжлалт эрхзүйн тогтолцоонд суурилсан уу?
Тийм
5.9 Дэд бүтэц, үйлчилгээний хүртээмж
эрүүл мэнд:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
боловсрол:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
техник зөвлөгөө:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт (жишээ нь, ХАА-аас өөр):
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
зах зээл:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
эрчим хүчний хангамж:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
зам тээвэр:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
усан хангамж ба ариутгал:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
санхүүгийн үйлчилгээ:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
6. Үр нөлөө ба дүгнэлт
6.1 Технологийн талбайд үзүүлсэн нөлөө
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн үр нөлөө
Үйлдвэрлэл
тэжээл үйлдвэрлэл
тэжээлийн чанар
Усны хүртээмж ба чанар
мал услах усны хүрэлцээ
Нийгэм-соёлын үр нөлөө
хүнсний аюулгүй байдал/ өөрийн хэрэгцээг хангах
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Some herbs (and fruits (trees) in the future)
амралт, рекреацийн боломжууд
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
enhanced biodiversity, shade and shelter
ГТМ/ газрын доройтлын мэдлэг
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Through training/community participation
Экологийн үр нөлөө
Усны эргэлт/ илүүдэл
усны чанар
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Certain degree purification through infiltration in the sediment accumulation zone
ус хураах / цуглуулах
гадаргын урсац
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Effect on hydrology (distinctness of runoff peak)
гүний усны түвшин / уст давхарга
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Certain deep-infiltration
ууршилт
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
more open water ponding – but also deep-infiltration and beneficial use for vegetation (transpiration)
Хөрс
хөрсний чийг
хөрсөн бүрхэвч
хөрс алдагдах
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Side banks stabilized
хөрс хуримтлагдах
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
sediments trapped
хөрс хагарах/ хагсах
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
sediment crust increased in the ponding area – but better soil structure at the side banks (revegetation) – overall positive impact.
Биологийн олон янз байдал: ургамал, амьтан
Ургамалын бүрхэвч
газрын дээрхи / доорхи карбон
ургамлын төрөл, зүйл
амьтны төрөл, зүйл
ашигт төрөл зүйл
Уур амьсгал болон гамшгийн эрсдлийг бууруулах
үер усны нөлөө
хөрсний гулсалт/ чулуун нуранги
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Through side bank stabilization.
бичил уур амьсгал
6.2 Технологийн талбайн гадна үзүүлсэн үр нөлөө
голын адагт үерлэх
голын адагт лаг шавар хуримтлагдах
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
especially when combined with upland measure: reference VALLERANI
хөрш зэргэлдээ газарт учирах хохирол
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Less tributary channel development (connectivity of upland areas); less downstream siltation
нийтийн/хувийн хэвшлийн дэд бүтцэд учрах хохирол
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
less runoff peakiness and siltation
6.3 Технологийн уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт, цаг агаарын гамшигт үзэгдэлд өртөх байдал ба эмзэг байдал (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)
Уур амьсгалын аажим өөрчлөлт
Уур амьсгалын аажим өөрчлөлт
| Улирал | Өсөх эсвэл буурах | Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| жилийн дундаж температур | Өсөлт | дунд зэрэг | |
| жилийн дундаж хур тундас | Бууралт | сайн |
Уур амьсгалаас хамаарах аюул (гамшиг)
Цаг уурын гамшигт үзэгдэл
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| орон нутгийн аадар бороо | сайн |
Усзүйн гамшиг
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| шар усны үер | маш сайн |
Биологийн гамшиг
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| цар тахал | сайн |
Уур амьсгалд хамаарах бусад үр дагавар
Уур амьсгалд хамаарах бусад үр дагавар
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| ургалтын хугацаа нэмэгдэх | маш сайн |
6.4 Өртөг ба ашгийн шинжилгээ
Бий болгох зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
сөрөг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Арчилгаа/урсгал зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
сөрөг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
бага зэрэг эерэг
Тайлбар:
During the initial stage potential benefits through vegetation do not materialize; main effects are on water and sediment retention. Long-term, the technology fosters the rehabilitation nature-based retention functions (very limited long-term maintenance required).
6.5 Технологи нэвтрүүлэлт
- жишээ/ туршилт
Боломжтой бол, тоогоор илэрхийл (өрхийн тоо эсвэл бүрхэх талбай):
1
Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн хүмүүсээс хэд нь өөрийн хүчээр технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн бэ, өөрөөр хэлбэл гадны тусламж дэмжлэг авалгүйгээр?
- 0-10%
6.6 Дасан зохицох
Бий болсон өөрчлөлтөд зохицуулан технологийг өөрчилсөн үү?
Үгүй
6.7 Технологийн давуу тал/боломжууд
| Газар ашиглагчдын тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
| Gully side bank vegetation useable as (livestock) fodder source; some herbs (later fruit tree benefits) for human consumption. |
| Gully is stable and does not expand e.g. tributaries. Uplands remain connected and productive. |
| Ponded water for livestock watering (during the rainy season). |
| Shelter and shade through vegetation. |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
| Sediments from the uplands are trapped; relatively fertile soil remains in the watershed. |
| Increased local soil moisture and consequential vegetation quantity and bio-diversity enhancement; increase carbon storage and other ecosystem services such as pollination. |
| Smoothened watershed hydrology is beneficial for downstream agriculture – especially when applied in a watershed context with downstream flood irrigation (MARAB) |
| Protection of downstream infrastructure (flooding and sediments). |
6.8 Технологийн дутагдалтай/сул тал/аюул болон тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах арга зам
| Газар ашиглагч нарын тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| implementation costs | Incentives (e.g. governmental) for communities to implement SLM; regulations and enforcement on environmental management – especially connected with entitlements of natural resources facilitation |
| Tensions between upstream and downstream watershed users (watershed hydrology) – especially affected through wrong design and failure (e.g. gully breakage) | Community-based and holistic watershed management – the share of benefits and commitment for maintenance. |
| Additional fodder supply might attract other foreign herders (overgrazing) | Community-based and holistic watershed management – and protection. |
| Technical skills needed for implementation | Rural communities’ capacity building programs |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| Expert design and implementation support required | Governmental and environmental organizations in control of design and support to local communities (training). |
| Requires upland SLM | Integrated watershed management and empowerment of local communities to manage and facilitate – provision of support (e.g. government and/or international projects). |
| Increased vegetation in a fragile ecosystem can lead to local pressure | Integrated watershed management and empowerment of local communities – especially sustainable grazing plans |
| Risk of wrong lessons learned: large water harvesting in gully systems (dams) created by locals | Capacity development programs; regulations and enforcement on environmental management. |
7. Ном зүй ба холбоосууд
7.1 Мэдээлэл цуглуулсан арга/эх үүсвэр
- Хээрийн уулзалт, судалгаа
The number of field visit is 5.
- Газар ашиглагчтай хийсэн ярилцлага
The number of land users that were interviewed is 10.
- ГТМ-ийн мэргэжилтэн/шинжээчтэй хийсэн ярилцлага
The number of SLM experts who were interviewed is 5.
Мэдээллийг хэзээ (газар дээр нь) цуглуулсан бэ?
09/08/2020
7.2 Ном, хэвлэлийн ишлэл
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Steven, E. (2017). Report on Majiddya Watershed Rehabilitation Project - Gully Plugs Plan /August 2017.
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Strohmeier, S. (2017). Dimensioning of Marab in Majidyya.
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
SEA. 1974. Les ouvrages en gabions – techniques rurales en Afrique. Secretariat d’Etat aux Affaires Etrangeres, Republique Francaise, 20, rue Monsieur, 75007 Paris.
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
FAO. 1977. Guidelines for watershed management. FAO Conservation Guide 1. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Rome, 1977
Холбоос ба модулууд
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаахХолбоосууд
Холбоос байхгүй байна
Модулууд
Модуль байхгүй байна