MAPPING, MONITORING, AND MITIGATION OF LAND DEGRADATION IN THE SULTANATE OF OMAN [Omã]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Laila AlShmali
- Editor: –
- Revisores: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
MAPPING, MONITORING, AND MITIGATION OF LAND DEGRADATION IN THE SULTANATE OF OMAN
approaches_5972 - Omã
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da abordagem
Pessoa(s) capacitada(s)
Especialista em GST:
Al-Sareeria Thuraya
00968 24404762
thuraya.alsareeri@meca.gov.om
Environment Authority
Muscat, Oman
Omã
Especialista em GST:
Al-Saadi Saleh Naghmush
00968 24404750
saleh.alsaadi@meca.gov.om
Environment Authority
Muscat, Oman
Omã
researcher:
Al-Wardy Malik
00968 24141224
mwardy@squ.edu.om
Sultan Qaboos University
Muscat, Oman
Omã
Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/avaliação da Abordagem (se relevante)
Sultan Qaboos University (SQU) - Omã1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
15/09/2013
O compilador e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através do WOCAT:
Sim
2. Descrição da abordagem de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da abordagem
Mapping of land degradation in the Sultanate of Oman to identify areas with various degrees of degradation, and factors and processes causing degradation.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da abordagem
Descrição detalhada da abordagem:
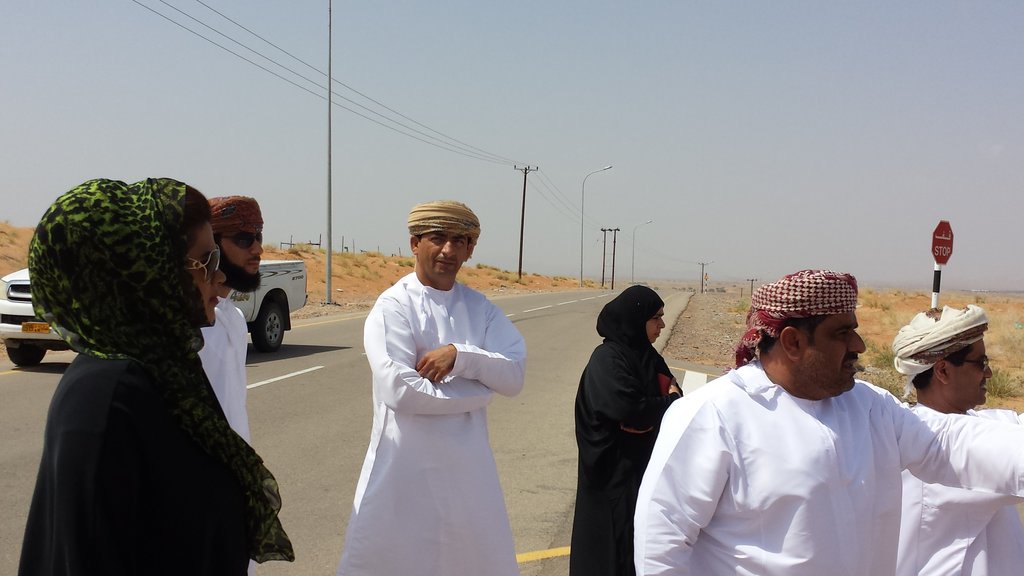
The Environment Authority has implemented land degradation mapping in the Sultanate of Oman in the Governorate of Dhofar, South and North Al Sharqiyah Governorates, and the Governorate of Al Dakhiliyah, in cooperation with Sultan Qaboos University, with the aim of identifying areas with various degrees of degradation and identifying the factors and processes causing degradation.
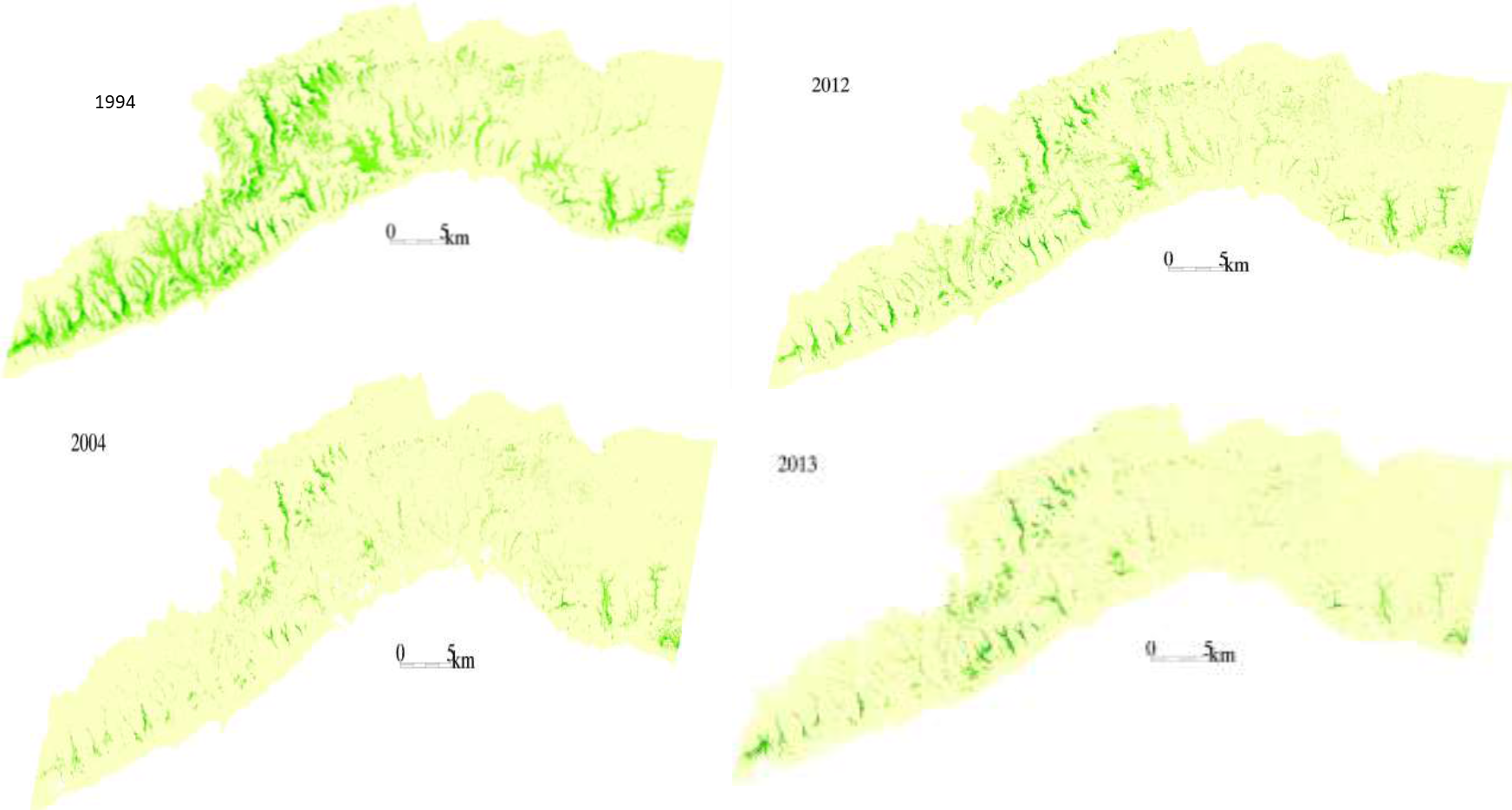
This investigation was based on high-resolution satellite imagery using NDVI as an Index of land degradation in the Dhofar Mountains and the invasion of mesquite (Prosopis juliflora.) in the plain of Salalah, as well as very high resolution aerial and satellite images of Jebal Al-Akhder derived from National Survey Authority. Precipitation data from two WMO stations were also utilized to test the link between precipitation and vegetation health. Vegetation was mapped to monitor changes and its health over time. In addition, a socio-economic survey in the Governorate of Dhofar was conducted, based on random sampling. The survey covered 6 different locations (Taqa, Taaqa farm, Zaik, Qiroon, Marbath, Al-Haqq and Taitam). The preliminary results clearly show that the study area has witnessed significant land use change between 1985 and 2013, marked by the emerging of a significant built-up area and water conservation infrastructure.
Spot images clearly show sharp changes in vegetation health through the years from 1994 to 2013. Vegetative vigour is lower in all years compared to 1994. Besides, the investigation shows a statistical relationship between rainfall and the status of the health of vegetation. Monsoon rainfall has an impact on the growth of vegetation. Around 2002-2003, the region suffered a major drought. Between 2012 and 2013, vegetative activity shows a decreasing trend. The analysis identified an area affected by the worst degree of land degradation. This area is situated in the southeastern of the Dhofar Mountains. In this area the process of land degradation is very active, with significant decrease in vegetation in 2013 compared to 2004. The mequite invasion in the Salalah Plain contributed to the degradation of natural vegetative cover in Dhofar Governorate. In nearly 30 years, the infested area almost quadrupled, indicating an average rate of expansion of 122,555m2 per year. The mesquite stands seem to have survived through the drought of 2002-2003.
The preliminary results of the survey clearly show that the mountains of Dhofar are under heavy anthropic pressure. The number of livestock is increasing and the native plant species are in great demand for cooking and heating.
Fortunately, the analysis identifies two areas, situated in the south-west of the study area, where vegetation has increased in vigor and density. The areas preserved from this process are usually inaccessible and far from human activities.
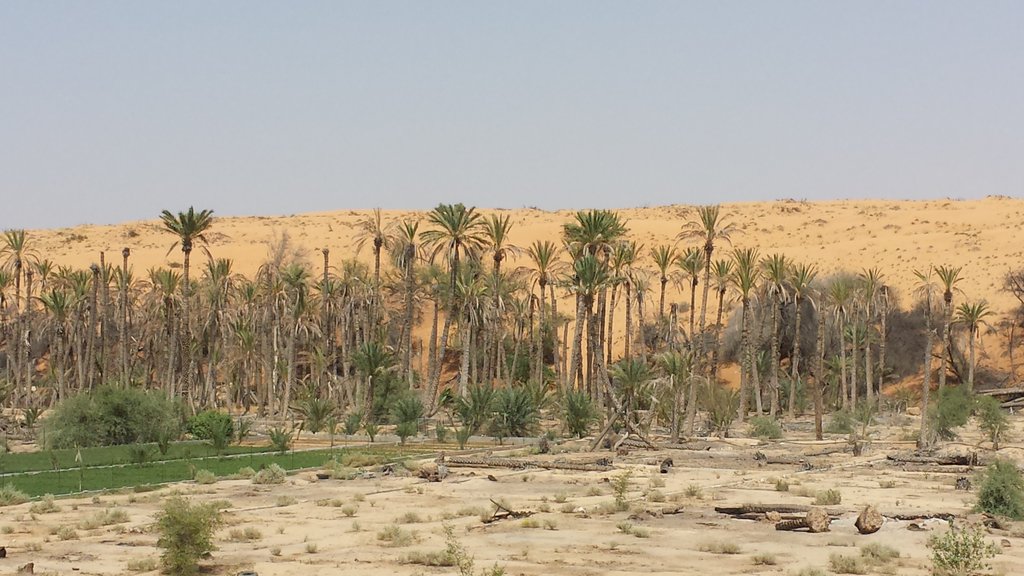
Vegetation cover change in Al-Jabal Al-Akhdar from 1985 to 2014 was analysed using very high resolution aerial and satellite images. Vegetation cover is also studied near settlements, dams, in wadis, and in agricultural areas. The change in total vegetation cover in the study area of Al-Jabal Al-Akhdar from 1985 to 2014 is very evident from the analysis of the data and maps produced.
Vegetation cover increased from 7.38 km2 during 1985 to 13.65 km2 in 2014. This change of vegetation cover was most noticeable in wadis and gullies where vegetation increased from 4.56 km2 during to 9.38 km2. One main factor that might be contributing to this increase of vegetation in wadis is the increase in the number of dams for storing surface water, as the number of dams increased from 7 in 1985 in the study area to 27 in 2014. Vegetation within and around 1 km of settlements in the study area increased from 2.09 km2 during 1985 to 5.45 km2 in 2014. In all other areas, that are distant from human activities, there is a considerable change in green vegetation cover between 1985 and 2014 where vegetation cover increased from 2.49 km2 in 1985 to 3.91 km2 in 2014. It is important to note here that vegetation cover density has a strong correlation with the amount of rainfall in Al-Jabal Al-Akhdar and there was a large difference in the annual rainfall between the two years, i.e. 1985 and 2014. The annual rainfall in 1985 was about 150mm for that particular year. The year 1984 was not much better where annual rainfall was lower than 200mm according to available records. The annual rainfall in 2013, the year preceding date of image in 2014, was 466mm, which is three times higher that that of 1985. Given the results of this study, there is a clear indication that the amount of rainfall plays a major role in defining the density of vegetation cover even if land degradation is taking place in very localized areas where there is pressure from grazing, urbanization, and tourism.
2.3 Fotos da abordagem
2.5 País/região/locais onde a abordagem foi aplicada
País:
Omã
Região/Estado/Província:
Governorate of Dhofar, North and South Al Sharqiyah Governorates and Governorate of Al Dakhiliyah
Especificação adicional de localização:
Governorate of Dhofar: Taqa, Taaqa farm, Zaik, Qiroon, Marbath, Al-Haqq and Taitam Governorate of Al Dakhiliyah: Al-Jabal Al-Akhdar
2.6 Datas de início e término da abordagem
Indique o ano de início:
2013
2.7 Tipo de abordagem
- Baseado em projeto/programa
2.8 Principais metas/objetivos da abordagem
1.Monitoring and survey of land degradation and areas vulnerable to degradation
2.Enhancing human abilities in land degradation issues
3.Identifying various degrees of degraded areas, and factors and processes causing degradation
4.Regular monitoring of degraded areas
2.9 Condição que propiciam ou inibem a implementação de tecnologia/tecnologias aplicada(s) segundo a abordagem
Normas e valores sociais/culturais/religiosos
- Propício
Cultural and religious values encourage the protection of land and planting of trees
Colaboração/coordenção de atores
- Propício
There is always a good collaboration between the government and academic/research institutions to determine the right approaches and technologies for better management practices
Quadro jurídico (posse de terra, direitos de uso da terra e da água)
- Inibitivo
In some regions land tenure is not defined which affects grazing activities in these regions making it difficult to implement any replanting or reforestation projects
3. Participação e papel das partes interessadas envolvidas
3.1 Partes interessadas envolvidas na abordagem e seus papéis
- Pesquisadores
Researchers from Sultan Qaboos University
Approach development, analysis, and survey
- Governo local
Municipalities, Authority departments, and Governor's offices
Field visits and survey, meeting community
- Governo nacional (planejadores, responsáveis pelas decisões)
Environment Authority
Funding, planning approach
3.2 Envolvimento do usuários de terra/comunidades locais nas diferentes fases da abordagem
| Envolvimento do usuários de terra/comunidades locais | Especifique quem estava envolvido e descreva as atividades | |
|---|---|---|
| Iniciação/motivação | Apoio externo | Governor's offices in respective regions played a major role in motivating community leaders to participate in the project |
| Implementação | Apoio externo | Regional directorates and Governor offices helped in organizing meetings with local communities to collect information about land use activities, including farming and grazing, in their respective villages |
3.3 Fluxograma (se disponível)
3.4 Decisão sobre a seleção de tecnologia/tecnologias de GST
Especifique quem decidiu sobre a seleção de tecnologia/tecnologias a serem implementadas:
- Políticos/líderes
Especifique em que base foram tomadas as decisões:
- Resultados de pesquisa
4. Suporte técnico, reforço das capacidades e gestão do conhecimento
4.1 Reforço das capacidades/formação
Foi oferecida formação aos usuários da terra/outras partes interessadas?
Sim
Especifique quem foi capacitado:
- Equipe de campo/consultores
Tipo de formação:
- Cursos
Assuntos abordados:
1.Understanding GIS and geographical approach to land degradation
2. Use of remote sensing techniques for data collection
3. Land degradation assessment in drylands
4.2 Serviço de consultoria
Os usuários de terra têm acesso a um serviço de consultoria?
Não
4.3 Fortalecimento da instituição (desenvolvimento organizacional)
As instituições foram fortalecidas ou estabelecidas através da abordagem?
- Sim, moderadamente
Especifique a que nível (níveis) as instituições foram fortalecidas ou estabelecidas:
- Nacional
Especifique o tipo de apoio:
- Reforço das capacidades/formação
4.4 Monitoramento e avaliação
Monitoramento e avaliação são partes da abordagem?
Sim
Caso afirmativo, esta documentação é destinada a ser utilizada para monitoramento e avaliação?
Não
4.5 Pesquisa
A pesquisa foi parte da abordagem?
Sim
Especifique os tópicos:
- Sociologia
- Ecologia
5. Financiamento e apoio material externo
5.1 Orçamento anual para o componente de GST da abordagem
Caso o orçamento exato seja desconhecido, indique a faixa:
- 100.000-1.000.000
5.2 Apoio financeiro/material concedido aos usuários da terra
Os usuários da terra receberam apoio financeiro/material para a implementação de tecnologia/tecnologias?
Não
5.4 Crédito
Foi concedido crédito segundo a abordagem para atividades de GST?
Não
5.5 Outros incentivos ou instrumentos
Foram utilizados outros incentivos ou instrumentos para promover a implementação das tecnologias de GST?
Não
6. Análise de impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos da abordagem
A abordagem concedeu autonomia aos usuários locais de terra, melhorou a participação das partes interessadas?
- Não
- Sim, pouco
- Sim, moderadamente
- Sim, significativamente
Stakeholders participated in collecting social data by visiting different towns and sitting with the community to explain the approach, define the problems, and evaluate solutions
A abordagem propiciou a tomada de decisão baseada em evidências?
- Não
- Sim, pouco
- Sim, moderadamente
- Sim, significativamente
Solutions and practices suggested resulted from extensive field work and image analysis
A abordagem mobilizou/melhorou o acesso aos recursos financeiros para implementação da GST?
- Não
- Sim, pouco
- Sim, moderadamente
- Sim, significativamente
Financial resources were mobilized and directed towards plantation of trees in degraded lands
A abordagem aprimorou o conhecimento e as capacidades de outras partes interessadas?
- Não
- Sim, pouco
- Sim, moderadamente
- Sim, significativamente
Training courses were developed for government staff to collect field and social data
A abordagem construiu/fortaleceu instituições, colaboração entre partes interessadas?
- Não
- Sim, pouco
- Sim, moderadamente
- Sim, significativamente
6.2 Principal motivação dos usuários da terra para implementar a GST
- Degradação do solo reduzida
- Consciência ambiental
- melhoria dos conhecimentos e aptidões de GST
6.3 Atividades de sustentabilidade de abordagem
Os usuários da terra podem manter o que foi implementado através da abordagem (sem apoio externo)?
- Incerto
6.4 Pontos fortes/vantagens da abordagem
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do compilador ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| 1-As the results show that the amount of rainfall plays a major role in defining the density of vegetation, water catchment techniques can be deployed during rainfall periods – especially during Dhofar monsoon characterized with white fog and light rains- such as fog harvesting, increasing recharge dams, using new irrigation techniques from dams for affected areas |
| 2-By mapping land degradation in the Sultanate, areas that need protective strategies and policies can be defined, to avoid the degradation of areas of similar features through the coordination with respective sectors including urban planning, tourism, and agriculture. |
| 3- As the analysis identifies areas where vegetation has increased in vigor and density, factors leading to that may be explored and studied in order to apply same factors in similar environments. |
6.5 Pontos fracos, desvantagens da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do compilador ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| 1-As the spread and type of vegetation and climatic conditions differs greatly from area to area in the Sultanate of Oman, different procedures and techniques need to be employed. | studying the general conditions and features of each area and applying different procedures and techniques based on specific characteristics. |
| 2-Analysis of vegetation change using satellite images in terrain characterized by deep slopes and deep valleys in some areas in the Sultanate is very difficult. | using very high resolution remotely sensed images |
| 3-High resolution remotely sensed images are sometimes unavailable for past periods, which hinder studying vegetation change in this region where using satellite is difficult as well. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- visitas de campo, pesquisas de campo
- entrevistas com usuários de terras
More than 500 questionnaires
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos