Community Land Use Planning in Arkhiloskalo [Geórgia]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Hanns Kirchmeir
- Editor: Kety Tsereteli
- Revisor: Rima Mekdaschi Studer
technologies_5762 - Geórgia
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Especialista em GST:
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Applying Landscape and Sustainable Land Management (L-SLM) for mitigating land degradation and contributing to poverty reduction in rural area (L-SLM Project)Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Regional Environmental Centre for the Caucasus (REC Caucasus) - Geórgia1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O compilador e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através do WOCAT:
Sim
1.4 Declaração de sustentabilidade da tecnologia descrita
A tecnologia descrita aqui é problemática em relação a degradação da terra de forma que não pode ser declarada uma tecnologia de gestão sustentável de terra?
Não
1.5 Referência ao(s) questionário(s) sobre abordagens GST (documentado(s) usando WOCAT)

Land Degradation Neutrality Transformative Projects and Programmes (LDN-TPP) … [Geórgia]
In the framework of the project ‘Generating Economic and Environmental Benefits from Sustainable Land Management for Vulnerable Rural Communities of Georgia’, Land Degradation Neutrality Transformative Projects and Programmes (LDN-TPP) were developed to implement the LDN targets at municipal level. The approach defines the process to break down global and international …
- Compilador/a: Daniel Zollner
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
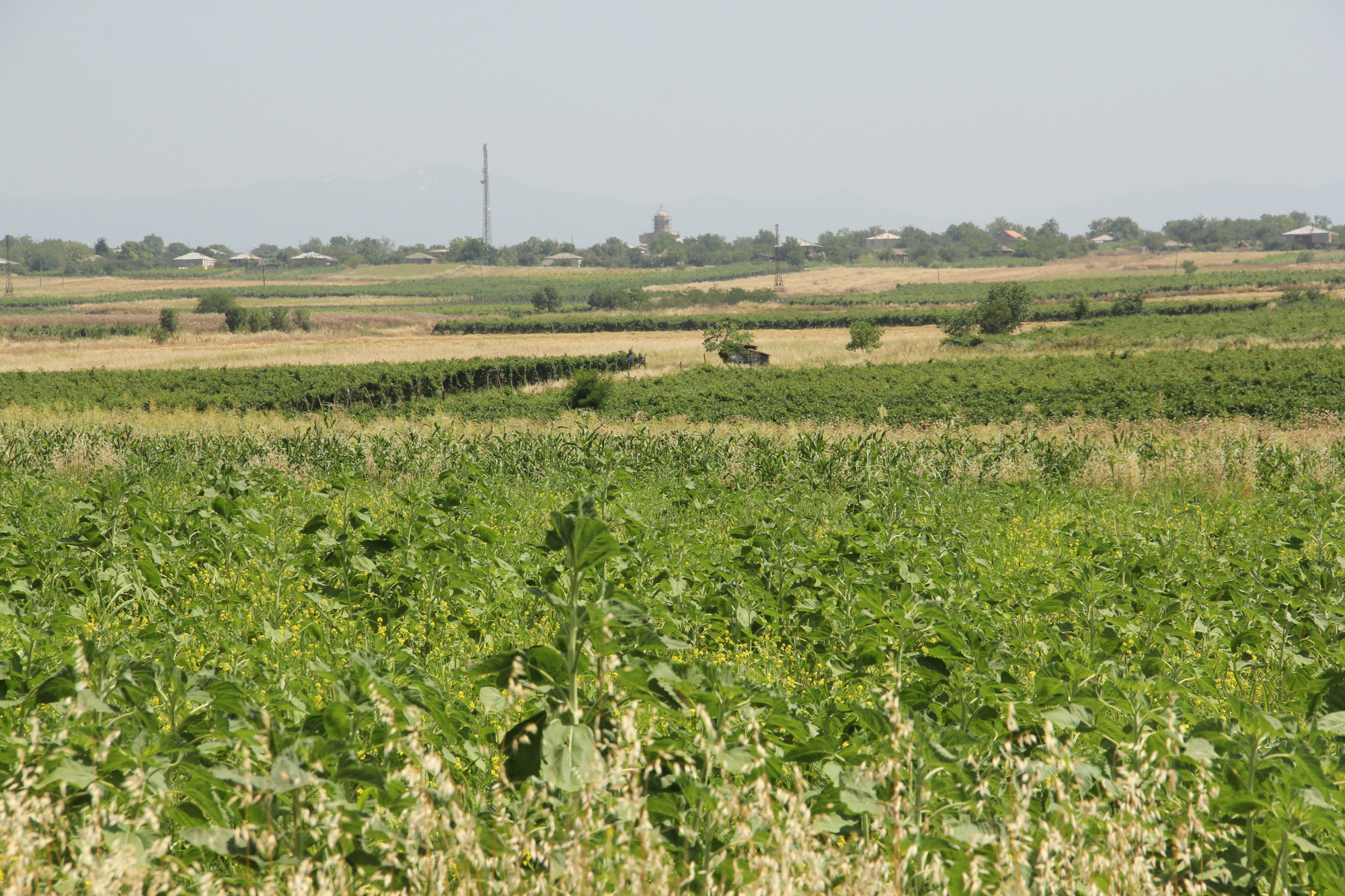
Unsustainable land use practices, such as deforestation, overgrazing and improper agricultural management systems are triggering the loss and degradation of valuable land resources in Georgia. Land use planning is one of the measures among others to contribute to support the integration of good Landscape and Sustainable Land Management (L-SLM) principles and practices into national policy and institutional framework to ensure the adoption of economically viable practices by rural communities. This technology is demonstrated in an application in Arkhiloskalo community in Eastern Georgia.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
The globally ongoing degradation of land resources is threatening our food security and functioning ecosystem services. Therefore, restoration of degraded land as defined by the Sustainable Development Goal (SDG 15.3) has become a strategic objective of the UNCCD. To achieve Land Degradation Neutrality (LDN), action on the national level is needed. Georgia is one of the 113 countries (as of Sept. 2017) willing to take part in the Target Setting Program (TSP).
One of the major problems which Georgia is facing today is an absence of a comprehensive and integrated approach in the land management sector. In addition, an irrelevant legal framework sometimes leads to additional “conflicts” with the evolved national strategy and policy packages.
The land-use planning in the village of Arkhiloskalo, Dedoplistskaro Municipality is one of the pilot activities linked to LDN (Land Degradation Neutrality). The project financed by Global Environment Facility (GEF) / UN Environment Programm (UNEP) was implemented by local partner REC Caucasus (The Regional Environmental Centre for the Caucasus) through E.C.O. Institute of Ecology (Austria).
The land-use plan documents the status quo of the current land use. It is a baseline that can be used to steer and monitor future developments. The land-use plan is based on field assessments made in summer 2019 and builds a baseline for future assessments/monitoring. The land-use plan on the village level helps to break down national LDN targets to the local level. The plan and the development of land-use scenarios help to anticipate the future gains and losses of land resources and reflect the national LDN-target on the local level. Local stakeholders can identify areas of degradation risk and areas which can be rehabilitated. The Arkhiloskalo land-use plan contributes to sustainable land use by recognizing the current situation of land use and its spatial distribution as well as identifying the strength and weaknesses of the current situation.
Methodology:
Mapping for Arkhiloskalo land use plan: The mapping result is a detailed documentation of size and spatial distribution of land cover categories. Change in land cover is an important indicator to monitor the loss and gains of land resources according to the LDN monitoring concept.
For the mapping of the settlements, arable land and gardens, maps from Google Earth and digital cadastre of parcels were used. In the field maps, each polygon has an assigned Map-ID number, which is unique for each village. Polygons with the same land use category and land-use intensity can have the same Map-ID. Next to the drawing of the polygon on the map, in a field form each polygon is described by:
- Map-ID;
- Current Land use category;
- Current Land-use intensity;
- Remark (a specification of the polygon if needed).
Classifications of land use categories: The land-use classification is based on the CLC - Corine Land Classification System (The CORINE Land Cover is a vector map with a scale of 1:10 000, a minimum cartographic unit (MCU) of 100 m². It maps homogeneous landscape patterns). The Corine Land Classification system classifies urban fabric, mine, dump and construction sites, arable land, permanent crops, pastures, forests, shrubs and herbaceous vegetation associations, Open spaces with little or no vegetation, inland wetlands and waters.
The pastureland was differentiated into different productivity classes. In the field three classes of vegetation cover and species composition: low, medium, and high productivity were assessed.
For the mapping in Arkhiloskalo the following land use categories were selected: Settlements and human infrastructure (Code from the Corine Land Classification system – e.g. SHR, name – e.g. Houses); Forests and shrub-land; Agricultural managed land; Natural and semi-natural habitats.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Geórgia
Região/Estado/Província:
Kakheti
Especificação adicional de localização:
The Village of Arkhiloskalo is locted in the Municipality of Dedoplitskaro.
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Se a Tecnologia estiver uniformemente distribuída por uma área, especifique a área coberta (em km2):
49,7
Se a área precisa não for conhecida, indicar a área aproximada coberta:
- 10-100 km2
Comentários:
The village Arkhiloskalo covers an area of 4,970 ha. The area ranges from the lower section in the North 250 m (Alasani river valley) up to 730 m at the ridge and then falls again to the South in the Shiraki Valley to 600 m.
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Indique o ano de implementação:
2018
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
The land-use plan approach is one of the measures among others to contribute to support the integration of good Landscape and Sustainable Land Management (L-SLM) principles and practices into national policy and institutional framework to ensure the adoption of economically viable practices by rural communities. This was a GEF-funded project.
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Melhora a produção
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
- Preservar/melhorar a biodiversidade
- Adaptar a mudanças climáticas/extremos e seus impactos
- Criar impacto econômico benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Sim
Especificar o uso misto da terra (culturas/ pastoreio/ árvores):
- Agrofloresta

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
- Cultura de árvores e arbustos
Cultivo anual - Especificar culturas:
- cereais - trigo (primavera)
- cereais - trigo (inverno)
- culturas oleaginosas - girassol, colza, outros
Cultivo de árvores e arbustos - Especificar culturas:
- frutas, outros
- uvas
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
Especifique:
summer
O cultivo entre culturas é praticado?
Não
O rodízio de culturas é praticado?
Não

Pastagem
Pastagem extensiva:
- Fazenda pecuária
Pastagem intensiva/produção de forragem:
- Semiestabulação/sem pastagem
- Pastos melhorados
Tipo de animal:
- gado - leite e carne bovina (por exemplo, zebu)
É praticado o manejo integrado de culturas e pecuária?
Não
Espécie:
gado - leite e carne bovina (por exemplo, zebu)
Contagem:
982

Assentamentos, infraestrutura
- Assentamentos, edificações
- Tráfego: estradas, ferrovias
Comentários:
All form of land cover and land use forms have been mapped.
3.3 O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
- Não (Continuar com a pergunta 3.4)
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Quebra-vento/cerca de árvores
- sistema rotativo (rotação de culturas, pousios, cultivo itinerante)
- Gestão de resíduos/gestão de águas residuais
- Land use planning
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas de gestão
- M2: Mudança de gestão/nível de intensidade
- M7: Outros
Comentários:
The land use planning started with mapping of current land use and included stakeholders input on strength and weaknesses. Based on this, development scenarios have been developed to change current land use approaches to a more sustainable way (e.g. restoration of windbreaks, crop rotation etc.)
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pelo vento
- Et: Perda do solo superficial
Comentários:
The loss of windbreaks caused an increased exposure of topsoil to wind erosion on fields with annual crops. The land use plan helps to quantify the current state of the windbreaks and underlines their functional importance.
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
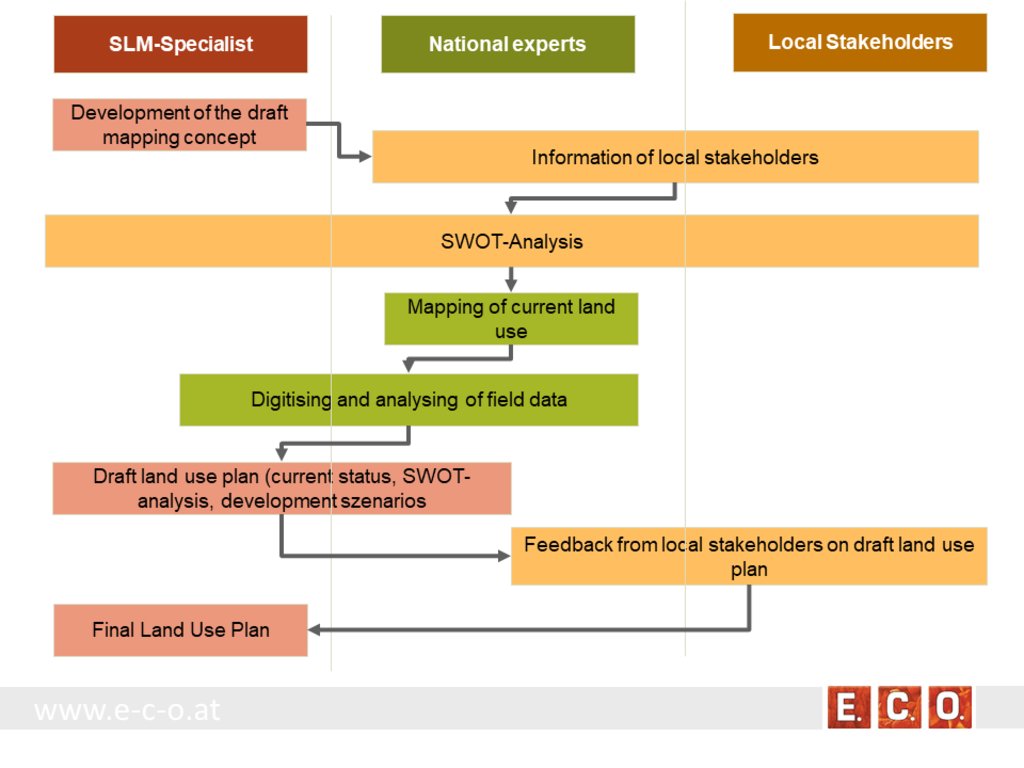
Key stages of implementation:
The land-use planning in the village of Arkhiloskalo, Dedoplistskaro Municipality is one of the pilot activities linked to LDN.
Together with the local stakeholders, a land-use plan has been worked out. The procedure of defining a spatial development plan for a municipality goes along three stages:
• Stage 1: Gather background information & implement pre-design studies and development of a mapping concept
• Stage 2: Information of local stakeholders on this activity and implementation of an SWOT analysis (Strength, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) related to the land use of the village
• Stage 3: Mapping and analyzing the current land use
• Stage 4: Preparation of a draft land use plan
• Stage 5: Reflection of the draft land use plan with local stakeholders
• Stage 6: Preparation of the final land use plan
Autor:
Hanns Kirchmeir
Data:
16/01/2020
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
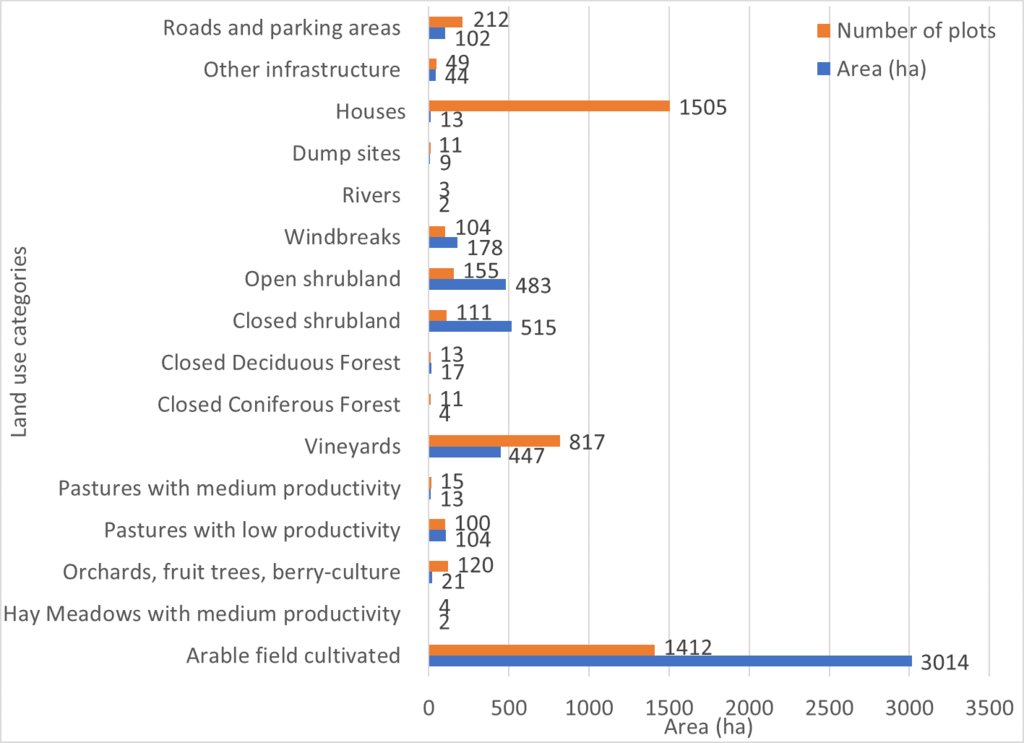
Absolute area sizes. The largest land use category is arable land (3,014 ha) followed by closed and open shrubland (515 ha and 483 ha, respectively). Vineyards cover a total of 447 ha whereas windbreaks cover 178 ha. Pastures with low productivity (104 ha) and roads and parking areas (102 ha) use almost the same amount of land. Other infrastructure covers 44 ha of land. Orchards, fruit trees and berry-culture use 21 ha of land. Closed deciduous forest (17 ha) covers only a few more hectares than pastures (13 ha). Houses are the most common plot category in Arkhiloskalo but use only around 13 ha of land which puts them on the same land-use level as pastures. Dumpsites (9 ha) use more than twice the area of closed coniferous forest (4 ha). Hay meadows and rivers cover around 2 ha of the area.
Autor:
Hanns Kirchmeir
Data:
20/11/2019
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
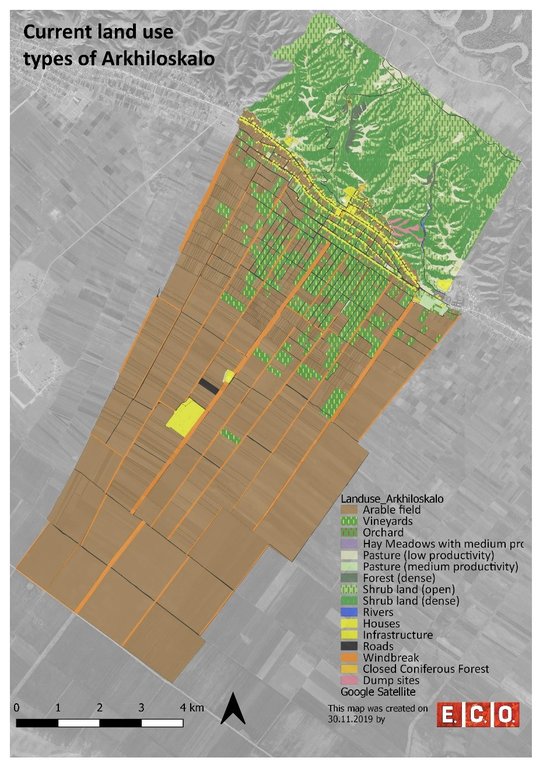
Map of current land-use categories in Arkhiloskalo. The land-use classification in this approach is based on the Corine Land Classification System. It was split into sub-categories where needed to meet the needs of local land use practices.
Autor:
Hanns Kirchmeir
Data:
13/11/2019
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
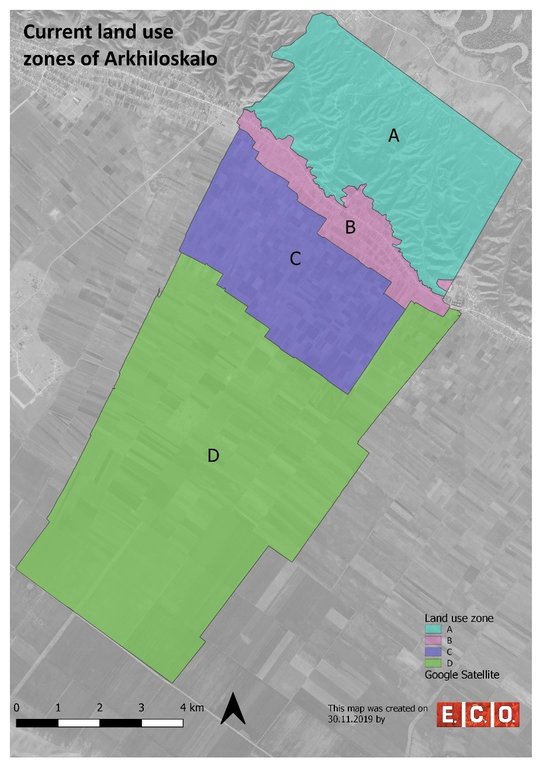
Based on the different land use, 4 different zones have been separated:
•Zone A: Steep North Slope
•Zone B. Settlement Area
•Zone C: Zone of perennial Crops
•Zone D: Zone of annual Crops
Autor:
Hanns Kirchmeir
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique como custos e entradas foram calculados:
- por área de tecnologia
Indique o tamanho e a unidade de área:
50 km²
Especifique a moeda utilizada para os cálculos de custo:
- USD
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
national expert 100 USD
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Gather background information & implement pre-design studies and development of a mapping concept | Winter/spring |
| 2. | Information of local stakeholders on this activity and implementation of an SWOT analysis (Strength, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) related to the land use of the village | Spring |
| 3. | Mapping and analyzing the current land use | Summer |
| 4. | Preparation of a draft land use plan | Autumn/Winter |
| 5. | Reflection of the draft land use plan with local stakeholders | Autumn/Winter |
| 6. | Preparation of the final land use plan | Autumn/Winter |
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
Se você não conseguir discriminar os custos na tabela acima, forneça uma estimativa dos custos totais para estabelecer a Tecnologia:
15000,0
Se o usuário da terra arca com menos que 100% dos custos, indique quem cobre os custos remanescentes:
REC-Caucasus, GEF-funded Project
Comentários:
The budget is $ 15 000 / per year. This amount includes the salaries of following expert, such as: National expert on SLM, National expert on LUP, International expert on SLM, International expert on LUP, Botanist, GIS expert. Also the above budget includes travels and missions in three municipalities, workshops in Akhmeta and Dedoplistskaro municipalities, workshops and public hearings in selected local communities (Arkhiloskalo and Shenako),
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
The field work of mapping and analysis of results took a lot of time as well as the stakeholder meetings.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
The driest month is January, with 25 mm of rainfall. The greatest amount of precipitation occurs in June, with an average of 108 mm. The difference in precipitation between the driest month and the wettest month is 83 mm.
Indique o nome da estação meteorológica de referência considerada:
Dedoplistskaro Met. Station
Zona agroclimática
- Semiárido
The climate is warm and temperate in Dedoplistskaro. The average annual temperature in Dedoplistskaro is 11.3 °C. The warmest month of the year is July, with an average temperature of 22.7 °C. The lowest average temperatures in the year occur in January, when it is around 0.1 °C.
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Indique se a tecnologia é aplicada especificamente em:
- Não relevante
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
The pastures are located on steep hill slope to the north, while the village and arable lands are located on the gently south facing terrace.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Textura do solo (>20 cm abaixo da superfície):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Alto (>3%)
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
5-50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Precário/nenhum
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável precária (tratamento necessário)
A qualidade da água refere-se a:
águas subterrâneas
A salinidade da água é um problema?
Não
Ocorre inundação da área?
Não
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Alto
Diversidade de habitat:
- Alto
Comentários e outras especificações sobre biodiversidade:
Especially the semi-natural landscapes of the slopes to the north are of high habitat and species diversity.
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Sedentário ou nômade:
- Sedentário
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- Menos de 10% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Pobre
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Nível de mecanização:
- Mecanizado/motorizado
Gênero:
- Homens
Idade dos usuários da terra:
- meia-idade
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
The village is very remote. Driving distance to the municipality is about 1h on bad roads.
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Média escala
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Comunitário/rural
- Indivíduo, intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Acesso livre (não organizado)
- Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água:
- Comunitário (organizado)
Os direitos de uso da terra são baseados em um sistema jurídico tradicional?
Sim
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
Effects will be visible based on the implementation of selected development scenario provided by Land use plan.
Diversidade de produtos
Comentários/especificar:
Effects will be visible based on the implementation of selected development scenario provided by Land use plan.
Renda e custos
Diversidade de fontes de rendimento
Comentários/especificar:
Effects will be visible based on the implementation of selected development scenario provided by Land use plan.
Impactos socioculturais
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Comentários/especificar:
Improvements by training and workshops, awareness raising.
Impactos ecológicos
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Cobertura vegetal
Comentários/especificar:
Reduced grazing in zone A (north slope) will increase the vegetation cover. Effects will be visible based on the implementation of selected development scenario provided by Land use plan.
Biomassa/carbono acima do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Reduced grazing in zone A (north slope) will increase the cover of shrubs and trees which will lead to increase of biomass. Effects will be visible based on the implementation of selected development scenario provided by Land use plan.
Diversidade animal
Comentários/especificar:
Effects will be visible based on the implementation of selected development scenario provided by Land use plan.
Diversidade de habitat
Comentários/especificar:
Diversification of land use and restoration of windbreaks will increase habitat diversity. Effects will be visible based on the implementation of selected development scenario provided by Land use plan.
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Velocidade do vento
Comentários/especificar:
Improvement of windbreaks will reduce wind speed and topoil erosion. Effects will be visible based on the implementation of selected development scenario provided by Land use plan.
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Poluição de água subterrânea/rio
Comentários/especificar:
Removal of uncontrolled dump sites will reduce groundwater and river pollution especially in the Alasani floodplain north of the community.
Sedimentos transportados pelo vento
Comentários/especificar:
The rehabilitation of windbreaks will have a positive impact on neighboring fields.
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Comentários:
The technology of land use planning is not sensitive to climate change but is an appropriate technology to adapt land use to future anticipated climate changes.
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
neutro/balanceado
Retornos a longo prazo:
neutro/balanceado
Comentários:
The land use planning process is an investment in future developments. Return of investment can be expected in oncoming years. The mapping result is a detailed documentation of size and spatial distribution land cover categories. Change in land cover is an important indicator to monitor the loss and gains according to the LDN monitoring concept. The land-use plan is based on field assessments made in summer 2019 and built a baseline for future change assessments as it includes data on land-use intensity which will enable to consider change in time dynamics and to monitor changes on the ground.
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- casos isolados/experimental
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
It was implemented as show case for one community
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 0-10%
6.6 Adaptação
A tecnologia foi recentemente modificada para adaptar-se as condições variáveis?
Não
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| The majority of the land users in village Arkhiloskalo have been using the same land and natural resources through decades and have good understanding of the natural conditions and climate change perspectives of the target area. The land use plan, the scenario development and the knowledge exchange in the workshops are have been considered as advantage for awareness raising, joint decision making and to start a positive change in short-term period. |
| The successful land-use system with improved environment conditions and benefit to the local farmers can lead to be a perfect example for the whole municipality of Dedoplistskaro as most part of its territory is agricultural land in semi-arid environment facing some rapid and significant challenges caused by climate change. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do compilador ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| The land use plan will help to optimize the management and to eliminate present challenges in the 4 separate zones and promote improved sustainable land- use, land-management practices like crop rotation and re-establishment of windbreaks. |
| The land-use plan helps to identify the strength, opportunities, weaknesses and threats and contribute to sustainable land-use and its management. E.g.: in the Zone A, Steep North Slope there is a high risk, that the waste in the dumpsites will be washed down in an uncontrolled manner into the natural and semi-natural habitats of the slope. The waste is partly burned and the wash out of toxic solute can harm nature and ground water. |
| Application of the technology helps to optimize management measures, which will reduce costs and labour forces, e.g., by increasing productivity of land and productivity of vineyards in the Zone C: zone of perennial crops. |
| The land-use map integrates climate mitigation. E.g. it helps to plan the re-establishment of the windbreaks, which significantly contributes to the reduction of wind erosion in the Zone D: Zone of annual crops. |
| The terrestrial evaluation of the current land use can also serve to evaluate remote sensing technologies for semi-automatic classification of land cover categories. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Lack of dialogue and trust could be one of the risks to succeed with the introduction of advanced methods of sustainable land management. | The proposed sustainable land-use practices and pilot activities should be planned in a way to have results on the ground in a short-term period to keep local farmers motivated. |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do compilador ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Risks: Land use plan Interest of farmers, guesthouse providers and local residents are conflicting. | This can be limited by good facilitation of focus group discussions between different stakeholder groups. |
| Local actors (farmers, guest house providers ...) are not interested in participating in the joint land-use planning process. | It will need a well-coordinated communication design to include all the local stakeholders in the process of practical and theoretical introduction to the principles of sustainable land-use. The communication should emphasize potential economic benefits to the local households together with advantages of the sustainability. This can be a key factor to get most of the local stakeholders engaged with the proposed sustainable land-use practices. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- visitas de campo, pesquisas de campo
2 days of joint field visit of the project team, 2 weeks of field-mapping of the national expert.
- entrevistas com usuários de terras
About 44 participants in workshops and 12 people interviewed.
- entrevistas com especialistas em GST
2 specialists
- compilação de relatórios e outra documentação existente
1 international expert and 3 national experts have been conducted for the feedback on the report.
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
12/08/2018
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Pilot project on land degradation neutrality in Georgia: Final Report.2017.Huber, M., Joseph, A., Kirchmeir, H., Ghambashidze, G.
Disponível de onde? Custos?
https://e-c-o.at/files/publications/downloads/D00813_ECO_policy_brief_LDN_Georgia_171025.pdf
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Applying Landscape and Sustainable Land Management (L-SLM) for mitigating land degradation and contributing to poverty reduction in rural areas: Final report. 2017. Kirchmeir, H., Joseph, A., Huber, M.
Disponível de onde? Custos?
Request at RECC Caucasus
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
limatologies at high resolution for the earth’s land surface areas. Sci. Data 4:170122 doi: 10.1038/sdata.2017. Karger, D. N. Conrad, O., Böhner, J., Kawohl, T., Kreft, H., Soria-Auza, R.W., Zimmermann, N.E., Linder H.P. & Kessler M.
Disponível de onde? Custos?
https://www.nature.com/articles/sdata2017122
7.4 Comentários gerais
It was not easy to consider the land use planning either to be a technology or an approach. Finally, we submitted as an approach.
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks

Land Degradation Neutrality Transformative Projects and Programmes (LDN-TPP) … [Geórgia]
In the framework of the project ‘Generating Economic and Environmental Benefits from Sustainable Land Management for Vulnerable Rural Communities of Georgia’, Land Degradation Neutrality Transformative Projects and Programmes (LDN-TPP) were developed to implement the LDN targets at municipal level. The approach defines the process to break down global and international …
- Compilador/a: Daniel Zollner
Módulos
Não há módulos