Communal grazing management [แอฟริกาใต้]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Anja Jansen van Vuuren
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Using benchmarks as demonstration of NRM strategies. Camp system vs. Open system.
technologies_1382 - แอฟริกาใต้
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Potchefstroom Universiteit vir CHO (Potchefstroom Universiteit vir CHO) - แอฟริกาใต้ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Department of Agriculture of Zambia (Department of Agriculture) - แซมเบีย1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.5 Reference to Questionnaire(s) on SLM Approaches (documented using WOCAT)

Communal stakeholders [แอฟริกาใต้]
Government funded project aimed at rangeland management to enhance natural recourse management. The community being the key stake holders.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Anja Jansen van Vuuren
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
Rangeland management of communal grazing land, to improve grazing capacity by applying rotation.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
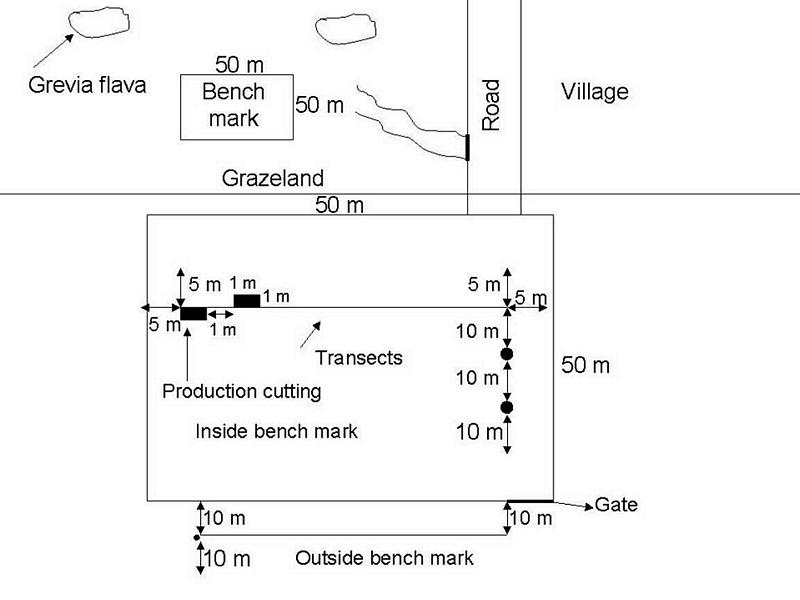
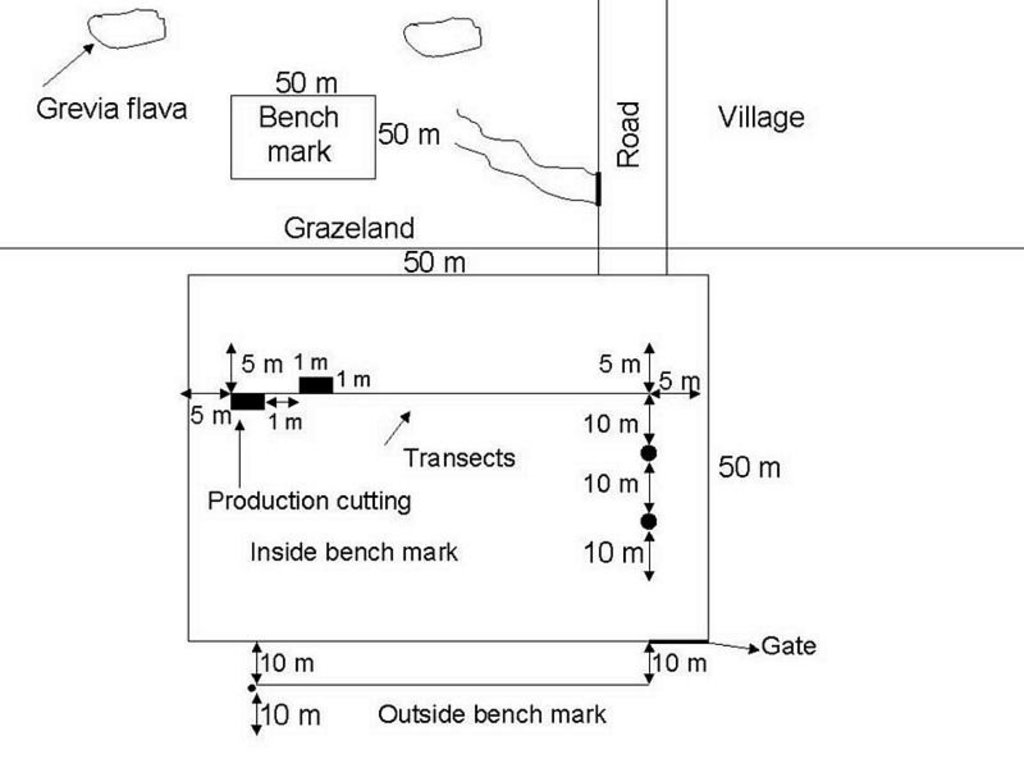
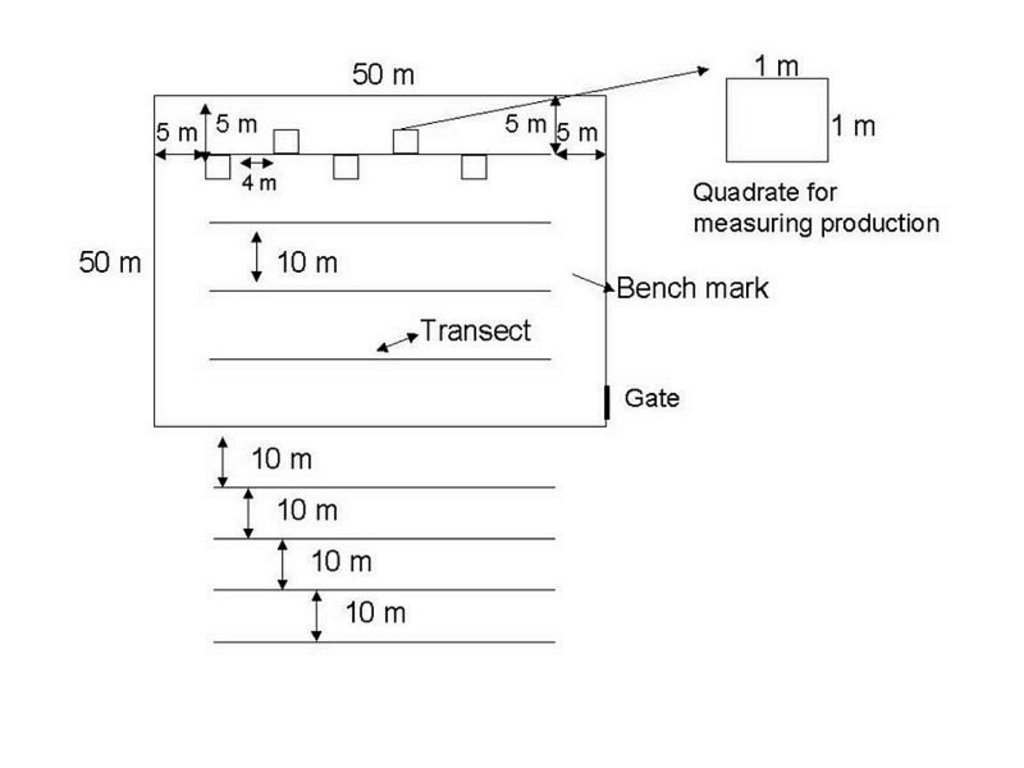
Benchmarks were identified and monitored to see how the production and vegetation would change if proper management was applied to a specific area. The benchmarks will only be grazed in the winter and rested in summer. The benchmarks were constructed with goat-proof fencing. Benchmarks will illustrate how grazing land can improve with the right management system.
Monitoring of vegetation is done twice a year.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
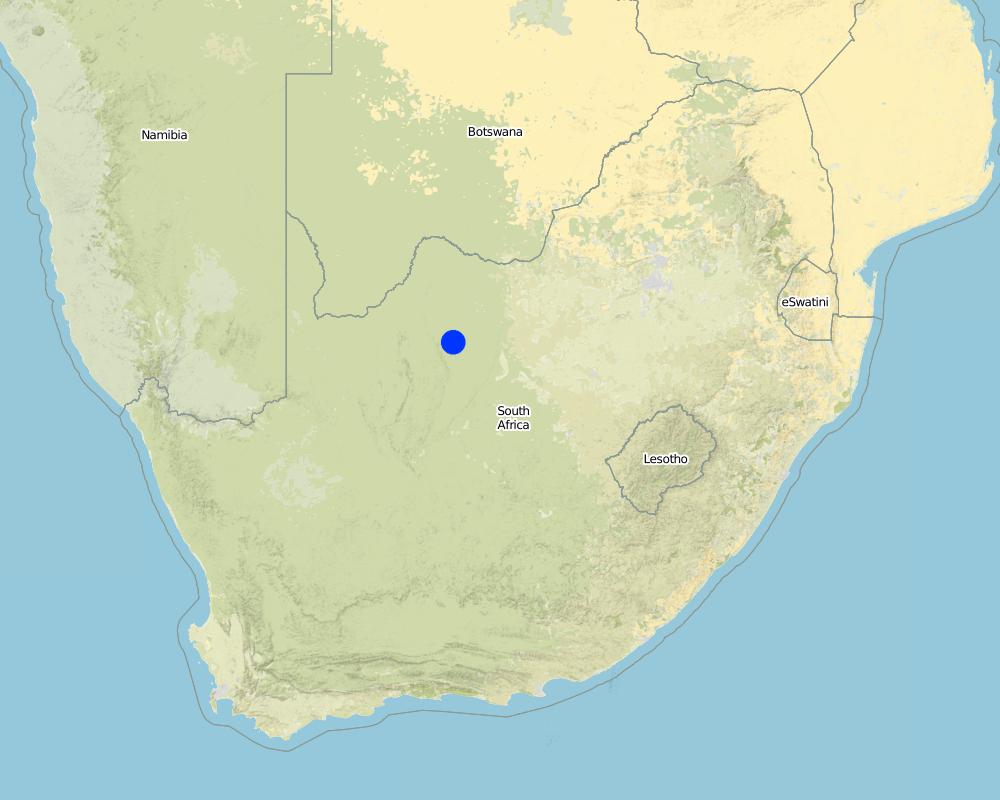
แอฟริกาใต้
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
North West Province
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Kudumane
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
If the Technology is evenly spread over an area, specify area covered (in km2):
1.0
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- 1-10 ตร.กม.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 1 km2.
Settlement situated 30 km from Kuruman. Lots of sheep and goats. Also cattle, donkeys and horses. Communal grazing.
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
The need to improve grazing lands.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- Monitoring SLM Technology
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
Extensive grazing:
- กึ่งโนแมนดิซึ่มหรือแพสโตแรลลิซึ่ม (Semi-nomadism/pastoralism)
Animal type:
- goats
- cattle
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main animal species and products: Communal grazing (free roaming goats)
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Over grazing, loss of palatable species and thus nutrients for cattle.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Reduced animal performance.
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: Communal grazing (free roaming goats)
Grazingland comments: Large community owned livestock herds.
Type of grazing system comments: Large community owned livestock herds.
Number of growing seasons per year: 1
Longest growing period in days: 210; Longest growing period from month to month: Oct - Apr
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การปิดล้อมพื้นที่ (หยุดการใช้ประโยชน์ สนับสนุนการฟื้นฟู)
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยการจัดการ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main measures: management measures
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน
- Wg (Gully erosion): การกัดกร่อนแบบร่องธารหรือการทำให้เกิดร่องน้ำเซาะ

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cn (Fertility decline): ความอุดมสมบูรณ์และปริมาณอินทรียวัตถุในดินถูกทำให้ลดลงไป (ไม่ได้เกิดจากสาเหตุการกัดกร่อน)

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านกายภาพ
- Pc (Compaction): การอัดแน่น

การเสื่อมโทรมของน้ำ
- Ha (Aridification): การเกิดความแห้งแล้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Main causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, overgrazing, droughts, inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (Lack of knowledge)
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
Technology
Location: Maketlele. North West Province
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, improvement of ground cover, increase of surface roughness, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, reduction in wind speed, increase in soil fertility, improvement of soil structure
Secondary technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, water spreading, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Change of land use type: Area divided into camps.
Layout change according to natural and human environment: Camps, benchmarks, fences constructed.
Other type of management: Rotational grazing.
ผู้เขียน:
Anja Jansen van Vuuren
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ระบุสกุลเงินที่ใช้คำนวณค่าใช้จ่าย:
- USD
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
-0.8
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
3.60
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Area divided into camps. | 6 months |
| 2. | Identification and construction of benchmarks. | 1 month |
| 3. | Initial survey. | 1 week |
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Constructing benchmarks | persons/day/ha | 133.0 | 3.2 | 425.6 | |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Fencing material | ha | 1.0 | 914.64 | 914.64 | |
| อื่น ๆ | Transport (10-7km/l) | ha | 1.0 | 67.07 | 67.07 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 1407.31 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | -1759.14 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Further surveys. | 2 weeks / twice a year |
| 2. | Data analysis. | 3 months / after each survey |
| 3. | Establishing a gradient. | 2 weeks / once |
| 4. | Maintenance of fencing. | continued / when necessary |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Maintenance and monitoring | persons/day/ha | 10.0 | 3.2 | 32.0 | |
| อื่น ๆ | Paper bags | ha | 1.0 | 8.05 | 8.05 | |
| อื่น ๆ | Data sheet | ha | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | |
| อื่น ๆ | Transport (10-7km/l) | ha | 1.0 | 129.27 | 129.27 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 170.32 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | -212.9 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Fencing of benchmark, conducting surveys and soil analysis.
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Cost of transport depends on the fuel price. The sites are situated far from accommodation. Maintenance of fences and soil analysis.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
Altitudinal zone: 1337 m a.s.l.
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ต่ำ (<1%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil depth on average: Sandy
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage / infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is low
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- เพื่อการยังชีพ (หาเลี้ยงตนเอง)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- > 50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
20% of the land users are rich.
55% of the land users are average wealthy.
25% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: State pension, mine workers, family working in the city.
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- เป็นแบบชุมชนหรือหมู่บ้าน
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Inside benchmark
คุณภาพพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Inside benchmark
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ภาระงาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Nobody wanted to help with surveys
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
การสูญเสียดิน
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยาอื่น ๆ
soil fertility
biodiversity
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านลบเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- > 50%
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
100 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Will increase with awareness adoption of technology.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
|
Improved rangelands. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Better cattle. |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
|
The committed ADC-manager How can they be sustained / enhanced? Meetings |
| The maintenance of benchmarks as examples. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Cattle must be reduced | Improve rangeland - larger carrying capacity |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Community participation | Give more information |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์

Communal stakeholders [แอฟริกาใต้]
Government funded project aimed at rangeland management to enhance natural recourse management. The community being the key stake holders.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Anja Jansen van Vuuren
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล