Check dams from stem cuttings [นิการากัว]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Mathias Gurtner
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Deborah Niggli, Alexandra Gavilano
Diques de postes prendedizos (Spanish)
technologies_1719 - นิการากัว
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Rodriguez Roger
PASOLAC
นิการากัว
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Mongalo Reinerio
Sociación Tierra y Vida (AT&V)
นิการากัว
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
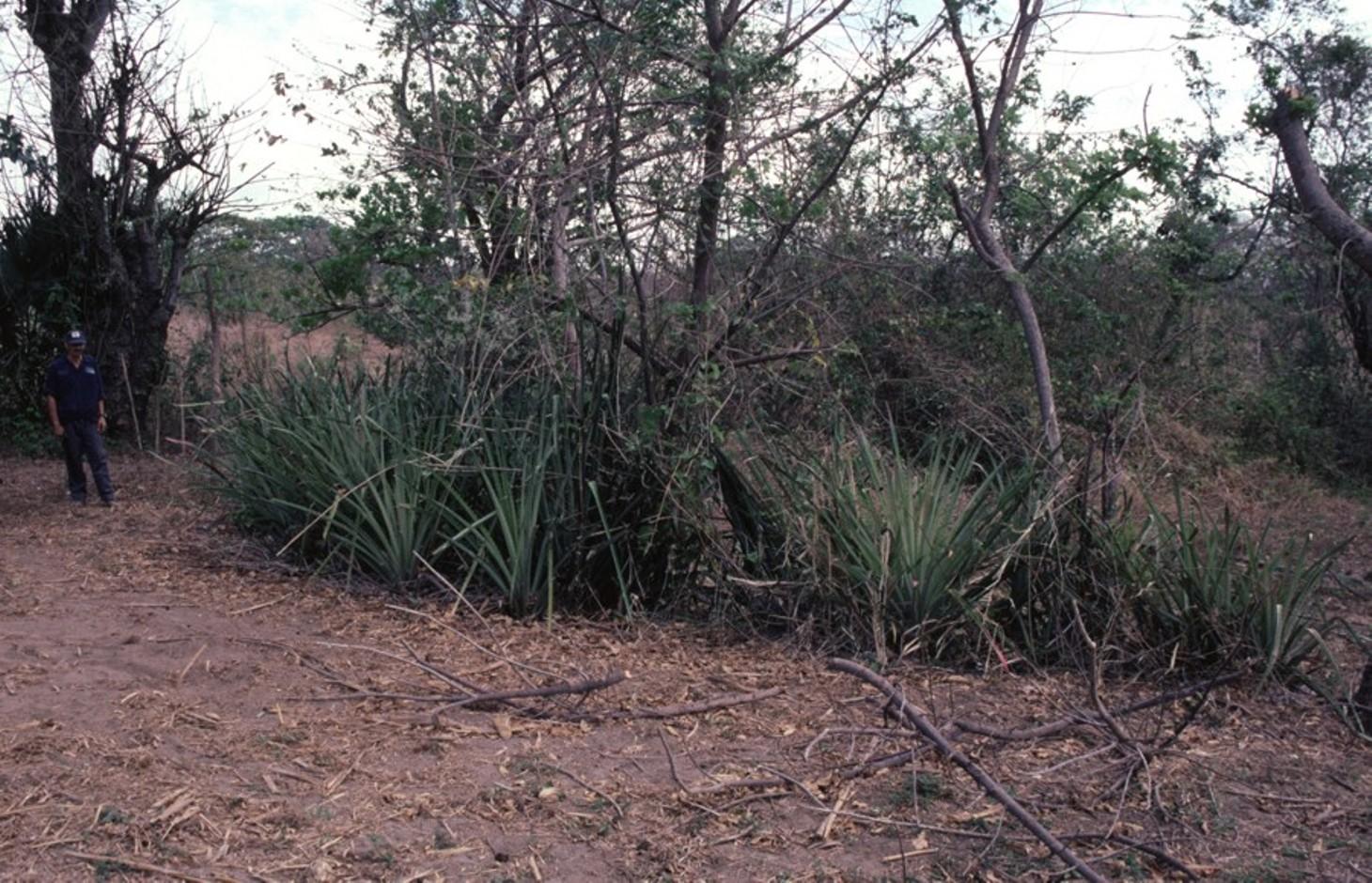
Gully rehabilitation by check dams made of stem cuttings from trees. These living barriers retard concentrated runoff and fill up the gullies gradually with sediment.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
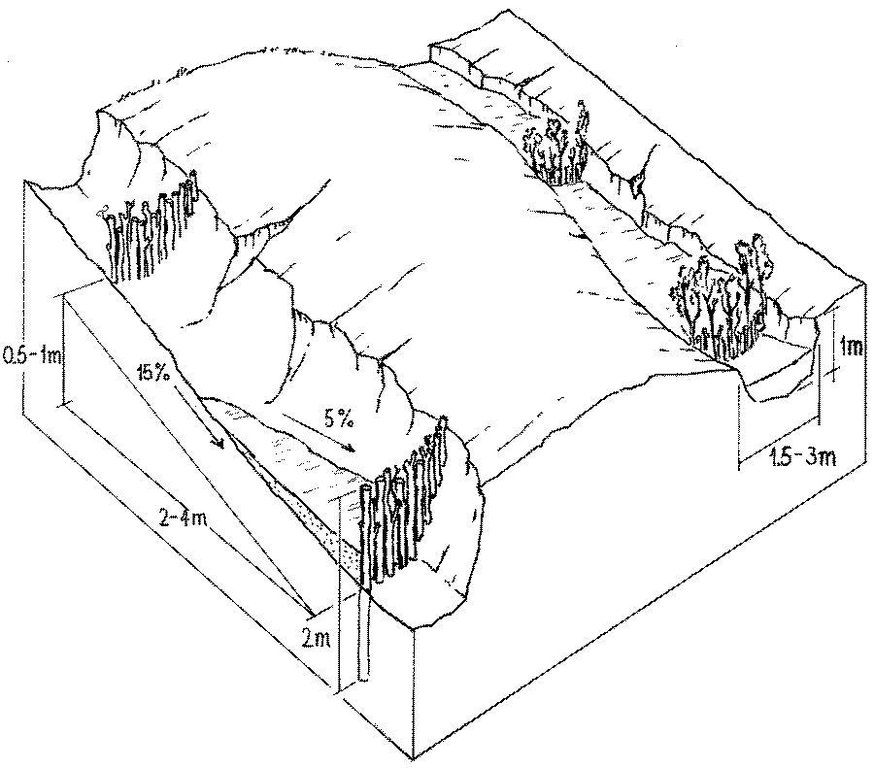
Stem cuttings from specific tree species have the ability to strike roots and continue growing after being planted into the earth. In this case study local species have been used to create check dams in gullies: these include jinocuebo (Simaroubaceaes bombacaceaes, and also jobo, tiguilote, pochote from the same family). Other suitable species are jocote (Spondias purpurea) and madero negro (Gliricidia sepium). As an option the pinapple-like piñuela (Bromelia pinguin) can be planted in association with the stem cuttings to further reinforce the system. Tree stems are cut into pieces 5-15 cm thick and 1.5-2.5 m long, depending on the depth of the gully. The cuttings are planted to half of their length, and formed into semi-circular barriers (see diagram). The dams retard runoff and thus retain eroded sediment. Spacing between dams depends on the gradient of the gully bed. For example on a 15% slope it is recommended to build a dam every 4 meters (see spacing under establishment activities). Between dams, the gully gradually fills up with eroded soil, the speed of the runoff is further reduced and agricultural land that has been divided by the gully is reconnected. Large and deep gullies may change over time into a sequence of narrow fertile terraces where crops can be grown.
However, the check dams should be seen as part of an integrated catchment management and protection plan, and thus be supported by other SWC measures on the lateral slopes, such as retention ditches and/or live barriers laid out along the contour. Erosion and runoff control on the sides of each gully is an essential part of the rehabilitation process. These check dams of rooted poles are more robust and durable than stone dams in soils of sandy/ loamy texture. On moderate and steep slopes a combination of stem cutting and stone dams is recommended.
After two to three years the barriers should be pruned - yielding wood and fodder. Dead poles should be replaced and the dam widened if necessary.
In this case study the dams are constructed in a semi-arid region with erratic rainfall where gullies are common on agricultural land, be it cropland or grazing land. The land users are mainly peasant farmers, growing crops for subsistence on smallholdings, and living in very poor conditions. This system of gully rehabilitation is promoted by an NGO entitled ‘Asociación Tierra y Vida’ through farmerto-farmer (campesino a campesino) extension.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
นิการากัว
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Santa Teresa, Paso de la Solera
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Carazo, Nicaragua
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 5 km2.
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 100, Longest growing period from month to month: May to August; Second longest growing period in days: 90, Second longest growing period from month to month: September to November

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): There is a range of factors that limit agricultural production in the area: soil degradation, extensive gully formation on crop land, low soil fertility, lack of inputs for crop production, erratic precipitation. Also, lack of interest/knowledge and lack of resources hinder the implementation of SWC measures.
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- มาตรการปลูกพืชขวางความลาดชัน (cross-slope measure)
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V5: อื่นๆ

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S4: คูน้ำแนวระดับ หลุม
- S5: เขื่อน ชั้นดินที่แน่นแข็งบ่อน้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Specification of other vegetative measures: stem cuttings; live barriers along contour (supp.)
Specification of other structural measures: check dams; retention ditches
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wg (Gully erosion): การกัดกร่อนแบบร่องธารหรือการทำให้เกิดร่องน้ำเซาะ
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ฟื้นฟูบำบัดที่ดินที่เสื่อมโทรมลงอย่างมาก
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
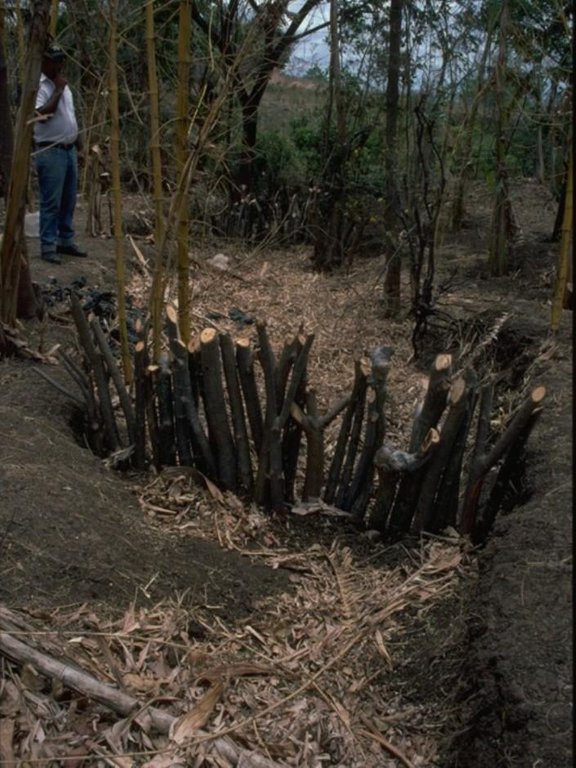
Stem cuttings planted in gullies to form living check dams: recently planted (left) and cuttings that have begun to take root and sprout, resulting in the gully becoming filled with trapped sediment (right).
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, levelling of land
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length
Construction material (wood): jinocuebo (Simaroubaceaes bombacaceaes, and also jobo, tiguilote, pochote from the same family), j
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 15%
ผู้เขียน:
Mats Gurtner
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Calculate and mark spacing between structures. | efore rainy season (April/May) |
| 2. | Cut poles out of selected local trees (diameter: 5–15 cm,length: 1.5–2.5 m depending on gully depth). | before rainy season (April/May) |
| 3. | Dig small semi-circular ditches at the gully bottom (the depth of theditch is half the length of the cuttings). | before rainy season (April/May) |
| 4. | Plant the cuttings vertically into the ditch; put the thicker cuttingsin the middle of the gully where runoff velocity is higher. | efore rainy season (April/May) |
| 5. | Fill ditch with excavated earth to fix the cuttings. | before rainy season (April/May) |
| 6. | Water to encourage rooting. | before rainy season (April/May) |
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | labour | ha | 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | tools | ha | 1.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | wheelbarrow | ha | 1.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | wood | ha | 1.0 | 60.0 | 60.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 190.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 190.0 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Duration of establishment phase: 2 month(s)
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Biotrampas: pruning the trees | every three years. |
| 2. | Cut-off drains: clearing of sediment, cutting bushes and grasses. | |
| 3. | Stone check dams: pruning trees and bushes every three years. After fullsedimentation, the dam may be increased in height. | |
| 4. | Wooden check dams: pruning trees and bushes | every three years. |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | labour | ha | 1.0 | 30.0 | 30.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | wood | ha | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 35.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 35.0 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Costs are calculated for a 100 m long, 2 m wide and 1 m deep gully with check dams every 4 m, on the basis of one gully per hectare.
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
The wood (for poles) belongs to the land users themselves, thus the ‘cost’ does not involve purchase.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
- ละเอียด/หนัก (ดินเหนียว)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ต่ำ (<1%)
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- เพื่อการยังชีพ (หาเลี้ยงตนเอง)
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- 10-50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Off-farm income specification: temporary or permanent migration, particularly young people
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ไม่ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
- รายบุคคล ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เช่า
- รายบุคคล
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
where gullies planted
การผลิตพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
eg madero negro=Gliricidium sepium
การผลิตไม้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
medium term
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
ภาระงาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
during establishment phase
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
สถาบันของชุมชน
การบรรเทาความขัดแย้ง
improves relationships between land users
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
การสูญเสียดิน
การหมุนเวียนและการเติมของธาตุอาหาร
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
น้ำท่วมพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
การทับถมของดินตะกอนพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
การเกิดมลพิษในน้ำบาดาลหรือแม่น้ำ
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านลบ
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
เป็นกลางหรือสมดุล
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- > 50%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
66% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
30% of all farmers approached by the project (about 400 out of 1,200 land users) have built these check dams. Seeds, tools and credits were provided as incentives; the reasons for implementation included both the attraction of the incentives and perceived ecological benefits in terms of rehabilitation of degraded areas.
34% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| Facilitated land management: area is no longer divided by gullies |
| Retards runoff speed: decreases erosion |
| Accumulation of fertile earth above the check dams, possibility of growing crops on ‘terraces’ between the structures |
| Increased soil moisture |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| The check dams used alone as SWC measure may not be adequate to withstand concentrated runoff | It is important to combine this technology with other SWC practices (e.g. retention ditches on slopes at both sides of gully, live fences, etc). |
| Only likely to be applied where land use rights are guaranteed. | |
| Labour intensive. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
01/02/2004
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Gurdiel G . La construcción de diques. Tierra Fresca, Simas-Enlace, Managua. 1993.
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Guía Técnica de Conservación de Suelos y Agua. PASOLAC, Managua. 2000.
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
LUPE . Manual Práctico de Manejo de Suelos en Laderas. Secretaría de Recursos Naturales, Tegucigalpa, Honduras. 1994.
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล