Territorial Natural Resource Management Observatory [Tunisia]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Wafa Saidi
- Editors: Siagbé Golli, Faouzi Harrouchi, faouzi BATTI, Fatma Maaloul, Tabitha Nekesa, Ahmadou Gaye
- Reviewers: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
approaches_6642 - Tunisia
1. General information
2. Description of the SLM Approach
3. Participation and roles of stakeholders involved
4. Technical support, capacity building, and knowledge management
5. Financing and external material support
6. Impact analysis and concluding statements
7. References and links
Links and modules
Collapse allLinks

Meslin: Mixed crops of cereals and legumes [Tunisia]
Meslin consists of a planting mix of cereals and legumes, formulated for both livestock feed and soil rehabilitation purposes.
- Compiler: Wafa Saidi

Biological consolidation of mechanical benches with olive trees [Tunisia]
The biological consolidation of embankments is an agricultural practice that entails planting embankments with arboricultural, pastoral, or forage species. This cultivation technique enhances the effectiveness and longevity of these structures.
- Compiler: Wafa Saidi

Dry Stone Walls [Tunisia]
Dry stone walls are durable landscaping structures created by arranging stones to construct small walls (without cement or plaster) either following contour lines or approximately perpendicular to the slope.
- Compiler: Wafa Saidi

Mechanical Benches [Tunisia]
Mechanical bench terraces are a landscaping technique employed on sloping terrain. These are essentially mechanically constructed earthen levees or embankments established along contour lines.
- Compiler: Wafa Saidi
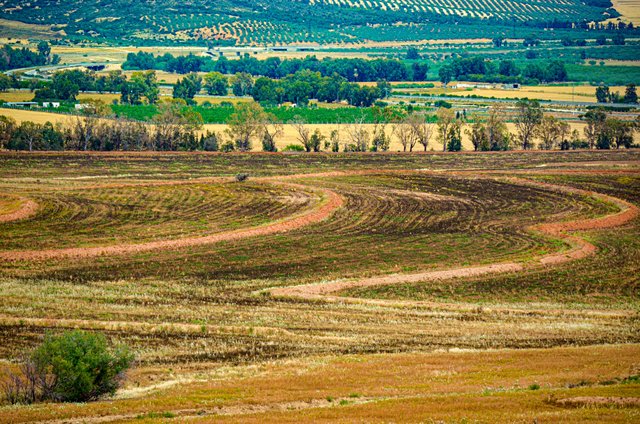

Contour tillage [Tunisia]
Contour ploughing is an agricultural technique involving the cultivation of sloping land along contour lines. This technique creates a succession of closely spaced ridges and furrows which help to retain water and soil.
- Compiler: Wafa Saidi
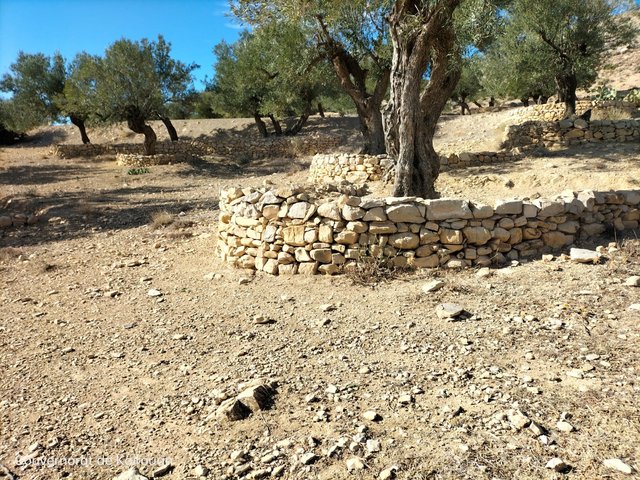

Individual Dry-Stone Basins [Tunisia]
Individual dry-stone basins are a traditional runoff water collection technique built in dry stone around the trunk of trees, mainly olive trees.
- Compiler: Wafa Saidi
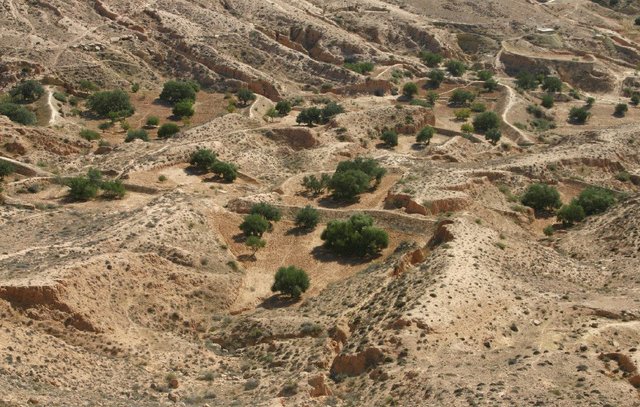

Jessour [Tunisia]
Jessour is an ancient runoff water harvesting technique widely practiced in the arid highlands
- Compiler: Mongi Ben Zaied
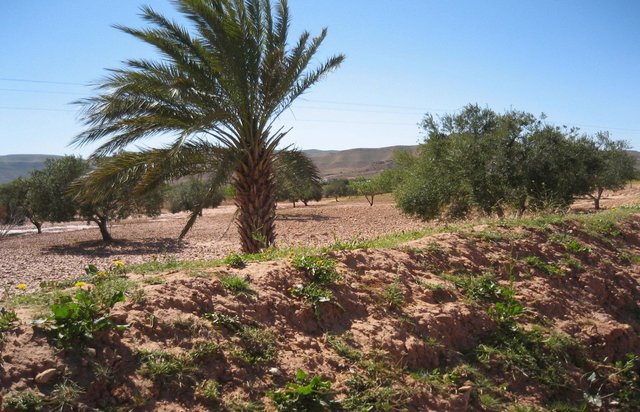

Tabia [Tunisia]
The tabia earthen dyke is a water harvesting technique used in the foothill and piedmont areas.
- Compiler: Mongi Ben Zaied
Modules
No modules