Securing the mobility of pastoralism through consultation and access to water sources [ប្រទេសឆាដ]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Bonnet Bernard
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ –
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យច្រើនទៀត៖ Donia Mühlematter, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Simone Verzandvoort, Joana Eichenberger
Projet Almy Al Afia
technologies_3356 - ប្រទេសឆាដ
- សង្ខេបជា PDF
- សេចក្តីសង្ខេបពេញលេញជាទម្រង់ PDF សម្រាប់បោះពុម្ព
- សេចក្តីសង្ខេបពេញលេញទម្រង់អ៊ីនធឺនេត
- សេចក្តីសង្ខេបពេញលេញ (មិនមានទម្រង់ជាក់លាក់)
- Securing the mobility of pastoralism through consultation and access to water sources: 12 ខែ មិនា ឆ្នាំ 2019 (inactive)
- Securing the mobility of pastoralists through consultation and access to water sources: 9 ខែ ឧសភា ឆ្នាំ 2018 (inactive)
- Securing the mobility of pastoralism through consultation and access to water sources: 2 ខែ វិច្ឆិកា ឆ្នាំ 2021 (public)
- Securing the mobility of pastoralism through consultation and access to water sources: 28 ខែ ឧសភា ឆ្នាំ 2018 (inactive)
- Securing the mobility of pastoralists through consultation and access to water sources: 13 ខែ ឧសភា ឆ្នាំ 2018 (inactive)
- Securing the mobility of pastoralists through consultation and access to water sources: 9 ខែ ឧសភា ឆ្នាំ 2018 (inactive)
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
បុគ្គលសំខាន់ម្នាក់ (ច្រើននាក់)
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
Bernard BONNET
IRAM
ប្រទេសបារាំង
ឈ្មោះគម្រោងដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃលើបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Book project: Guidelines to Rangeland Management in Sub-Saharan Africa (Rangeland Management)1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
1.4 សេចក្តីប្រកាសស្តីពីចីរភាពនៃការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស
តើបច្ចេកទេសដែលបានពណ៌នានេះមានបញ្ហាដែលផ្តោតលើការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី, បើដូច្នេះវាមិនអាចត្រូវបានប្រកាសថាជាបច្ចេកទេសនៃការគ្រប់គ្រងប្រកបដោយចីរភាពទេ?
ទេ
មតិយោបល់:
Degradation of natural resources is taken into account in the management of water resources for pastoral land, and in the social approach prior to the development of the technology. For example, the locations of new sites for water supply structures should correspond to the capacity of the grazing land in terms of the period of access, the quantity of available resources and the integration of the area into a larger coherent landscape (especially the complementary relationship between the agropastoral zones in the south and the pastoral zones in the north). Several impact assessments and preliminary analyses have been carried out, including diagnoses of the pastoralist system with regard to the logistics of the movements of the herds, the social organisation related to the management of the areas, diagnoses of the grasslands, geophysical analyses, etc.
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
Securing the mobility of pastoralism through access to water sources (open wells and ponds in pastoral areas) and marking the livestock routes for transhumance: the case of the project Almy Al Afia in Chad and its consultative approach.
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
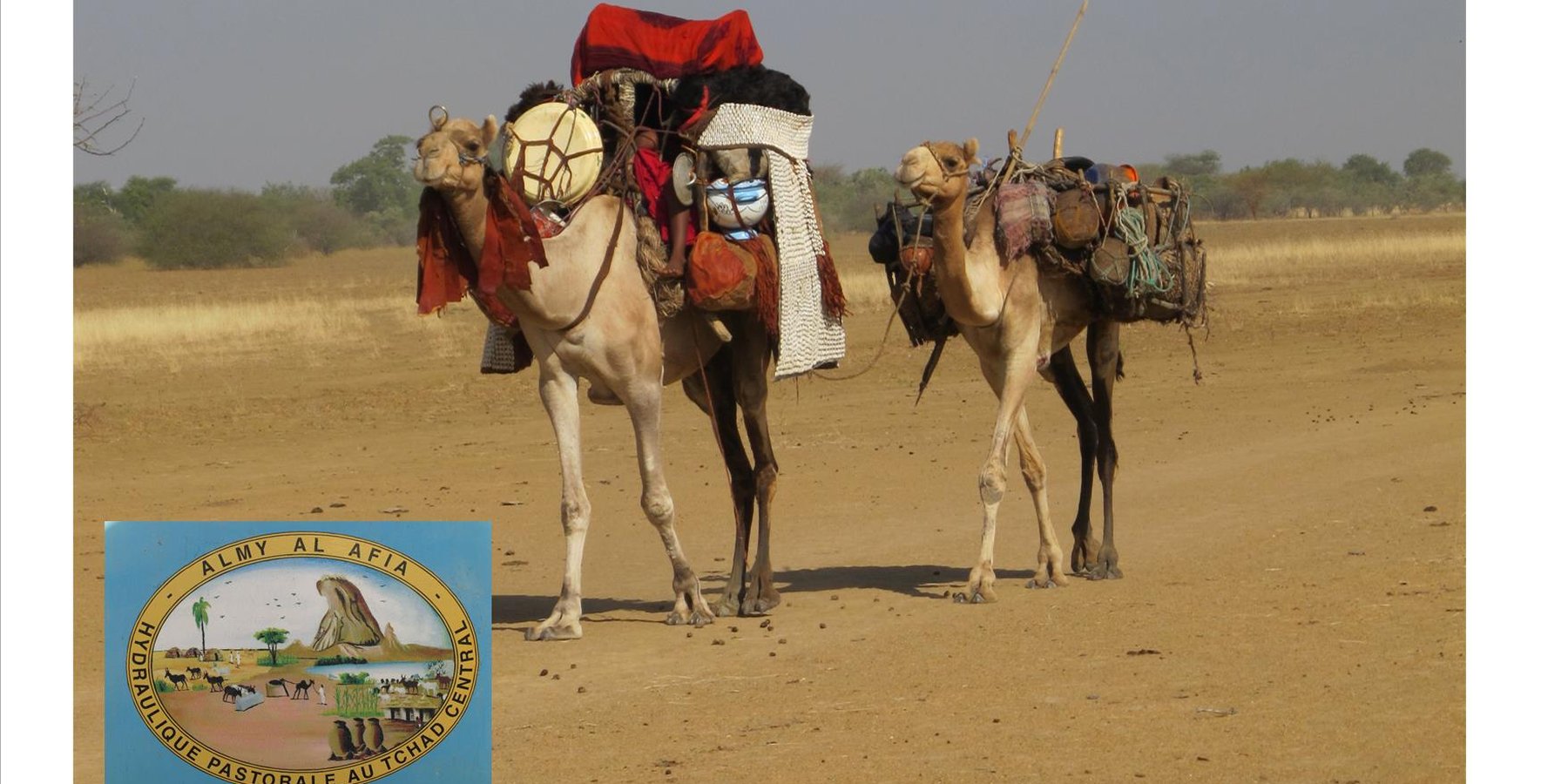
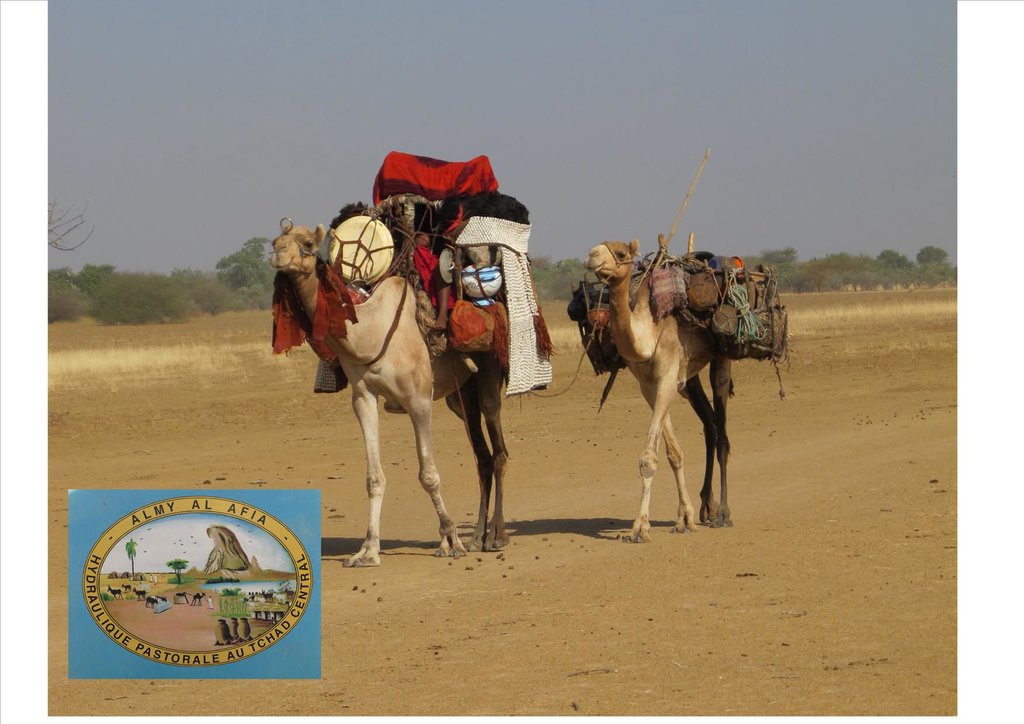
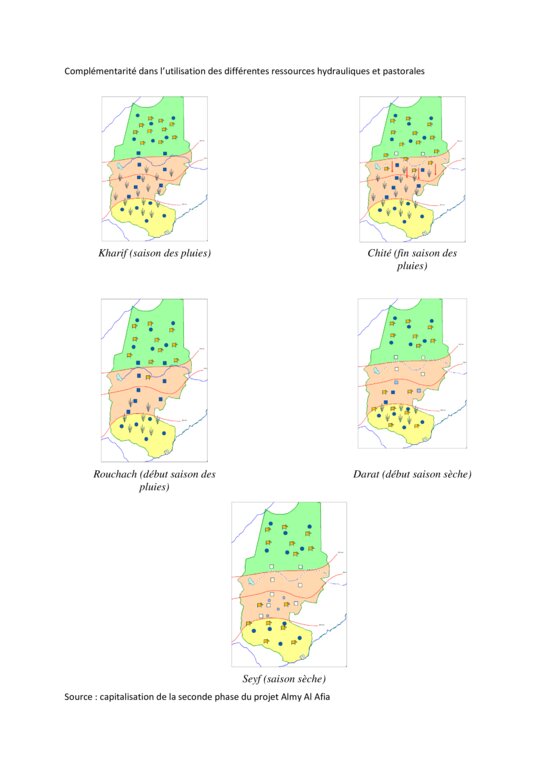
Livestock keeping is one of the main economic resources in Chad (in support of 40% of the population and 18% of the GDP, Ministry of Livestock, General census). Pastoralism in the country is based on the mobility of herds in a context of irregular precipitation and variable forage resources in time and space, and benefits from complementary relationships between the different ecological zones. In Chad, herds are taken in regular movements with the seasons between the Sahelian and the Sudanese grazing areas. The former are nutritious but limited in quantity, while the latter are more abundant but of lower quality, and not accessible until the fields are cleared after the harvest (meta-evaluation of projects on pastoral water sources, IIED, 2013). Thus, pastoral livestock keeping is founded on mobility and rangeland management, and on building complementary relationships and trade around farming systems and cultivated areas. The pastoralist systems are economically competitive (limited use of food inputs), and occur in marginal land which is characterized by conflicts, riots and a high level of insecurity (Conference of N'Djamena: 'Pastoral livestock keeping: a sustainable contribution to development and security in Saharan and Sahelian regions'). In the pastoral zone of Chad, where access to water is limited, the management and control of water sources by a social group in practice also leads to the monitoring and control of the use of grazing land which becomes available when water is present.
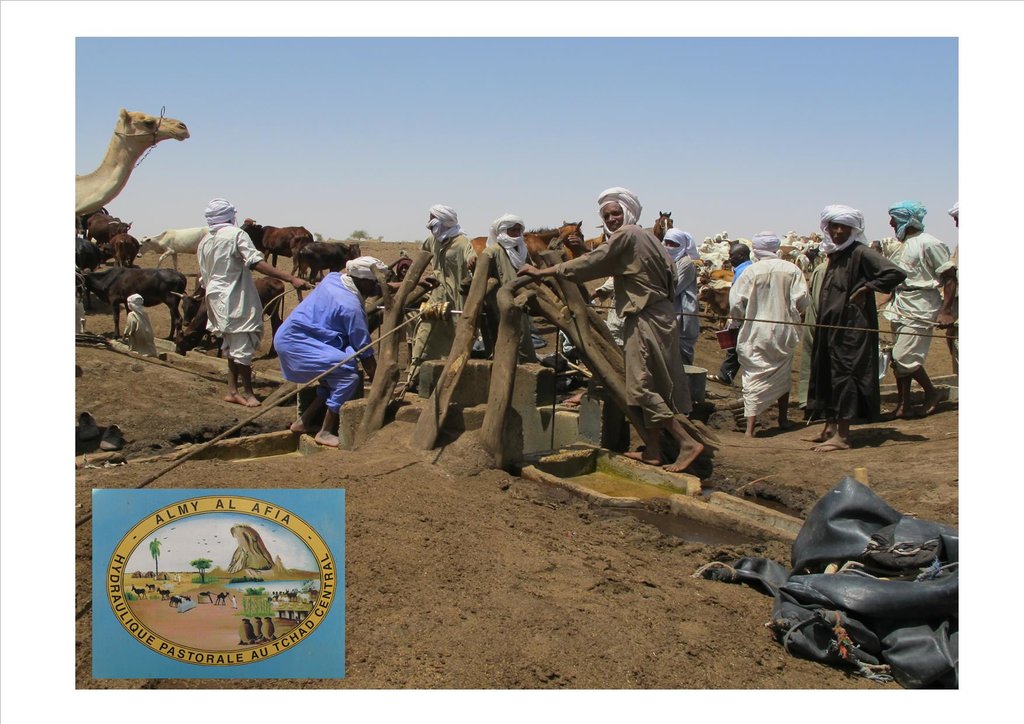
The project Almy Al Afia (2004-2016), developed by a partnership between the AFD and the Ministry of Water of Chad, operated in two regions of central Chad. The project Almy Al Afia was based on an entry 'development', concurrently with a process to consult and involve joint agencies. The project has improved approaches of preceding initiatives: concerted action and identification of water sources derived from the dialogue between users and authorities, and development of the local management of infrastructures and rangeland. The latter counteracts an exclusively private management or, instead, an ineffective public management which promotes free access to water sources and grazing land.
The project has enabled to address the following points:
1. Support mobility in pastoralism by enhancing the access to water (rehabilitation and construction of 160 wells; digging of 31 ponds for pastoral use);
2. Maintain or build processes of consultation and restoring security (joint committees for consultation and prevention of conflicts during transhumance);
3. Promote the proper use of water supply structures, in time and space (rehabilitated and new wells, excavated ponds) by context-specific management (strengthening of traditional management systems) and encourage the maintenance of infrastructure.
The pastoral ponds should be constructed in locations of existing water sources (natural ponds in suitable places, i.e. with a clayey soil capable to retain water). The existing water source is enlarged and improved by rural engineering (enlargement of the surface, deepening).
The wells are rehabilitated. Most wells were constructed several decades ago and are severely damaged. The water supply structures all have different and complementary functions. The deep wells in the pastoral zone are generally used throughout the year, and are overexploited. The way in which these structures are managed is strongly anchored in the region. The District officer delegates the management to 'Heads of Wells'. These old wells, which are used day and night, are often in a poor condition. Rehabilitating degraded wells is given priority over digging new wells because of the substantial potential for conflict. The water supply structures in areas of dry forest are less old and smaller in number. These wells are less frequently used and function as an alternative water source when the traditional ponds, water reservoirs and wells have dried up. They allow to delay the movement of the herds towards grazing areas in the Sahelian zone.
The strip between these two zones is used for agropastoralism. Herds cannot remain there. Therefore the project has facilitated the movement of the herds to the zones further south. The pastoral ponds close to the livestock routes for the transhumance were created in a way to be easily used by the herders, but also to encourage short stays.
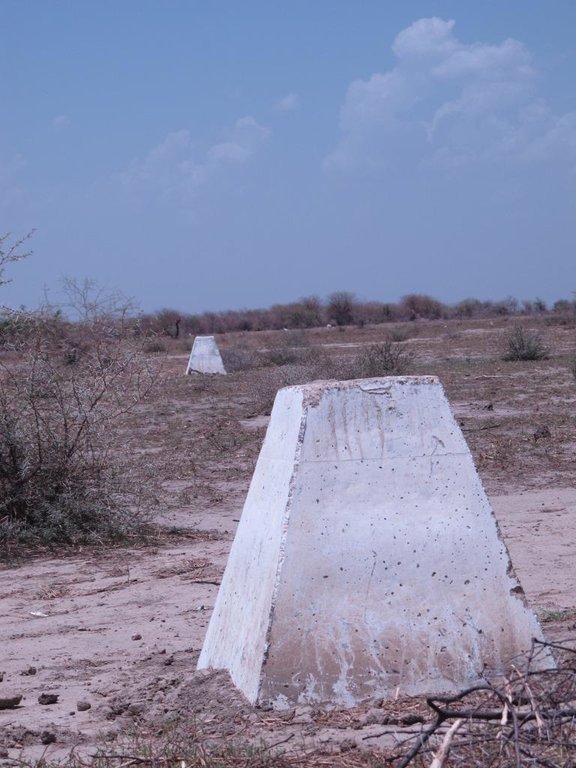
The approach was combined with consultation through joint committees for the prevention of conflicts, and at a later stage by marking of sections of the livestock routes for the transhumance. Many meetings were held with the users of the land management structures and policy makers, with the aim to identify and negotiate the target sites and to anticipate methods for the management and maintenance of the structures. This has enabled to maintain an atmosphere of social stability conducive to cooperation. Along almost 550 km of the livestock routes for the transhumance, sections were marked ('mourhals' in Chadian Arabic). The demarcation was not intended to enclose the herds in the livestock corridors (from which they can move freely outside the growing seasons for agricultural crops), but rather to implement the results of the consultations on the land use on the ground. The committees for the prevention of conflicts, which were supported by the project, also played a major role.
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
2.4 វីដេអូនៃបច្ចេកទេស
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
ប្រទេសឆាដ
តំបន់/រដ្ឋ/ខេត្ត:
Regions of Batha and of Guéra
បញ្ជាក់បន្ថែមពីលក្ខណៈនៃទីតាំង:
Although the sites where the technology was applied are at the local scale, the project has considered pastoralism and the relationships between the two regions at the broader landscape scale.
បញ្ជាក់ពីការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស:
- ត្រូវបានផ្សព្វផ្សាយត្រឹមតំបន់មួយ
ប្រសិនបើមិនច្បាស់ពីទំហំផ្ទៃដី សូមធ្វើការប៉ាន់ប្រម៉ាណ:
- 10-100 គម2
មតិយោបល់:
Main towns of the two relevant regions (Ati for the region of Batha and Mongo for the region of Guéra).
The water sources constitute an anchorage point for the herds. The surrounding grazing land is controlled by the access to the water supply points (impact zone with a radius of 15 to 20 km around the wells). Apart from the area directly influenced by the technology, complementary relationships between the zones provide an added value: hence the zone targeted by the decision-making process of the herders is very large.
Map
×2.6 កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត
បង្ហាញឆ្នាំនៃការចុះអនុវត្ត:
2018
2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តដោយរបៀបណា:
- តាមរយៈការបង្កើតថ្មីរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
- ជាផ្នែកនៃប្រព័ន្ធប្រពៃណី (> 50 ឆ្នាំ)
មតិយោបល់ (ប្រភេទនៃគម្រោង ។ល។):
Projects on pastoral water resources like the project Almy Al Afia primarily focus on the development of water sources for pastoralism. The phases preceding the implementation are extremely important, because they are based on consultation and on the appreciation of local management systems. These phases include registration, selection of construction sites and the development of guidelines.
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.1 គោលបំណងចម្បង (១ ឬច្រើន) នៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
- កាត់បន្ថយ, បង្ការ, ស្តារឡើងវិញនូវការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
- អភិរក្សប្រព័ន្ធអេកូឡូស៊ី
- ការពារតំបន់ទីជម្រាល/តំបន់ខ្សែទឹកខាងក្រោមបញ្ចូលជាមួយបច្ចេកទេសផ្សេងទៀត
- អភិរក្ស/ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងជីវចម្រុះ
- កាត់បន្ថយហានិភ័យនៃគ្រោះមហន្តរាយ
- បង្កើតផលប្រយោជន៍សេដ្ឋកិច្ច
- បង្កើតផលប្រយោជន៍សង្គម
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស

ដីសម្រាប់ចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ
វាលស្មៅធំៗ:
- ពនេចរ
- ពាក់កណ្តាលពនេចរ
ប្រភេទសត្វ:
- សត្វអូដ្ធ
មតិយោបល់:
Number of growing seasons per year: 1
Livestock density: Variable depending on zones and seasons.
3.4 ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹក
ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹកនៅកន្លែងអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស:
- ទឹកភ្លៀង
មតិយោបល់:
In these zones, rainfall is erratic in terms of spatial distribution and in quantity. Hence, grazing areas are not uniformly covered from year to year. The mobility of herds is the only way to adapt to this variability.
3.5 ក្រុម SLM ដែលបច្ចេកទេសស្ថិតនៅក្នុង
- កសិរុក្ខកម្ម (pastoralism) និងការគ្រប់គ្រងដីសម្រាប់ចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ
- ការគ្រប់គ្រងទឹកក្រោមដី
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស

វិធានការរចនាស័ម្ពន្ធ
- S8: អនាម័យ/ទំនប់ទឹកកង្វក់

វិធានការគ្រប់គ្រង
- M2: ការផ្លាស់ប្តូរការគ្រប់គ្រង/ កម្រិតអាំងតង់ស៊ីតេ
- M3: ប្លង់យោងទៅតាមធម្មជាតិ និងបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ការហូរច្រោះដីដោយសារទឹក
- Wt: ការបាត់ដីស្រទាប់លើដោយការហូរច្រោះ

ការបាត់ដីដោយសារខ្យល់
- Et: ការបាត់បង់ដីស្រទាប់លើ
- Eo: ផលប៉ះពាល់នៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាព

ការបាត់បង់រូបសាស្ត្រនៃដី
- Ps: ការស្រុតចុះនូវសារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៃដី ការពន្លិចដី

ការធ្លាក់ចុះជីវសាស្ត្រនៃដី
- Bc: ការថយចុះនូវគម្របរុក្ខជាតិ
- Bq: ការថយចុះនូវជីវម៉ាស/ បរិមាណ

ការបាត់បង់ទឹក
- Hs: ការប្រែប្រួលបរិមាណទឹកនៅលើផ្ទៃដី
- Hg: ការប្រែប្រួលបរិមាណទឹកនៅក្រោមដី
- Hp: ការថយចុះគុណភាពទឹកនៅលើផ្ទៃដី
- Hq: ការថយចុះគុណភាពទឹកនៅក្រោមដី
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
បញ្ជាក់ពីគោលដៅរបស់បច្ចេកទេស ដែលផ្តោតទៅការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី:
- ការការពារការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
- ការកាត់បន្ថយការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
4.1 គំនូសបច្ចេកទេសនៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ទាក់ទងនឺងគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស):
The wells (new and rehabilitated) and the demarcation of the livestock routes are the outcome of a long process of outreach. The communications between the local level (taking account of the views of future users) and the level of decision-making (administration) enable social agreements to be formalized. These agreements set the rules for the selection of the locations of the water supply structures, their management and maintenance.
ឈ្មោះអ្នកនិពន្ធ:
Project Almy Al Afia
កាលបរិច្ឆេទ:
2016
4.2 ព័ត៌មានទូទៅដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងការគណនាធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
កំណត់របៀបនៃការគណនាថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូល:
- ក្នុងឯកតាបច្ចេកទេស
បញ្ជាក់ឯកតា:
Structure (new well, rehabilitation or km of markings)
ផ្សេងៗ/ រូបិយប័ណ្ណជាតិ (បញ្ជាក់):
FCFA
កំណត់ថ្លៃឈ្នួលជាមធ្យមនៃការជួលកម្លាំងពលកម្មក្នុងមួយថ្ងៃ:
1000 FCFA
4.3 សកម្មភាពបង្កើត
| សកម្មភាព | រយៈពេល (រដូវកាល) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Outreach / awareness raising | Four to six meetings prior to the signing of the social agreements |
| 2. | Construction of the facilities | Four to six months, depending on the type of structure and its depth |
| 3. | Monitoring the management | Regular visits of the project team to support the implementation of adapted management practices |
មតិយោបល់:
The implementation of the different phases varies greatly in terms of the location of the outreach activities and the duration of the construction work.
4.4 ថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូលដែលត្រូវការសម្រាប់ការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Rehabilitated wells (mean depth 56 m) | 1 | 93,0 | 10497939,0 | 976308327,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Geophysical assessment for new wells | 1 | 158,0 | 17979914,0 | 2840826412,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Exploration drilling for new wells (mean depth 96 m) | 1 | 220,0 | 6005415,0 | 1321191300,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | New wells (mean depth 45 m) | 1 | 62,0 | 45145740,0 | 2799035880,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Pastoral ponds (6000 m3 on average) | 1 | 31,0 | 23008065,0 | 713250015,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Markers (8 signs / km) | 1 | 492,0 | 1069203,0 | 526047876,0 | |
| ផ្សេងៗ | Outreach on new wells (/site) | 1 | 62,0 | 213428,0 | 13232536,0 | |
| ផ្សេងៗ | Outreach on rehabilitation (/site) | 1 | 93,0 | 248695,0 | 23128635,0 | |
| ផ្សេងៗ | Outreach on marking (/km) | 1 | 492,0 | 52088,0 | 25627296,0 | |
| ផ្សេងៗ | None | None | ||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 9238648277,0 | |||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 9238648277,0 | |||||
មតិយោបល់:
The context of pastoralism has taken the project approach to not ask compensation from users: if the users are never the same, then who should be charged? Who will collect the payments and manage the collected funds? In addition, most of the water supply structures are far from financial institutions, which causes problems in securing these funds. Therefore the users contribute in terms of day-to-day maintenance of structures, by mobilizing labour in particular.
4.5 សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
| សកម្មភាព | ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Mobilising indigenous groups for day-to-day maintenance of structures (dredging, cleaning) | Depending on the type of structure (generally monthly) |
4.6 កំណត់ថ្លៃដើមសម្រាប់ការថែទាំ/ សកម្មភាពរបស់បច្ចេកទេស (ក្នុងរយៈពេលមួយឆ្នាំ)
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Support missions for the management and maintenance of the water supply structures (2 missions per structure for the entire project) | 1 | 155,0 | 53000,0 | 8215000,0 | |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Support mission for the management and maintenance of the markings | 1 | 100,0 | 53000,0 | 5300000,0 | |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេស | 13515000,0 | |||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 13515000,0 | |||||
មតិយោបល់:
The amount of financial support varied with the type of structure (more support for management and maintenance is needed for new structures than for rehabilitated structures) and with their location or specific problem (in the case of structures located in the agropastoral zones). Financial support to the markings of the livestock corridors was indirectly provided through the committees for the prevention and management of conflicts.
4.7 កត្តាសំខាន់បំផុតដែលមានឥទ្ធិពលដល់ការចំណាយ
ពណ៌នាពីកត្តាប៉ះពាល់ចម្បងៗទៅលើថ្លៃដើម:
The costs of the constructions are highly dependent on their location (costs for the supply and disposal of equipment and materials), on the price of inputs (cement, etc.), and especially on the type of structure (depth of the wells, geological environment). The costs of the supply and disposal of equipment and materials include costs for the installation of the structures (water, cement, labour, machinery) on the construction sites (which are often far away from routes and towns), and costs for the disposal of the equipment after the construction is completed. The costs of supply and disposal can be significant with respect to the costs of the structure itself.
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
លក្ខណៈពិសេស/ មតិយោបល់លើរដូវភ្លៀង:
One rainy season per year (from June to September)
បញ្ជាក់ឈ្មោះឯកសារយោងនៃស្ថានីយឧតុនិយម:
Ati
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- មានភ្លៀងតិចតួច
- ស្ងួត
The target region includes large areas extending over important gradients (encompassing boundaries of the desert zone, the forested zone and the cotton-growing zone).
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
បញ្ជាក់ថាតើបច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានអនុវត្តន៍នៅក្នុង:
- មិនពាក់ព័ន្ធទាំងអស់
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- គ្រើម/ មានពន្លឺ (ខ្សាច់)
វាយនភាពដី (> 20 សម ស្រទាប់ក្នុង):
- គ្រើម/ មានពន្លឺ (ខ្សាច់)
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៅស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ:
- ទាប (<1%)
5.4 ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
នីវ៉ូទឹកក្រោមដី:
> 50 ម
ទឹកលើដីដែលអាចទាញយកប្រើប្រាស់បាន:
មិនមាន/ គ្មាន
គុណភាពទឹក (មិនបានធ្វើប្រត្តិកម្ម):
ទឹកពិសារដែលមានគុណភាពល្អ
តើមានបញ្ហាភាពទឹកប្រៃហូរចូលមកដែរឬទេ?
បាទ/ចា៎
សូមបញ្ជាក់:
Depending on the zones: presence of sodium carbonate.
តើទឹកជំនន់កំពុងកើតមាននៅតំបន់នេះដែររឺទេ?
ទេ
5.5 ជីវៈចម្រុះ
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃប្រភេទ:
- កម្រិតមធ្យម
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃទីជម្រក:
- កម្រិតមធ្យម
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
នៅមួយកន្លែង ឬពនេចរ :
- ពាក់កណ្តាលពនេចរ
- ពនេចរ
ទីផ្សារនៃប្រព័ន្ធផលិតកម្ម:
- ពាក់កណ្តាលពាណិជ្ជកម្ម (ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ខ្លួនឯង/ ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម)
ចំណូលក្រៅកសិកម្ម:
- តិចជាង 10% នៃចំណូល
កម្រិតជីវភាព:
- មិនល្អខ្លាំង
- មិនល្អ
ឯកជន ឬក្រុម:
- ជាក្រុម/ សហគមន៍
កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់គ្រឿងយន្ត:
- ប្រើកម្លាំងពលកម្ម
យេនឌ័រ:
- ស្ត្រី
- បុរស
អាយុរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- យុវវ័យ
- វ័យកណ្តាល
5.7 ទំហំផ្ទៃដីជាមធ្យមនៃដីប្រើប្រាស់ដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី ក្នុងការអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
- < 0.5 ហិកតា
- 0.5-1 ហិកតា
- 1-2 ហិកតា
- 2-5 ហិកតា
- 5-15 ហិកតា
- 15-50 ហិកតា
- 50-100 ហិកតា
- 100-500 ហិកតា
- 500-1,000 ហិកតា
- 1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
- > 10,000 ហិកតា
តើផ្ទៃដីនេះចាត់ទុកជាទំហំកម្រិតណាដែរ ខ្នាតតូច មធ្យម ឬខ្នាតធំ (ធៀបនឹងបរិបទតំបន់)?
- ខ្នាតធំ
មតិយោបល់:
Transhumance, and more generally pastoral mobility, applies to large geographical scales and long periods. The areas involved are very large, far above 10.000 ha.
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី:
- ក្រុម
កម្មសិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- ជាក្រុម (មានដែនកំណត់)
កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក:
- ជាក្រុម (មានដែនកំណត់)
5.9 ការប្រើប្រាស់សេវាកម្ម និងហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ
សុខភាព:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការអប់រំ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ជំនួយបច្ចេកទេស:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការងារ (ឧ. ការងារក្រៅកសិដ្ឋាន):
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទីផ្សារ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ថាមពល:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ផ្លូវ និងការដឹកជញ្ជូន:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទឹកផឹក និងអនាម័យ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
សេវាកម្មហិរញ្ញវត្ថុ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
ទឹកដែលអាចប្រើប្រាស់បានសម្រាប់ការចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
n/a
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
n/a
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Expansion of the areas covered by water supply points. Reduced closure of water supply points (rehabilitation), opening-up of new grazing land, securing the movement of livestock and people.
គុណភាពទឹកសម្រាប់ការចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
n/a
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
n/a
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើវប្បធម៌សង្គម
សន្តិសុខស្បៀង/ ភាពគ្រប់គ្រាន់ខ្លួនឯង
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Preserving the capacity of herders and their families to move, to choose their trajectories rather than responding to imposed conditions.
កម្មសិទ្ធដីប្រើប្រាស់/ ទឹក
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
n/a
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
n/a
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Upgrading of traditional management systems of water supply structures.
ស្ថាប័នសហគមន៍
ការកាត់បន្ថយជម្លោះ
ស្ថានភាពក្រុមដែលមានបញ្ហាក្នុងសង្គម និងសេដ្ឋកិច្ច
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ី
ដី
គម្របដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Reduction of the impacts of the concentration of livestock and people in small areas. Promotes the complementary relations between the zones (pressure relief in some zones and use and maintenance of other zones), and over the seasons.
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គដី/ការបូនក្រោមដី
ជីវចម្រុះ៖ ដំណាំ, សត្វ
ដំណាំគម្រប
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃរុក្ខជាតិ
ការកាត់បន្ថយហានិភ័យនៃគ្រោះមហន្តរាយ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ
ផលប៉ះពាល់នៃគ្រោះរាំងស្ងួត
6.2 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្រៅបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
n/a
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
n/a
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Increased access to groundwater through the rehabilitation of wells and the construction of new wells.
វាយតម្លៃផលប៉ះពាល់ក្រៅបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស (វាស់វែង):
As explained above, in these zones with low rainfall and scarce natural water sources of temporary character (ponds), it is essential to combine the use of surface water with the use of water from deep permanent groundwater bodies. When they have the choice, herders almost exclusively choose sources with surface water (avoiding effort to extract the water). But when these sources run dry, they fall back on using wells (and deep groundwater). The rehabilitation of old wells and the construction of new wells in zones without wells contributes to increasing the availability of water.
6.3 ភាពប្រឈម និងភាពរួសនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ/ គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ (ដែលដឹងដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
| រដូវកាល | កើនឡើង ឬថយចុះ | លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ | ថយចុះ | មិនល្អ | |
| បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំរដូវកាល | សើម/រដូវភ្លៀង | ថយចុះ | មិនល្អ |
គ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ (មហន្តរាយ)
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយអាកាសធាតុ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| រាំងស្ងួត | ល្អ |
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមាន
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមាន
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមាន
មតិយោបល់:
The profitability is considered in relation to the number of animals/herds involved. The costs of construction and rehabilitation are certainly significant, but the water supply structures are used for thousands of animals (in case of the most heavily used wells); most animals drink every two days. Therefore the costs per head of livestock are limited. The wells are long lasting, and therefore the returns are positive in the short and the long term.
6.5 ការទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
- > 50%
បើអាច សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីបរិមាណ (ចំនួនគ្រួសារ និង/ ឬតំបន់គ្របដណ្តប់):
The technology responds to a substantial need, but also corresponds to the capacity of land users to use and maintain the structures. The energy supply is provided by animal traction, and does not require external energy sources.
ក្នុងចំណោមគ្រួសារទាំងអស់ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើមានប៉ុន្មានគ្រួសារដែលចង់ធ្វើដោយខ្លួនឯង ដោយមិនទទួលបានសម្ភារៈលើកទឹកចិត្ត/ប្រាក់ឧបត្ថម្ភ?:
- 91-100%
មតិយោបល់:
Access to water is such a large problem that it requires all the land users who enter the zone to be informed when a water supply structure is rehabilitated or constructed. The involvement of traditional leaders in the management of the structures, and the system of representatives of the traditional leadership in the various other zones (Khalifas) contributes to the spontaneous dissemination of the information.
6.6 ការបន្សុំា
តើថ្មីៗនេះ បច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានកែតម្រូវដើម្បីបន្ស៊ាំទៅនឹងស្ថានភាពប្រែប្រួលដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
6.7 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៃបច្ចេកទេស
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៅកន្លែងរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
|---|
| Permanent access to water. |
| Reopening of water supply structures and consolidation of access to water at some degraded sites. |
| Agencies and authorities for conflict prevention. |
| Marking of sections of livestock corridors with conflict situations. |
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
| Full commitment of groups (access to water is a major problem). |
| Continuation of the approach through the development of other projects and inclusion at the national level. |
6.8 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យនៃបច្ចេកទេស និងវិធីសាស្ត្រដោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| Interventions are limited with regard to the needs (rehabilitation in particular). | By larger investments and better integration of the approach in public action. |
| There is a need to extend the approach, in particular the support to the consultative bodies. | Formalize support to the consultation process. |
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រងឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
|
Recognition of the experiences, the approach and the methodology in other interventions. Outreach and awareness raising are performed during the project, but at the end the management of the infrastructure is no longer supported. The government should be able to follow up on the support (mechanism for monitoring and maintenance). |
Formalize support to the consultation process. |
| There is a need to mainstream outreach and consultation (lengthy process). | Formalize support to the consultation process. |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.1 វិធីសាស្ត្រ/ ប្រភពនៃព័ត៌មាន
- តាមការចុះទីវាល ការស្រាវជ្រាវនៅទីវាល
Progress reports and thematic reports of the project Almy Al Afia
- ការសម្ភាសន៍ជាមួយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
Follow-up and evaluation of the project activities (logbook, annual update)
- ការចងក្រងពីរបាកការណ៍ និងឯកសារផ្សេងៗទៀតដែលមាន
Creating value from lessons learned in the project Almy Al Afia (Republic of Chad, Ministry of Water)
តើពេលណាដែលទិន្នន័យបានចងក្រង (នៅទីវាល)?
2016
7.2 ឯកសារយោងដែលបានចេញផ្សាយ
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Capitalisation des enseignements de la deuxième phase du projet Almy Al Afia, Main document, DHP, Antea/Iram, March 2016
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
Republic of Chad, General Secretariat, Ministry of Water, Directorate of Pastoral Water Resources
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Document de Suivi-Evaluation des activités du PHPTC II, tableau de bord des activités du projet, DHP, Antea/Iram, mars 2016
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
Republic of Chad, General Secretariat, Ministry of Water, Directorate of Pastoral Water Resources
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Note Entretiens Techniques du PRAPS, Accès et gestion durable des espaces pastoraux (chemins de transhumance, aires de pâturages et de repos), PRAPS, 2016, B. Bonnet, A. H. Dia, P. Ndiaye, I. Touré
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
Republic of Chad, General Secretariat, Ministry of Water, Directorate of Pastoral Water Resources
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Evaluation et capitalisation de 20 ans d’intervention du Groupe AFD portant sur le secteur de l’Hydraulique Pastorale au Tchad, IIED, May 2013, S. Krätli, M. Monimart, B. Jallo, J. Swift, C. Hesse
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
Republic of Chad, General Secretariat, Ministry of Water, Directorate of Pastoral Water Resources
7.3 ការភ្ជាប់ទៅកាន់ព័ត៌មានពាក់ព័ន្ធលើប្រព័ន្ធអនឡាញ
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
Platform on pastoralism in Chad
វេបសាយ:
www.plateforme-pastorale-tchad.org/
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
Website of PRAPS-TD
វេបសាយ:
www.praps.cilss.int/index.php/praps-pays-tchad/
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
Website of Iram
វេបសាយ:
https://www.iram-fr.org/elevage-pastoralisme-et-hydraulique-pastorale.html
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
AFD in Chad
វេបសាយ:
http://www.afd.fr/fr/page-region-pays/tchad
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់
គ្មានការតភ្ជាប់
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល