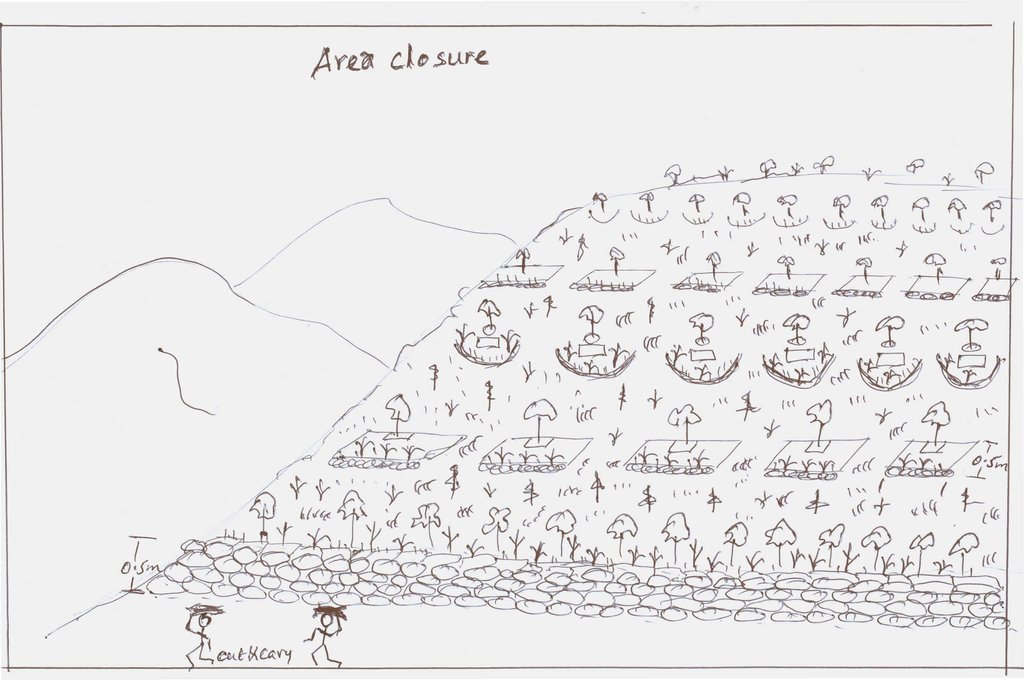
Area closure on degraded lands [Этиоп]
- Шинийг нээх:
- Шинэчлэх:
- Мэдээлэл цуглуулсан: Gizaw Desta Gessesse
- Редактор: –
- Хянагчид: Deborah Niggli, Alexandra Gavilano
Yetrakot Meret mekelel (Amharic)
technologies_1598 - Этиоп
Бүлгүүдийг үзэх
Бүгдийг харуулах Бүгдийг хаах1. Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
1.2 Технологийг үнэлэх, баримтжуулах ажилд хамаарах мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүс, байгууллагуудын холбоо барих мэдээлэл
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн :
Bekure Melese
WLRC
Этиоп
Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн төслийн нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Water and Land Resource Centre Project (WLRC)1.3 WOCAT-аар баримтжуулсан өгөгдлийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцөл
Эмхэтгэгч болон гол мэдээлэгч хүн(хүмүүс) WOCAT аргачлалаар баримтжуулсан мэдээллийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцлийг хүлээн зөвшөөрсөн.
Тийм
1.4 Технологи тогтвортой гэдгийг баталгаажуулах
Энэ технологи азрын доройтлыг бууруулахад нөлөө үзүүлэхгүй тул газрын тогтвортой менежментийн технологи болж чадахгүй юу?
Үгүй
1.5 ГТМ Арга барилын Асуулга (ууд) руу хандах (WOCAT ашиглан баримтжуулсан)

'Cut and Carry' Grazing system or 'Zero Grazing' … [Этиоп]
Cut and carry grazing system (alternatively called zero grazing) is an approach where the community is consulted to identify and agree on areas to be closed and protected from free grazing; establish user groups are established to share the fodder biomass harvested from communal closed areas equitably; they utilize tree/shrub …
- Мэдээлэл цуглуулсан: Gizaw Desta Gessesse
2. ГТМ Технологийн тодорхойлолт
2.1 Технологийн товч тодорхойлолт
Технологийн тодорхойлолт:
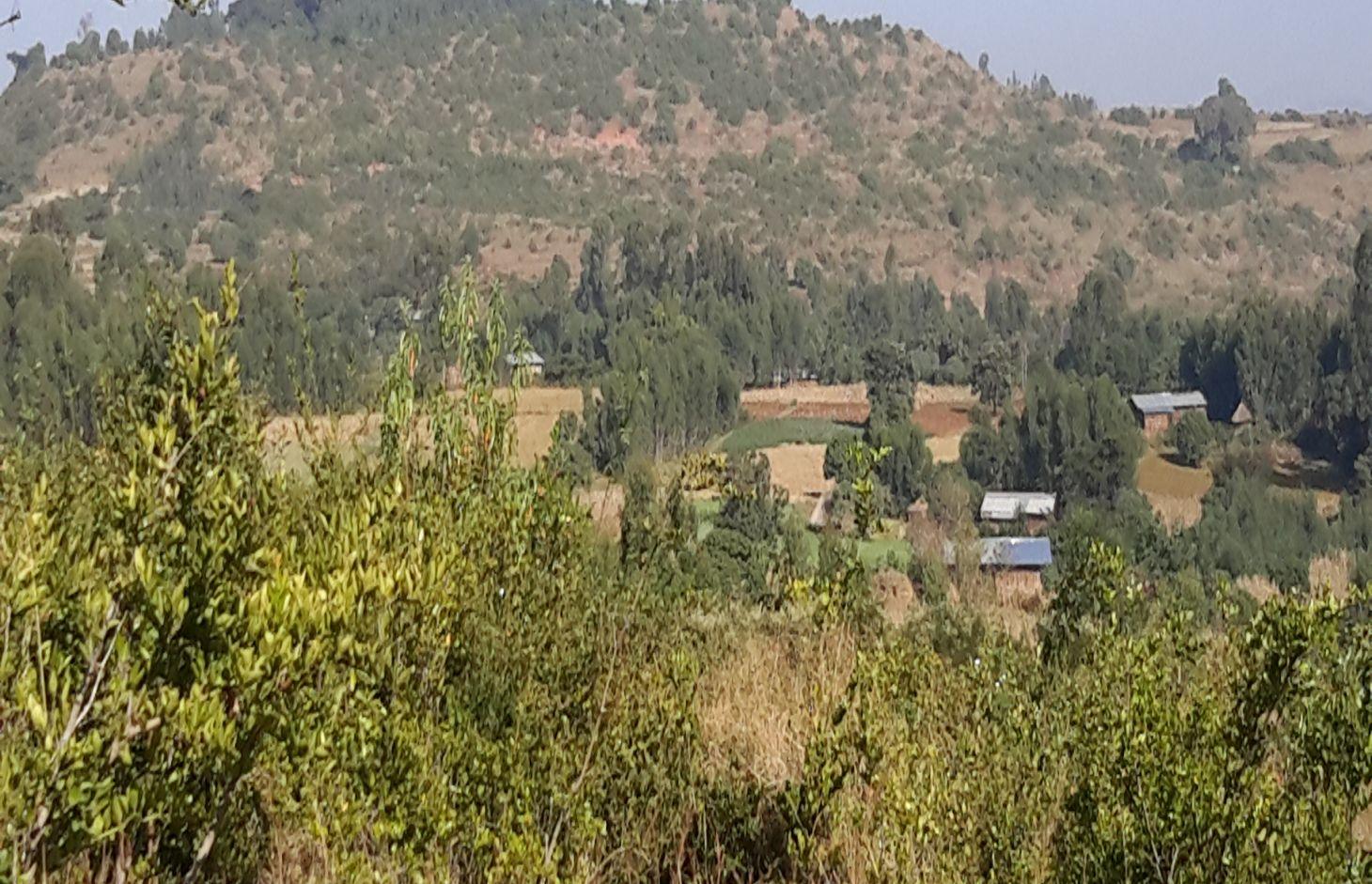
Area closure on degraded lands is a land management practice used to rehabilitate and conserve the natural resource bases, and enhance its natural regeneration and restoring capacity and productive functions by excluding animal and human interferences through community consultation and collective actions.
2.2 Технологийн дэлгэрэнгүй тайлбар
Тодорхойлолт:
Area closure is a land management practice that helps to rehabilitate degraded lands, restore the biophysical conditions like soil, vegetation and hydrology by avoiding the interference of animals and human. Because of over grazing and erosion impact, areas delineated for closure are usually degraded shrub or pasture lands that served for grazing. First of all, implementing area closure requires continuous dialogue and discussion with community to reach consensus to close. The community wants to make sure they have benefited from the technology as the land was serving for grazing. They should take the responsibility and create sense of ownership to implement conservation measures, protect and maintain closure areas, and regulate utilization of benefits gained out of it. Questions raised from the community must be discussed thoroughly ahead of the implementation. What part of the degraded land? For what purpose the area is closed? Who are the users? Who are responsible to protect and manage the developed resourcess? How is the benefit sharing among identified users? Commonly, the shared benefits from area closures are hay for livestock through cut-and-carry system, timbers from plantations, and honey production.
Depending on the soil, rainfall and slope conditions different structural and vegetative measures are integrated to enhance the fast regeneration of plant species, restore the soil and increase water availability. It includes enrichment used to rehabilitate and increase the vegetation cover, vegetative and structural measures to retain the soil and water on its place. Structures such as hillside terrace often integrated with grass or shrub hedgerows is used to control soil erosion. In-situ water harvesting structures such as trenches or half moon or eye brow are used to harvest and infiltrate rain or runoff water to increase regeneration and survival of planted trees. Trees and/or shrub species that have high rehabilitation and multipurpose values are used as enrichment plantations. Closed areas need collective action to protect, maintain and manage the common resources. Collective user rights have to be entitled to bring equity on resource sharing and minimize social conflicts.
The purposes of area closure are: 1) rehabilitate degraded lands, 2) protect and restore the natural resource base, and 3) change into productive land and enhance economic and environmental functions of rehabilitated lands.
Implementation of area closure begins with the selection and demarcation of area through genuine participation of land users. After identifying the area to be closed, at establishment stage construction of ditches and terraces is made using stones combined with grasses or shrubs of multipurpose value such as Vetiver grass, Dinsho grass, Bana grass, susbania, etc. Depending on site conditions, enrichment tree species which have rehabilitation and soil restoration purposes are planted in the form of wood lot or scattered tree plantation. Among the common species, A. albida, A. saligna, A. decurrense, Gravilia robusta, etc. are used to rehabilitate and serve as fuel wood and timber. In moisture stress areas structures like trench, level bunds, and half moon should be constructed to increase survival rate of planted tree/shrub species whereas in areas having sufficient moisture these structures, depending on the landforms and soil drainage conditions, help to increase infiltration and recharging of ground water in downstream areas. Therefore, site selection and demarcation, construction of soil conservation and moisture conservation structures, and seedling management and plantation of multipurpose trees, shrubs and grasses are the activities accomplished at establishment stage of area closure. The required inputs are stones, seeds/seedlings, grass cuttings/splits, hand tools, and collective labor. For recurrent maintenance activities, seedlings and cuttings for re-plantation purpose or replace dead seedlings, stones to repair damage stone terraces and moisture conservation structures. Harvesting and transporting of area closure products such as grass and timber become a recurrent activity. Person days per hectare per year required for plantation (preparation of holes and planting) is 11.5, for harvesting and transporting harvested grass is 30, and for terrace construction is 26.5.
Area closure management is commonly practiced on degraded hills where soil is highly depleted, its water holding capacity is low, and vegetation is denuded. Usually degraded lands are used to serve for communal grazing system. The degree of land degradation becomes severe where there are high livestock and human population pressure. Management of closure area and the benefit sharing has to be regulated using agreed bylaws.
The living condition depends on subsistence crop-livestock mixed farming. On average households have 5-6 family size. Crop production is meant for home consumption with small surplus for local market. The services related to water supply, energy supply, and infrastructure are low. Besides it is an asset, animals often used to cope shocks during drought periods.
2.3 Технологийн гэрэл зураг
2.5 Энэ үнэлгээнд хамрагдсан технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн улс орон / бүс нутаг / байршил
Улс :
Этиоп
Улс/аймаг/сум:
Amhara National Regional State
Байршлын дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт:
Mecha / Yilmana Densa / Bahir Dar Zuria
Технологи өргөн дэлгэрсэн эсхийг тодорхойл:
- газар дээр жигд тархсан
Хэрэв талбайн хэмжээ тодорхойгүй бол талбайн хэмжээг ойролцоогоор тодорхойлно уу.
- 1-10 км2
2.6 Хэрэгжих огноо
Байгуулсан тодорхой оныг мэдэхгүй бол баримжаа хугацааг тодорхойл:
- <10 жилийн өмнө (саяхны)
2.7 Технологийн танилцуулга
Технологийг хэрхэн нэвтрүүлснийг тодорхойл:
- Гадны төсөл/хөтөлбөрийн дэмжлэгтэйгээр
Тайлбар (төслийн төрөл г.м.):
Area closure as an integrated SLM technology is practiced in recent years. However, the land users have their own traditional practice by closing grass lands or shrub lands during the rainy season.
3. ГТМ технологийн ангилал
3.1 Технологийн үндсэн зорилго (д)
- Экосистемийг хамгаалах
3.2 Технологи хэвтрүүлсэн газрын одоогийн газар ашиглалтын хэлбэр(д)
Нэг газр нутгийн хэмжээнд хэрэгжих холимог газар ашиглалт:
Тийм
Газар ашиглалтын холимог тогтолцоог (тарилан/бэлчээр/ой мод) тодорхойл:
- Агро-бэлчээр (тарилан-мал аж ахуйн хослуулсан тогтолцоог хамруулан ойлгоно)

Тариалангийн газар
- Олон наст (модлог биш) тариалан
- Мод, бут тариалах
- Vetiver grass, Dinsho grass, Bana grass, susbania
- A. albida, A. saligna, A. decurrense, Gravilia robusta, napier
Нэг жил дэх ургамал ургах улирлын тоо:
- 1
Тодорхойлно уу:
Longest growing period in days: 220, Longest growing period from month to month: May to December; Second longest growing period in days: 180, Second longest growing period from month to month: June to November

Бэлчээрийн газар
Нүүдлийн бэлчээр ашиглалт:
- Хагас нүүдлийн бэлчээрийн аж ахуй
Эрчимжсэн бэлчээр / тэжээл үйлдвэрлэл:
- Хадлан буюу бэлчээрт ашиглагдахгүй талбай

Байгалийн ой / модтой газар
Бүтээгдэхүүн ба үйлчилгээ:
- Мод бэлтгэл
- Түлшний мод
- Бэлчээрийн талбай/Хариулгатай бэлчээрлэлт
Тайлбар:
Livestock density (if relevant):
> 100 LU /km2
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Land degradation due to different forms of soil erosion and nutrient depletion, excess removal of crop residues, excessive overgrazing, shortage of pasture lands and its low productivity, excessive and inappropriate construction of traditional ditches, and increased demand of trees for the purpose of fuel wood and timber.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Soil erosion and soil nutrient depletion, shortage of cultivated land, shortage of grazing land and wood for fuel wood
3.4 Усан хангамж
Технологи хэрэгжүүлсэн газрын усан хангамж:
- Байгалийн усалгаатай
3.5 Технологи ГТМ-ийн аль бүлэгт хамаарах
- газар нутаг чөлөөлөх (ашиглалтыг зогсоох, нөхөн сэргээх)
3.6 Технологийг бүрдүүлэх ГТМ арга хэмжээ

Ургамалжилтын арга хэмжээ
- V1: Мод ба бут, сөөг
- V2: Өвс ба олон наст өвслөг ургамал

Барилга байгууламжийн арга хэмжээ
- S2: Далан, хаалт
- S3: Шаталсан суваг, шуувуу, гольдрол
- S4: Шаталсан шуудуу, нүх, хэвгий

Менежментийн арга хэмжээ
- М1: Газар ашиглалтын хэлбэрийг өөрчлөх
- М2: Ашиглалтын менежмент/эрчимийг өөрчлөх
Тайлбар:
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour, scattered / dispersed, in blocks
3.7 Технологийн шийдвэрлэсэн газрын доройтлын үндсэн төрлүүд

Хөрс усаар эвдрэх
- Wt: Хөрсний гадаргын угаагдал
- Wo: Усны элэгдлийн дам нөлөө

Хөрсний химийн доройтол
- Cn: Үржил шим болон органик агууламж буурах (элэгдлийн шалтгаангүй)

Биологийн доройтол
- Bc: Ургамлан нөмрөг багасах
- Bh: Амьдрах орчин доройтох
Тайлбар:
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), overgrazing, population pressure, governance / institutional
Secondary causes of degradation: soil management, over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts), land tenure, education, access to knowledge and support services
3.8 Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх, сааруулах ба нөхөн сэргээх
Газрын доройтолтой холбоотойгоор Технологи ямар зорилго тавьсан болохыг тодорхойл:
- Газрын доройтлыг багасгах сааруулах
- Хүчтэй доройтсон газрыг нөхөн сэргээх/ сайжруулах
4. Техникийн нөхцөл, хэрэгжилтийн үйл ажиллагаа, материал ба зардал
4.1 Технологийн техникийн зураг
Техник тодорхойлолт (техник зурагтай уялдана):
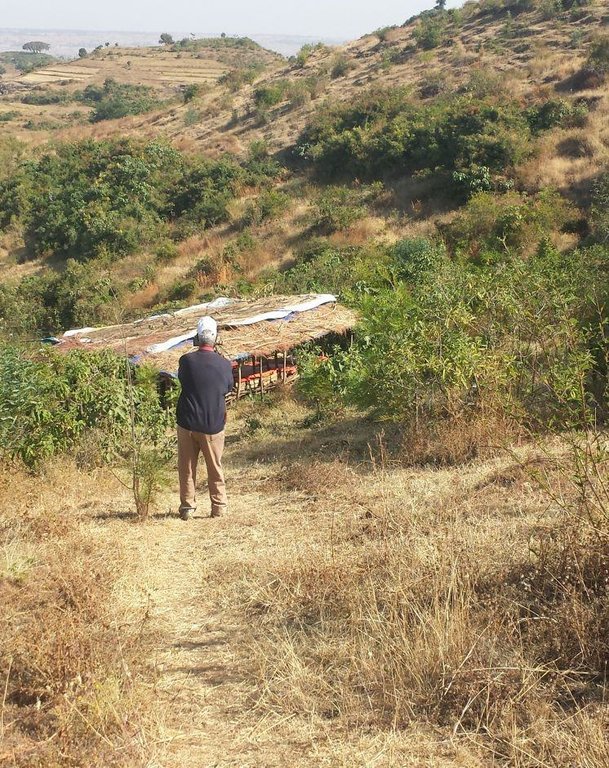
Integrated practices of area closure including hillside bunds, trenches, micro-basins, and trees/shrubs
Location: Debre Yacob Learning Watershed. Mecha/West Gojam/Amhara
Date: 2014-5-23
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (Field staffs need to acquire technical knowledge on how to integrate different practices and strategies depending on the conditions and degree of degradation.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low (Land users require low knowledge. Once they implement practices in the closure area, they are able to coordinate and respect the bylaws and equitable distribution of benefits.)
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, improvement of ground cover, increase of biomass (quantity)
Secondary technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase in organic matter, increase / maintain water stored in soil
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): 4000-6000
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 5
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5-1.0
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 160
In blocks
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 2
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 2
Trees/ shrubs species: Gravilia, Susbania, Acacia decurrence
Grass species: Napier
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 20-30%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 0.5%
Diversion ditch/ drainage
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.3-0.7
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.2-2.8
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 100-250
Waterway
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.3
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.5-2.0
Bund/ bank: level
Spacing between structures (m): 5
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.5
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1-1.5
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 15-35%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Change of land use type: Initially, the land is highly degraded and waste land. After an increase in vegetation cover and biomass, its use is thus changed from waste/shrub land/open grazing to cut-and-carry grazing system
Change of land use practices / intensity level: The land use management is changed from open access /communal grazing or shrub land to regulated or organized form of land use management
Зохиогч:
Bekure Melese, WLRC
4.2 Материал болон зардалд хамаарах ерөнхий мэдээлэл
бусад/үндэсний мөнгөн нэгж (тодорхойл):
ETB
Хэрэв боломжтой бол үндэсний валютын Америк доллартай харьцах харьцааг бичнэ үү (тухайлбал, 1 ам.дол. = 79,9 Бразил реал): 1 ам.дол. =:
20.0
Хөлсний ажилчны нэг өрдийн ажлын хөлсийг тодорхойл:
2.50
4.3 Байгуулах үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа (улирал) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Preparation of seedlings | March-May |
| 2. | Transporting seedlings | July |
| 3. | Transporting grass splits | July |
| 4. | Sowing seeds on bunds | July |
| 5. | Planting of trees and shrubs | July |
| 6. | Planting of grass splits or cuttings | July |
| 7. | Construction of bunds or terraces | February-April |
| 8. | Construction of cutoff drains and ditches | Fegruary-April |
| 9. | Construction of waterways | February-April |
| 10. | Surveying or layout of structures | January-March |
| 11. | Consultation of the community | |
| 12. | Establish bylaws to control free grazing | |
| 13. | Establish user groups and arrange equitable benefit sharing |
4.4 Байгуулалтад шаардагдах зардал ба материал
| Хөрөнгө оруулалтыг дурьдана уу | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн өртөг | Материал бүрийн нийт өртөг | % газар ашиглачаас гарсан зардал | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | labour | ha | 1.0 | 1766.0 | 1766.0 | 80.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | tools | ha | 1.0 | 300.6 | 300.6 | 50.0 |
| Таримал материал | seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 405.6 | 405.6 | 100.0 |
| Таримал материал | seeds | ha | 1.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| Барилгын материал | stone | ha | 1.0 | 1300.0 | 1300.0 | 100.0 |
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг | 3792.2 | |||||
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 189.61 | |||||
Тайлбар:
Duration of establishment phase: 15 month(s)
4.5 Засвар үйлчилгээ / давтагдах үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа/ давтамж | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Preparation of seedlings | March-May |
| 2. | Seedling transportation | July |
| 3. | Grass split transportation | July |
| 4. | Planting seedlings | July |
| 5. | Planting grass splits | July |
| 6. | Maintenance of bunds / cutoff drains | |
| 7. | Enforcing bylaws | Throught the year |
| 8. | Benefit sharing among user groups | Throughout the year |
4.6 Засвар үйлчилгээ / урсгал үйл ажиллагаанд шаардагдах зардал ба материал (жилээр)
| Хөрөнгө оруулалтыг дурьдана уу | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн өртөг | Материал бүрийн нийт өртөг | % газар ашиглачаас гарсан зардал | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | labour | ha | 1.0 | 624.0 | 624.0 | 29.0 |
| Таримал материал | seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 250.0 | 250.0 | 100.0 |
| Технологийг арчилах тордоход шаардагдах нийт үнэ өртөг | 874.0 | |||||
| Технологи сайжруулах нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 43.7 | |||||
Тайлбар:
Machinery/ tools: Spade, pickaxe, crowbar,
4.7 Зардалд нөлөөлж байгаа хамгийн чухал хүчин зүйл
Өртөг зардлыг тодорхойлох гол хүчин зүйлсийг дурьдана уу:
The costs of area closure affected by the labour availability, regeneration capacity of trees on the degraded lands
5. Хүн, байгалийн хүрээлэн буй орчин
5.1 Уур амьсгал
Жилийн нийлбэр хур тундас
- <250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1,000 мм
- 1,001-1,500 мм
- 1,501-2,000 мм
- 2,001-3,000 мм
- 3,001-4,000 мм
- > 4,000 мм
Агро-уур амьсгалын бүс
- Хагас чийглэг
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 Байрзүйн зураг
Дундаж налуу:
- Тэгш (0-2 %)
- Бага зэрэг хэвгий (3-5 %)
- Дунд зэрэг хэвгий (6-10 % )
- Долгиорхог (11-15 %)
- Толгодорхог (16-30 %)
- Эгц налуу (31-60 % )
- Огцом эгц налуу (>60 %)
Гадаргын хэлбэр:
- Тэгш өндөрлөг/тэгш тал
- Зоо, хяр
- Уулын энгэр, хажуу
- Ухаа, гүвээ, дов толгод
- Уулын бэл
- Хөндий, хоолой, нам хотос
Өндөршлийн бүс:
- 0-100 м д.т.д
- 101-500 м д.т.д
- 501-1,000 м д.т.д
- 1,001-1,500 м д.т.д
- 1,501-2,000 м д.т.д
- 2,001-2,500 м д.т.д
- 2,501-3,000 м д.т.д
- 3,001-4,000 м д.т.д
- > 4,000 м д.т.д
5.3 Хөрс
Хөрсний дундаж зузаан:
- Маш нимгэн (0-20 см)
- Нимгэн (21-50 см)
- Дунд зэрэг зузаан (51-80 см)
- Зузаан (81-120 cм)
- Маш зузаан (>120 cм)
Хөрсний бүтэц (өнгөн хөрс):
- Дунд зэрэг (шавранцар)
- Хүнд (шаварлаг)
Өнгөн хөрсний органик нэгдэл:
- Бага (<1 % )
5.4 Усны хүртээм ба чанар
Хөрсний усны гүн:
> 50 м
Гадаргын усны хүртээмж:
Дунд зэрэг
Усны чанар (цэвэрлээгүй):
Муу чанарын ундны ус (цэвэршүүлэх шаардлагатай)
5.5 Биологийн төрөл зүйл
Зүйлийн олон янз байдал:
- Бага
5.6 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчидын онцлог шинж
Үйлдвэрлэлийн системийн зах зээлийн чиг баримжаа:
- Амь зуух арга хэлбэрийн (өөрийгөө хангах)
Фермээс гадуурх орлого:
- Нийт орлогын %10 доош хувь
Чинээлэг байдлыг харьцангуй түвшин:
- Ядуу
- Дундаж
Хувь хүн эсвэл бүлэг:
- бүлэг / олон нийтийн
Хүйс:
- Эмэгтэй
- Эрэгтэй
Газар ашиглагчдын бусад шаардлагатай шинж чанарыг тодорхойл:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Women has their own role in the establishment of the rea closure by collecting stones, support construction and planting activities. In addition they will harvest and transport fodder for livestock
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
80% of the land users are average wealthy.
20% of the land users are poor.
5.7 Технологи нэвтрүүлэхэд газар ашиглагчийн ашигласан газрын дундаж талбай
- < 0.5 га
- 0.5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1,000 га
- 1,000-10,000 га
- > 10,000 га
Энэ нь жижиг, дунд, том оворт тооцогдох уу (орон нутгийн чиг баримжаагаар)?
- Бага-хэмжээний
5.8 Газар эзэмшил, газар ашиглах эрх, ус ашиглах эрх
Газар өмчлөл:
- Төр засаг
Ус ашиглах эрх:
- Нээлттэй хүртэх (зохион байгуулалтгүй)
- Нэгдлийн хэлбэрээр (зохион байгуулалттай)
5.9 Дэд бүтэц, үйлчилгээний хүртээмж
эрүүл мэнд:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
боловсрол:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
техник дэмжлэг:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт (жишээ нь, ХАА-аас өөр):
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
зах зээл:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
эрчим хүч:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
зам ба тээвэр:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
ундны ус ба ариутгал:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
санхүүгийн үйлчилгээ:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
6. Үр нөлөө ба дүгнэлт
6.1 Технологийн талбай дахь үр нөлөө
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн үр нөлөө
Үйлдвэрлэл
тэжээл үйлдвэрлэл
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Mainly serve for grass harvest
малын бүтээмж
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Cut and carry improve the production
Үйлдвэрлэлийн газар
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
By improving the land use management, production area for pasture increased
Орлого, зарлага
орлогын олон янз эх үүсвэр
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
People try to diverse apiculture production in closed areas
хөдөлмөр хүчний хэмжээ
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Labor requirement to harvest and transport fodder and pasture increase
Нийгэм-соёлын үр нөлөө
олон нийтийн институц
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Establishment of user groups and watershed users association
ГТМ/ газрын доройтлын талаархи мэдлэг
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Increase the level of awareness that area closure can shortly reverse land degradation
маргааныг шийдвэрлэх
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Reduce conflict arise due to pasture shortage
Нийгэм, эдийн засгийн хувьд эмзэг бүлгийнхний нөхцөл байдал
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Some rural unemployed youths get employed in apiculture production and fruit production
contribution to human well-being
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
The livestock production is moderately improved due to increase in biomass/ pasture harvest
Экологийн үр нөлөө
Усны эргэлт/ илүүдэл
усны хэмжээ
гадаргын урсац
гүний усны түвшин / уст давхарга
Хөрс
хөрсний чийг
хөрсөн бүрхэвч
хөрс алдагдах
Биологийн: ургамал, амьтан
газрын дээрхи / доорхи С
ургамлын төрөл, зүйл
амьдрах орчны олон янз байдал
Уур амьсгал болон гамшгийн эрсдлийг бууруулах
түймрийн эрсдэл
6.2 Технологийн талбайн гадна үзүүлсэн үр нөлөө
хуурай улиралд ашиглах найдвартай, тогтвортой урсгал
ГТМ хэрэгжхээс өмнөх тоо хэмжээ:
End of Nov
ГТМ хэрэгжсэнээс хойшхи тоо хэмжээ:
Mar-April
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Because of high vegetation cover, the recharrging capacity improved resulting in prolonging the stream flow/baseflow
Доод урсгалын үер
урсацын адагт лаг шавар хуримтлагдана
6.3 Технологийн уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт ба Уур амьсгалаас хамаарах аюул/гамшигт үзэгдэлд өртөх байдал ба эмзэг байдал (газар ашиглагч нарын дүгнэлтээр)
Уур амьсгалаас хамаарах аюулууд (гамшигууд)
Цаг уурын гамшигууд
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| Орон нутгийн аадар бороо | Сайн |
Уур амьсгалын гамшигууд
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| Ган гачиг | Сайн |
Гидрологийн гамшиг
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| усны үер (гол) | Сайн биш |
6.4 Зардал ба үр ашгийн шинжилгээ
Үр ашгийг барилга байгууламжийн зардалтай (газар ашиглагчдын үзэл бодлоор) хэрхэн харьцуулах вэ?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
Бага зэрэг эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
Эерэг
Үр ашгийг засвар үйлчилгээ/ урсгал зардалтай (газар ашиглагчдын үзэл бодлоор) хэрхэн харьцуулах вэ?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
Эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
Маш эерэг
Тайлбар:
Short term economic benefits can be attained by harvesting forage biomass for livestock while in the long term downstream agricultural productivity can be improved as they witnessed the change in stream flows to be used for irrigation. This is very much pronounced in Aba Gerima watershed where farmers in the downstream get to access more water.
6.5 Технологи нутагшуулах
Тайлбар:
The technology is implemented in group or at community level.
The spontaneous adoption of this technology is possible without integrating plantations of improved trees/shrubs and grasses
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Adoption to area closure is increasing as it provides better pasture for livestock and benefit those who do not have power or for poor community groups
6.7 Технологийн давуу тал/боломжууд
| Газар ашиглагчдын тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
| Increase in vegetation cover and biomass production for livestock feed |
| Increase the duration and flow of streams |
| Decrease erosion |
| Decrease transmission of animal disease often a problem during open grazing system |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
| Increase the fodder and grass biomass production for livestock feed |
| Increase the regeneration of lost plant diversities |
| Create alternative livelihood options (off farm activities like honey production, timber, tree or fodder seed production) |
| Enhance the micro-climatic conditions and on-site vegetation cover, organic matter, and soil water holding capacity. In addition it improves off-site surface and subsurface water flows |
6.8 Технологийн дутагдалтай/сул тал/аюул болон тэдгээрийн хэрхэн даван туулах арга замууд
| Газар ашиглагч нарын тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| Land users' perceived that implementation of the technology decreases open access to communal pasture lands to maximize their benefit | Awareness creation activities has to be provided |
| Shortage of labor to harvest and transport forages to feed animals | Cost effective technologies to prepare feed, handle and transport forage has to be introduced and adopted. It can be overcomed by organizing service provider groups. |
| The amount of pasture/fodder produced and shared among users is much less than the feed requirement of all animals hold by a household | Introduce fodder species producing high biomass and high quality fodder; decrease livestock number per household. |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| Labor constraint for cut-and -carry for stall feeding | It can be sustained through organizing service providers groups |
| Stall feeding restricted the cross breeding of animals in the village easily accessible during open grazing | Artificial insemination and bull services and synchronization breeding system has to be promoted |
7. Ном зүй ба холбоосууд
7.1 Мэдээллийн аргууд / эх сурвалжууд
- Хээрийн уулзалт, судалгаа
- Газар ашиглагчтай хийсэн ярилцлага
7.2 Хүртээмжтэй ном, бүтээлийн ишлэл
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Sustaining the win-win benefits of improved grazing land management in EthiopiaPost written by Wolde Mekuria, WLE. March 30, 2015
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
WLE post
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
http://www.bioone.org/doi/pdf/10.1659/0276-4741(2005)025%5B0044%3ATROCIC%5D2.0.CO%3B2
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Vegetation Improvement in Communal Closed Areas in Tigray, Ethiopia.Sarah Tewolde-Berhan 1,4, Ralph Mitlöhner 2, Bart Muys3 , and Mitiku Haile 4
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Natural Regeneration Practice in Degraded High Lands of Ethiopia Through Area Enclosure Wondie Mebrat, Department of Biology, Adigrat University, Adigrat, Tigray, Ethiopia, 2015
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Area Closure: Rehabilitation of Degraded Lands and Grasslands and its Multiple Benefits. WLRC Brief No. 2. June 2015
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
www.wlrc-eth.org
Холбоос ба модулууд
Бүгдийг харуулах Бүгдийг хаахХолбоосууд

'Cut and Carry' Grazing system or 'Zero Grazing' … [Этиоп]
Cut and carry grazing system (alternatively called zero grazing) is an approach where the community is consulted to identify and agree on areas to be closed and protected from free grazing; establish user groups are established to share the fodder biomass harvested from communal closed areas equitably; they utilize tree/shrub …
- Мэдээлэл цуглуулсан: Gizaw Desta Gessesse
Модулууд
Модуль байхгүй байна