Marab - Water Harvesting Based Floodplain Agriculture [Йордан]
- Шинийг нээх:
- Шинэчлэх:
- Эмхэтгэгч: Joren Verbist
- Хянан тохиолдуулагчид: Mira Haddad, Enrico Bonaiuti
- Хянагч: Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Marab in Arabic “المرب”
technologies_5770 - Йордан
Бүлгүүдийг үзэх
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаах1. Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
1.2 Технологийг үнэлэх, баримтжуулах ажилд хамаарах мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүс, байгууллагуудын холбоо барих мэдээлэл
Мэдээлэл өгсөн хүн (с)
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
Strohmeier Stefan
International Center of Agriculture Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA)
Йордан
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
Natural Resources Economist Social, Economy & Policy Research:
Dhehibi Boubaker
International Center of Agriculture Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA)
Йордан
Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн төслийн нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
ICARDA Institutional Knowledge Management InitiativeТехнологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA) - Ливан1.3 ВОКАТ-аар баримтжуулсан өгөгдлийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцөл
Эмхэтгэгч болон гол мэдээлэгч хүн(хүмүүс) WOCAT аргачлалаар баримтжуулсан мэдээллийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцлийг хүлээн зөвшөөрсөн:
Тийм
1.4 Технологи тогтвортой гэдгийг баталгаажуулах
Энэ технологийг газрын доройтлыг бууруулж, газрын тогтвортой менежментийг хангахад тохиромжтой гэж үзэж болох уу?
Үгүй
Тайлбар:
This technology conserves soil and water; it reduces surface water and sediment losses from dryland watersheds. The technology is located in downstream/lowland floodplains, and ideally, it is implemented in an integrated watershed approach. In the present case study, the ‘Marab’ is linked with two main upstream measures: Upland micro-water harvesting (Vallerani system) and gully/channel measures (gully plugs)
2. ГТМ Технологийн тодорхойлолт
2.1 Технологийн товч тодорхойлолт
Технологийн тодорхойлолт:
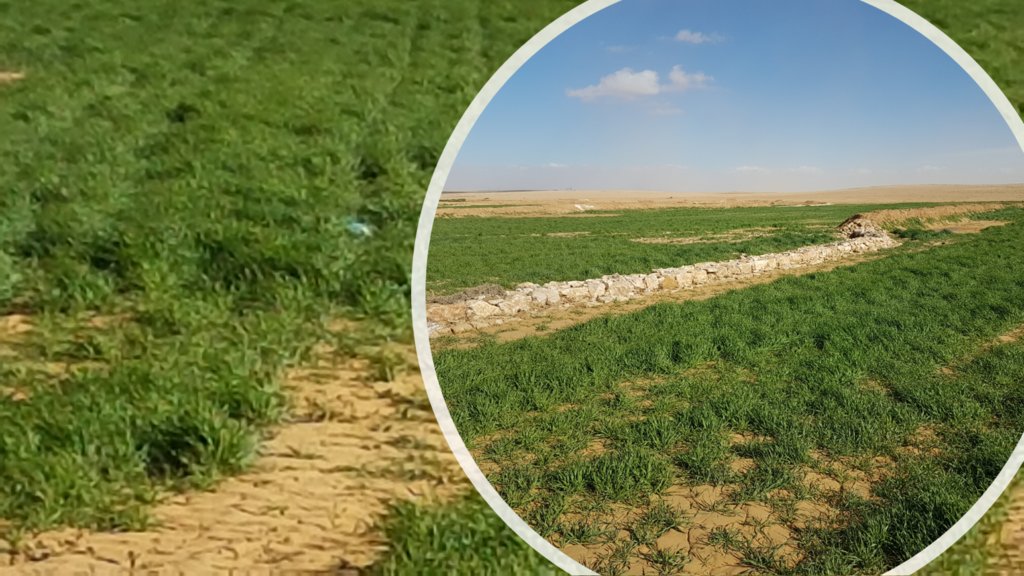
The Marab is a local downstream water harvesting measure in an integrated watershed context, where up/midstream users and applied land management practices affect the Marab.
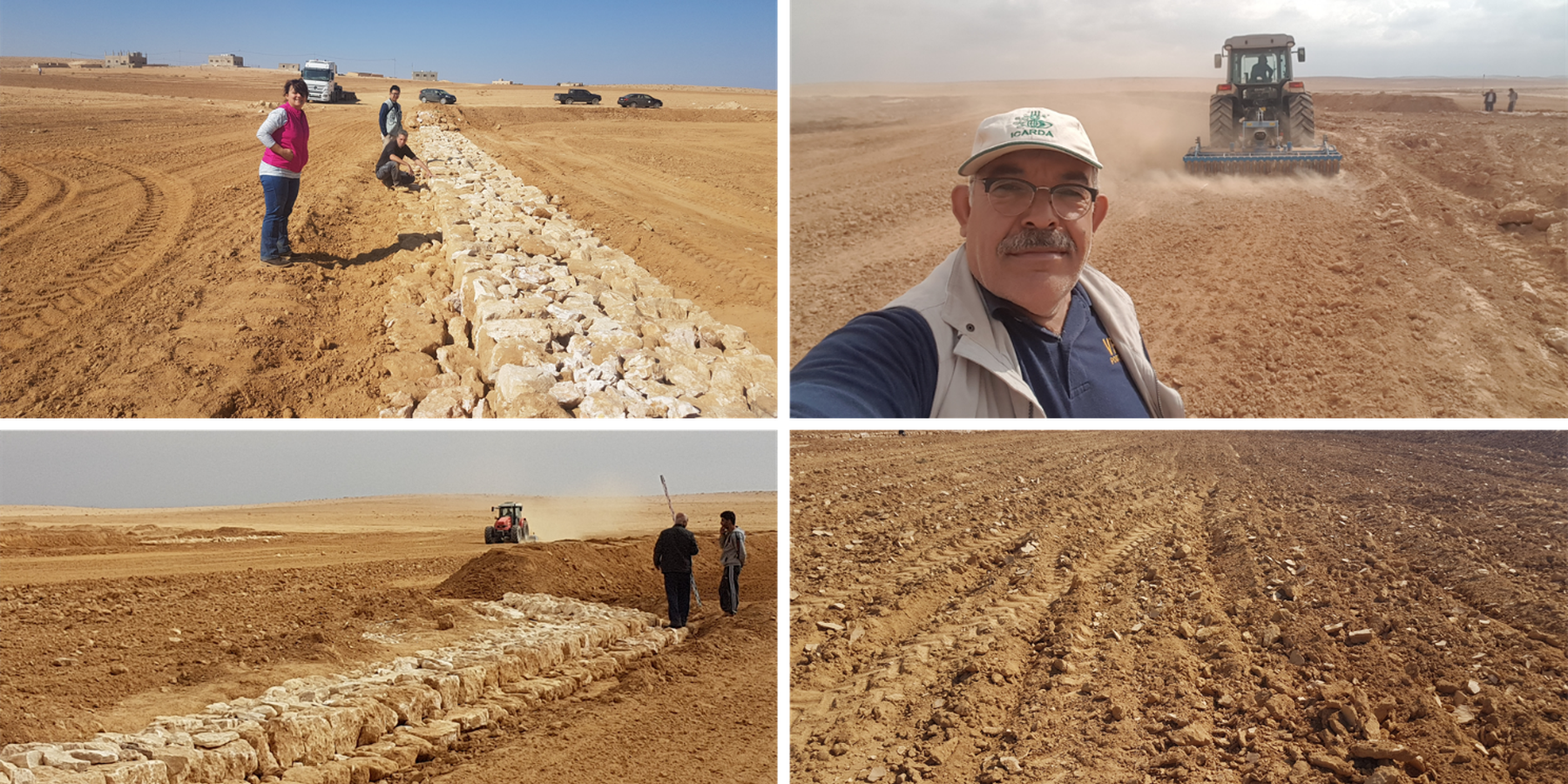
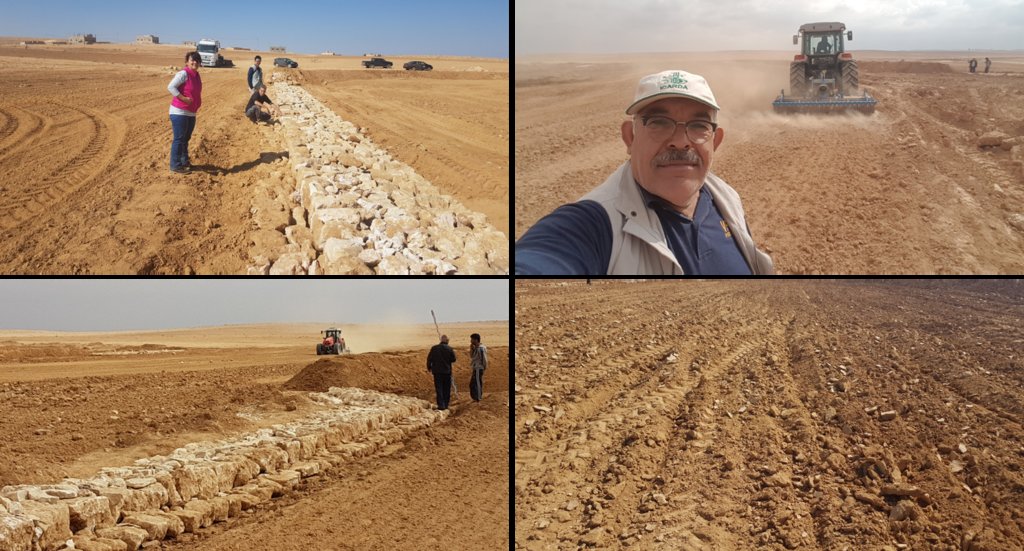
The technology diverts and spreads excess runoff over deep-soil flood plains. The technology comprises local gully-filling, grading/leveling of seed bed, and construction of a bund-and-spillway system creating several compartments for flood-irrigated agriculture.
2.2 Технологийн дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт
Тодорхойлолт:
Arid drylands of Jordan receive less than 200mm average annual rainfall. The specific site is located close by Al Majeddyeh village, around 30km south-east of Amman. The average annual rainfall at the site is around 130mm. The average temperature is above 18 degrees Celsius. The human environment is characterized by agro-pastoralists. These are farmers that live in permanent houses but transport their livestock to graze. As consequence of the natural environment and mis-management (e.g. overgrazing) desertification has been an increasingly problem, not only from an environmental perspective (e.g. carbon stocking; lack of water), but also from an socio-economic perspective, because desertification leads to reduced productive lands, consequently resulting in less income for the rural population.
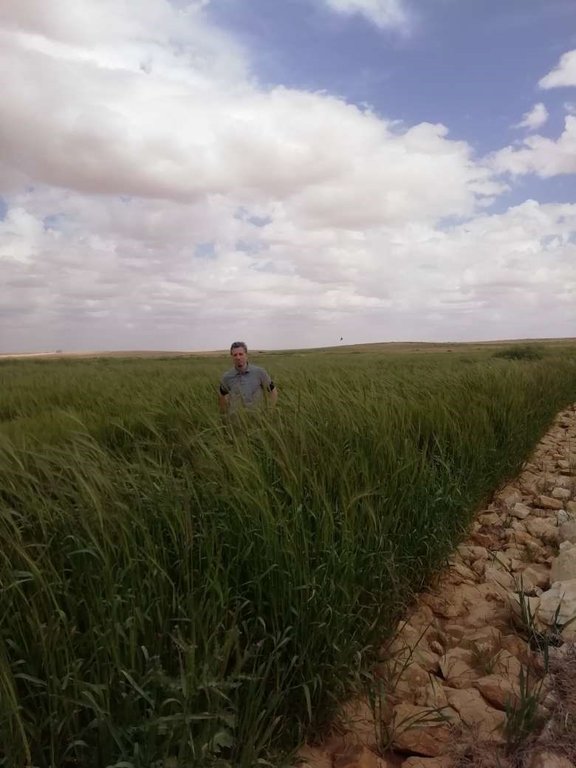
Therefore, the aim of the technology is to achieve high-yield agriculture through flood/macro-catchment water harvesting in arid environments commonly unsuitable for field crop agriculture, creating beneficial impact for local land users. The high yield barley is fed to the livestock (goats and sheeps) of the local agro-pastoralists. Applied in an integrated watershed approach, it meets agricultural demands and motivates sustainable dryland ecosystem management in the uplands. The Marab-technology has a buffering effect on extreme runoff through water retention, for further use in downstream areas, including the trapping of relative fertile sediments from upstream. As the Marab increases yields, it also improves the livelihood of the local population.
The Marab-technology is a macro-catchment water harvesting technology. The Marab is located in the natural depression of the watershed (10 square kilometres), therefore most of the water from the watershed is captured here, instead of being spilled away. Combining this natural depression with the construction of bunds and specific soil leveling, leads to decreased run-off, thus highly increased water infiltration and soil moisture. Thereby, the biomass-production increased as well.
The watershed is characterized by degraded lands upstream (720 ha), where low yield and subsidized barley cultivation is practiced, and by gullies. In a limited part (12 ha) of the upstream area, Vallerani micro-catchments are implemented as a pilot-plot. This might seem contradicting since upstream micro-catchment water harvesting decreases the water in the Marab downstream. However, the Vallerani micro-catchments also have beneficial impacts on the watershed and the Marab, such as flattening peak water flows, reducing erosion and providing fodder. The reduction in water run-off for the Marab as consequence of the Vallerani structures is not significant, due to the small size of the pilot area. But the relations between upstream and downstream should be taken into account.
Upstream watershed measures to buffer and/or avoid extreme runoff events (extreme downstream flooding) in the Marab such as micro-catchment water harvesting structures (Vallerani tractor plow system) and the out-planting of native shrub seedlings, as well as the stabilization of erosive gully systems through gully plugging and revegetation of side banks are advised to be taken before implementing the Marab technology downstream, as they safeguard and protect the Marab. But they are not further into account in this documentation.
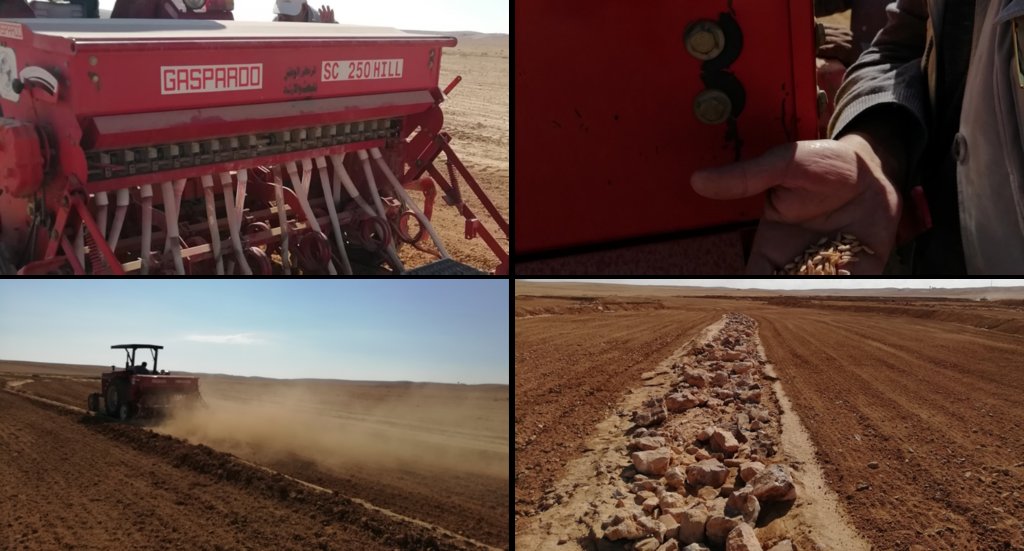
Establishment of the downstream Marab system includes:
•Local filling of downstream gull(system) with deep soil
•Leveling/grading of flood plains
•Construction of earth bunds
•Construction of the spillways (stone made)
• Seedbed preparation for planting annual crop such as barley
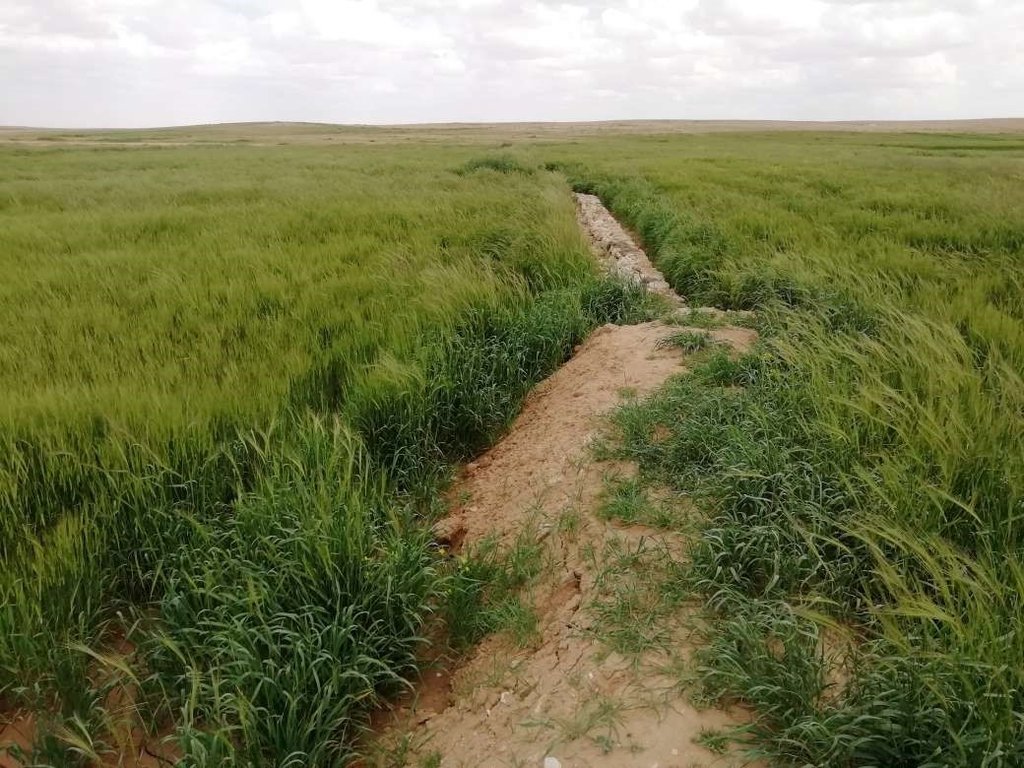
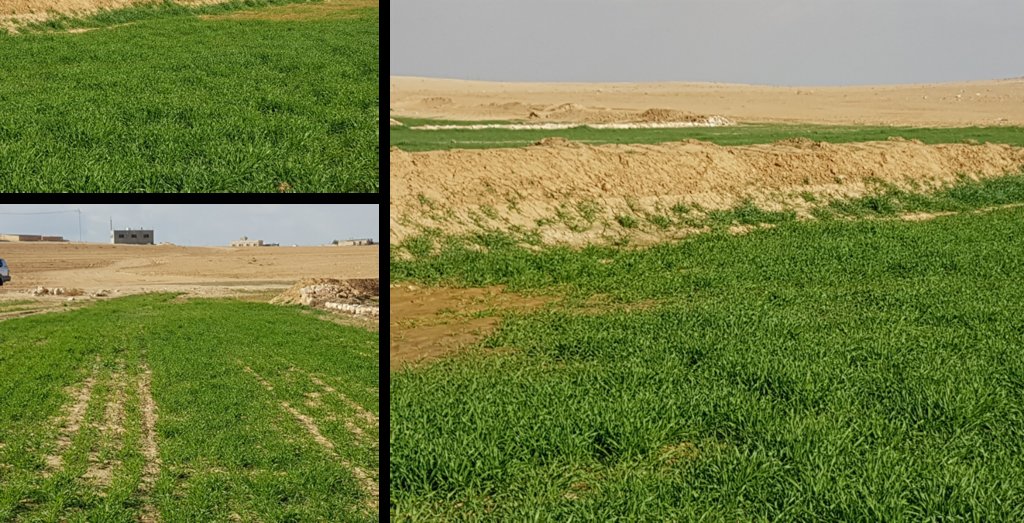
Marab agricultural production is high and stable. It can reach around 5-6 t ha-1 of barley, compared with the low and strongly varying yields of around 0.05-0.30 t ha-1 in traditionally, without macro water harvesting, cultivated barley. Marab barley produces grains (for fodder and reseeding purposes) and requires local inputs, such as fertilizer. The Marab mitigates downstream flooding and loss of sediments from the watershed. Local farmers applying the Marab technology are very satisfied, because of the extremely increased yield as consequence of the technology. However, as water is captured in the watershed, tensions may arise between the downstream (Marab) users and the upstream users.
2.3 Технологийн гэрэл зураг
2.5 Энэ үнэлгээнд хамрагдсан технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн улс орон/ бүс нутаг/ байршил
Улс:
Йордан
Улс/аймаг/сум:
Al Jiza District
Байршлын дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт:
Al Majeddyeh Village
Технологи өргөн дэлгэрсэн эсхийг тодорхойл:
- тодорхой газар хэрэгжсэн/ жижиг талбайд төвлөрсөн
Технологи(иуд) нэвтрүүлсэн талбай тусгай хамгаалалттай газар нутагт байрладаг уу?
Үгүй
Map
×2.6 Хэрэгжсэн хугацаа
Хэрэгжүүлсэн он:
2017
2.7 Технологийн танилцуулга
Технологийг хэрхэн нэвтрүүлснийг тодорхойл:
- Туршилт/судалгааны үр дүн
- Гадны төсөл/хөтөлбөрийн дэмжлэгтэйгээр
3. ГТМ технологийн ангилал
3.1 Технологийн үндсэн зорилго (ууд)
- үйлдвэрлэлийг сайжруулах
- газрын доройтлыг бууруулах, сэргийлэх, нөхөн сэргээх
- гамшгийн эрсдлийг бууруулах
- уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт/ экстрим байдал болон түүний нөлөөлөлд дасан зохицох
- үр ашигтай эдийн засгийн нөлөөг бий болгох
3.2 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын одоогийн газар ашиглалтын хэлбэр(үүд)
Нэг газр нутгийн хэмжээнд хэрэгжих холимог газар ашиглалт:
Тийм
Газар ашиглалтын холимог тогтолцоог (тарилан/бэлчээр/ой мод) тодорхойл:
- Агро-бэлчээр (тарилан-мал аж ахуйн хослуулсан тогтолцоог хамруулан ойлгоно)

Тариалангийн талбай
- Нэг наст үр тариа
Нэг наст үр тариа - Таримлыг тодорхойлно уу:
- үр тариа - арвай
Жилд ургамал ургах улирлын тоо:
- 1
Сөөлжлөн тариалалт хийгддэг үү?
Үгүй
Таримлыг ээлжлэн тариалдаг уу?
Үгүй

Бэлчээрийн газар
Бэлчээрийн мал аж ахуй:
- Хагас нүүдлийн бэлчээрийн аж ахуй
Эрчимжсэн мал аж ахуй / тэжээл үйлдвэрлэл:
- Хадлан буюу бэлчээрт ашиглагдахгүй талбай
Амьтдын төрөл зүйл:
- ямаа
- хонь
Тариалан-мал аж ахуйн нэгдсэн менежмент хэрэгждэг үү?
Үгүй
3.3 Технологи хэрэгжүүлснээр газар ашиглалтад өөрчлөлт гарсан уу?
Технологи хэрэгжүүлснээр газар ашиглалтад өөрчлөлт гарсан уу?
- Үгүй (3.4 руу шилжинэ үү)
3.4 Усан хангамж
Технологи хэрэгжүүлсэн газрын усан хангамж:
- Байгалийн усалгаатай
Тайлбар:
The Marab facilitates uniform distribution of excess rainwater obtained from the upland (partly Vallerani micro-catchments) and the water is conveyed through rehabilitated gullies to the Marab. (Some) Micro catchments and rehabilitated gullies are essential to avoid damaging water peaks, harming the Marab-structures. The Marab is rainfed and naturally flood irrigated.
3.5 Технологи ГТМ-ийн аль бүлэгт хамаарах вэ
- хөрс/ ургамлын бүрхэвч сайжруулах
- Ус хуримтлуулах
- Усны урсац зохицуулах болон салаалах
3.6 Технологийг бүрдүүлэх ГТМ арга хэмжээ

Агрономийн арга хэмжээ
- А3: Хөрсний гадаргыг сайжруулах
- А4: Хөрсний үе давхаргыг сайжруулах

Барилга байгууламжийн арга хэмжээ
- S2: Далан, хаалт
- S3: Шаталсан суваг, шуудуу, голдирол
3.7 Технологид харгалзах газрын доройтлын төрөл

хөрс усаар эвдрэх
- Wt: Хөрсний гадаргын угаагдал
- Wg: Гуу жалгын элэгдэл
- Wo: Усны элэгдлийн дам нөлөө

хөрсний физик доройтол
- Pk: Гадарга дээр хагсах, хагарах

биологийн доройтол
- Bc: Ургамлан нөмрөг багасах
- Bq: биомасс буурах

усны доройтол
- Ha: Хуурайшилт
3.8 Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх, сааруулах ба нөхөн сэргээх
Газрын доройтолтой холбоотойгоор Технологи ямар зорилго тавьсан болохыг тодорхойл:
- Газрын доройтлыг бууруулах
Тайлбар:
Retaining surface runoff and locally infiltrating water through bunds increase soil moisture hence agricultural yield increases (e.g. biomass, vegetation cover) , soil crusting decreases (in some selected ponding areas it might increase) - and because of trapping top-soil sediments and residues from the uplands, soil fertility increases likewise.
4. Техникийн нөхцөл, хэрэгжүүлсэн үйл ажиллагаа, материал ба зардал
4.1 Технологийн техник зураг
Техник тодорхойлолт (техник зургийн тайлбар):
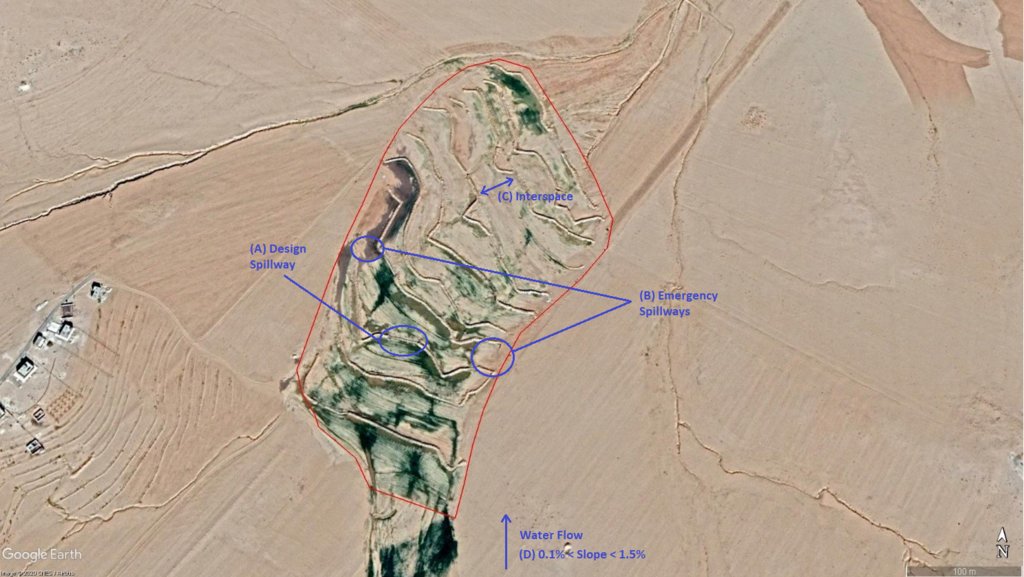
The overall Marab (reshaped flood plain) area is 10 hectares. The natural flood plain was leveled up to the sides; the natural slope in flow direction ranges between 0.1 and 1.5% (D). The later stone bund construction (soil relocation) and siltation/erosion processes over time develop a slight step-terraced bund compartment system, with the single compartments having much smaller slope than the overall Marab. At the sides, the levelled area slightly increases towards the natural terrain (natural terrain at the sides is around 0.1 to 0.3m higher compared with the leveled Marab). This avoids side outflow of water during design storms (*). Bund structures, along the contour, are built with a loader up to around 0.7 to 1.0m height and around 2.0 – 3.0m bottom width. The bunds are built with compaction through the loader. Interspace between the bunds is between 10-50 meters (C), depending on the local slope in the flow direction, having around 0.1 to 0.3m soil surface elevation difference between the bunds. Stone made design-spillways (A) are being constructed around the middle of each bund, with certain position change between the bund in downstream direction. Thus, spillways do not perfectly align with respect to the bund, but create a meandering flow around the center. The stone-protected design-spillways are designed to safely route at least the expected 2-5 year return period flood event. The Marab plain is not perfectly even, especially at the sides, to avoid water flowing around the bunds during design storms. However, the Marab-technology is also designed to cope with more extreme events, a storm of 5-10 return period, without significant damages. Therefore, there are emergency-spillways (**) implemented at the sides of each bund (B). These emergency-spillways allow excess water to flow out sideways rather than flow over the bund which would damage the structures. Note:
Based on above considerations and calculations bund spillway lengths reach 50-60m in the specific watershed.
* A design storm is a rainfall event that results in a flood event as water accumulates throughout the watershed. The Marab is designed to harvest the water optimally by (design) spill ways that keep the water in the Marab. A design storm relates to a certain return period. In general a longer return period (i.e. less frequent) accounts for a more intense event hence a more severe flooding event.
** An emergency spill way is a structure that is designed to discharge excess water coming from storms more extreme than the design storm (i.e. with less frequent storms). In practice this means that the Marab is protected from excess water.
Зохиогч:
Joren Verbist (Extracted from Google Earth Pro on Jan 7th 2019)
Он, сар, өдөр:
19/12/2020
Техник тодорхойлолт (техник зургийн тайлбар):
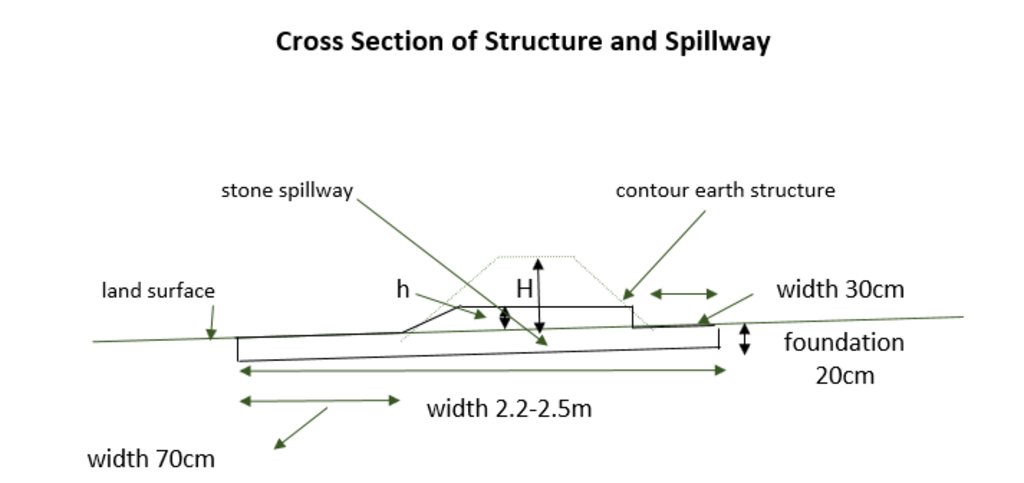
The cross-section shows the dimensions. Downstream of a bund the width is 70 centimeter. The foundation is 20 centimeter high. The upstream width is 30 centimeter. The total width of the bund varies between 2.2 meter and 2.5 meter.
Зохиогч:
Stefan Strohmeier
Он, сар, өдөр:
01/07/2020
4.2 Материал болон зардалд хамаарах ерөнхий мэдээлэл
Үнэ өртөг, оруулсан хувь нэмрийг хэрхэн тооцсоныг тодорхойл:
- Технологийн нэгж тус бүр
Талбайн хэмжээ ба нэгжийг тодорхойл:
10 ha
Үнэ өртөгийг тооцоход ашигласан мөнгөн нэгж:
- Ам.доллар
Хөлсний ажилчны нэг өдрийн цалингийн хэмжээг тодорхойлно уу:
35
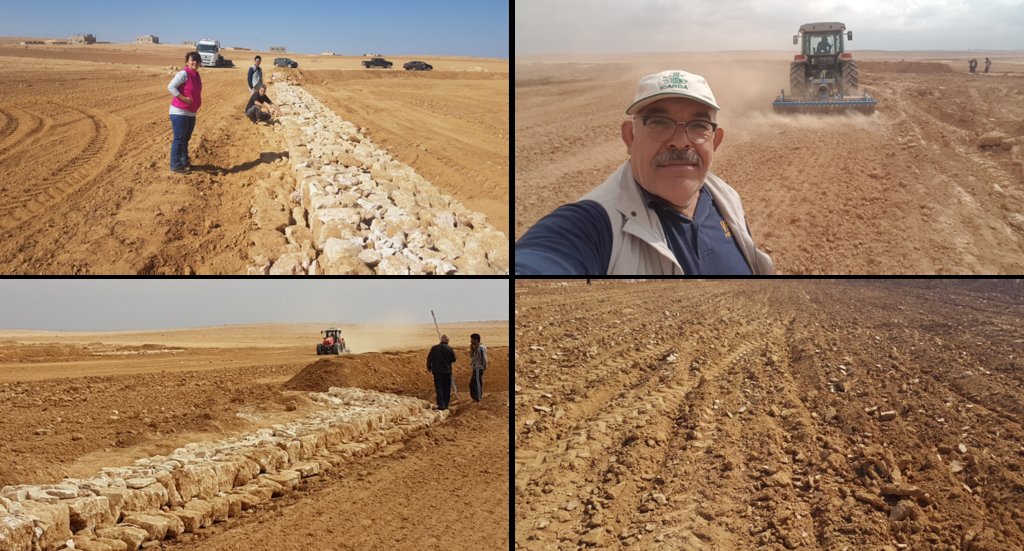
4.3 Бий болгох үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа (улирал) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Implement upstream watershed rehabilitation measure (e.g. Upstream Vallerani micro water harvesting) | Prior of Marab-Technology construction |
| 2. | Implement gully rehabilitation measure (e.g. Midstream gully rehabilitation) | Prior of Marab-Technology construction |
| 3. | Marab site selection (flood plain): topographic assessment (slope, soil depth, etc.) and consideration of watershed hydrology (e.g. for bund and spillway design) | Before the rainy season |
| 4. | Grading/levelling of natural flood plain incl. gully fill (with soil material) | season (Aug. – Nov.) |
| 5. | Implement bund structures (based on step 4) | season (Aug. – Nov.) |
| 6. | Construct stone made design and emergence spillways (based on step 5) | season (Aug. – Nov.) |
| 7. | Preparation of compartmentalized agricultural fields (bund interspaces) for field crop agriculture | season (Aug. – Nov.) |
Тайлбар:
The upstream measures as the Vallerani System and gully rehabilitation are strongly recommended but are not taken into account as costs in this documentation. Because this documentation focuses specifically on the Marab-technology.
4.4 Бий болгоход шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Local Workers | person-days | 50.0 | 35.0 | 1750.0 | |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Land Survey | person-days | 6.0 | 35.0 | 210.0 | |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Engineer (+assistance) | person-days | 15.0 | 50.0 | 750.0 | |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Drivers of heavy machinery | person-days | 12.0 | 35.0 | 420.0 | |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Grader | machine-days | 3.0 | 250.0 | 750.0 | |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Loader | machine-days | 10.0 | 250.0 | 2500.0 | |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Deep Plow | machine-days | 3.0 | 200.0 | 600.0 | |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Tractor (to pull the shallow and deep plow) | machine-days | 5.0 | 200.0 | 1000.0 | |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Shallow Plow | machine-days | 2.0 | 200.0 | 400.0 | |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Water Tank Truck | Tank | 1.0 | 50.0 | 50.0 | |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Small Equipment (Shovel, pickaxe, buckets) | Equipment | 1.0 | 200.0 | 200.0 | |
| Барилгын материал | Stones | Kubic Metre | 200.0 | 10.0 | 2000.0 | |
| Бусад | Transportation of heavy machinery | 1.0 | 2000.0 | 2000.0 | ||
| Бусад | Security | 1.0 | 300.0 | 300.0 | ||
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг | 12930.0 | |||||
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 12930.0 | |||||
Хэрэв газар ашиглагч нийт зардлын 100% -иас бага хэсгийг төлсөн бол хэн голлох зардлыг гаргасан бэ:
ICARDA and National Agricultural Research Centre (NARC)
Тайлбар:
These costs are for establishment (so one-time) and are for the total Marab-technology i.e. 10 ha.
4.5 Арчилгаа/ урсгал үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа/ давтамж | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Maintaining the structures based on observations and possible damages after the rainy season, so no clear maintenance plans | Before the rainy season (Oct. – Nov.)/upon observation |
Тайлбар:
Excludes annual farming costs (e.g. seedbed preparation)
4.6 Арчилгаа/урсгал ажилд шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг (нэг жилд)
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Engineer | person days per year | 2.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Worker | person days per year | 6.0 | 35.0 | 210.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Loader | machine days per year | 1.0 | 250.0 | 250.0 | 100.0 |
| Барилгын материал | Stones | Kubic Metre | 10.0 | 10.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| Технологийн арчилгаа/урсгал үйл ажиллагаанд шаардагдах нийт үнэ өртөг | 660.0 | |||||
| Технологи арчилах ба урсгал ажлын нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 660.0 | |||||
Тайлбар:
The costs of practicing agriculture (e.g. cost of seeds and fertilizer) are not taken into account, since these costs were also made before the implementation of this technology.
4.7 Зардалд нөлөөлж байгаа хамгийн чухал хүчин зүйл
Өртөг, зардалд нөлөөлөх гол хүчин зүйл:
The special and heavy machinery affect the cost significantly, since these were not available in the area. The implementation of the technology is labour intensive, therefore labour costs are significant as well. However, these costs are initially, so these specific costs are almost zero after establishment. In addition, all the maintenance is payed for by the land users. So, only the establishment was payed for by external parties.
5. Байгаль ба нийгмийн нөхцөл
5.1 Уур амьсгал
Жилийн нийлбэр хур тундас
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1,000 мм
- 1,001-1,500 мм
- 1,501-2,000 мм
- 2,001-3,000 мм
- 3,001-4,000 мм
- > 4,000 мм
Жилийн дундаж хур тунадас (хэрэв мэдэгдэж байвал), мм:
130.00
Хур тунадасны талаархи тодорхойлолт/ тайлбар:
In the specific site/dry areas of Jordan rainy season usually ranges from November until April
Queen Alia International Airport long-time avergae annual rainfall is around 150 mm (around 10km west of the site)
At the site a rainfall tipping bucket has been installed in 2016.
Холбогдох цаг уурын станцын нэр:
Queen Alia International Airport
Агро-уур амьсгалын бүс
- хуурай
The maximum temperature usually occurres in August.
The average daily maximum temperature is 25.01 °C.
The average daily minimum temperature is 8.5 °C
5.2 Гадаргын хэлбэр
Дундаж налуу:
- хавтгай (0-2 %)
- бага зэрэг налуу (3-5 %)
- дунд зэрэг налуу (6-10 % )
- хэвгий (11-15 %)
- налуу (16-30 %)
- их налуу (31-60 % )
- эгц налуу (>60 %)
Гадаргын хэлбэр:
- тэгш өндөрлөг / тал
- нуруу
- уулын энгэр
- дов толгод
- бэл
- хөндий
Өндрийн бүслүүр:
- 0-100 д.т.д. м.
- 101-500 д.т.д. м.
- 501-1,000 д.т.д м.
- 1,001-1,500 д.т.д м.
- 1,501-2,000 д.т.д м.
- 2,001-2,500 д.т.д. м.
- 2,501-3,000 д.т.д. м.
- 3,001-4,000 д.т.д м.
- > 4,000 д.т.д. м.
Технологи дараах асуудалд хандсан эсэхийг тодорхойл:
- гүдгэр нөхцөл
Гадаргын талаархи тодорхойлолт ба бусад тайлбар:
The Marab itself is rather concave (depression shape) / natural depression. However, the bund structures are convex, spreading water over the field.
5.3 Хөрс
Хөрсний дундаж зузаан:
- маш нимгэн (0-20 см)
- нимгэн (21-50 см)
- дунд зэрэг зузаан (51-80 см)
- зузаан (81-120 cм)
- маш зузаан (>120 cм)
Хөрсний бүтэц (өнгөн хөрс):
- дундаж (элсэнцэр, шавранцар)
- нарийн /хүнд (шаварлаг)
Хөрсний бүтэц (>20 см-ээс доош):
- дундаж (элсэнцэр, шавранцар)
Өнгөн хөрсөнд агуулагдах ялзмаг:
- бага (<1 % )
5.4 Усны хүртээмж ба чанар
Гүний усны түвшин:
> 50 м
Гадаргын усны хүртээмж:
хангалтгүй/ байхгүй
Усны чанар (цэвэршүүлээгүй):
ашиглах боломжгүй
Усны чанар гэж:
гадаргын ус
Усны давсжилтын асуудал бий юу?
Үгүй
Энэ газар үерт автдаг уу?
Тийм
Тогтмол байдал:
байнга
5.5 Биологийн олон янз байдал
Зүйлийн олон янз байдал:
- Бага
Амьдрах орчны олон янз байдал:
- Бага
5.6 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчдын тухай мэдээлэл
Суурьшмал эсвэл нүүдлийн:
- Хагас-нүүдэлийн
Үйлдвэрлэлийн системийн зах зээлийн чиг баримжаа:
- холимог (амьжиргаа ба худалдаанд)
Бусад эх үүсвэрээс олох орлого:
- Нийт орлогын 10 %-иас доош
Чинээлэг байдлын түвшин:
- ядуу
- дундаж
Хувь хүн эсвэл бүлэг:
- Хувь хүн / өрх
Механикжилтын түвшин:
- механикжсан / мотортой
Хүйс:
- эрэгтэй
Газар ашиглагчийн нас:
- залуус
- дунд нас
Газар ашиглагчдын бусад шинж чанарыг тодорхойл:
The actual land users are often poor Jordanians or Syrian refugees. However, the owners of the livestock are relatively rich. The landowners are responsible for the maintenance of the intervention.
5.7 Газар ашиглагчийн технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын дундаж талбайн хэмжээ
- < 0.5 га
- 0.5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1,000 га
- 1,000-10,000 га
- > 10,000 га
Энэ талбай том, жижиг, дунд алинд хамаарах вэ (орон нутгийн нөхцөлд харгалзуулна уу)?
- дунд-хэмжээний
Тайлбар:
10ha
5.8 Газар эзэмшил, газар ашиглах эрх, ус ашиглах эрх
Газар өмчлөл:
- хувь хүн, өмчийн гэрчилгээтэй
Газар ашиглах эрх:
- түрээсийн хэлбэрээр
- хувь хүн
- NA
Газар ашиглах эрх нь уламжлалт эрхзүйн тогтолцоонд суурилсан уу?
Тийм
5.9 Дэд бүтэц, үйлчилгээний хүртээмж
эрүүл мэнд:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
боловсрол:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
техник зөвлөгөө:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт (жишээ нь, ХАА-аас өөр):
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
зах зээл:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
эрчим хүчний хангамж:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
зам тээвэр:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
усан хангамж ба ариутгал:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
санхүүгийн үйлчилгээ:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
6. Үр нөлөө ба дүгнэлт
6.1 Технологийн талбайд үзүүлсэн нөлөө
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн үр нөлөө
Үйлдвэрлэл
газар тариалангийн үйлдвэрлэл
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
The crops produced are used as fodder
тэжээл үйлдвэрлэл
ГТМ хэрэгжихээс өмнөх тоо хэмжээ:
0.05ton/ha
ГТМ хэрэгжиснээс хойшхи тоо хэмжээ:
5ton/ha
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
The production of the fodder is increased as the barley yield is mostly used to feed animals and also the stubble is grazed.
тэжээлийн чанар
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
The barley is fed to the livestock
үйлдвэрлэлийн газар
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Due to the bunds (but very limited and inevitable)
газрын менежмент
Орлого, зарлага
ХАА-н зардал
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Expenses are slightly increased due to possible maintenance of the Marab. However, the increased yield justifies this.
тухайн аж ахуйн орлого
ажлын хэмжээ
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Due to possible maintenance
Нийгэм-соёлын үр нөлөө
хүнсний аюулгүй байдал/ өөрийн хэрэгцээг хангах
ГТМ/ газрын доройтлын мэдлэг
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
During the construction, local community were hired as workers, this has significantly boosted their knowlegde about SLM.
Экологийн үр нөлөө
Усны эргэлт/ илүүдэл
ус хураах / цуглуулах
гадаргын урсац
усны урсац
гүний усны түвшин / уст давхарга
Хөрс
хөрсний чийг
хөрсөн бүрхэвч
хөрс алдагдах
хөрс хуримтлагдах
хөрс хагарах/ хагсах
хөрсний органик нэгдэл/ хөрсөнд агуулагдах карбон
Биологийн олон янз байдал: ургамал, амьтан
Ургамалын бүрхэвч
газрын дээрхи / доорхи карбон
Уур амьсгал болон гамшгийн эрсдлийг бууруулах
үер усны нөлөө
гангийн нөлөө
6.2 Технологийн талбайн гадна үзүүлсэн үр нөлөө
голын адагт үерлэх
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Reduced downstream flooding is desired
голын адагт лаг шавар хуримтлагдах
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Reduced downstream siltation is desired
6.3 Технологийн уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт, цаг агаарын гамшигт үзэгдэлд өртөх байдал ба эмзэг байдал (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)
Уур амьсгалын аажим өөрчлөлт
Уур амьсгалын аажим өөрчлөлт
| Улирал | Өсөх эсвэл буурах | Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| жилийн дундаж хур тундас | Бууралт | сайн |
Уур амьсгалаас хамаарах аюул (гамшиг)
Цаг уурын гамшигт үзэгдэл
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| орон нутгийн аадар бороо | маш сайн |
Усзүйн гамшиг
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| шар усны үер | маш сайн |
6.4 Өртөг ба ашгийн шинжилгээ
Бий болгох зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
бага зэрэг сөрөг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Арчилгаа/урсгал зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
маш эерэг
Тайлбар:
The initial investment is quite large. Therefore, the short term returns is classified as slightly negative. After some seasons with good (stable) crop yield the return of investment is positive. Long term benefits are classified positively.
6.5 Технологи нэвтрүүлэлт
- 1-10 %
Боломжтой бол, тоогоор илэрхийл (өрхийн тоо эсвэл бүрхэх талбай):
These are some farmers that live near the Marab. They try to copy the Marab in their fields.
Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн хүмүүсээс хэд нь өөрийн хүчээр технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн бэ, өөрөөр хэлбэл гадны тусламж дэмжлэг авалгүйгээр?
- 91-100%
Тайлбар:
The local farmers like the technology and acknowledge its positive impacts. They would like to have a Marab themselves (even if their locally owned lands are not suitable in many cases). Local agro-pastoralists copy and apply parts of the technology (especially the bund
system). However, it strongly recommended that implementing a Marab-technology is done as a community-based project/intervention; the Marab technology should be part of an integrated watershed management plan, located at the most suitable location for the entire community.
6.6 Дасан зохицох
Бий болсон өөрчлөлтөд зохицуулан технологийг өөрчилсөн үү?
Тийм
Хэрэв Тийм бол ямар өөрчлөлтөд дасан зохицсон бэ:
- уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт/ экстрим үзэгдэл
Дасан зохицох зорилгоор технологид хийсэн өөрчлөлт (хийц, материал, төрөл зүйл г.м.):
The spillway design can be adapted to variable surface runoff occurrence (affected by climate change).
6.7 Технологийн давуу тал/боломжууд
| Газар ашиглагчдын тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
| The farmers highly appreciate the improved economic situation as consequence of the increased yield. |
| A strength of the Marab technology is that water is harvested and minimally spilled away, preventing top-soil erosion and accumulating soil organic matter consequently preserving soil fertility. |
| The crop produces grains: can be (partially) used for re-seeding in the coming seasons; economic gain + increase resilience. |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
| Economic improvement through targeted agricultural interventions in the most suitable location(s) of a watershed. This aims at decreasing the pressure on the fragile dry land ecosystem. The locally increased yield raises awareness on non-sufficient field crop agriculture in uplands (commonly achieved) and might increase the willingness for more nature-based sustainable land management measures in the less fertile and runoff generating (more vulnerable uplands) parts of the watershed. Therefore, the Marab technology could be a starting point for a watershed rehabilitation initiative. |
| The Marab technology creates an opportunity for multiple crop introduction (due to natural flood irrigation) – aside from barley monoculture (agro-diversity). |
| Increased water infiltration conserves water and might lead to deep percolation (groundwater recharge). |
6.8 Технологийн дутагдалтай/сул тал/аюул болон тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах арга зам
| Газар ашиглагч нарын тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| The Marab depends on upstream water users; can lead to increased tensions | Agreement among the community - conducting contacts/contracts among upstream and downstream farmers. Joint watershed management and benefit share could be mediate these tension. And might even lead to watershed rehabilitation. |
| High initial investment and partially high maintenance costs (including machinery) | Once the implementation is linked with larger environmental benefits – communities might receive funds from the government or international donors. |
| Loss of cultivation area where the bunds are placed | Unavoidable. However, the gain of interspaces exceeds these losses several times. |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| Tensions among multiple actors in the watershed (selection of Marab area) | Develop institutions that could avoid these tensions by establishing agreements, contracts, rules, or regulations. |
| Heavy machinery in a vulnerable ecosystems – can induce other requests/use by locals (improper use) | Targeted policies in place & enforcements |
| Increasing wealth inequality between farmers and/or communities. | Creation of institutions, which assure fair distribution. This would benefit the whole watershed. |
7. Ном зүй ба холбоосууд
7.1 Мэдээлэл цуглуулсан арга/эх үүсвэр
- Хээрийн уулзалт, судалгаа
- Газар ашиглагчтай хийсэн ярилцлага
- ГТМ-ийн мэргэжилтэн/шинжээчтэй хийсэн ярилцлага
- тайлан болон бусад эх сурвалжийн бүрдэл
Мэдээллийг хэзээ (газар дээр нь) цуглуулсан бэ?
15/04/2020
7.2 Ном, хэвлэлийн ишлэл
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Strohmeier, S. (2017). Dimensioning of Marab in Majidyya.
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Strohmeier, S. (2017). Watershed Restoration in Baia Areas of Jordan Technology Packages for Controlling and Monitoring Gully Erosion.
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
https://mel.cgiar.org/projects/jordan-watershed-restoration-project
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Mira Haddad, Stefan Strohmeier. (12/12/2017). Treated upland areas map. Jordan: International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA).
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/9108
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Stefan Strohmeier, Mira Haddad, Ismail Shukri. (8/11/2018). Marab - water harvesting based agriculture.
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/9069
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Boubaker Dhehibi, Mira Haddad, Stefan Strohmeier, Masnat El-Hiary. (24/7/2020). Enhancing a Traditional Water Harvesting Technique in Jordan’s Agro-pastoral Farming System. Lebanon: International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA).
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/11506
7.3 Холбогдох мэдээллийн интернет холбоос
Гарчиг/ тодорхойлолт:
WATER HARVESTING FOR RESTORING RANGELANDS IN JORDAN
URL:
https://www.icarda.org/media/drywire/water-harvesting-restoring-rangelands-jordan
Холбоос ба модулууд
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаахХолбоосууд
Холбоос байхгүй байна
Модулууд
Модуль байхгүй байна