Marab - Water Harvesting Based Floodplain Agriculture [จอร์แดน]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Joren Verbist
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: Mira Haddad, Enrico Bonaiuti
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Marab in Arabic “المرب”
technologies_5770 - จอร์แดน
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
วิทยากรหลัก
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Strohmeier Stefan
International Center of Agriculture Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA)
จอร์แดน
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Natural Resources Economist Social, Economy & Policy Research:
Dhehibi Boubaker
International Center of Agriculture Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA)
จอร์แดน
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
ICARDA Institutional Knowledge Management Initiativeชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA) - เลบานอน1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
This technology conserves soil and water; it reduces surface water and sediment losses from dryland watersheds. The technology is located in downstream/lowland floodplains, and ideally, it is implemented in an integrated watershed approach. In the present case study, the ‘Marab’ is linked with two main upstream measures: Upland micro-water harvesting (Vallerani system) and gully/channel measures (gully plugs)
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
The Marab is a local downstream water harvesting measure in an integrated watershed context, where up/midstream users and applied land management practices affect the Marab.
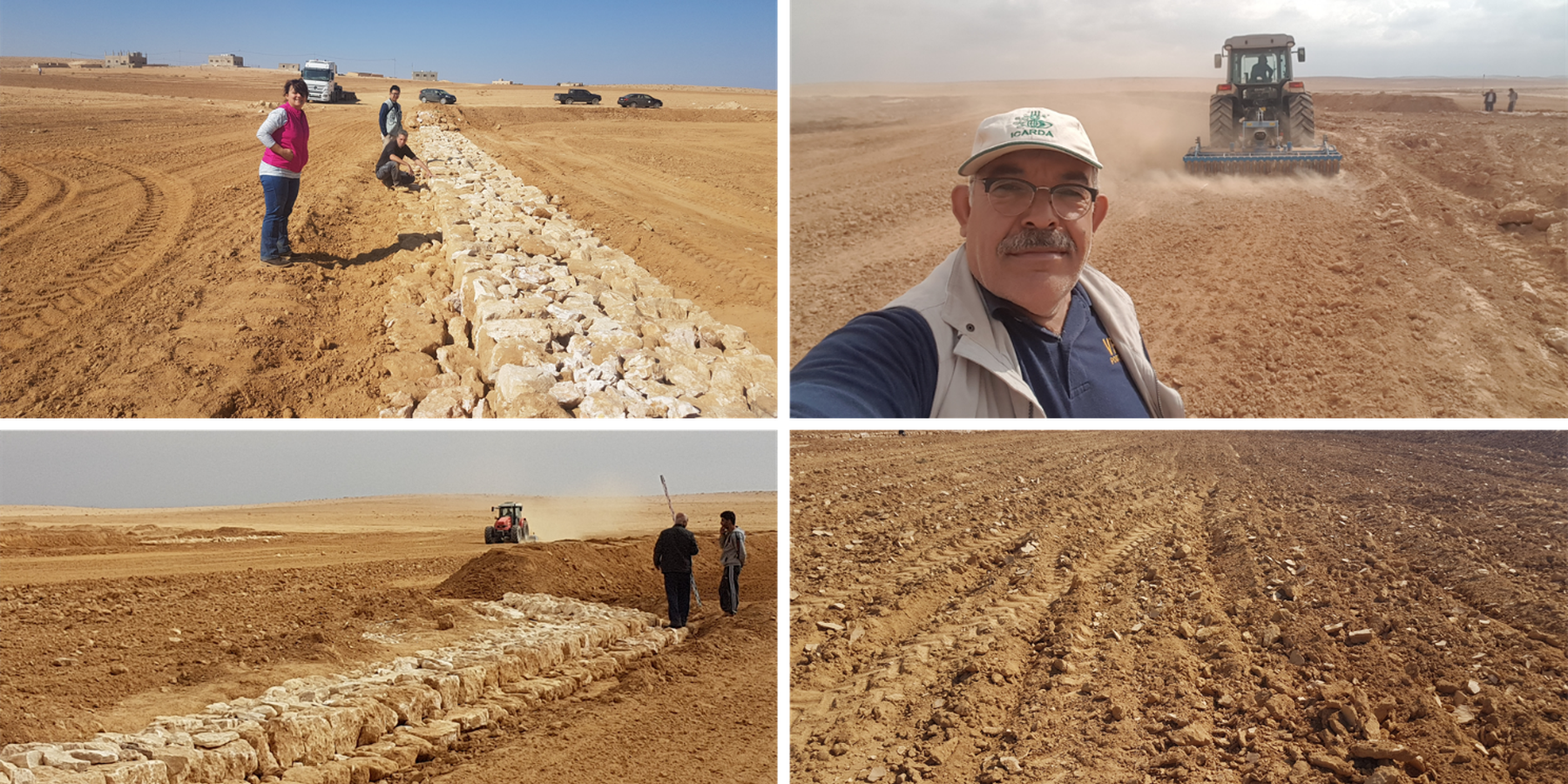
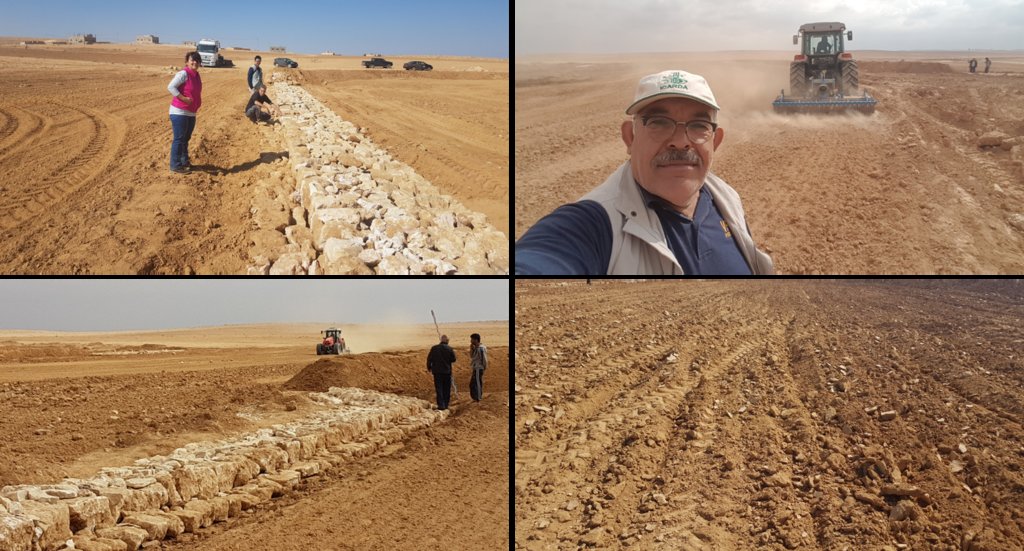
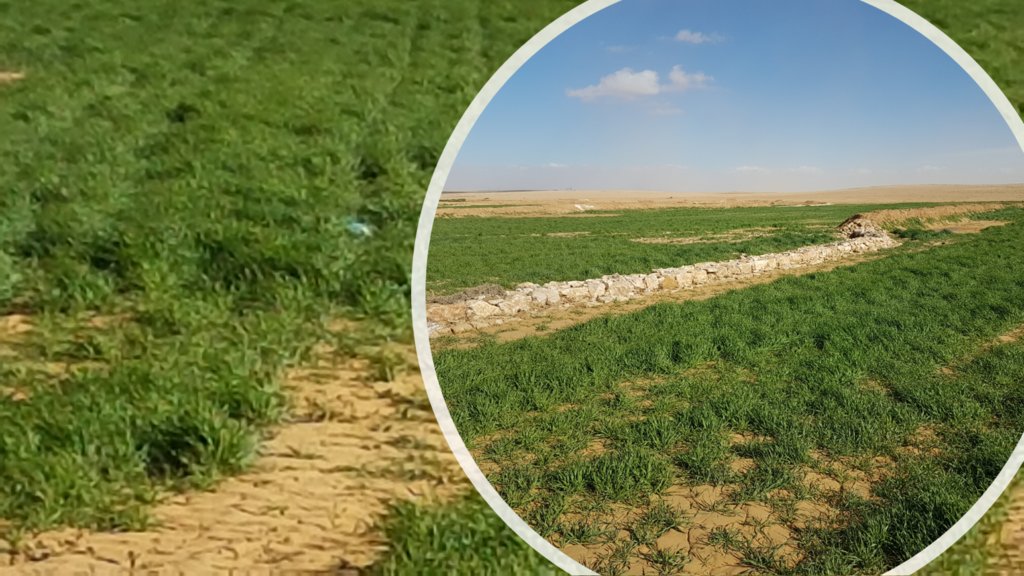
The technology diverts and spreads excess runoff over deep-soil flood plains. The technology comprises local gully-filling, grading/leveling of seed bed, and construction of a bund-and-spillway system creating several compartments for flood-irrigated agriculture.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
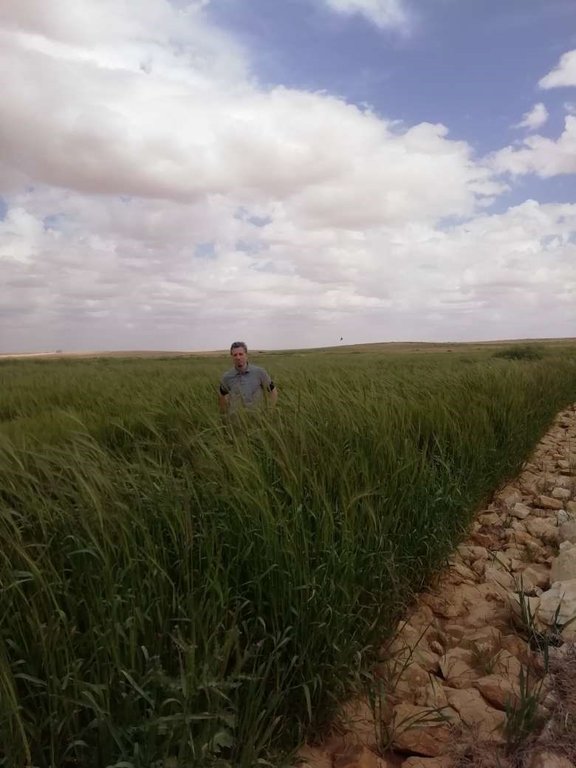
Arid drylands of Jordan receive less than 200mm average annual rainfall. The specific site is located close by Al Majeddyeh village, around 30km south-east of Amman. The average annual rainfall at the site is around 130mm. The average temperature is above 18 degrees Celsius. The human environment is characterized by agro-pastoralists. These are farmers that live in permanent houses but transport their livestock to graze. As consequence of the natural environment and mis-management (e.g. overgrazing) desertification has been an increasingly problem, not only from an environmental perspective (e.g. carbon stocking; lack of water), but also from an socio-economic perspective, because desertification leads to reduced productive lands, consequently resulting in less income for the rural population.
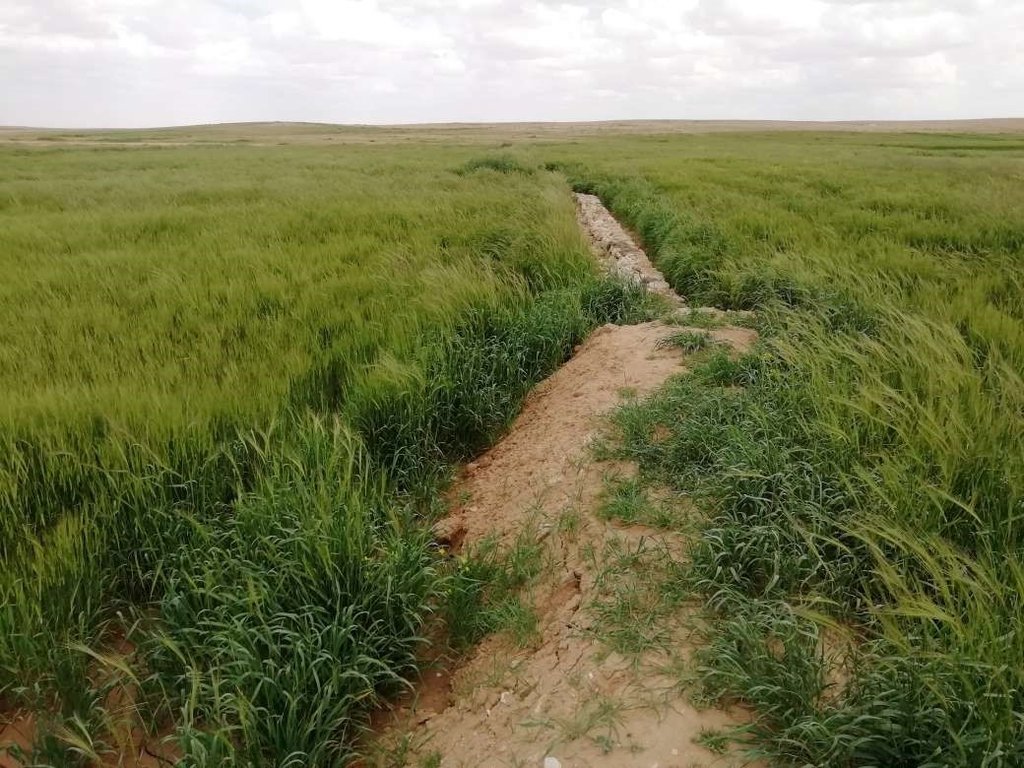
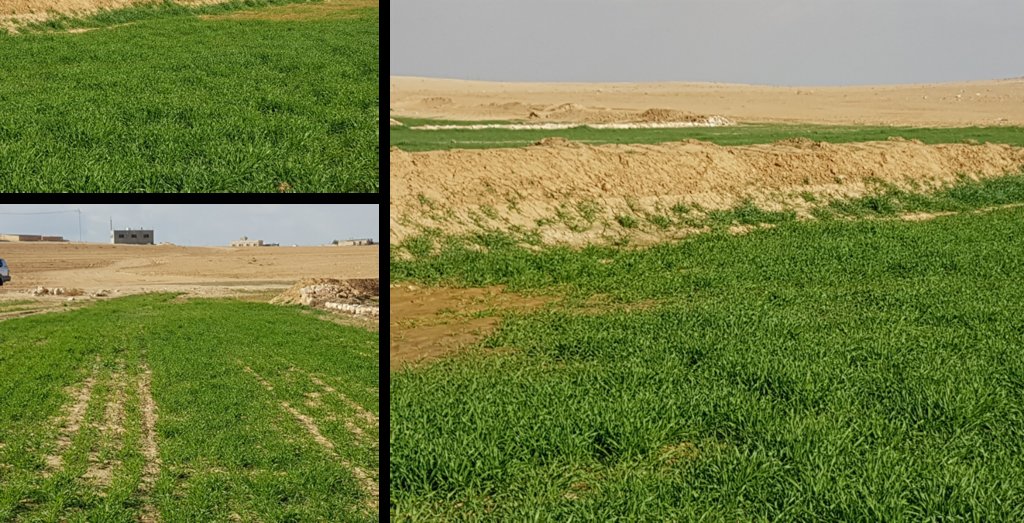
Therefore, the aim of the technology is to achieve high-yield agriculture through flood/macro-catchment water harvesting in arid environments commonly unsuitable for field crop agriculture, creating beneficial impact for local land users. The high yield barley is fed to the livestock (goats and sheeps) of the local agro-pastoralists. Applied in an integrated watershed approach, it meets agricultural demands and motivates sustainable dryland ecosystem management in the uplands. The Marab-technology has a buffering effect on extreme runoff through water retention, for further use in downstream areas, including the trapping of relative fertile sediments from upstream. As the Marab increases yields, it also improves the livelihood of the local population.
The Marab-technology is a macro-catchment water harvesting technology. The Marab is located in the natural depression of the watershed (10 square kilometres), therefore most of the water from the watershed is captured here, instead of being spilled away. Combining this natural depression with the construction of bunds and specific soil leveling, leads to decreased run-off, thus highly increased water infiltration and soil moisture. Thereby, the biomass-production increased as well.
The watershed is characterized by degraded lands upstream (720 ha), where low yield and subsidized barley cultivation is practiced, and by gullies. In a limited part (12 ha) of the upstream area, Vallerani micro-catchments are implemented as a pilot-plot. This might seem contradicting since upstream micro-catchment water harvesting decreases the water in the Marab downstream. However, the Vallerani micro-catchments also have beneficial impacts on the watershed and the Marab, such as flattening peak water flows, reducing erosion and providing fodder. The reduction in water run-off for the Marab as consequence of the Vallerani structures is not significant, due to the small size of the pilot area. But the relations between upstream and downstream should be taken into account.
Upstream watershed measures to buffer and/or avoid extreme runoff events (extreme downstream flooding) in the Marab such as micro-catchment water harvesting structures (Vallerani tractor plow system) and the out-planting of native shrub seedlings, as well as the stabilization of erosive gully systems through gully plugging and revegetation of side banks are advised to be taken before implementing the Marab technology downstream, as they safeguard and protect the Marab. But they are not further into account in this documentation.
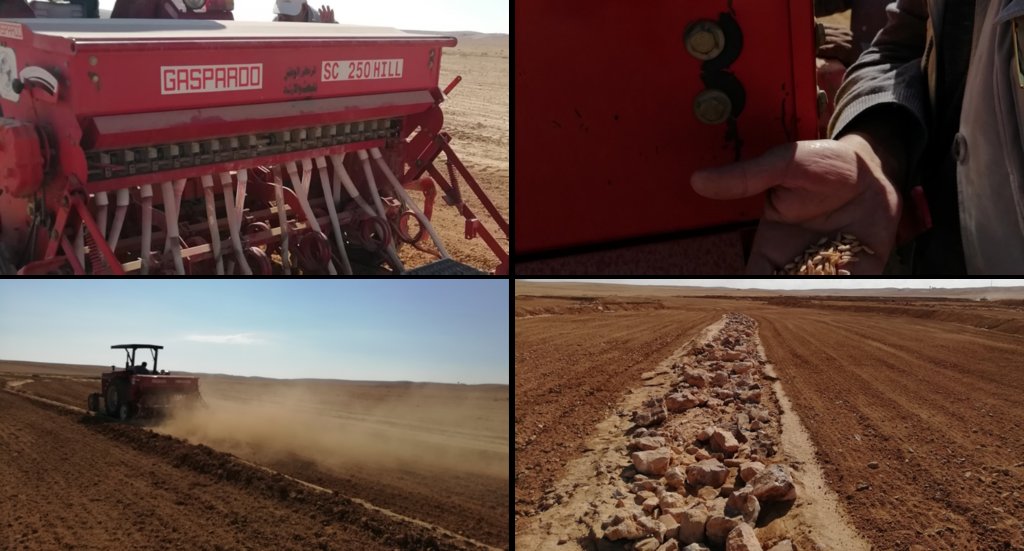
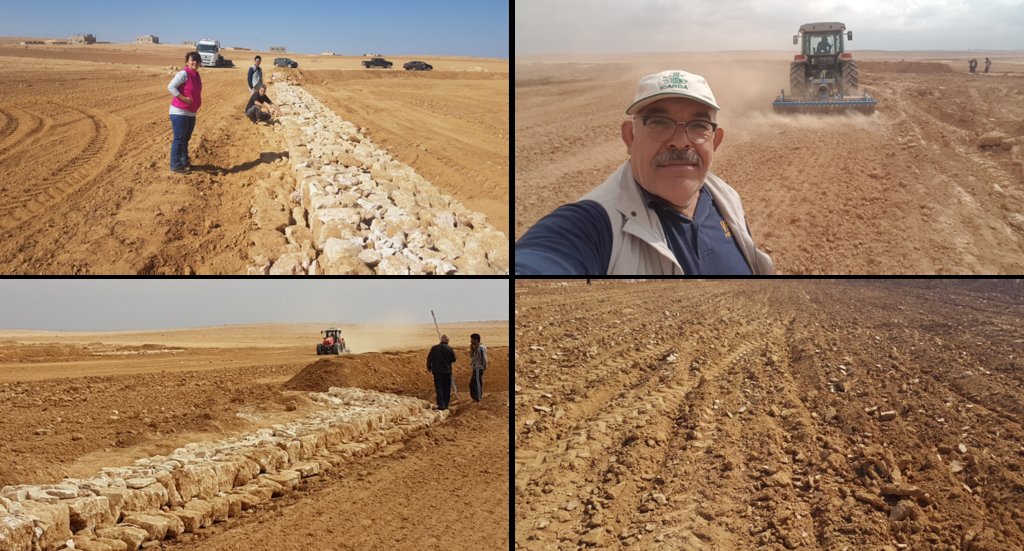
Establishment of the downstream Marab system includes:
•Local filling of downstream gull(system) with deep soil
•Leveling/grading of flood plains
•Construction of earth bunds
•Construction of the spillways (stone made)
• Seedbed preparation for planting annual crop such as barley
Marab agricultural production is high and stable. It can reach around 5-6 t ha-1 of barley, compared with the low and strongly varying yields of around 0.05-0.30 t ha-1 in traditionally, without macro water harvesting, cultivated barley. Marab barley produces grains (for fodder and reseeding purposes) and requires local inputs, such as fertilizer. The Marab mitigates downstream flooding and loss of sediments from the watershed. Local farmers applying the Marab technology are very satisfied, because of the extremely increased yield as consequence of the technology. However, as water is captured in the watershed, tensions may arise between the downstream (Marab) users and the upstream users.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
จอร์แดน
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Al Jiza District
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Al Majeddyeh Village
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- ใช้ ณ จุดที่เฉพาะเจาะจงหรือเน้นไปยังบริเวณพื้นที่ขนาดเล็ก
Is/are the technology site(s) located in a permanently protected area?
ไม่ใช่
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ระบุปีที่ใช้:
2017
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ในช่วงการทดลองหรือการทำวิจัย
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
- ปรับตัวเข้ากับการเปลี่ยนแปลงภูมิอากาศของโลก สภาพภูมิอากาศที่รุนแรงและผลกระทบ
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจที่เป็นประโยชน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ใช่
Specify mixed land use (crops/ grazing/ trees):
- Agro-pastoralism (incl. integrated crop-livestock)

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- cereals - barley
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
Is intercropping practiced?
ไม่ใช่
Is crop rotation practiced?
ไม่ใช่

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
Extensive grazing:
- กึ่งโนแมนดิซึ่มหรือแพสโตแรลลิซึ่ม (Semi-nomadism/pastoralism)
ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์ที่มีการจัดการแบบเข้มข้นหรือการผลิตอาหารสัตว์:
- ตัดแล้วขนไป / ไม่มีการปล่อยแทะเล็มเอง (Cut-and-carry / zero grazing)
Animal type:
- goats
- sheep
Is integrated crop-livestock management practiced?
ไม่ใช่
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
- No (Continue with question 3.4)
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The Marab facilitates uniform distribution of excess rainwater obtained from the upland (partly Vallerani micro-catchments) and the water is conveyed through rehabilitated gullies to the Marab. (Some) Micro catchments and rehabilitated gullies are essential to avoid damaging water peaks, harming the Marab-structures. The Marab is rainfed and naturally flood irrigated.
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การปรับปรุงดิน / พืชคลุมดิน
- การเก็บเกี่ยวน้ำ
- การผันน้ำและการระบายน้ำ
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A3: การรักษาหน้าดิน
- A4: การรักษาดินชั้นล่าง

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S2: ทำนบ เขื่อนดิน
- S3: Graded ditches, channels, waterways
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน
- Wg (Gully erosion): การกัดกร่อนแบบร่องธารหรือการทำให้เกิดร่องน้ำเซาะ
- Wo (Offsite degradation): ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านกายภาพ
- Pk (Slaking and crusting): การอุดตันของช่องว่างในดินหรือรูพรุน

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านชีวภาพ
- Bc (Reduction of vegetation cover): การลดลงของจำนวนพืชที่ปกคลุมดิน
- Bq (Quantity/biomass decline): การลดลงของปริมาณหรือมวลชีวภาพ

การเสื่อมโทรมของน้ำ
- Ha (Aridification): การเกิดความแห้งแล้ง
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Retaining surface runoff and locally infiltrating water through bunds increase soil moisture hence agricultural yield increases (e.g. biomass, vegetation cover) , soil crusting decreases (in some selected ponding areas it might increase) - and because of trapping top-soil sediments and residues from the uplands, soil fertility increases likewise.
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
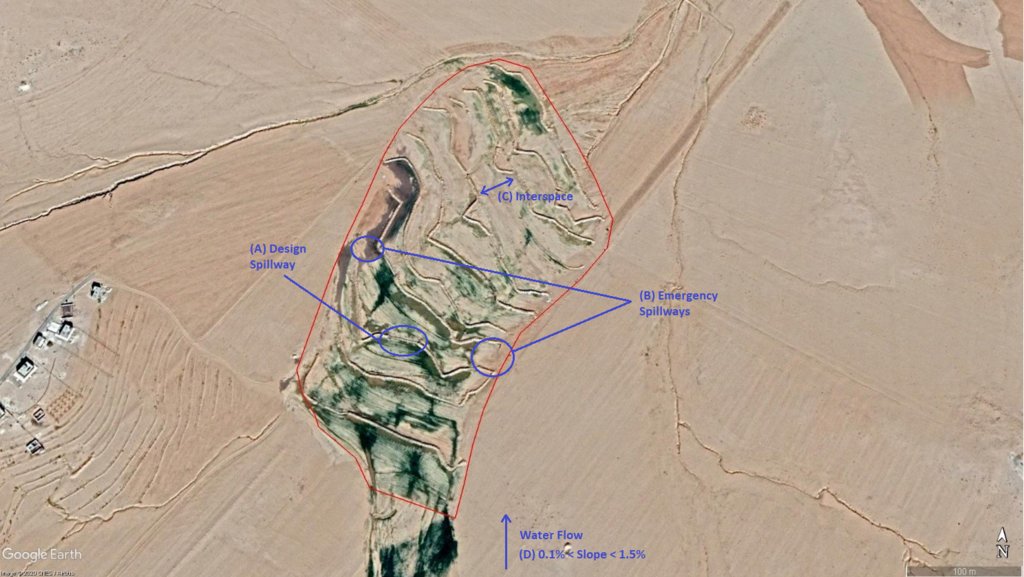
The overall Marab (reshaped flood plain) area is 10 hectares. The natural flood plain was leveled up to the sides; the natural slope in flow direction ranges between 0.1 and 1.5% (D). The later stone bund construction (soil relocation) and siltation/erosion processes over time develop a slight step-terraced bund compartment system, with the single compartments having much smaller slope than the overall Marab. At the sides, the levelled area slightly increases towards the natural terrain (natural terrain at the sides is around 0.1 to 0.3m higher compared with the leveled Marab). This avoids side outflow of water during design storms (*). Bund structures, along the contour, are built with a loader up to around 0.7 to 1.0m height and around 2.0 – 3.0m bottom width. The bunds are built with compaction through the loader. Interspace between the bunds is between 10-50 meters (C), depending on the local slope in the flow direction, having around 0.1 to 0.3m soil surface elevation difference between the bunds. Stone made design-spillways (A) are being constructed around the middle of each bund, with certain position change between the bund in downstream direction. Thus, spillways do not perfectly align with respect to the bund, but create a meandering flow around the center. The stone-protected design-spillways are designed to safely route at least the expected 2-5 year return period flood event. The Marab plain is not perfectly even, especially at the sides, to avoid water flowing around the bunds during design storms. However, the Marab-technology is also designed to cope with more extreme events, a storm of 5-10 return period, without significant damages. Therefore, there are emergency-spillways (**) implemented at the sides of each bund (B). These emergency-spillways allow excess water to flow out sideways rather than flow over the bund which would damage the structures. Note:
Based on above considerations and calculations bund spillway lengths reach 50-60m in the specific watershed.
* A design storm is a rainfall event that results in a flood event as water accumulates throughout the watershed. The Marab is designed to harvest the water optimally by (design) spill ways that keep the water in the Marab. A design storm relates to a certain return period. In general a longer return period (i.e. less frequent) accounts for a more intense event hence a more severe flooding event.
** An emergency spill way is a structure that is designed to discharge excess water coming from storms more extreme than the design storm (i.e. with less frequent storms). In practice this means that the Marab is protected from excess water.
ผู้เขียน:
Joren Verbist (Extracted from Google Earth Pro on Jan 7th 2019)
วันที่:
19/12/2020
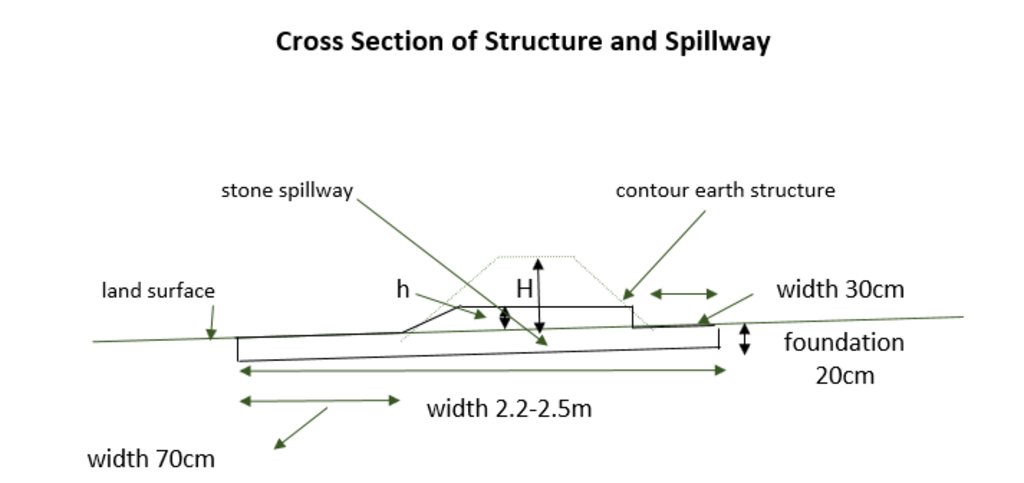
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
The cross-section shows the dimensions. Downstream of a bund the width is 70 centimeter. The foundation is 20 centimeter high. The upstream width is 30 centimeter. The total width of the bund varies between 2.2 meter and 2.5 meter.
ผู้เขียน:
Stefan Strohmeier
วันที่:
01/07/2020
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อพื้นที่ที่ใช้เทคโนโลยี
ระบุขนาดและหน่วยพื้นที่:
10 ha
ระบุสกุลเงินที่ใช้คำนวณค่าใช้จ่าย:
- USD
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
35
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Implement upstream watershed rehabilitation measure (e.g. Upstream Vallerani micro water harvesting) | Prior of Marab-Technology construction |
| 2. | Implement gully rehabilitation measure (e.g. Midstream gully rehabilitation) | Prior of Marab-Technology construction |
| 3. | Marab site selection (flood plain): topographic assessment (slope, soil depth, etc.) and consideration of watershed hydrology (e.g. for bund and spillway design) | Before the rainy season |
| 4. | Grading/levelling of natural flood plain incl. gully fill (with soil material) | season (Aug. – Nov.) |
| 5. | Implement bund structures (based on step 4) | season (Aug. – Nov.) |
| 6. | Construct stone made design and emergence spillways (based on step 5) | season (Aug. – Nov.) |
| 7. | Preparation of compartmentalized agricultural fields (bund interspaces) for field crop agriculture | season (Aug. – Nov.) |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The upstream measures as the Vallerani System and gully rehabilitation are strongly recommended but are not taken into account as costs in this documentation. Because this documentation focuses specifically on the Marab-technology.
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Local Workers | person-days | 50.0 | 35.0 | 1750.0 | |
| แรงงาน | Land Survey | person-days | 6.0 | 35.0 | 210.0 | |
| แรงงาน | Engineer (+assistance) | person-days | 15.0 | 50.0 | 750.0 | |
| แรงงาน | Drivers of heavy machinery | person-days | 12.0 | 35.0 | 420.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Grader | machine-days | 3.0 | 250.0 | 750.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Loader | machine-days | 10.0 | 250.0 | 2500.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Deep Plow | machine-days | 3.0 | 200.0 | 600.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Tractor (to pull the shallow and deep plow) | machine-days | 5.0 | 200.0 | 1000.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Shallow Plow | machine-days | 2.0 | 200.0 | 400.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Water Tank Truck | Tank | 1.0 | 50.0 | 50.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Small Equipment (Shovel, pickaxe, buckets) | Equipment | 1.0 | 200.0 | 200.0 | |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Stones | Kubic Metre | 200.0 | 10.0 | 2000.0 | |
| อื่น ๆ | Transportation of heavy machinery | 1.0 | 2000.0 | 2000.0 | ||
| อื่น ๆ | Security | 1.0 | 300.0 | 300.0 | ||
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 12930.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 12930.0 | |||||
ถ้าผู้ใช้ที่ดินรับภาระน้อยกว่า 100% ของค่าใช้จ่าย ให้ระบุว่าใครเป็นผู้รับผิดชอบส่วนที่เหลือ:
ICARDA and National Agricultural Research Centre (NARC)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
These costs are for establishment (so one-time) and are for the total Marab-technology i.e. 10 ha.
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Maintaining the structures based on observations and possible damages after the rainy season, so no clear maintenance plans | Before the rainy season (Oct. – Nov.)/upon observation |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Excludes annual farming costs (e.g. seedbed preparation)
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Engineer | person days per year | 2.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Worker | person days per year | 6.0 | 35.0 | 210.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Loader | machine days per year | 1.0 | 250.0 | 250.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Stones | Kubic Metre | 10.0 | 10.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 660.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 660.0 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The costs of practicing agriculture (e.g. cost of seeds and fertilizer) are not taken into account, since these costs were also made before the implementation of this technology.
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
The special and heavy machinery affect the cost significantly, since these were not available in the area. The implementation of the technology is labour intensive, therefore labour costs are significant as well. However, these costs are initially, so these specific costs are almost zero after establishment. In addition, all the maintenance is payed for by the land users. So, only the establishment was payed for by external parties.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ระบุปริมาณน้ำฝนเฉลี่ยรายปี (ถ้ารู้) :หน่วย ม.ม.
130.00
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
In the specific site/dry areas of Jordan rainy season usually ranges from November until April
Queen Alia International Airport long-time avergae annual rainfall is around 150 mm (around 10km west of the site)
At the site a rainfall tipping bucket has been installed in 2016.
ระบุชื่อของสถานีตรวดวัดอากาศที่ใช้อ้างอิงคือ:
Queen Alia International Airport
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- แห้งแล้ง
The maximum temperature usually occurres in August.
The average daily maximum temperature is 25.01 °C.
The average daily minimum temperature is 8.5 °C
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- บริเวณสันเขา (convex situations)
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
The Marab itself is rather concave (depression shape) / natural depression. However, the bund structures are convex, spreading water over the field.
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
- ละเอียด/หนัก (ดินเหนียว)
เนื้อดินล่าง (> 20 ซ.ม.ต่ำจากผิวดิน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ต่ำ (<1%)
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
> 50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ไม่ดีหรือไม่มีเลย
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
ใช้ประโยชน์ไม่ได้
Water quality refers to:
surface water
ความเค็มของน้ำเป็นปัญหาหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
กำลังเกิดน้ำท่วมในพื้นที่หรือไม่:
ใช่
บ่อยครั้ง:
บ่อยครั้ง
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ต่ำ
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งที่อยู่:
- ต่ำ
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน:
- กึ่งเร่ร่อน
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- < 10% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- จน
- พอมีพอกิน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- การใช้เครื่องจักรหรือเครื่องยนต์
เพศ:
- ชาย
อายุของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
- ผู้เยาว์
- วัยกลางคน
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
The actual land users are often poor Jordanians or Syrian refugees. However, the owners of the livestock are relatively rich. The landowners are responsible for the maintenance of the intervention.
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดกลาง
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
10ha
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เช่า
- รายบุคคล
- NA
Are land use rights based on a traditional legal system?
ใช่
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The crops produced are used as fodder
การผลิตพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
0.05ton/ha
หลังจาก SLM:
5ton/ha
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The production of the fodder is increased as the barley yield is mostly used to feed animals and also the stubble is grazed.
คุณภาพพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The barley is fed to the livestock
พื้นที่สำหรับการผลิต
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to the bunds (but very limited and inevitable)
การจัดการที่ดิน
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ค่าใช่จ่ายของปัจจัยการผลิตทางการเกษตร
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Expenses are slightly increased due to possible maintenance of the Marab. However, the increased yield justifies this.
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
ภาระงาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to possible maintenance
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
ความมั่นคงด้านอาหาร / พึ่งตนเองได้
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
During the construction, local community were hired as workers, this has significantly boosted their knowlegde about SLM.
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
การเก็บเกี่ยวหรือการกักเก็บน้ำ
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
การระบายน้ำส่วนเกิน
น้ำบาดาลหรือระดับน้ำในแอ่งน้ำบาดาล
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
การสูญเสียดิน
การสะสมของดิน
การเกิดแผ่นแข็งที่ผิวดิน /การเกิดชั้นดาน
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ต่ำกว่าดินชั้น C
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
การปกคลุมด้วยพืช
มวลชีวภาพ/เหนือดินชั้น C
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
ผลกระทบจากน้ำท่วม
ผลกระทบจากภัยแล้ง
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
น้ำท่วมพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Reduced downstream flooding is desired
การทับถมของดินตะกอนพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Reduced downstream siltation is desired
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | increase or decrease | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ฝนประจำปี | ลดลง | ดี |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ดีมาก |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมฉับพลัน | ดีมาก |
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านลบเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The initial investment is quite large. Therefore, the short term returns is classified as slightly negative. After some seasons with good (stable) crop yield the return of investment is positive. Long term benefits are classified positively.
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- 1-10%
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
These are some farmers that live near the Marab. They try to copy the Marab in their fields.
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 91-100%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The local farmers like the technology and acknowledge its positive impacts. They would like to have a Marab themselves (even if their locally owned lands are not suitable in many cases). Local agro-pastoralists copy and apply parts of the technology (especially the bund
system). However, it strongly recommended that implementing a Marab-technology is done as a community-based project/intervention; the Marab technology should be part of an integrated watershed management plan, located at the most suitable location for the entire community.
6.6 การปรับตัว
เทคโนโลยีได้รับการปรับเปลี่ยนเมื่อเร็วๆนี้ เพื่อให้ปรับตัวเข้ากับสภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือไม่:
ใช่
ถ้าตอบว่าใช่ ให้ระบุว่าเงื่อนไขการเปลี่ยนแปลงใดที่ถูกปรับตัว:
- การเปลี่ยนแปลงแบบค่อยเป็นค่อยไปและสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ
ให้ระบุการปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี (การออกแบบ วัสดุหรือชนิดพันธุ์ เป็นต้น):
The spillway design can be adapted to variable surface runoff occurrence (affected by climate change).
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| The farmers highly appreciate the improved economic situation as consequence of the increased yield. |
| A strength of the Marab technology is that water is harvested and minimally spilled away, preventing top-soil erosion and accumulating soil organic matter consequently preserving soil fertility. |
| The crop produces grains: can be (partially) used for re-seeding in the coming seasons; economic gain + increase resilience. |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| Economic improvement through targeted agricultural interventions in the most suitable location(s) of a watershed. This aims at decreasing the pressure on the fragile dry land ecosystem. The locally increased yield raises awareness on non-sufficient field crop agriculture in uplands (commonly achieved) and might increase the willingness for more nature-based sustainable land management measures in the less fertile and runoff generating (more vulnerable uplands) parts of the watershed. Therefore, the Marab technology could be a starting point for a watershed rehabilitation initiative. |
| The Marab technology creates an opportunity for multiple crop introduction (due to natural flood irrigation) – aside from barley monoculture (agro-diversity). |
| Increased water infiltration conserves water and might lead to deep percolation (groundwater recharge). |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| The Marab depends on upstream water users; can lead to increased tensions | Agreement among the community - conducting contacts/contracts among upstream and downstream farmers. Joint watershed management and benefit share could be mediate these tension. And might even lead to watershed rehabilitation. |
| High initial investment and partially high maintenance costs (including machinery) | Once the implementation is linked with larger environmental benefits – communities might receive funds from the government or international donors. |
| Loss of cultivation area where the bunds are placed | Unavoidable. However, the gain of interspaces exceeds these losses several times. |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Tensions among multiple actors in the watershed (selection of Marab area) | Develop institutions that could avoid these tensions by establishing agreements, contracts, rules, or regulations. |
| Heavy machinery in a vulnerable ecosystems – can induce other requests/use by locals (improper use) | Targeted policies in place & enforcements |
| Increasing wealth inequality between farmers and/or communities. | Creation of institutions, which assure fair distribution. This would benefit the whole watershed. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
- การสัมภาษณ์ผู้เชี่ยวชาญด้าน SLM หรือผู้ชำนาญ
- การเก็บรวบรวมมาจากรายงานและเอกสารที่มีอยู่
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
15/04/2020
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Strohmeier, S. (2017). Dimensioning of Marab in Majidyya.
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Strohmeier, S. (2017). Watershed Restoration in Baia Areas of Jordan Technology Packages for Controlling and Monitoring Gully Erosion.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
https://mel.cgiar.org/projects/jordan-watershed-restoration-project
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Mira Haddad, Stefan Strohmeier. (12/12/2017). Treated upland areas map. Jordan: International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA).
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/9108
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Stefan Strohmeier, Mira Haddad, Ismail Shukri. (8/11/2018). Marab - water harvesting based agriculture.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/9069
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Boubaker Dhehibi, Mira Haddad, Stefan Strohmeier, Masnat El-Hiary. (24/7/2020). Enhancing a Traditional Water Harvesting Technique in Jordan’s Agro-pastoral Farming System. Lebanon: International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA).
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/11506
7.3 Links to relevant online information
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
WATER HARVESTING FOR RESTORING RANGELANDS IN JORDAN
URL:
https://www.icarda.org/media/drywire/water-harvesting-restoring-rangelands-jordan
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล