The programme of landscape revitalization and integrated river basin management in the Slovak republic for the year 2011 - retention measures in the Sobotište village. [สโลวาเกีย]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Zuzana Studvova
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: David Streiff
Program revitalizácie krajiny a integrovaného manažmentu povodí v Slovenskej republike pre rok 2011 - vodozádržné opatrenia v obci Sobotište. (Slovak language)
approaches_2680 - สโลวาเกีย
- บทสรุปทั้งหมดในรูปแบบของ PDF
- บทสรุปทั้งหมดในรูปแบบของ PDF เพื่อพิมพ์
- บทสรุปทั้งหมดในรูปหน้าเว็บ
- บทสรุปทั้งหมด (ไม่มีการจัดเรียง)
- The programme of landscape revitalization and integrated river basin management in the Slovak republic for the year 2011 - retention measures in the Sobotište village.: 2 สิงหาคม 2017 (inactive)
- The programme of landscape revitalization and integrated river basin management in the Slovak republic for the year 2011 - retention measures in the Sobotište village.: 2 สิงหาคม 2017 (public)
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของแนวทาง
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินแนวทาง (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Sustainable Hill Cultivation Programme1.3 เงื่อนไขที่เกี่ยวข้องกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกไว้ผ่านทาง WOCAT
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล (ภาคสนาม):
01/01/2015
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การอ้างอิงถึงแบบสอบถามเรื่องเทคโนโลยี SLM
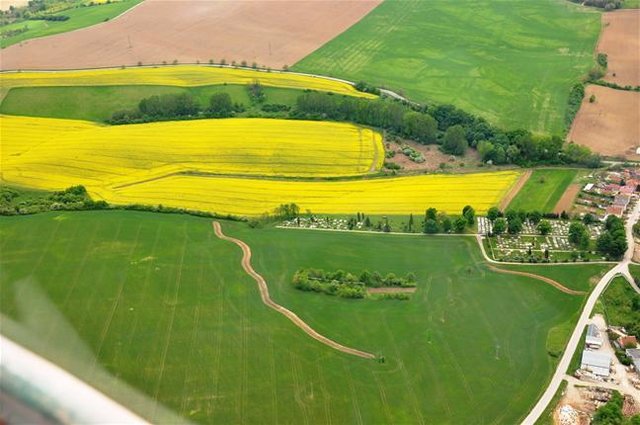

Level ditches in cropland [สโลวาเกีย]
Conservation measures for eroded cropland. The technology contains level ditches of various lengths, which are digged along a contour.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Zuzana Studvova
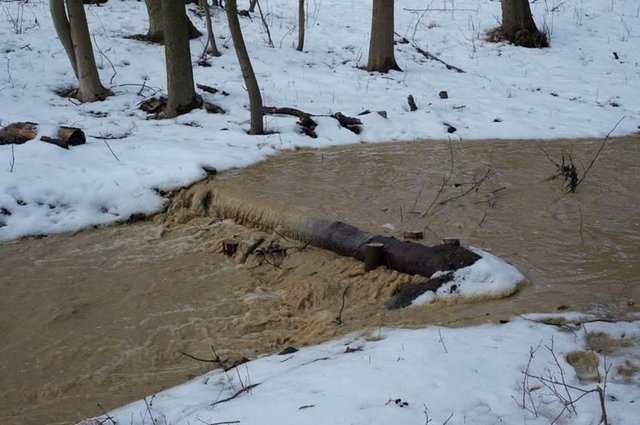

Wooden check dams [สโลวาเกีย]
Small wooden check dams built in erosion rills, grooves or gorges to reduce flood risk.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Zuzana Studvova
2. คำอธิบายของแนวทาง SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของแนวทาง
This approach is devoted to the implementation of 'The Landscape Revitalisation Programme and integrated river basins management of the Slovak Republic' in the Sobotište village.
2.2 การอธิบายอย่างละเอียดของแนวทาง
การอธิบายอย่างละเอียดของแนวทาง:
Aims / objectives: The objective of the first implementation project for 2011 was to create, activate and systematically implement a minimum of 6 million m³ of water retention elements in mountain and foothill areas of forest-agricultural landscape in Slovakia. A particular aim was to create and build landscape water retention systems, terrain elements, facilities and technical solutions in forest, agricultural and urban areas in selected village locations, with the abovementioned cyclical rainwater retention capacity, which will then be operated and
maintained. Another project objective was to force and socially support the creation of employment at community and regional level. The creation of water retention elements and the implementation of revitalisation measures required the creation of a minimum of 2,500 jobs of a seasonal and temporary nature in 2011, including extending existing specialist capacities. This whould also extend the work skills and knowledge necessary for revitalisation of the landscape.
833 municipalities showed interest to participate in this project/approach, while 200 municipalities met the criteria. The project created about 3,500 seasonal jobs in 2011, particularly in regions with high unemployment.
Methods: Criteria and their significance for including villages into the first implementation project are
as follows:
1. 45% - historic or regularly repeated occurrence of flash flooding,
2. 35 % - village is situated in a location with a high potential risk of flooding, in accordance
with modelled potential for the occurrence of flooding. A map of regional and local
potential for flooding in the area of Slovakia1
is at Appendix No. 1,
3. 10% - location of a village in the upper part of river basins, so the implemented measures
will positively decrease the risk of flooding for highest possible number of villages in the
given river basins,
4. 10% - the ratio of documented unemployment is taking into account so citizens of villages
with a high ratio of documented unemployment could contribute towards revitalisation
works.
The submitted methodology of the whole flood potential of Slovakia was prepared on the basis of the work of J. Minár and Co. (2005). The mentioned work focuses upon the
presentation of methodology and results for evaluating the flood creation potential within the whole of Slovakia. It also includes a general description of the modelling of hydrological
processes. The method presented in this work is a good alternative for fast, effective and relatively financially undemanding but still sufficiently reliable analysis of flood risks of
larger areas. The actual calculation of total potential for flooding took place in the technological environment of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) in the following steps
with the stated data:
- calculation of the morphometric potential (incline, horizontal articulation of the
topography, slope length, speed of surface run-off),
- partial synthetic geological potential (infiltration and drainage properties of the soil,
retention properties of the land cover, breaking effect of land cover, size of river basin,
shape of river basin),
- overall potential of the land for the creation of flood situations (climatic and
hydrological characteristics and data).
Stages of implementation: Management of the first implementation project was carried out by the Executive Manager of the Programme of Landscape Revitalization and Integrated River Basin Management in SR in cooperation with the Government Representative for Local Government and for Integrated River Basin and Landscape Management and other interested departments of the Government Office SR.
2.3 รูปภาพของแนวทาง
2.5 ประเทศ ภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่ได้นำแนวทางไปใช้
ประเทศ:
สโลวาเกีย
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด: :
Slovakia
ข้อมูลเฉพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง:
Senica / Sobotište
Map
×2.6 วันที่เริ่มต้นและสิ้นสุดของแนวทาง
ระบุปีที่เริ่ม:
2011
การสิ้นสุดลง (ถ้าแนวทางไม่ได้ใช้อีกต่อไป):
2012
2.7 ประเภทของแนวทาง
- ใช้โครงงานหรือแผนงานเป็นฐาน
2.8 เป้าหมายหรือวัตถุประสงค์หลักของแนวทาง
The Approach focused mainly on SLM with other activities
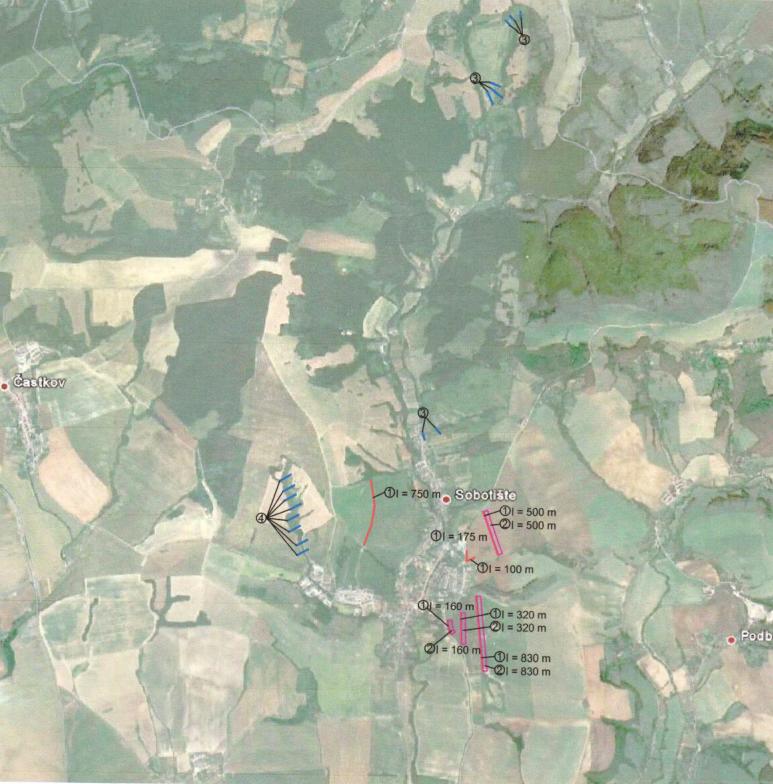
The Sobotište of village was greatly affected in 2011 by floods from storm rainfall. Problems with floods, however, occur regularly, especially at the Teplica and the Sobotišský stream. Some problems have been recorded in farmland and meadows, in places of concentrated runoff during the storm rainfalls, long lasting rainfalls, and snow melting. Floods endanger villages and make severe damage. The goal of the approach is to eliminate damage to healt and properties.
Water retention measures are proposed in the territory of Sobotište, localities of Kubiny, Staré Hory, Javorec, Kaničkov Jarok and Padelky. It is expected that the proposed water retention measures will support the accumulation and infiltration of water into the soil and retard runoff from farmland, meadows, and pastures. With the proper function of measures the surface runoff in farmland will decrease and slow down, and community will not endanger as much as previously.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: In general, the main problems within the implementation of projects are mostly legislative regulations that hamper the SLM and the implementation of technologies. The big problem is protection zone of particular rivers connected to administrative and legislative laws and regulations. Some difficulties detected were the execution of permissions for the implementations of methods and technologies that would help to achieve the sustainable land management.
Second problem is land consolidation. The process of the land consolidation is too long to be achieved and accomplished in time. Especially if the public call of the application submission for subsidies needs the consolidation of land to be already solved.
Third, the measures cannot be more expensive than the protected object.
Four, there is lack of money for the purchasing the land in municipalities.
Five, there is very poor law enforcement and recovery of law and claims.
2.9 เงื่อนไขที่เอื้ออำนวยหรือเป็นอุปสรรคต่อการนำเทคโนโลยีภายใต้แนวทางนี้ไปปฏิบัติใช้
การมีไว้ให้หรือการเข้าถึงแหล่งการเงินและบริการ
- เป็นอุปสรรค
Treatment through the SLM Approach:
กรอบแนวทางในการดำเนินการด้านกฎหมาย (การถือครองที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและน้ำ)
- เป็นอุปสรรค
ownership of the land
Treatment through the SLM Approach:
3. การมีส่วนร่วมและบทบาทของผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสียที่เกี่ยวข้อง
3.1 ผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสียที่เกี่ยวข้องในแนวทางนี้และบทบาท
- ผู้ใช้ที่ดินระดับท้องถิ่นหรือชุมชนระดับท้องถิ่น
The approach involved socially and economically disadvantaged ethnicities
- ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM หรือที่ปรึกษาการเกษตร
- รัฐบาลแห่งชาติ (ผู้วางแผน ผู้ทำการตัดสินใจ)
3.2 การเกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดินระดับท้องถิ่นหรือชุมชนระดับท้องถิ่นในช่วงต่างๆของแนวทาง
| ความเกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดินระดับท้องถิ่นหรือชุมชนระดับท้องถิ่น | ระบุผู้ที่มีส่วนเกี่ยวข้องและอธิบายกิจกรรม | |
|---|---|---|
| การริเริ่มหรือการจูงใจ | ระดมกำลังด้วยตนเอง | Government |
| การวางแผน | ระดมกำลังด้วยตนเอง | Government, SLM specialist |
| การดำเนินการ | ระดมกำลังด้วยตนเอง | Municipalities, land users |
| การติดตามตรวจสอบหรือการประเมินผล | ระดมกำลังด้วยตนเอง | Municipalities, land users |
| Research | ไม่ลงมือ |
3.4 การตัดสินใจเลือกใช้เทคโนโลยี SLM
ระบุผู้ที่ทำการตัดสินใจเลือกเทคโนโลยีมากกว่าหนึ่งวิธีไปปฏิบัติใช้:
- ผู้ใช้ที่ดินเป็นผู้ตัดสินใจหลัก โดยการสนับสนุนจากผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM
การอธิบาย:
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by mainly by land users supported by SLM specialists
4. การสนับสนุนด้านเทคนิค การสร้างขีดความสามารถ และการจัดการด้านความรู้
4.1 การสร้างขีดความสามารถ / การอบรม
ได้มีการจัดอบรมให้แก่ผู้ใช้ที่ดินหรือผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสียคนอื่น ๆ หรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
4.2 การบริการให้คำแนะนำ
ผู้ใช้ที่ดินมีการเข้าถึงการรับบริการให้คำปรึกษาหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
4.3 การเสริมความแข็งแกร่งให้กับสถาบัน (การพัฒนาองค์กร)
สถาบันได้รับการจัดตั้งขึ้นมาหรือเสริมความแข็งแกร่งโดยแนวทางนี้หรือไม่:
- ไม่
4.4 การติดตามตรวจสอบและประเมินผล
การติดตามตรวจสอบและประเมินผลเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของแนวทางหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
4.5 การวิจัย
การวิจัยเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของแนวทางหรือไม่:
ใช่
ระบุหัวข้อเรื่อง:
- เทคโนโลยี
ให้ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมและให้ระบุผู้ทำการวิจัย:
Research was carried out on-farm
5. การสนับสนุนด้านการเงินและวัสดุอุปกรณ์
5.1 ระบุงบประมาณประจำปีสำหรับแนวทาง SLM นี้
ถ้าหากว่างบประมาณประจำปีไม่เป็นที่ทราบแน่นอน ให้ระบุช่วงลงไป:
- 10,000-100,000
แสดงความคิดเห็น (แหล่งของการระดมทุน ผู้บริจาคคนสำคัญ):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: government: 100.0%
5.2 การสนับสนุนด้านการเงิน / วัสดุอุปกรณ์ให้แก่ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
ผู้ใช้ที่ดินได้รับการสนับสนุนด้านการเงิน / วัสดุอุปกรณ์ไปปฏิบัติใช้เทคโนโลยีหรือไม่:
ใช่
ถ้าใช่ ให้ระบุประเภทของการสนับสนุน เงื่อนไขและผู้จัดหามาให้:
Government funds and subsidies
5.3 เงินสนับสนุนสำหรับปัจจัยนำเข้า (รวมถึงแรงงาน)
- อุปกรณ์
| ระบุปัจจัยนำเข้าที่ได้รับการสนับสนุน | เห็นด้วยระดับไหน | ระบุเงินสนับสนุน |
|---|---|---|
| เครื่องจักร | ได้รับการช่วยเหลือทางการเงินแบบเต็ม | |
| เครื่องมือ | ได้รับการช่วยเหลือทางการเงินแบบเต็ม | |
- การเกษตร
| ระบุปัจจัยนำเข้าที่ได้รับการสนับสนุน | เห็นด้วยระดับไหน | ระบุเงินสนับสนุน |
|---|---|---|
| เมล็ด | ได้รับการช่วยเหลือทางการเงินแบบเต็ม | |
| ปุ๋ย | ได้รับการช่วยเหลือทางการเงินแบบเต็ม | |
- วัสดุสำหรับการก่อสร้าง
| ระบุปัจจัยนำเข้าที่ได้รับการสนับสนุน | เห็นด้วยระดับไหน | ระบุเงินสนับสนุน |
|---|---|---|
| หิน | ได้รับการช่วยเหลือทางการเงินแบบเต็ม | |
| ไม้ | ได้รับการช่วยเหลือทางการเงินแบบเต็ม | |
5.4 เครดิต
มีการจัดหาเครดิตมาให้ภายใต้แนวทาง SLM หรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการหรือแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์

Level ditches in cropland [สโลวาเกีย]
Conservation measures for eroded cropland. The technology contains level ditches of various lengths, which are digged along a contour.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Zuzana Studvova

Wooden check dams [สโลวาเกีย]
Small wooden check dams built in erosion rills, grooves or gorges to reduce flood risk.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Zuzana Studvova
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล