Kiwi fruit cultivation [ເນໂປ]
- ການສ້າງ:
- ປັບປູງ:
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: Shreedip Sigdel
- ບັນນາທິການ: –
- ຜູ້ທົບທວນຄືນ: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
kiwi (theki) fal kheti (Main Contributor: Samden Sherpa, ICIMOD)
technologies_1686 - ເນໂປ
ເບິ່ງພາກສ່ວນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດ1. ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປ
1.2 ຂໍ້ມູນ ການຕິດຕໍ່ພົວພັນ ຂອງບຸກຄົນທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ແລະ ສະຖາບັນ ທີ່ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນການປະເມີນເອກກະສານ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຜຸ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
Sherpa Samden Lama
ICIMOD
ເນໂປ
ຊື່ສະຖາບັນ (ຫຼາຍສະຖາບັນ) ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ / ປະເມີນ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
ICIMOD International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) - ເນໂປ1.3 ເງື່ອນໄຂ ກ່ຽວກັບ ການນໍາໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນເອກະສານ ທີ່ສ້າງຂື້ນ ໂດຍຜ່ານ ອົງການພາບລວມຂອງໂລກ ທາງດ້ານແນວທາງ ແລະ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການອານຸລັກ ທໍາມະຊາດ (WOCAT)
ຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ແລະ ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ ທີ່ໃຫ້ຂໍ້ມູນ (ຫຼາຍ) ຍິນຍອມ ຕາມເງື່ອນໄຂ ໃນການນຳໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນ ເພື່ອສ້າງເປັນເອກກະສານຂອງ WOCAT:
ແມ່ນ
2. ການອະທິບາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
2.1 ຄໍາອະທິບາຍສັ້ນຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການກຳໜົດຄວາມໝາຍ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
Kiwi fruit cultivation on sloping land in the mid-hill areas of Nepal can help prevent soil erosion and is a sustainable land management practice. This high value crop introduces biodiversity and improves livelihoods by providing a source of cash income.
2.2 ການອະທິບາຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການພັນລະນາ:
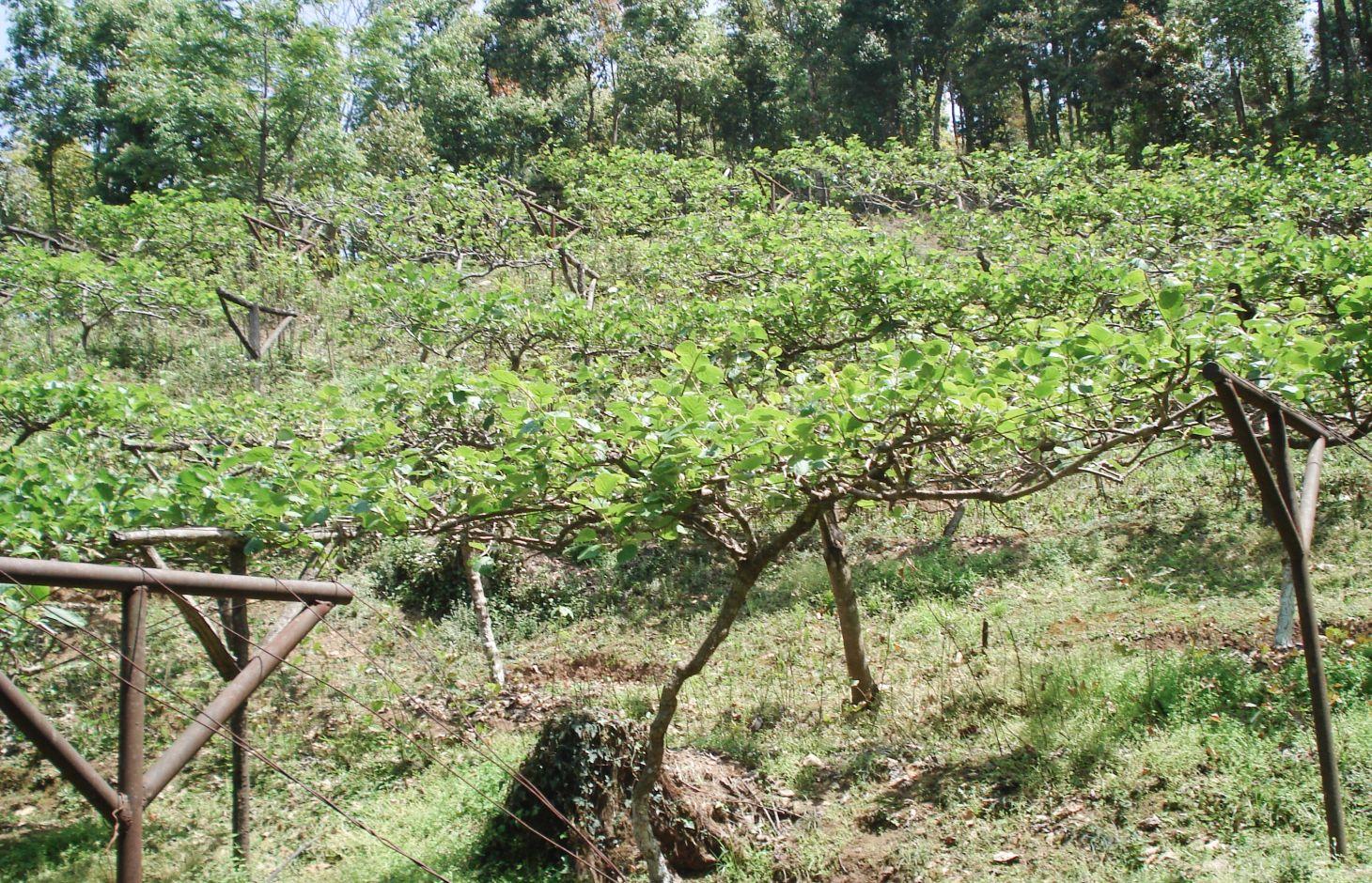
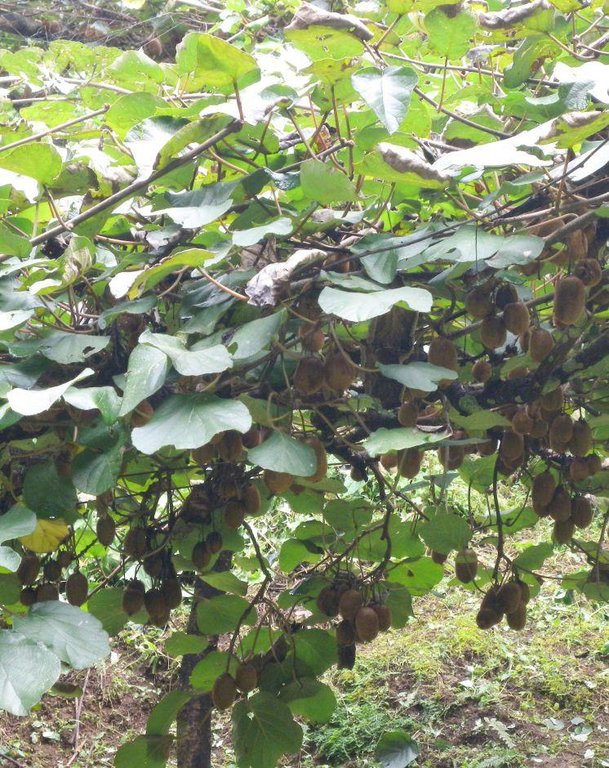
The kiwi fruit is native to China. Previously called Chinese gooseberry, it is now more commonly known by its marketing name of kiwi fruit. Kiwi fruits grow on large vines that are similar to grapevines in their general growth and fruiting habits as well as their training and trellising requirements. The fruit normally ripens within 25 weeks after the flowers first appear. The fruits range in weight from 40 to 90 g and can be picked shortly after the first frost in autumn; after that, they can be kept in cold storage for 4–6 months at oC. Kiwi vines can be grown on a wide range of soil types at elevations ranging from 1000 m to 2500 m. The kiwi plant is dioecious, meaning individual plants are either male or female. Only female plants bear fruit, but only when pollinated by a male plant. Vines of both sexes are essential for fruit production, and they must flower at the same time to ensure pollination. One male pollinator vine is required for eight female vines. The vines are commonly supported on sturdy structures strong enough to bear the heavy fruit, which might otherwise break the rather weak vines. T-bars or hitching post trellises are recommended to support the large fruiting area in the form of a canopy and provide easy access to the fruit.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Seedlings can be planted in the spring as soon as there is little chance of frost. Vines need to be pruned both in summer and in winter to maintain a balance between kiwi plant growth and profitable fruit production. Excessive plant growth is removed during the growing season to keep the kiwi canopy open and to remove non-fruiting wood. Harvesting can begin from the end of November. Frequent weeding is required to reduce competition for moisture and fertilizer. Kiwi fruit requires abundant water; during the dry season the newly planted kiwi vines need deep watering once a week.
2.3 ຮູບພາບຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
2.5 ປະເທດ / ເຂດ / ສະຖານທີ່ບ່ອນທີ່ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຮັບການນໍາໃຊ້ ແລະ ທີ່ຖືກປົກຄຸມດ້ວຍການປະເມີນຜົນ
ປະເທດ:
ເນໂປ
ຂໍ້ມູນເພີ່ມເຕີມຂອງສະຖານທີ່:
Lalitpur District
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ການແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
- ແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍຢ່າງໄວວາໃນພື້ນທີ່
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ກະຈາຍໄປທົ່ວພື້ນທີ່, ໃຫ້ລະບຸເນື້ອທີ່ ທີ່ຖືກປົກຄຸມ (ເປັນ ກິໂລຕາແມັດ):
0.01
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.01 km2.
2.7 ການນໍາສະເໜີ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຖືກຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດຄືແນວໃດ?
- ໃນໄລຍະການທົດລອງ / ການຄົ້ນຄວ້າ
3. ການໃຈ້ແຍກ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໃນການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
3.1 ຈຸດປະສົງຫຼັກ (ຫຼາຍ) ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ, ປ້ອງກັນ, ຟື້ນຟູ ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
- ສ້າງຜົນກະທົບ ທາງເສດຖະກິດ ທີ່ເປັນປະໂຫຍດ
3.2 ປະເພດການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃນປະຈຸບັນ() ທີ່ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຖືກນໍາໃຊ້

ດິນທີ່ປູກພືດ
- ພືດຢືນຕົ້ນ (ບໍ່ແມ່ນໄມ້)
- ເປັນໄມ້ຢືນຕົ້ນ ແລະ ໄມ້ພຸ່ມ ຈາກການປູກພືດ
ການປູກພືດຢືນຕົ້ນ(ບໍ່ແມ່ນໄມ້ໄມ້ຢືນຕົ້ນ) - ໃຫ້ລະບຸປະເພດພືດ:
- ໝາກເບີລີ
- kiwi
ຈໍານວນ ລະດູການ ປູກໃນປີໜຶ່ງ:
- 2
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): When sloping land is not used for agricultural production and not planted with ground cover or other vegetation (such as contour hedgerows), the fertile soil can be eroded and washed away by heavy monsoon rains.
3.5 ການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ຢູ່ໃນກຸ່ມການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
- ການປັບປຸງແນວພັນພືດ / ແນວພັນສັດ
3.6 ມາດຕະການ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ ປະກອບດ້ວຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ມາດຕະການ ທາງດ້ານພືດພັນ
- V1: ເປັນໄມ້ຢືນຕົ້ນ ແລະ ການປົກຫຸ້ມຂອງໄມ້ພຸ່ມ
3.7 ປະເພດດິນເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຫຼັກທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ດິນເຊາະເຈື່ອນ ໂດຍນໍ້າ
- Wt: ການສູນເສຍຊັ້ນໜ້າດິນ / ການເຊາະເຈື່ອນຜິວໜ້າດິນ

ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຂອງດິນ ທາງເຄມີ
- Cn: ຄວາມອຸດົມສົມບູນ ລົດໜ້ອຍຖອຍລົງ ແລະ ສານອິນຊີວັດຖຸລົດລົງ (ບໍ່ແມ່ນສາເຫດມາຈາກການເຊາະເຈື່ອນ)
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires)
3.8 ການປ້ອງກັນ, ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ, ຫຼືການຟື້ນຟູຂອງການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເປົ້າໝາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ພົວພັນ ກັບຄວາມເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ:
- ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
4. ຂໍ້ກໍາໜົດ, ກິດຈະກໍາການປະຕິບັດ, ວັດຖຸດິບ, ແລະຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
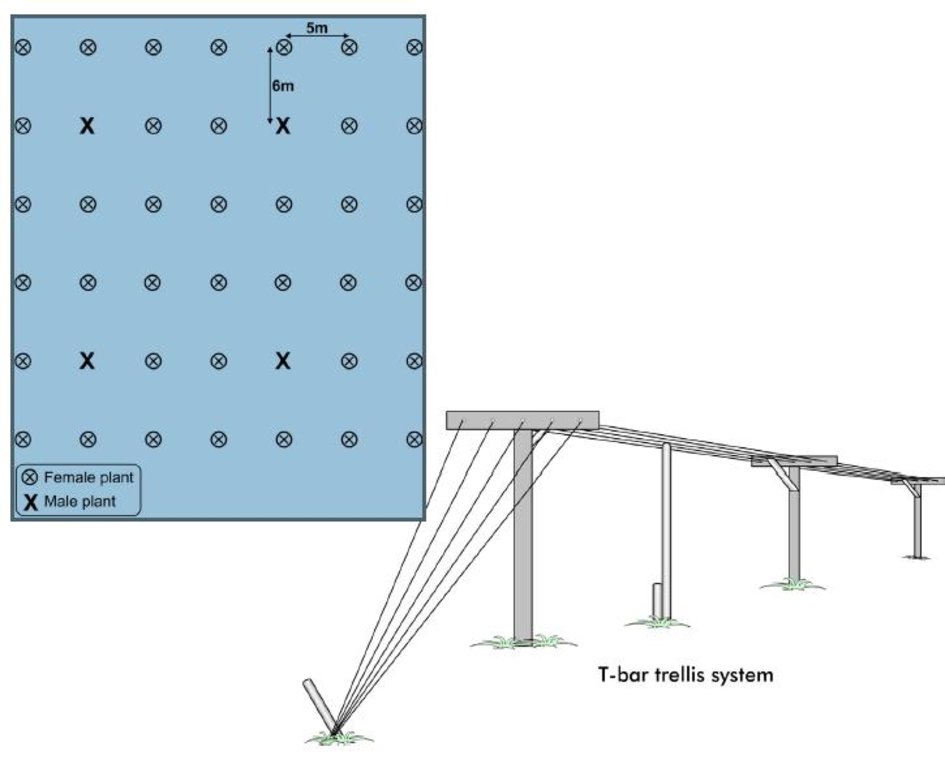
4.1 ເຕັກນິກ ໃນການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງເຕັກນິກ (ທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ ກັບການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດ ທາງດ້ານເຕັກນີກ):
Above: Layout of a kiwi orchard. The ideal density of kiwi plants in an orchard is 300 per ha, or in terms of the units of measure commonly used in Nepal, 15 plants per ropani. The plants are spaced 6 m apart and the distance between the rows is 5 m, with a male to female plant ratio of 1:8.
Below: T-bars are used as trellis supports for the kiwi vines. The T-bars are 2.5–3 m long iron posts that are anchored into the ground; they extend approximately 1.8 m above the ground and 60–70 cm deep into the soil. The arms of the T-bar extend 1–1.2 m. The bars are spaced approximately 4.5 m apart with galvanized wire strung between them and pulled taught to form the trellis itself. The end posts are braced by 4–5 wires that are secured into the ground (as shown).
The kiwi plants should be at least
0.6 m away from the T-bars. The centre wire supports the main cordons, and the outer wires support the fruiting lateral parts.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase of biomass (quantity), Reduce soil erosion
Secondary technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, reduction of slope angle
ຜູ້ຂຽນ:
AK Thaku
4.2 ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປກ່ຽວກັບການຄິດໄລ່ປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າໃນການຜະລິດ ແລະ ມູນຄ່າອື່ນໆ
ລະບຸ ວິທີການ ຄຳໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ແລະ ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າ ທີ່ໄດ້ຄິດໄລ່:
- ຕໍ່ພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸຫົວໜ່ວຍ ຂະໜາດ ແລະ ເນື້ອທີ່:
ha
ລະບຸ ສະກຸນເງິນທີ່ໃຊ້ສໍາລັບ ການຄິດໄລ່ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ:
- USA
ລະບຸ ຄ່າຈ້າງ ຄ່າແຮງງານສະເລ່ຍ ຕໍ່ ວັນ:
3.7
4.3 ການສ້າງຕັ້ງກິດຈະກໍາ
| ກິດຈະກໍາ | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | • The plot where the vines are to be planted is prepared by clearing and weeding.• The seedling pits are prepared at least 2 months before planting. Typically the pits are 1 m x 1 m and 1 m deep. The pits are filled with compost (30 kg per pit ) and covered with soil to a height of 0.3 m above the ground. | 2 months |
| 2. | • Seedlings are planted in the winter to the same depth as in the nursery; they are planted 6 m apart in rows spaced 5 m apart.• The plants are pruned back to single, healthy shoots 15–30 cm high. |
4.4 ຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ປັດໄຈຂາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນໃນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ
| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ແຮງງານ | Prepare pits and seedlings | persons/day/ha | 136.0 | 3.6765 | 500.0 | |
| ວັດສະດຸໃນການປູກ | Planting material | ha | 1.0 | 1500.0 | 1500.0 | |
| ຝຸ່ນ ແລະ ຢາຊີວະພາບ | Compost / manure | ha | 1.0 | 150.0 | 150.0 | |
| ວັດສະດຸກໍ່ສ້າງ | Iron pole | ha | 1.0 | 3500.0 | 3500.0 | |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 5650.0 | |||||
| ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍທັງໝົດ ສຳລັບການສ້າງຕັ້ງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເປັນສະກຸນເງີນໂດລາ | 5650.0 | |||||
4.5 ບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ / ແຜນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ກິດຈະກໍາ
| ກິດຈະກໍາ | ໄລຍະເວລາ / ຄວາມຖີ່ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Permanent sod is maintained between the plant rows. Frequent weeding is required especially during the rainy season.• Both summer and winter pruning is required. | |
| 2. | • Cuttings from branches that fruited during the previous season (typically less than a pencil width in thickness) are collected during the winter pruning for propagation.• Overhead sprinkler irrigation is used for commercial kiwi production.• Kiwi vines are fertilized with manure in the early spring |
4.6 ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ແລະ ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນສໍາລັບການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາກິດຈະກໍາ / ແຜນປະຕິບັດ (ຕໍ່ປີ)
| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ແຮງງານ | Maintenance and prunning | persons/day/ha | 122.0 | 3.6885 | 450.0 | |
| ອຸປະກອນ | Secateurs | ha | 1.0 | 50.0 | 50.0 | |
| ອຸປະກອນ | Binding wire | ha | 1.0 | 650.0 | 650.0 | |
| ຝຸ່ນ ແລະ ຢາຊີວະພາບ | Compost / manure | ha | 1.0 | 150.0 | 150.0 | |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ໃຊ້ໃນການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 1300.0 | |||||
| ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍທັງໝົດ ສຳລັບການບົວລະບັດຮກສາເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເປັນສະກຸນເງີນໂດລາ | 1300.0 | |||||
4.7 ປັດໄຈ ທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
ໃຫ້ອະທິບາຍ ປັດໃຈ ທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ຕົ້ນທຶນ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ:
The above establishment cost is for a plantation of 300 plants on one hectare; the recurrent annual maintenance cost has been calculated for a plantation of 300 plants per ha per year. All costs are estimated based on experience gained at the ICIMOD Knowledge Park at Godavari.
5. ສະພາບແວດລ້ອມທໍາມະຊາດ ແລະ ມະນຸດ
5.1 ອາກາດ
ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນປະຈໍາປີ
- < 250 ມີລິແມັດ
- 251-500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 501-750 ມີລິແມັດ
- 751-1,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,001-1,500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,501-2,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 2,001-3,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 3,001-4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- > 4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
ເຂດສະພາບອາກາດກະສິກໍາ
- ເຄີ່ງຄວາມຊຸ່ມ
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 ພູມິປະເທດ
ຄ່າສະເລ່ຍ ຄວາມຄ້ອຍຊັນ:
- ພື້ນທີ່ຮາບພຽງ (0-2%)
- ອ່ອນ (3-5 %)
- ປານກາງ (6-10 %)
- ມ້ວນ (11-15 %)
- ເນີນ(16-30%)
- ໍຊັນ (31-60%)
- ຊັນຫຼາຍ (>60%)
ຮູບແບບຂອງດິນ:
- ພູພຽງ / ທົ່ງພຽງ
- ສັນພູ
- ເປີ້ນພູ
- ເນີນພູ
- ຕີນພູ
- ຮ່ອມພູ
ເຂດລະດັບສູງ:
- 0-100 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 101-500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- > 4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
5.3 ດິນ
ຄວາມເລິກ ຂອງດິນສະເລ່ຍ:
- ຕື້ນຫຼາຍ (0-20 ຊັງຕີແມັດ)
- ຕື້ນ (21-50 ຊຕມ)
- ເລີກປານກາງ (51-80 ຊຕມ)
- ເລິກ (81-120 ຊມ)
- ເລິກຫຼາຍ (> 120 cm)
ເນື້ອດິນ (ໜ້າດິນ):
- ປານກາງ (ດິນໜຽວ, ດິນໂຄນ)
ຊັ້ນອິນຊີວັດຖຸ ເທິງໜ້າດິນ:
- ສູງ (> 3 %)
ຖ້າເປັນໄປໄດ້ ແມ່ນໃຫ້ຕິດຄັດ ການພັນລະນາດິນ ຫຼື ຂໍ້ມູນສະເພາະຂອງດິນ, ຕົວຢ່າງ, ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ປະເພດຂອງດິນ, ຄ່າຄວາມເປັນກົດ / ເປັນດ່າງຂອງດິນ, ສານອາຫານ, ດິນເຄັມ ແລະ ອື່ນໆ.
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 ມີນໍ້າ ແລະ ຄຸນນະພາບ
ລະດັບ ນໍ້າໃຕ້ດິນ:
< 5 ແມັດ
ການມີນໍ້າ ເທິງໜ້າດິນ:
ດີ
ຄຸນນະພາບນໍ້າ (ບໍ່ມີການບໍາບັດ):
ມີນໍ້າດື່ມ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ ແລະ ຂໍ້ກໍານົດ ເພີ່ມເຕີມ ກ່ຽວກັບ ຄຸນນະພາບ ແລະ ປະລິມານ ຂອງນ້ຳ:
Water quality (untreated): Also for agricultural use (irrigation)
5.5 ຊີວະນາໆພັນ
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ທາງສາຍພັນ:
- ສູງ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ ແລະ ລັກສະນະສະເພາະ ເພີ່ມເຕີມກ່ຽວກັບ ຊີວະນາໆພັນ:
695 species of flora and 230 species of fauna have been documented within the Knowledge Park's 30 ha area
5.6 ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ລະບົບ ການຕະຫຼາດ ແລະ ຜົນຜະລິດ:
- ປະສົມປົນເປ( ກຸ້ມຕົນເອງ/ເປັນສິນຄ້າ)
ລາຍຮັບ ທີ່ບໍ່ໄດ້ມາຈາກ ການຜະລິດ ກະສິກໍາ:
- > 50 % ຂອງລາຍຮັບທັງໝົດ
ລະດັບ ການຫັນເປັນກົນຈັກ:
- ການໃຊ້ແຮງງານຄົນ
- ສັດລາກແກ່
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
5.7 ເນື້ອທີ່ສະເລ່ຍຂອງດິນ ທີ່ຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ເຮັດເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- <0.5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 0.5-1 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1-2 ເຮັກຕາ
- 2-5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 5-15 ເຮັກຕາ
- 15-50 ເຮັກຕາ
- 50-100 ເຮັກຕາ
- 100-500 ເຮັກຕາ
- 500-1,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1,000-10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- > 10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
5.8 ເຈົ້າຂອງທີ່ດິນ, ສິດໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ, ແລະ ສິດທິການນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ
ເຈົ້າຂອງດິນ:
- ລັດ
ສິດທິ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
- ຊຸມຊົນ (ທີ່ມີການຈັດຕັ້ງ)
- ບຸກຄົນ
ສິດທິ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ:
- ຊຸມຊົນ (ທີ່ມີການຈັດຕັ້ງ)
- ບຸກຄົນ
5.9 ການເຂົ້າເຖິງການບໍລິການ ແລະ ພື້ນຖານໂຄງລ່າງ
ຖະໜົນຫົນທາງ ແລະ ການຂົນສົ່ງ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
Labour:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
6. ຜົນກະທົບ ແລະ ລາຍງານສະຫຼຸບ
6.1 ການສະແດງຜົນກະທົບ ພາຍໃນພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງເສດຖະກິດສັງຄົມ
ມີນໍ້າ ແລະ ຄຸນນະພາບ
ຄວາມຕ້ອງການ ນໍ້າຊົນລະປະທານ
ຜົນກະທົບດ້ານວັດທະນາທໍາສັງຄົມ
ການຄໍ້າປະກັນ ສະບຽງອາຫານ / ກຸ້ມຢູ່ກຸ້ມກິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Kiwi is considered an elite fruit and it is usually too expensive for local consumption
ສະຖາບັນ ການຈັດຕັ້ງຊຸມຊົນ
ຄວາມຮູ້ກ່ຽວກັບ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ / ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
livelihood and human well-being
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Kiwi production can be a good source of cash income as it is a high value crop. Kiwi fruit is high in nutrients, eating kiwis has been show to boost the immune system, to help regulate blood pressure, and to be beneficial for cardiac patients
ຜົນກະທົບຕໍ່ລະບົບນິເວດ
ດິນ
ການປົກຄຸມຂອງດິນ
ການສູນເສຍດິນ
ຊີວະນານາພັນ: ສັດ, ພືດ
ມວນຊີວະພາບ / ຢູ່ເທິງຊັ້ນດິນ C
ຜົນກະທົບຕໍ່ລະບົບນິເວດອື່ນໆ
Pollen for bees
biodiversity
efficient use of land
competition with other plants for water, nutrients, and sunlight when intercropping
6.2 ຜົນກະທົບທາງອ້ອມ ຈາກການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ນໍ້າຖ້ວມຢູ່ເຂດລຸ່ມນໍ້າ
ການປ້ອງກັນ / ຄວາມອາດສາມາດ ການກັ່ນຕອງ
6.3 ການປ້ອງກັນ ແລະ ຄວາມບອບບາງ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢິ ໃນການປ່ຽນແປງສະພາບດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ແລະ ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງກັບອາກາດທີ່ມີການປ່ຽນແປງທີ່ຮຸນແຮງ / ໄພພິບັດທາງທໍາມະຊາດ (ຮັບຮູ້ໄດ້ໂດຍຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ)
ອາກາດ ທີ່ກ່ຽວພັນກັບຄວາມຮຸນແຮງ (ໄພພິບັດທາງທໍາມະຊາດ)
ໄພພິບັດທາງອຸຕຸນິຍົມ
| ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|
| ພະຍຸຝົນ | ດີ |
| ພາຍຸລົມທ້ອງຖິ່ນ | ບໍ່ດີ |
ໄພພິບັດທາງພູມອາກາດ
| ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|
| ແຫ້ງແລ້ງ | ບໍ່ດີ |
ຜົນສະທ້ອນສະພາບອາກາດອື່ນໆທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ
ຜົນສະທ້ອນສະພາບອາກາດອື່ນໆທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ
| ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|
| Mild winter frost | ດີ |
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
A net canopy can be used to protect the vines from hail storms and help prevent fruit from dropping prematurely
6.4 ການວິເຄາະຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ຜົນປະໂຫຍດ
ຈະເຮັດປະໂຫຍດເພື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍກັບສິ່ງກໍ່ສ້າງ (ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ) ໄດ້ແນວໃດ?
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກຫຼາຍ
ຈະໄດ້ຮັບຜົນປະໂຫຍດເມື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບ / ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍໃນການບຳລຸງຮັກສາທີເ່ກີດຂື້ນອິກ (ຈາກທັດສະນະຄະຕິຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ) ໄດ້ແນວໃດ?
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກເລັກນ້ອຍ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກຫຼາຍ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The approximate annual income from kiwi production is USD 11,765/ha/year. The technology provides on-farm employment opportunities for both men and women.
6.5 ການປັບຕົວຮັບເອົາເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- ກໍລະນີດຽວ / ການທົດລອງ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Kiwi fruit is gaining in popularity in Nepal; at present it is cultivated commercially by farmers in Kavre, Lalitpur, Dolakha, and Ilam Districts as well as in the Kathmandu Valley. The technology is widely accepted. Kiwi saplings were initially supplied by ICIMOD and by a private nursery in Kavre District.
Driver for adoption:
• Increased market demand for kiwi fruit
• A good alternative for sloping land management
• Kiwi cultivation is a source of income generation
Constraints
• It has been difficult to meet the high demand for kiwi seedlings. The scarcity of seedlings is the main bottleneck limiting the uptake of kiwi production.
6.7 ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຈຸດດີ / ໂອກາດ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ |
|---|
|
Orchards are easy to establish and farmers can readily learn what is needed for kiwi cultivation How can they be sustained / enhanced? Awareness and training programmes can help farmers quickly learn what is needed for kiwi cultivation. |
|
The benefits of the technology are easy to observe; farmers generate cash income from selling kiwi fruit, juice, and jam. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Awareness and training programmes can help farmers quickly learn what is needed for kiwi cultivation and postharvest processing. |
|
Soil erosion is decreased due to increased groundcover. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Awareness and training programmes can help farmers quickly learn what is needed for kiwi cultivation. |
|
Kiwi cultivation provides on-farm employment opportunities. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Awareness and training programmes can help farmers quickly learn what is needed for kiwi cultivation. |
6.8 ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແລະ ວິທີການແກ້ໄຂບັນຫາ
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ/ຂໍ້ບົກຜ່ອງ/ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| The initial costs associated with establishing the orchard may be a little expensive for many farmers, these include the purchase of: T-bar trellises, seedlings, iron rods, and wire. | Begin by using locally available materials such as bamboo poles to make T-bar trellis. |
7. ເອກະສານອ້າງອີງ ແລະ ການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
7.1 ວິທີການ / ແຫຼ່ງຂໍ້ມູນ
7.3 ເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ກັບຂໍ້ມູນທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງໂດຍກົງ
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
Kiwi fruit production guide. Tuscaloosa, Alabama, United States: Alabama University, Himelrick, DG; Powell, A (1998)
URL:
http://www.aces.edu/pubs/docs/A/ANR-1084/ANR-1084.pdf
ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ ແລະ ເນື້ອໃນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ບໍ່ມີຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ເນື້ອໃນ
ບໍ່ມີເນື້ອໃນ