Remote Sensing as a Tool for Land Degradation Neutrality Monitoring [Грузия]
- Создание:
- Обновить:
- Составитель: Hanns Kirchmeir
- Редакторы: Natia Kobakhidze, Christian Goenner
- Рецензент: Rima Mekdaschi Studer
technologies_5488 - Грузия
Просмотреть разделы
Развернуть все Свернуть все1. Общая информация
1.2 Контактные данные специалистов и организаций, участвующих в описании и оценке Технологии
co-compiler:
co-compiler:
Название проекта, содействовавшего документированию/оценке Технологии (если применимо)
Integrated Biodiversity Management, South Caucasus (IBiS)Название организации (-ий), содействовавших документированию/оценке Технологии (если применимо)
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ)1.3 Условия, регламентирующие использование данных, собранных ВОКАТ
Составитель и ответственный(-ые) специалист(-ы) согласны с условиями, регламентирующими использование собранных ВОКАТ данных:
Да
1.4 Декларация по устойчивости описываемой Технологии
Вызывает ли описанная здесь Технология проблемы деградации земель настолько, что ее нельзя назвать природосберегающей?
Нет
1.5 Ссылка на Анкету (ы) по Подходам УЗП (документируется с использованием ВОКАТ)

Land Degradation Neutrality Transformative Projects and Programmes (LDN-TPP) … [Грузия]
In the framework of the project ‘Generating Economic and Environmental Benefits from Sustainable Land Management for Vulnerable Rural Communities of Georgia’, Land Degradation Neutrality Transformative Projects and Programmes (LDN-TPP) were developed to implement the LDN targets at municipal level. The approach defines the process to break down global and international …
- Составитель: Daniel Zollner

Integrated Pasture Management Planning in Mountainous Regions [Грузия]
The unsustainable use of pastures and forest areas has led to soil erosion, degradation, desertification and loss of biodiversity in the high mountain areas of the South Caucasus. The development of pasture passports is part of a broader approach to a strategic pasture management plan for Tusheti. This showcase includes …
- Составитель: Hanns Kirchmeir
2. Описание Технологии УЗП
2.1 Краткое описание Технологии
Определение Технологии:
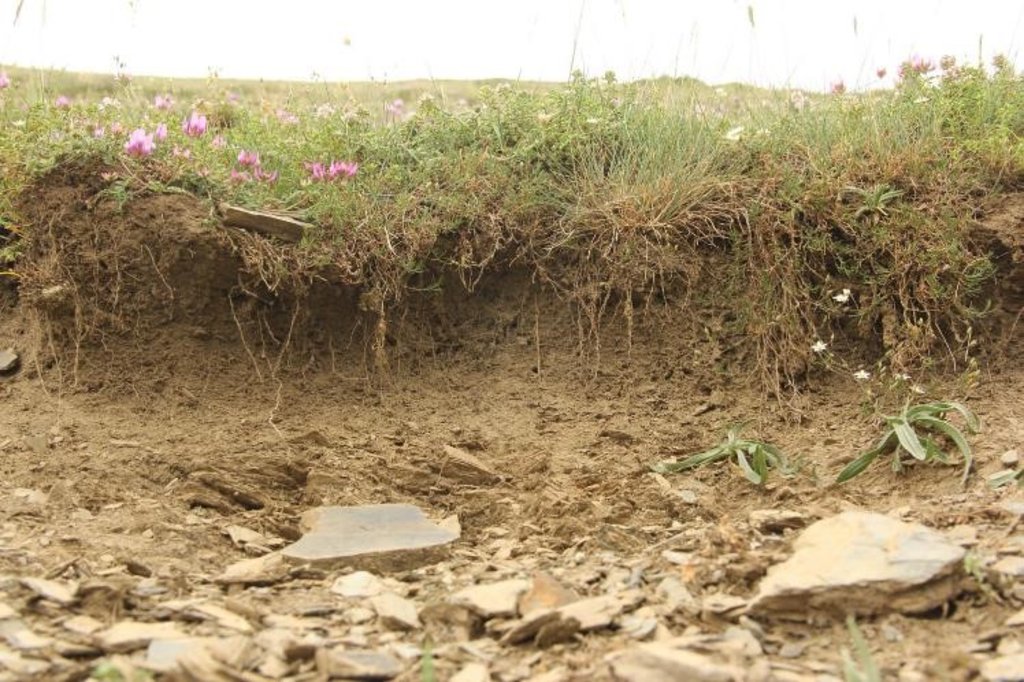
Land degradation contributes to biodiversity loss and the impoverishment of rural livelihoods in Tusheti. Above all, however, land degradation are triggered by climate change as traditional land use practise might not be adapted to new climate conditions which can cause or speed up degradation processes significantly. On the other hand, degraded land often leads to low biomass volumes and this reduces the ecosystem capability to stabilise local climate conditions. The concept of Land Degradation Neutrality (LDN) and the method of using remote sensing for monitoring land degradation are tools to identify the need for local planning processes. This showcase describes the LDN monitoring concept, national targets and the technology to assess indicators, mechanism and incentives for LDN.
2.2 Подробное описание Технологии
Описание:
Purpose
The continuing global degradation of land resources threatens food security and the functioning of ecosystem services by reducing or losing their biological or economic productivity. Unsustainable land-use practices such as deforestation, overgrazing and inappropriate agricultural management systems trigger the loss and degradation of valuable land resources in Georgia. These effects are visible in all countries of the South Caucasus. About 35% of the agricultural land in Georgia is severely degraded, 60% is of low to middle production quality.
Land Degradation Neutrality (LDN)
LDN is a new international concept to combat the ongoing degradation of valuable soil resources. The LDN concept was developed by the UNCCD to encourage countries to take measures to avoid, reduce or reverse land degradation, with the vision of achieving a zero-net loss of productive land. To combat land degradation in Georgia, in 2017, the national LDN Working Group set voluntary national targets to address specific aspects of LDN, and submitted them to the UNCCD Secretariat.
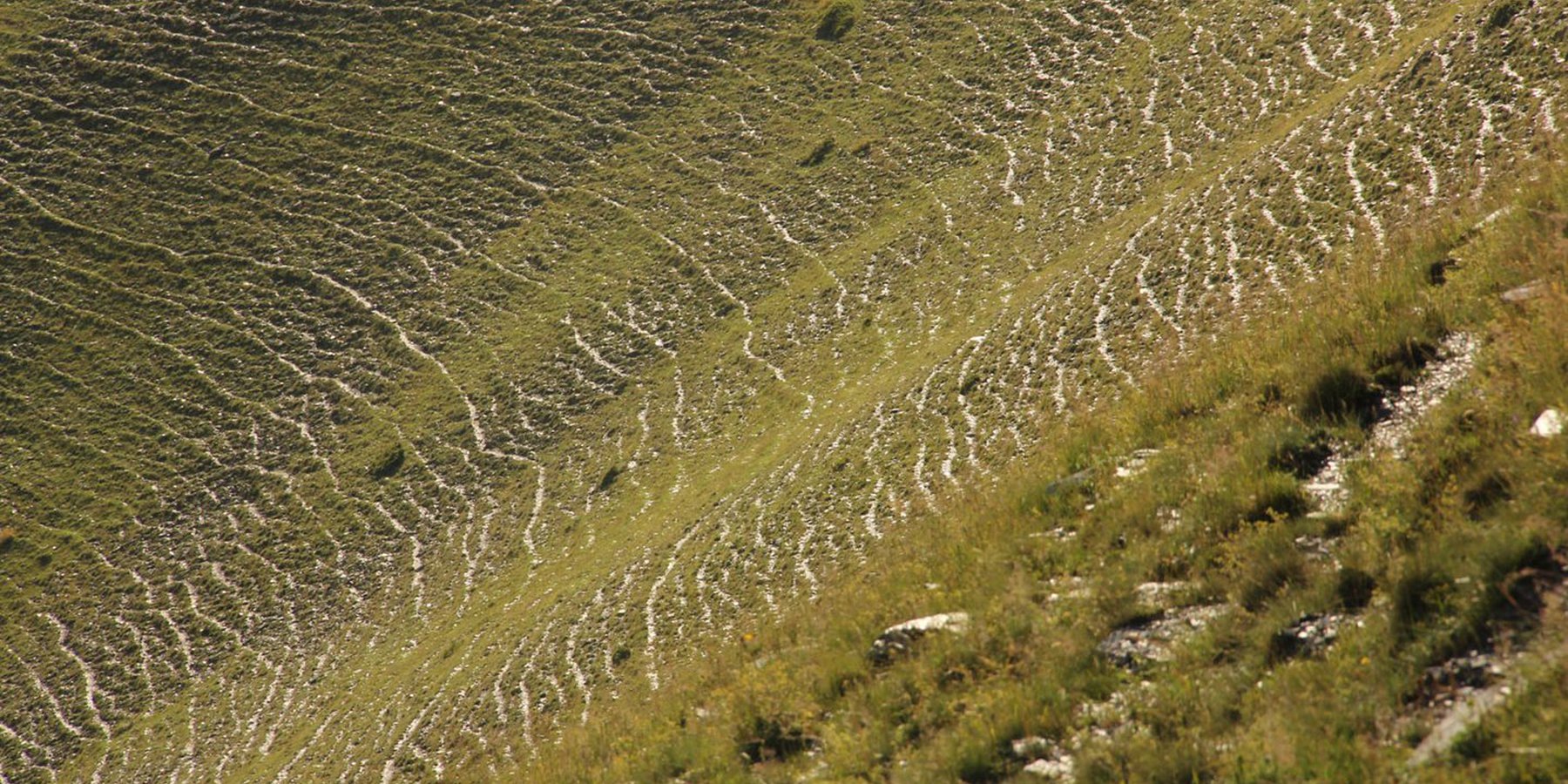
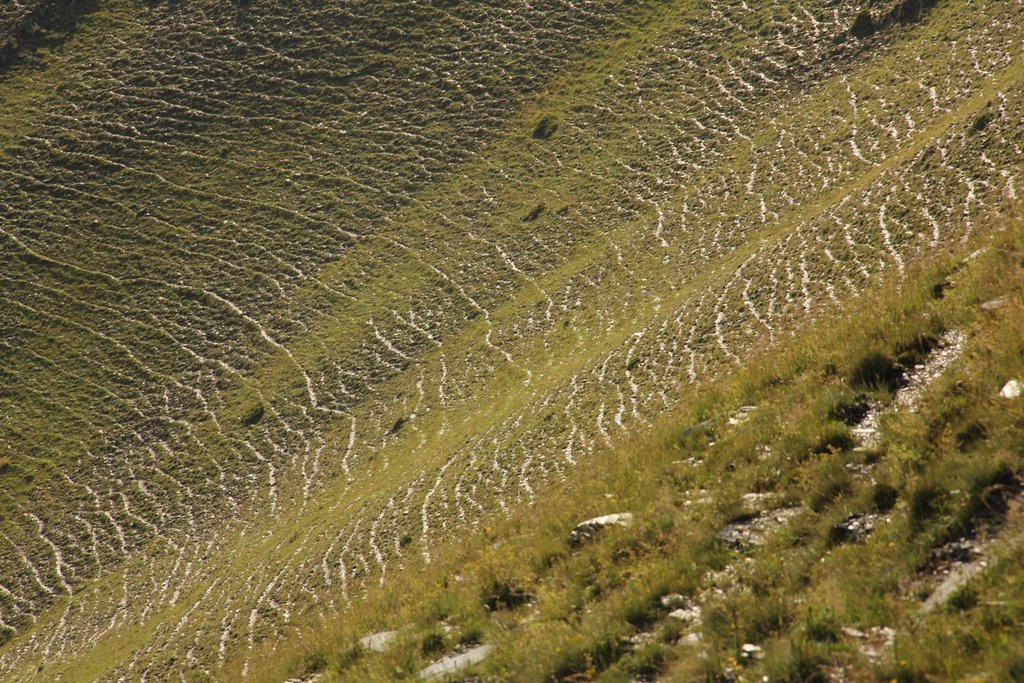
To effectively set up counter measures to combat land degradation it is important to have detailed spatial information on land cover and land cover changes as well as on trends in degradation (like size of areas effected by erosion). Therefore a remote sensing toolset was developed and tested in the pilot are of Tusheti protected landscapes in the High Caucasus in Georgia. This region shows increasing soil erosion problems by uneven distribution of grazing activities and was selected for developing erosion control measures within the Integrated Biodiversity Management in the South Caucasus Program (IBiS) funded by the Deutsche Gesellschaft für internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ).
Sensitivity Model
The Integrated Biodiversity Management in the South Caucasus (IBiS) project in cooperation with national experts in Georgia, developed and applied a remote sensing toolset called "Erosion Sensitivity Model". This remote sensing toolset helps to assess the current state and the general erosion risk. The sensitivity model is based on the RUSLE – Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation. The tool allows the calculation of erosion caused by rainfall and surface run-off. The RUSLE equation incorporates a combination of different input factors such as precipitation (R), soil type (K), slope (LS), vegetation cover (C) and protection measures (P). In this way, the estimated average soil loss in tonnes per acre per year (A) can be calculated as follows: A = R * K * LS * C * P.
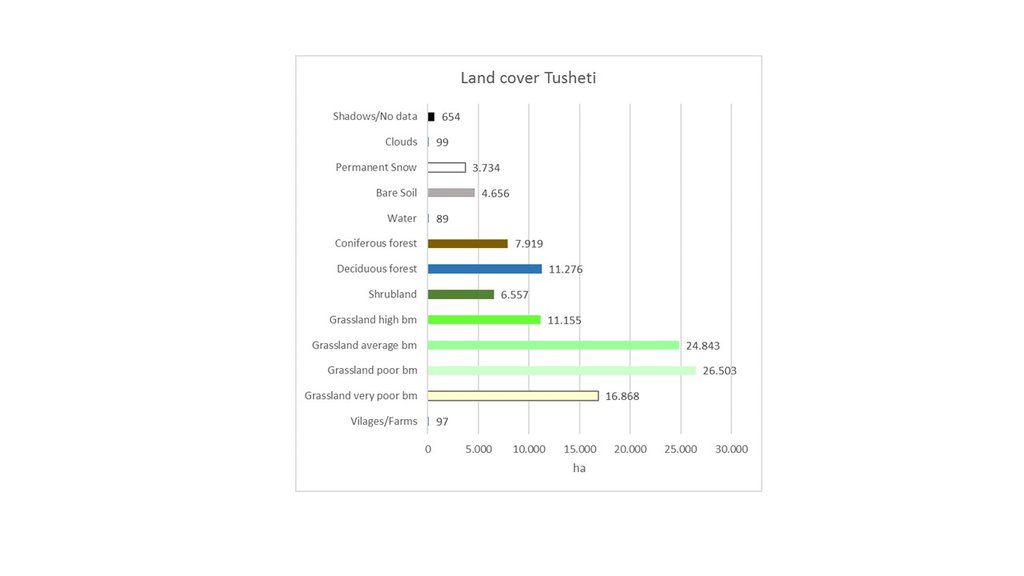
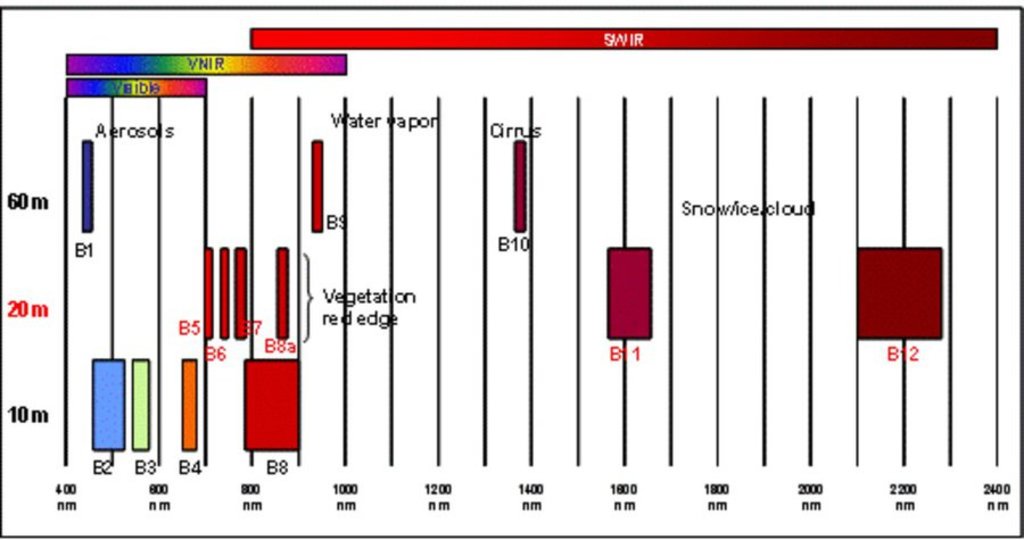
The rainfall factor (R) results from a quotient from the monthly and annual mean value of precipitation. The data come from the data platform “CHELSA – Climatologies at high resolution for the earth’s land surface areas”. For the soil type factor (K), a soil map of 1:200,000 was taken. Then, depending on the soil type, different contents of sand, silt, loam and clay were used to calculate the K factor. The slope length and steepness factor (LS) is calculated from a digital elevation model (DEM) with a raster resolution of 10x10m. The DEM is derived from the topographic map 1:25,000. The global elevation model derived from SRTM data (Shuttle Radar Topography Mission) has a resolution of 30x30 m and is available worldwide free of charge. The land cover factor (C) describes the vegetation cover that protects the soil from erosion. The vegetation cover slows down the speed of the raindrops and reduces the erosive effect of the rain. It slows down surface water runoff and stabilises the soil through root systems. The main indicators, land cover and productivity, can be assessed by remote sensing. The data from satellites need to be classified and calibrated by field data (ground truthing). The technology for the assessment of these indicators with Sentinel 2 satellite images was developed and applied in 2016 to 2018 in the Tusheti region (Akhmeta municipality) in the framework of the GIZ-IBiS project. Based on spectral information from airborne or satellite images, the density of the vegetation was calculated and mapped. There are well developed vegetation indices and classification systems to derive different land cover types and vegetation densities (mainly described by the Leaf Area Index LAI or biomass indices). The LAI is the area of the leaf surface (in square meters) per square meter ground surface. Since the real surface area of the leaves is hardly measurable, the amount of biomass is a proxy for the LAI. The P-factor is rarely considered in large-scale modelling of soil erosion risk as it is difficult to estimate it with very high accuracy. Therefore, to refine the model, a more detailed DEM (digital elevation model) is required (e.g., from satellite images). Based on the input factors, a soil erosion risk map was calculated for the whole territory of the Tusheti Protected Areas (113,660 ha). Based on the different spectral bands of the Sentinel 2 satellite image, a land cover map was calculated using the Support Vector Machine (SVM) technology and spectral image information.
The results have been integrated in the development of pasture management plans ("pasture passports"). This maps and documents are indicating areas of high erosion risk that need to be excluded from grazing and the maximum number of livestock has been calculated based on the biomass maps and will be integrated into the lease contracts.
The repetition of the remote sensing after some years (e.g. 5 years) will help to evaluate, if the measures in the pasture management have been successful to stop the degradation processes.
2.3 Фотографии, иллюстрирующие Технологию
2.5 Страна/ регион/ места, где применяется Технология, информация о которых собрана в данной Анкете
Страна:
Грузия
Административная единица (Район/Область):
Tusheti region, Akhmeta municipality
Охарактеризуйте пространственное распространение Технологии :
- равномерно-однородное применение на определенной площади
Если технология равномерно занимает территорию, укажите площадь покрытия (в км2):
1000,0
Технология применяется на ООПТ?
Да
Если да, укажите:
The area is in the Tusheti Protected Areas (Tusheti Strict Nature Reserve, Tusheti National Park, Tusheti Protected Landscape).
Пояснения:
The whole territory was analysed by remote sensing and field records for calibration were collected on sample plots from different places in Tusheti.
Map
×2.6 Сколько лет применяется данная Технология
Год начала реализации:
2016
2.7 Внедрение Технологии
Укажите, как именно Технология УЗП была внедрена:
- через проекты/ внешнее вмешательство
3. Классификация Технологии УЗП
3.1 Основные цели и задачи реализации Технологии
- повышение производства
- снижение или предотвращение деградации земель, восстановление нарушенных земель
- сохранение/ повышение биоразнообразия
- provide information to make a spatial-territorial planning
3.2 Текущий(-ие) тип(-ы) землепользования на территории, где применяется Технология
Комбинированное землепользование в пределах одной и той же земельной единицы:
Да
Укажите сочетания типов землепользования (посевы / пастбища / деревья):
- Агро-пастбищное хозяйство ( включая растениеводство-животноводство)

Пахотные угодья и плантации
- Однолетние культуры
Ежегодный урожай - Уточните культуры:
- зерновые культуры - ячмень
- корневые / клубнеплодные культуры - картофель
Число урожаев за год:
- 1
Применяются ли посевы в междурядьях?
Нет
Применяется ли севооборот?
Нет

Пастбищные угодья
Экстенсивный выпас:
- Перегонное скотоводство
Вид животных:
- cattle - dairy and beef (e.g. zebu)
- овца
Используется ли комплексное земледельческо-животноводческое хозяйство?
Нет
3.3 Изменилось ли использование земель в связи с внедрением Технологии?
Изменилось ли использование земель в связи с внедрением Технологии?
- Нет (см. пункт 3.4)
3.4 Водоснабжение
другое (например, паводковое):
- rainfed and mixed rained-irrigation
3.5 Категория УЗП, к которой относится Технология
- Кочевое животноводство и пастбищное хозяйство
- Улучшение почвенного/ растительного покрова
3.6 Мероприятия УЗП, выполняемые в рамках Технологии

управленческие мероприятия
- У2: Изменение формы/ интенсивности хозяйствования

другие мероприятия
Поясните:
It is a monitoring technology to evaluate land management activities.
Пояснения:
On some pilot plots technologies to control erosion and stop land degradation have been tested. This includes fencing, rotational pasture management, mulching and installing check dams to stop gully erosion.
3.7 Основные проблемы деградации земель, на решение которых направлена Технология

водная эрозия почв
- ВЭп: поверхностная эрозия/смыв верхних почвенных горизонтов
- ВЭл: овражная эрозия / оврагообразование

ухудшение физических свойств почв
- Фу: уплотнение

биологическая деградация
- Бр: сокращение растительного покрова
- Бк: сокращение количества биомассы
Пояснения:
The main drivers of land degradation in the pilot area are overgrazing and trampling, off-road driving as well as infrastructure development (especially inappropriate road construction in steep slopes).
3.8 Предотвращение и снижение деградации земель, или восстановление нарушенных земель
Укажите цель Технологии по отношению к деградации земель :
- предотвращение деградации земель
- снижение деградации земель
Пояснения:
The monitoring tools presented here help to monitor the development of land degradation and to evaluate measures and development trends.
4. Технические характеристики, мероприятия по практической реализации, вложения и стоимость
4.1 Технический рисунок, иллюстрирующий Технологию
Спецификация (пояснения к техническому рисунку):
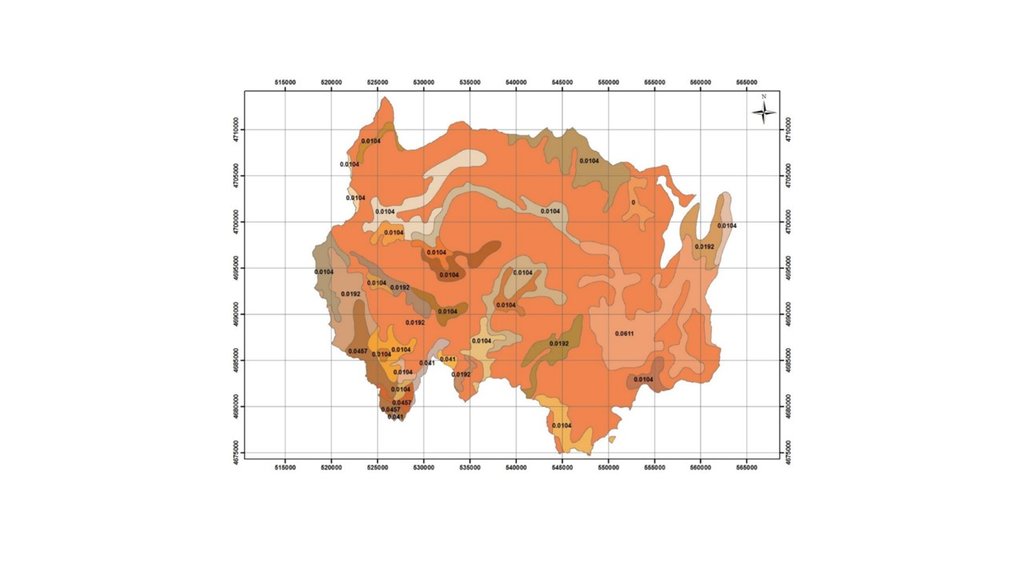
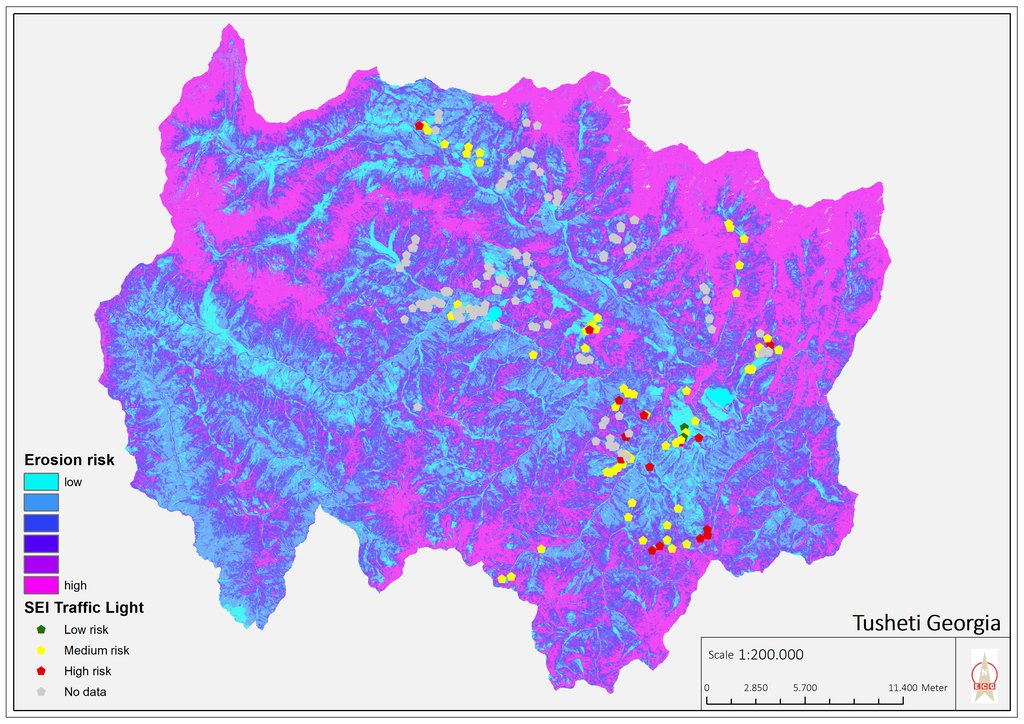
Map of erosion hot spots (pink colour) and the location of field sample plots for evaluation and ground truthing.
Автор:
Hanns Kirchmeir
Дата:
11/09/2019
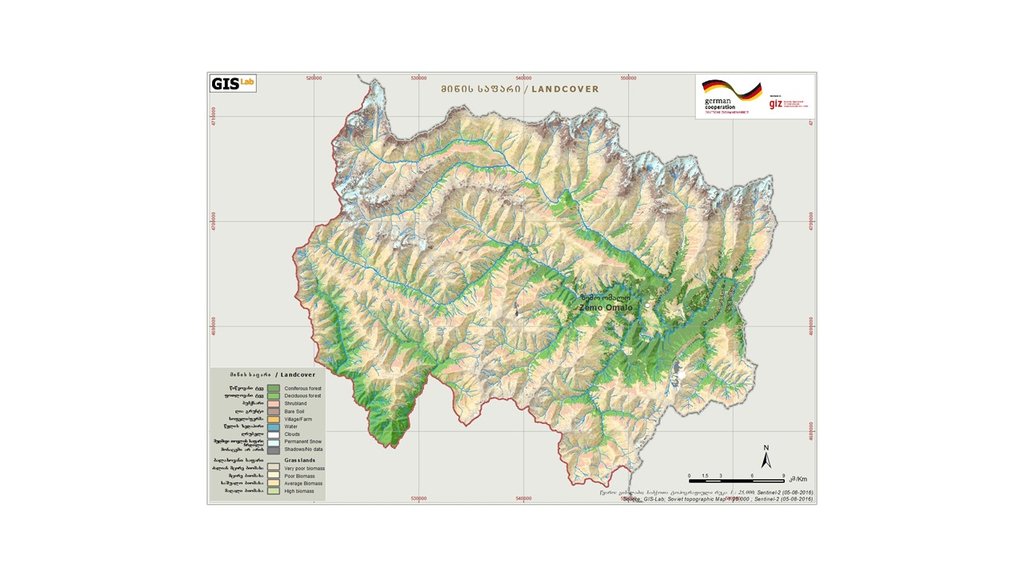
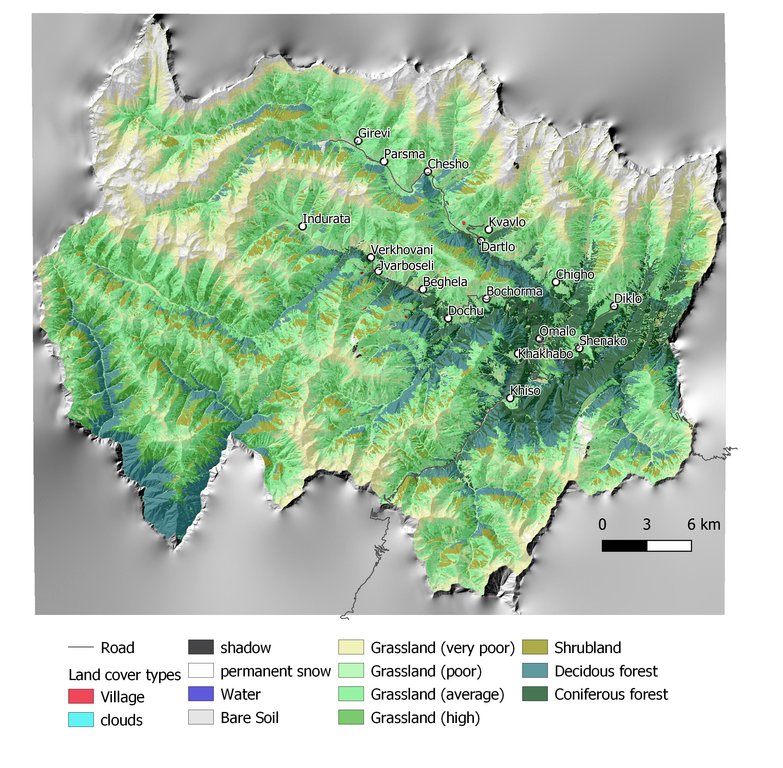
Спецификация (пояснения к техническому рисунку):
Map of land cover classification derived from satellite images. The different grassland types are classified by their biomass as an indicator of productivity and current state. Repeating the satellite image classification with the same parameters after 5 or 10 years can give a clear picture of changes in the land cover.
Автор:
Hanns Kirchmeir
Дата:
11/09/2019
4.2 Общая информация по необходимым вложениям и стоимости
Уточните, как рассчитывались затраты и вложения:
- на площадь, где применяется Технология
Укажите размер и единицу площади:
1000 km2
Укажите денежные единицы, использованные для подсчета затрат:
- Доллары США
Укажите среднюю дневную заработную плату наемных работников:
100
4.3 Мероприятия, необходимые для начала реализации
| Деятельность | Время (сессия) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | National level. Baseline: Field assessment for remote sensing calibration (1x/20 years) | 2017 |
| 2. | Sentinel satellite image classification (multi temporal data from 2017) | 2017 |
| 3. | Statistical data from GEOSTAT Agricultural census | 2014-2016 |
| 4. | Analysis of soil carbon content from existing profiles | 2003 - 2006 |
| 5. | Conduct ongoing monitoring | 5 years intervals |
| 6. | Update sentinel satellite image classification | 1x year |
| 7. | Update statistical data from GEOSTAT Agricultural census | 4x/year |
| 8. | Resampling of soil carbon content near existing profiles | 1x/5 years |
| 9. | Municipal level. Spatial planning: Assessment of current stage of land degradation, anticipated gains and losses | 1x/10 years |
| 10. | Revision of spatial planning on Municipal level. | 1x / 5 years |
4.4 Вложения и затраты, необходимые для начала реализации
| Опишите затраты | Единица | Количество | Затраты на единицу | Общая стоимость на единицу | % затрат, оплаченных землепользователями | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Оплата труда | Remote Sensing analysis by Sentinel Satellite data | person days | 50,0 | 200,0 | 10000,0 | |
| Оплата труда | Collecting field data for satellite image callibration | person days | 40,0 | 200,0 | 8000,0 | |
| Оплата труда | Soil sampling (for carbon content) | person days | 20,0 | 200,0 | 4000,0 | |
| Оплата труда | Including results in spatial planning | person days | 10,0 | 200,0 | 2000,0 | |
| Общая стоимость запуска Технологии | 24000,0 | |||||
| Общие затраты на создание Технологии в долларах США | 24000,0 | |||||
Пояснения:
This covers the implementation of the baseline. Calibrating the model for erosion risk and land cover classification is an big investment but can be extended to larger areas than 1000 km² with similar resources.
4.5 Поддержание/ текущее обслуживание
| Деятельность | Сроки/ повторяемость проведения | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Repeating the application of the calibrated remote sensing model for monitoring repitition | with 5 years interval |
| 2. | Repetition of soil samples for assessing soil carbon content | with 5 years interval |
| 3. | Analysing the results and integrate them in spatial planning and policy making | with 5 years interval |
4.6 Стоимость поддержания/ текущего обслуживания ( в год)
| Опишите затраты | Единица | Количество | Затраты на единицу | Общая стоимость на единицу | % затрат, оплаченных землепользователями | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Оплата труда | Applying the calibrated remote sensing model for monitoring repetition | person days | 20,0 | 200,0 | 4000,0 | |
| Оплата труда | Repetition of soil samples for assessing soil carbon content | person days | 10,0 | 200,0 | 2000,0 | |
| Оплата труда | Analysing results and integrating in spatial planning | person days | 10,0 | 200,0 | 2000,0 | |
| Общая стоимость поддержания Технологии | 8000,0 | |||||
| Общие затраты на поддержание Технологии в долларах США | 8000,0 | |||||
Пояснения:
For the repetition of the remote sensing no new calibration of the GIS-model is needed. Only the field samples for soil carbon need to be repeated.
4.7 Наиболее значимые факторы, влияющие на стоимость затрат
Опишите наиболее значимые факторы, влияющие на стоимость затрат:
Field sample collection;
Remote sensing experts.
5. Природные и социально-экономические условия
5.1 Климат
Среднегодовое количество осадков
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1000 мм
- 1001-1500 мм
- 1501-2000 мм
- 2001-3000 мм
- 3001-4000 мм
- > 4000 мм
Укажите среднегодовое количество осадков (если известно), мм:
800,00
Пояснения/ комментарии по осадкам:
The climate is generally suitable for agriculture with an annual precipitation of up to 800 mm, with hot and humid springs, rainfall peaks in May and June with hot and dry summers.
Агроклиматическая зона
- Умеренно-влажная
- полузасушливая
5.2 Рельеф
Склоны (преобладающие):
- пологие (0-2%)
- покатые (3-5%)
- покато-крутые (6-10%)
- крутые (11-15%)
- очень крутые (16-30%)
- чрезвычайно крутые (31-60%)
- обрывистые (>60%)
Формы рельефа:
- плато/ равнины
- гребни хребтов/холмов
- склоны гор
- склоны холмов
- подножья
- днища долин
Зона высотной поясности:
- 0-100 м над уровнем моря
- 101-500 м н.у.м.
- 501-1000 м н.у.м.
- 1001-1500 м н.у.м.
- 1501-2000 м н.у.м.
- 2001-2500 м н.у.м.
- 2501-3000 м н.у.м.
- 3001-4000 м н.у.м.
- > 4 тыс. м н.у.м.
Укажите, приурочено ли применение Технологии к специфическим условиям:
- не имеет значения
Комментарии и дополнительные сведения по условиям рельефа/ топографии :
The remote sensing approach was applied for the total landscape of Tusheti, including a great variety of land-forms, altitudes ranging from 1600-4000 m a.s.l.
5.3 Почвы
Средняя мощность почв:
- поверхностные (0-20 см)
- неглубокие (21-50 см)
- умеренно глубокие (51-80 см)
- глубокие (81-120 см)
- очень глубокие (> 120 см)
Гранулометрический состав (верхнего горизонта):
- средние фракции (суглинистый, супесчаный)
Гранулометрический состав (на глубине более 20 см):
- средние фракции (суглинистый, супесчаный)
Содержание органического вещества в верхнем горизонте:
- среднее (1-3%)
5.4 Доступность и качество воды
Уровень грунтовых вод:
на поверхности
Доступность поверхностных вод:
средняя
Качество воды (без обработки):
питьевая вода плохого качества (необходима обработка)
Качество воды относится к:
одновременно грунтовые и поверхностные воды
Является ли солёность воды проблемой?
Нет
Происходят ли периодические затопления территории?
Нет
5.5 Биоразнообразие
Видовое разнообразие:
- средняя
Разнообразие местообитаний:
- высокое
5.6 Характеристика землепользователей, применяющих Технологию
Осёдлый или кочевой:
- Полукочевой
Рыночная ориентация производства:
- смешанный (натуральный / коммерческий)
Доходы из других источников:
- < 10% всех доходов
Относительный уровень достатка:
- плохой
Индивидуальное или коллективное хозяйство:
- частное/ домовладение
Уровень механизации:
- ручной труд
- тягловая сила
Пол:
- женщины
- мужчины
Возраст землепользователей:
- средний возраст
Укажите другие важные характеристики землепользователей:
The technology is applied by the Government.
5.7 Средняя площадь земель, используемых землепользователями с применением Технологии
- < 0,5 га
- 0,5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1000 га
- 1000-10000 га
- > 10000 га
Считается ли это мелким, средним или крупным хозяйством (по местным масштабам)?
- среднего размера
Пояснения:
The pasture units are fom 200 to 600 hectares and are based on the old Soviet grazing scheme.
5.8 Собственность на землю, права на земле- и водопользование
Землевладелец:
- государственная
Право землепользования:
- общинное (контролируемое)
- аренда
Право водопользования:
- неограниченное (неконтролируемое)
Права на землепользование основаны на традиционной правовой системе?
Нет
5.9 Доступ к базовым услугам и инфраструктуре
медицинское обслуживание:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
образование:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
технические консультации:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
занятость (вне хозяйства):
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
рынки:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
электроснабжение:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
транспорт и дорожная сеть:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
водоснабжение и канализация:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
финансовые услуги:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
6. Воздействия и заключительные положения
6.1 Влияние Технологии УЗП в пределах территории ее применения
Экологическое воздействие
Почвы
почвенный покров
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Within the timeframe until 2030, specific process indicators to assess the progress will be done.
Другие экологические последствия
Changes in the quality of forests
Комментарий/ пояснения:
tree height, stand density
Changes of the quality of pastures
Комментарий/ пояснения:
biomass production
Changes in the quality of arable land
Комментарий/ пояснения:
yield
Укажите оценку внешних воздействий (измерений):
The monitoring technology was applied for the first time to draw a baseline. Based on the results, activities have been planned and pilot measures have been implemented (exclusion from grazing, reforestation, regulation of grazing intensity). Future replications of the monitoring will show changes and evaluate success of measures. The technologies to control erosion are described separately in the WOCAT database (Community-based Erosion Control [Azerbaijan]; Pasture-weed control by thistle cutting [Georgia]; High-altitude afforestation for erosion control [Armenia]; Slope erosion control using wooden pile walls [Armenia])
6.2 Влияние Технологии за пределами территории ее применения
Укажите оценку внешних воздействий (измерений) :
The technology is only about the monitoring (see above).
6.3 Подверженность и чувствительность Технологии УЗП к постепенным изменениям климата и экстремальным погодным явлениям/ стихийным бедствиям, связанным с изменением климата (в понимании землепользователей)
Постепенное изменение климата
Постепенное изменение климата
| Сезон | увеличение или уменьшение | Насколько успешно Технология справляется с этим? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| сезонное количество осадков | лето | снизилось | очень хорошо |
Пояснения:
Technology is sensitive, it shows the climate change, the impact of the global change locally. The technology itself is not affected by climatic changes.
6.4 Анализ эффективности затрат
Насколько получаемый результат сопоставим с первоначальными вложениями (с точки зрения землепользователей)?
Эффективность затрат в краткосрочной перспективе:
влияние незаметно
Эффективность затрат в долгосрочной перспективе:
позитивное
Насколько получаемый результат сопоставим с текущими расходами по поддержанию технологии (с точки зрения землепользователей)?
Эффективность затрат в краткосрочной перспективе:
влияние незаметно
Эффективность затрат в долгосрочной перспективе:
слабо позитивное
Пояснения:
The monitoring technology was applied for the first time to draw a baseline. Based on the results, activities have been planned and pilot measures have been implemented (exclusion from grazing, reforestation, regulation of grazing intensity). Future replications of the monitoring will show changes and evaluate success of measures. The technologies to control erosion are described separately in the WOCAT database (Community-based Erosion Control [Azerbaijan]; Pasture-weed control by thistle cutting [Georgia]; High-altitude afforestation for erosion control [Armenia]; Slope erosion control using wooden pile walls [Armenia]).
The costs of the remote sensing approach have not been invested by the land owners but by GIZ and the Ministry. Therefore there are no direct negative impact caused by the investment. The maintenance will be covered by public authorities as well. The positive impact for the land users are the clearly delineated pasture unit giving the exact area of grassland and the accessible amount of fodder biomass. By this, the lease-rate can be found according to the productivity and the number of livestock can be adapted to the carrying capacity of the land within the lease contract.
6.5 Внедрение Технологии
- отдельные случаи/ эксперимент
Если возможно, дайте количественную характеристику (число домохозяйств и/или площадь применения):
The technology is desigend to be applied by national or regional addministrations and not by land owners themselves.
6.6 Адаптация
Была ли Технология УЗП изменена в недавнее время с целью адаптации к меняющимся условиям среды?
Нет
6.7 Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности Технологии
| Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности по мнению землепользователей |
|---|
| The monitoring technology can help to find erosion and degradation hot spots and based on this spatial information counter measures can be applied to save the productivity of land. As the income from agricultural activities and livestock breeding is of high priority in this pilot region, the protection of the productivity of land is of high importance to the local land users. |
| Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности по мнению составителя или других ключевых специалистов |
|---|
| The presented remote sensing technologies are a cost efficient and objective way to monitor land degradation and land use changes on large areas on long time periods. Based on this spatial data, land use regulations can be integrated in spatial planning and other legal and practical frameworks (e.g. pasture lease contracts) to counter act the degradation processes. The success of the measures and the development of degradation and rehabilitation can be monitored by the same toolset. |
6.8 Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски Технологии и пути их преодоления
| Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски по мнению землепользователей | Возможные пути их преодоления/снижения? |
|---|---|
| The technology is complex and cannot be applied by the land user her-/himself and is sometimes hard to understand. Therefore they might mistrust in the results and are not eager to accept regulations and measures to stop degradation. | Transparent documentation of the technology and regular field visits to evaluate together with the land owners and users the remote sensing results in the field. |
| Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски по мнению составителя или ответственных специалистов | Возможные пути их преодоления/снижения? |
|---|---|
| The institutional setup on the national level for the regular application of the remote sensing technology and the storage and management of the monitoring data is not established yet. GIS, remote sensing and soil experts are of limited availability. | Institutional capacity building and academic training courses provided at the Georgian universities can help to overcome these limitations. |
| Field data for calibration of satellite images (biomass volumes, classified land cover types, soil types, land management types) with exact information on the spatial location are rare and costly to be created. | Such data and information should be organised and gathered on national level across different sectors (agriculture, forestry, spatial planing, nature conservation ...). This would help to reduce significantly the costs and remote sensing could be applied on much larger areas. |
7. Справочные материалы и ссылки
7.1 Методы сбора/ источники информации
- выезды на места, полевые обследования
Three field visits with national and international experts as well as representatives of administrations and local stakeholders.
- опросы землепользователей
Meeting with cooperation partners, key village stakeholders from three pilot municipalities.
- опросы специалистов/экспертов по УЗП
Three mission meetings with 35 experts.
- данные, собранные из отчетов и достоверных документов
Pilot project on land degradation neutrality in Georgia Final Report. 20.10.2017.
GISLab 2016: Development of Land Cover and Erosion Risk Map based on remote sensing for Tusheti Protected Areas. Study within the frame of GIZ-IBIS.
7.2 Ссылки на опубликованные материалы
Название, автор, год публикации, ISBN:
Land Degradation Neutrality 25.10.2017
Где опубликовано? Стоимость?
https://e-c-o.at/files/publications/downloads/D00813_ECO_policy_brief_LDN_Georgia_171025.pdf
7.3 Ссылки на соответствующую онлайн-информацию
Название/ описание:
Tools for satellite image analysis
Адрес в сети Интернет:
http://step.esa.int/main/snap-2-0-out-now/
Название/ описание:
UNCCD Good Practice Guidance on SDG Indicator 15.31. (Sims et al. 2017)
Адрес в сети Интернет:
https://www.unccd.int/sites/default/files/relevant-links/2017-10/Good%20Practice%20Guidance_SDG%20Indicator%2015.3.1_Version%201.0.pdf
7.4 Общие комментарии
UNCCD Good Practice Guidance on SDG Indicator 15.31. (Sims et al. 2017) gives a detailed technical overview on methods and approaches to calculate LDN indicators by means of remote sensing data.
Ссылки и модули
Развернуть все Свернуть всеСсылки

Land Degradation Neutrality Transformative Projects and Programmes (LDN-TPP) … [Грузия]
In the framework of the project ‘Generating Economic and Environmental Benefits from Sustainable Land Management for Vulnerable Rural Communities of Georgia’, Land Degradation Neutrality Transformative Projects and Programmes (LDN-TPP) were developed to implement the LDN targets at municipal level. The approach defines the process to break down global and international …
- Составитель: Daniel Zollner

Integrated Pasture Management Planning in Mountainous Regions [Грузия]
The unsustainable use of pastures and forest areas has led to soil erosion, degradation, desertification and loss of biodiversity in the high mountain areas of the South Caucasus. The development of pasture passports is part of a broader approach to a strategic pasture management plan for Tusheti. This showcase includes …
- Составитель: Hanns Kirchmeir
Модули
Нет модулей