Water retention polders to improve water management [德国]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Martin Maier
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger, David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Polder zum Wassermanagement entwickelt durch lokale Experten (Nordsee Region)
technologies_1583 - 德国
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
SLM专业人员:
Kleyer Michael
University of Oldenburg
德国
SLM专业人员:
Karrasch Leena
University of Oldenburg
德国
SLM专业人员:
Mayer Martin
University of Oldenburg
德国
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Book project: Making sense of research for sustainable land management (GLUES)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Sustainable Coastal Land Management (COMTESS / GLUES)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
University of Oldenburg (University of Oldenburg) - 德国1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷

Stakeholder participation in integrated assessment and planning of … [德国]
Stakeholders have been involved in integrated assessment to develop action-oriented land use options addressing possible climate change adaptation measures as alternatives to traditional coastal protection strategies.
- 编制者: Martin Maier
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Water retaining polders to reduce flood risk due to heavy rainfall or runoff at high tide in embanked coastal lowlands. Delineation of the retention area and land use within the retention area was developed in a participatory process with local experts.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
In the 19th and 20th century land was reclaimed from the sea to make use of the exposed fertile soils for agriculture through a process known as ‘impoldering’. The reclaimed land is now characterized by intensive grazing and cropland. This is a region where agriculture is the most important form of land use. However, the land needs to be regularly drained. Given the expected increase in precipitation in winter due to climate change, the corresponding increase in freshwater discharge needs to be managed. Furthermore, the periods when natural discharge into the sea oc-curs are likely to decrease – because of rising sea levels also caused by climate change. Consequently, in winter and spring, greater quantities of freshwater will need to be pumped into the sea rather than discharged naturally at the low or ‘ebb’ tide. Specially embanked water retention polders will be required to temporarily impound water as part of a multifunctional approach to coastal zone management.
Purpose of the Technology: These retention polders could be a cost-effective alternative to expensive invest-ments in extra pumping capacities to prevent submergence of low-lying cultivated areas. The primary aim is to restrict floods to the retention polders when the drain-age network is overburdened and cannot deal with the predicted extra demands in the future. The high evapotranspiration from the open waterbody, and the reeds growing within, will also help with reducing the amount of water. During dry sum-mers, the water in the retention polder could also be put to creative use as a source of irrigation. Another potential advantage is that subsurface saltwater intrusion in the region could be prevented by the freshwater-filled polders. During extreme storm surges and in the rare case of breaches in the sea wall, the retention polders would serve as an extra line of defence by holding seawater.
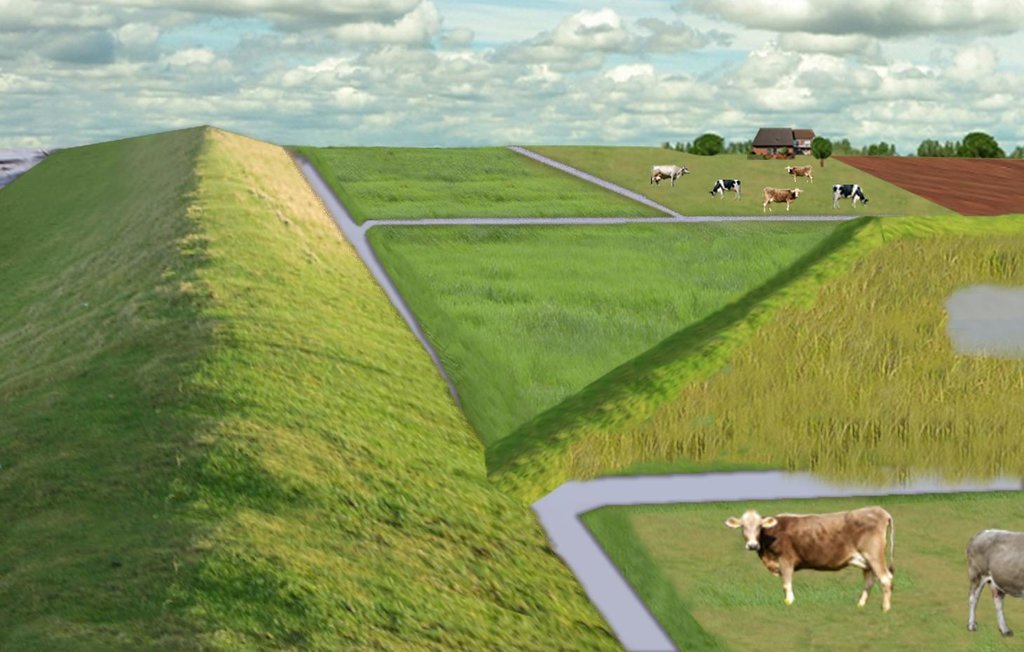
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: An embankment enclosing approx. 500 ha will be able to store up to 2,500,000 m³ of water. This will improve the drainage of an area of approx. 49,000 ha. The invest-ment for building this water retention area is high – but for the reasons stated it serves a necessary purpose at a cost which is lower than the alternative – increased pumped drainage installations. Maintenance costs will be lower than the drainage alternative as only the integrity of the embankment needs to be monitored regularly. Currently, agricultural land use within the polders is adapted to higher water levels and occasional flooding. Within the embanked area there will be a change from the current use of mainly crop land to extensive grazing, open water and reed stands.
Natural / human environment: Some parts within the retention polder will be used for agricultural purposes, while the wetter parts will be set aside. In these latter sections, undisturbed natural regen-eration will take place. A landscape comprising various different elements, without any extreme forms of intensive land use such as large areas of monocultures will be the result. Thus requirements for agricultural use and tourism will be addressed.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
德国
区域/州/省:
Germany, Lower Saxony
有关地点的进一步说明:
Landkreis Aurich
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 33.7 km2.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 10-50年前
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 在实验/研究期间
- 通过项目/外部干预
3. SLM技术的分类
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是
具体说明混合土地使用(作物/放牧/树木):
- 农牧业(包括农牧结合)

农田

牧场
集约放牧/饲料生产:
- 收割和携带/零放牧
- 改良牧场
动物类型:
- 牛 - 奶制品
- 牛 - 非奶牛牛肉
产品和服务:
- 肉类
- 奶类
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Flood events and droughts may substantially disrupt the contemporary land use in the future and lead to higher drainage costs and higher economic risks for agricultural production. This may reduce the ecological and economic viability of the current intensive and highly productive land use under a changing climate.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): There is no awareness of risks due to climate change in the land users point of view.
Cut-and-carry/ zero grazing: cows for milk
Improved pasture: cattle for milk and meat
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Other: Oo: Other: wastelands, deserts, glaciers, swamps, recreation areas, etc
Constraints of infrastructure network (roads, railways, pipe lines, power lines): needs to be adapted to regular flooding
Constraints of recreation (landscape is used for recreation and tourism ): change in landscape due to retention area
Constraints of nature conservation area (protected sites): wetter conditions in retention area
Number of growing seasons per year: 1
Longest growing period in days: 240Longest growing period from month to month: March to October
Livestock density: > 100 LU /km2
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 是(请在技术实施前填写以下有关土地利用的问题)

水道、水体、湿地
- 沼泽、湿地

不毛之地
具体说明:
wastelands
注释:
Mixed: Mp: Agro-pastoralism
3.4 供水
注释:
Water supply: rainfed, mixed rainfed - irrigated
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 地表水管理(泉、河、湖、海)
- 湿地保护/管理
- Flood prevention
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

结构措施
- S5:大坝、集水斗、水池

管理措施
- M1:改变土地使用类型
- M2:改变管理/强度级别
注释:
Main measures: structural measures
Secondary measures: management measures
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

化学性土壤退化
- Cs:盐化/碱化

水质恶化
- Hs:地表水良变化
- Hg:地下水/含水层水位的变化
- Hq:地下水水质下降
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Hs: change in quantity of surface water
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Cs: salinisation / alkalinisation, Hg: change in groundwater / aquifer level, Hq: decline of groundwater quality
Main causes of degradation: change of seasonal rainfall (Climate change, higher rainfall in winter, lower in summer), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (Heavy rainfall in winter due to climate change expected), floods (Flooding due to heavy rainfall in winter)
Secondary causes of degradation: droughts (Droughts due to less rainfall in summer (climate change)), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (Sea level rise)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
注释:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
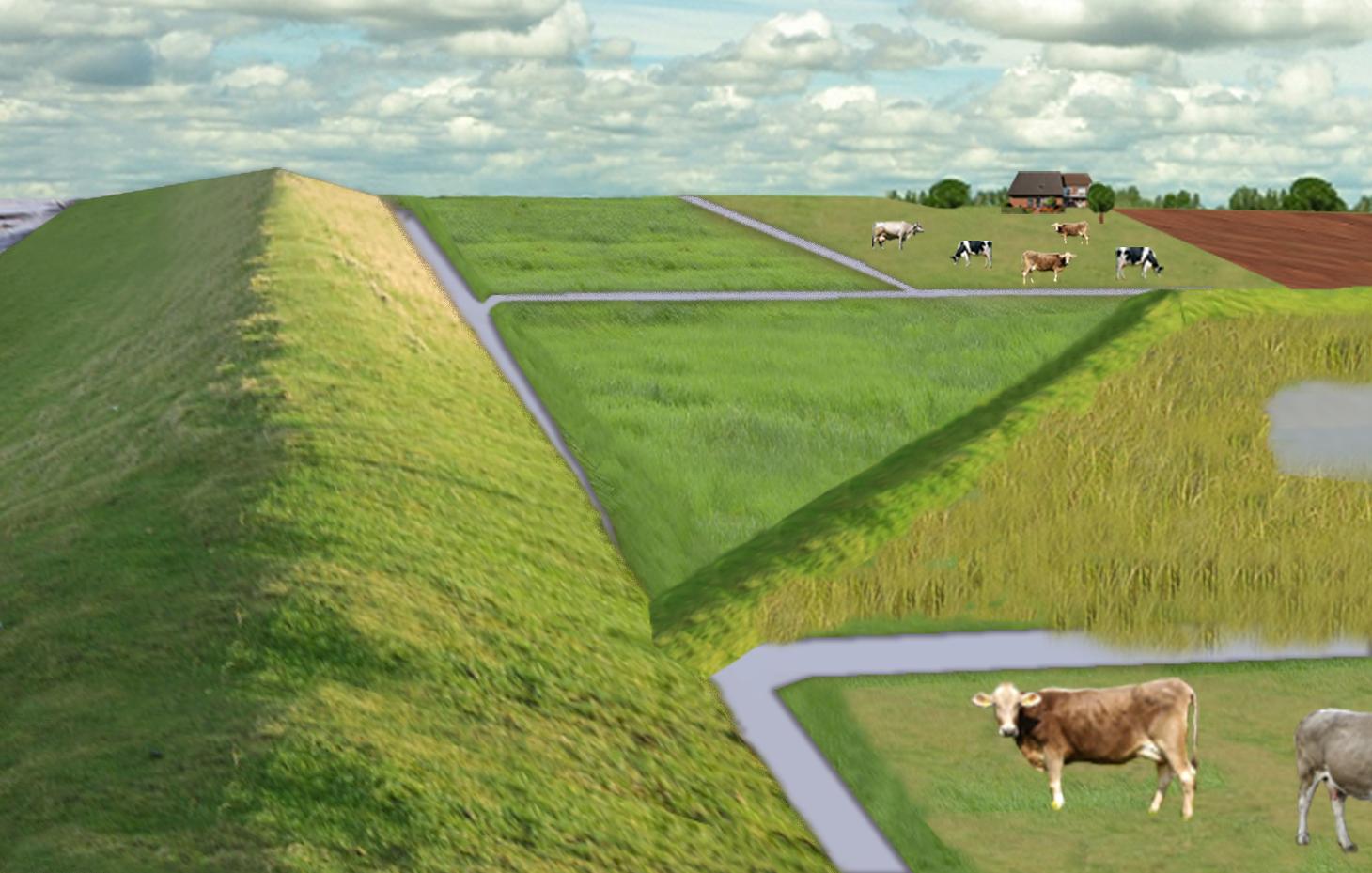
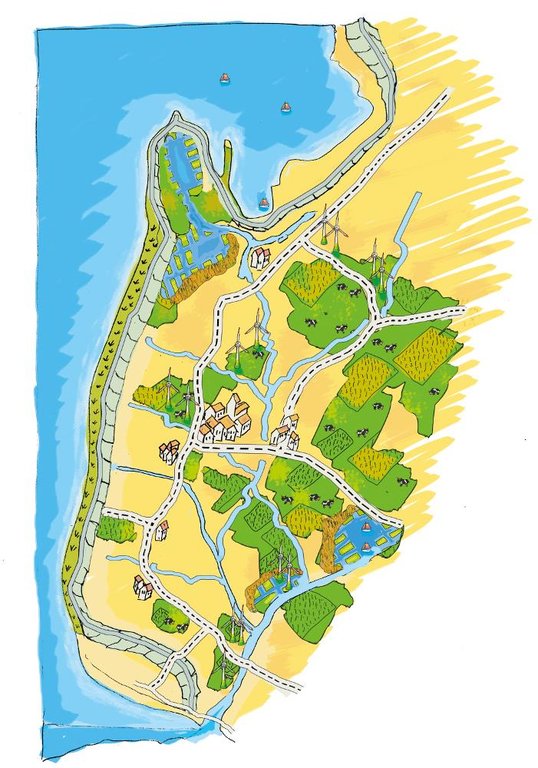
The figure shows the study region, located on the North Sea coast. The whole area is protected by a sea wall (grey). Crop fields (yellow), grasslands (green) and the drainage system (light blue) char-acterize the region. In contrast to T_GER001en and T_GER002en small water bodies (blue) surrounded by reeds (brown) act as water retention polders. Agricultural land use in some retention areas is adapted to the ground water levels and flooding frequencies. This results in parts of the retention areas being taken out of agricultural production and undisturbed development of natural habitats occurring. In other parts of the retention areas extensive grazing or reed farming will be practiced. This leads to a mosaic of different land uses in the landscape. Retention areas of 500 ha are able to store up to 2,500,000 m³ water. The height of the dams depends on the elevation of the landscape but in general a height of less than 2 m is sufficient.
Location: Krummhörn. County of Aurich, Lower Saxony
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (To generate income in the retention area (without existing agricultural methods))
Technical knowledge required for water board: high (To build a new adapted drainage system with retention areas)
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap
Secondary technical functions: increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
Dam/ pan/ pond
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 2
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 13000
Construction material (earth): sand core and clay cover
Specification of dams/ pans/ ponds: Capacity 2500000m3
Catchment area: 49000ham2
Beneficial area: 49000ham2
Other specifications: size of retention area (embanked area): 500.00 ha
Change of land use type: Within the retention area the conditions are wetter than before. Therefore the agricultural land use needs to be changed to an adapted land use.
Change of land use practices / intensity level: Under the wetter conditions only a less intensive land use is possible, e.g. no crop fields but instead extensive grazing or cessation of agricultural land use.
作者:
Udo Schotten
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Euro
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
0.94
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
100.00
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Building of dams | during winter months |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | Dam | 1.0 | 10000000.0 | 10000000.0 | |
| 设备 | Machine use | Dam | 1.0 | 4000000.0 | 4000000.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Earth | Dam | 1.0 | 112000.0 | 112000.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 14112000.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 15012765.96 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 3 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Control of dams | once a year |
| 2. | Maintenance of dams | once a year |
| 3. | Maintenance of drainage system | once a year (mean of many years) |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | Dam | 1.0 | 500.0 | 500.0 | |
| 设备 | Machine use | Dam | 1.0 | 200.0 | 200.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Earth | Dam | 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | |
| 其它 | Maintenance per km ditch | Dam | 1.0 | 2270.7 | 2270.7 | |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 3070.7 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 3266.7 | |||||
注释:
Machinery/ tools: digger, open truck
The main investment is based on a dam length of 13 km to build up the retention area of a size of 500 ha. The length of the drainage network for the whole watershed (retention area and the surroundings) is 1,134 km. Maintenance costs of drainage network are based on long term annual mean cost of 2,270.72 Euro per km including pumping costs.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
The establishment costs are for the whole retention area (500 ha). The establishment period will be half a year.
Mainly the elevation in the region determines the costs as the height of the dams depend on the elevation. Typical heights are 1 m up to 2 m with a slope of 1:3.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 潮湿的
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
表土有机质:
- 高(>3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility is high
Soil drainage/infiltration is meidum
Soil water storage capacity is high
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
< 5米
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
仅供农业使用(灌溉)
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 低
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 员工(公司、政府)
机械化水平:
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
1% of the land users are very rich and own 1% of the land.
49% of the land users are rich and own 24% of the land.
50% of the land users are average wealthy and own 50% of the land.
and own 25% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Many farmers do additional work in companies
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 大规模的
注释:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: 5-15 ha, 15-50 ha, 50-100 ha, 100-500 ha
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,未命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
Under wet conditions in the retention area a crop production is not possible any more.
饲料生产
注释/具体说明:
Under wet conditions in the retention area an intensive fodder production is not possible any more.
饲料质量
注释/具体说明:
Under wet conditions in the retention area the optiomal fodder quality can not ensured any more.
生产故障风险
注释/具体说明:
Regarding crops: The retention area is used for excess water and may be flooded during growing season.
收入和成本
农业投入费用
注释/具体说明:
Only adjusted land use takes place, therefore the expenses are reduced nearly to 0.
农业收入
收入来源的多样性
注释/具体说明:
Due to land use adapted to the conditions the typical land use is not possible and a diversitfication will take place with reed mowing and extensive grazing in the retention area.
其它社会经济效应
Intrusion by saline groundwater
社会文化影响
娱乐机会
注释/具体说明:
Diversification of landscape by building the retention area will increase the attractivity for recreation and tourists.
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
Less intensive land use results in more diversity and conservation of regional species and habitats.
冲突缓解
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
注释/具体说明:
'Regional belonging' and 'feeling of safety' are measured. The amount of increase is modelled and will be added here.
生态影响
水循环/径流
水量
注释/具体说明:
Typical for the region are wet situations. These typical wet conditions are restored by cessation of drainage system within the retention area.
水质
注释/具体说明:
Updwelling of saline groundwater is prevented by increased water level in the retention area.
地下水位/含水层
注释/具体说明:
By water in the retention are the recharge of groundwater will increase and prevent salinization.
蒸发
注释/具体说明:
Instead of pumping water into the sea a higher amount is evapotranspirated naturally.
土壤
土壤水分
注释/具体说明:
Typical for the region are wet situations. These typical wet conditions are restored by cessation of drainage system within the retention area.
盐度
注释/具体说明:
By water in the retention are the recharge of groundwater will increase and prevent salinization.
土壤有机物/地下C
注释/具体说明:
By wetter conditions the soil organic matter will be increased.
生物多样性:植被、动物
植物多样性
注释/具体说明:
By diversification of land use the number of species will be increased, especially due to extensive land use.
动物多样性
注释/具体说明:
By diversification of land use the number of species will be increased, especially due to extensive land use.
栖息地多样性
注释/具体说明:
By diversification of land use the number of habitats will be increased.
减少气候和灾害风险
碳和温室气体的排放
注释/具体说明:
Modelled is the global warming potential by gas emissions. Not yet clear if it is benefit or disadvantage. Model will show.
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
水资源可用性
旱季稳定可靠的水流
注释/具体说明:
Water stored in retention area can be used for irrigation during dry summer months.
下游洪水
注释/具体说明:
Measured m3 of excess water in the catchment area, leading to floods or needs to be pumped. Exact values from modelling will be added as soon as possible!
对邻近农田的破坏
对公共/私人基础设施的破坏
Reduced hazard towards adverse events
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 好 |
| 局地风暴 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 未知 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
消极
长期回报:
稍微积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
非常积极
注释:
The benefits will be visible in an longer time frame. There will be benefits of the investments when considering sea level rise in the upcoming 100 years.
6.5 技术采用
注释:
Comments on spontaneous adoption: The SLM Technology is not implemented by land users but needs to be implemented in spatial planning of the federal state. We expect that there is a chance for implementation.
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The SLM Technology was developed together with regional experts. It seems that the ideas developed, merge more often in their recent discussion and an implementation is likely.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
The retention area will supplement the drainage of the arable fields and pastures outside the retention area How can they be sustained / enhanced? Combine with other technical solutions for protection against flooding. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Prevention of flooding during strong rainfalls and possibility to irrigate during dry periods How can they be sustained / enhanced? The larger the retention areas are the more water can be stored |
|
Prevention of salt water intrusion in the region How can they be sustained / enhanced? Fresh water in the retention areas prevents saline ground water from intrusion. Build polders in areas where saline ground water intrudes. |
|
Endangered species might obtain new habitats in the retention area How can they be sustained / enhanced? Extensive land use can help to optimize the habitats for endan-gered species and increase attractiveness for tourism. |
|
Through investments in building retention polders the very ex-pensive strengthening of the existing drainage system is no longer necessary. How can they be sustained / enhanced? By increasing the attractiveness for tourism alternative benefits for land owner can be generated. |
|
Multi-functional land use in the catchment and in the retention area How can they be sustained / enhanced? Support farmers with land in the retention area (e.g. financially or with additional agricultural land outside the retention area). Sup-port discussions between farmers’ associations and nature con-servation agencies. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The retention polders will change the landscape and this may reduce the value of the region for tourism | Include tourist concerns within the retention area (accessibility, information, attractiveness) |
| Endangered species might lose habitats when building up the retention polders | Do not build a retention area where endangered species live |
| Loss of livelihoods | Retention areas should be planned for parts of the landscape without settlements |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Loss of land for agricultural production | Create retention polders where the productivity is already low. Encourage alternative land use (for example reed production) in the retention polders. |
| High water levels (especially with changing levels) may generate high emissions of greenhouse gases. | Ground water levels should kept stable near to the soil surface. |
| Retention area is probably too small if pessimistic sea level rise predictions come true. | Increase size of retention polders. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
http://www.comtess.uni-oldenburg.de/
7.3 链接到网络上的相关信息
标题/说明:
http://www.comtess.uni-oldenburg.de/
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Stakeholder participation in integrated assessment and planning of … [德国]
Stakeholders have been involved in integrated assessment to develop action-oriented land use options addressing possible climate change adaptation measures as alternatives to traditional coastal protection strategies.
- 编制者: Martin Maier
模块
无模块