Implementation of a fog water capture system in a conservation area in the community of Shaushi. [ອີກວາດໍ]
- ການສ້າງ:
- ປັບປູງ:
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: Raul Galeas
- ບັນນາທິການ: –
- ຜູ້ທົບທວນຄືນ: Tatenda Lemann, Johanna Jacobi
Shaushi Community, La Matriz Parish, Canton Quero, Province of Tungurahua.
technologies_4050 - ອີກວາດໍ
ເບິ່ງພາກສ່ວນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດ1. ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປ
1.2 ຂໍ້ມູນ ການຕິດຕໍ່ພົວພັນ ຂອງບຸກຄົນທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ແລະ ສະຖາບັນ ທີ່ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນການປະເມີນເອກກະສານ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ບັນດາຜູ້ຕອບແບບສອບຖາມທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ()
Galeas Raul
0986027084
raul12hc@gmail.com
CONDESAN
Calle Germán Alemán E12-123 y Carlos Arroyo del Río.
ອີກວາດໍ
1.3 ເງື່ອນໄຂ ກ່ຽວກັບ ການນໍາໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນເອກະສານ ທີ່ສ້າງຂື້ນ ໂດຍຜ່ານ ອົງການພາບລວມຂອງໂລກ ທາງດ້ານແນວທາງ ແລະ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການອານຸລັກ ທໍາມະຊາດ (WOCAT)
ເມື່ອໃດທີ່ໄດ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ (ຢູ່ພາກສະໜາມ)?
01/05/2017
ຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ແລະ ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ ທີ່ໃຫ້ຂໍ້ມູນ (ຫຼາຍ) ຍິນຍອມ ຕາມເງື່ອນໄຂ ໃນການນຳໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນ ເພື່ອສ້າງເປັນເອກກະສານຂອງ WOCAT:
ແມ່ນ
1.4 ແຈ້ງການວ່າ ດ້ວຍຄວາມຍືນຍົງຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ດັ່ງກ່າວໄດ້ອະທິບາຍ ເຖິງບັນຫາ ກ່ຽວກັບ ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນບໍ? ຖ້າບໍ່ດັ່ງນັ້ນ ມັນບໍ່ສາມາດ ຢັ້ງຢືນໄດ້ວ່າ ເປັນເຕັກໂນໂລຊີ ໃນການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ? :
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Land management practice is intended to preserve and restore soil conditions in the area of implementation.
2. ການອະທິບາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
2.1 ຄໍາອະທິບາຍສັ້ນຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການກຳໜົດຄວາມໝາຍ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
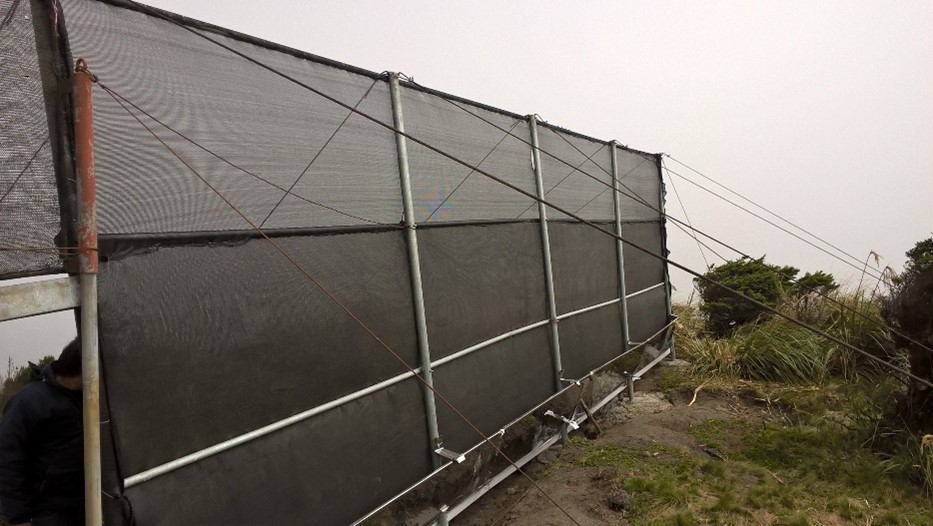
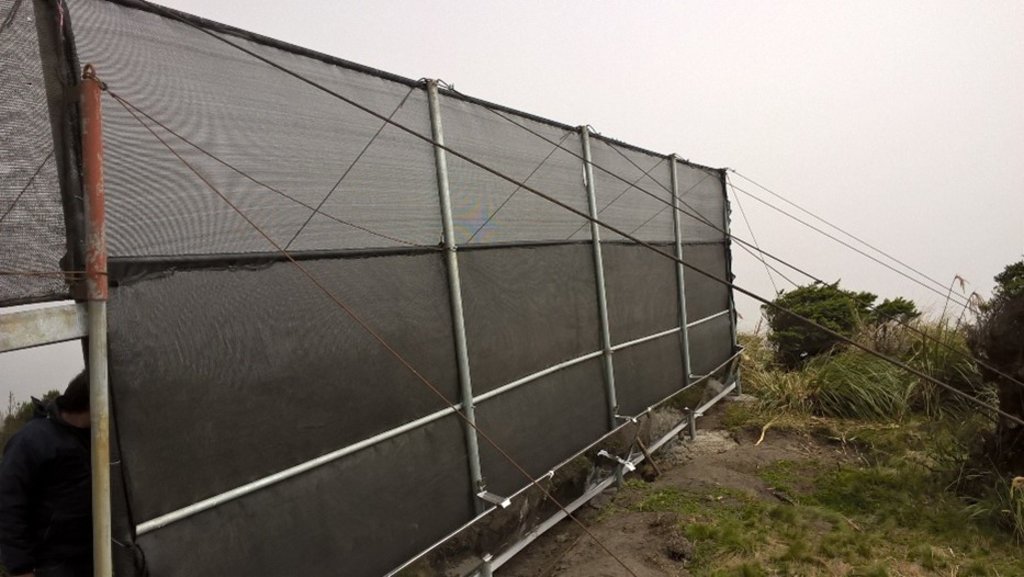
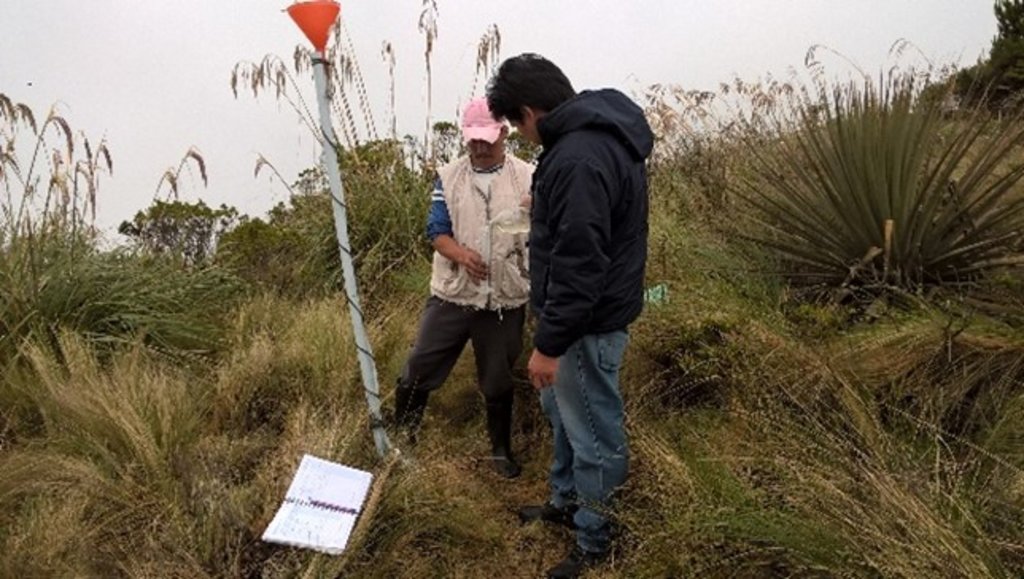
The practice consists in the installation of a water capture system, coming from the fog of the Cerro Shaushi zone, that allows to cover the need of water for domestic consumption of the inhabitants of the upper zone of the Community of Shaushi.
2.2 ການອະທິບາຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການພັນລະນາ:
The technology was applied in the Shaushi community in La Matriz parish, Canton Quero, province of Tungurahua. It consists in the installation of fog water capture system, declaration of a conservation and protection area, and participatory monitoring of water quality and quantity. Among the purposes of the technology is to make the population aware of the sustainable use of the territory and of the environmental services it provides, and to motivate them to take an active part in the conservation and protection of natural areas and water sources. Major activities are the periodic revision of the water capture system, repair and/or replacement of deteriorated or destroyed elements, and the continuous evaluation of the functionality of the practice, and continuous monitoring of water quality and quantity. The main benefit is the availability of water for human consumption in quantity and quality, conservation of natural areas, improvement of the relationship between human beings and nature, and to have hydrometeorological information for research purposes. The users of the practice are satisfied with its implementation and the benefits perceived so far, as they have been able to demonstrate the improvements described. As an opportunity for improvement, the need to deepen the knowledge about the páramo ecosystem and its benefits within the community is established. In addition, the initiative to implement this system in other geographical points is proposed, considering its benefits and the natural conditions of the area that make possible the availability of water for the community.
2.3 ຮູບພາບຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
2.5 ປະເທດ / ເຂດ / ສະຖານທີ່ບ່ອນທີ່ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຮັບການນໍາໃຊ້ ແລະ ທີ່ຖືກປົກຄຸມດ້ວຍການປະເມີນຜົນ
ປະເທດ:
ອີກວາດໍ
ພາກພື້ນ / ລັດ / ແຂວງ:
Tungurahua
ຂໍ້ມູນເພີ່ມເຕີມຂອງສະຖານທີ່:
Shaushi
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The reserve tank stores water from the fog water capture system and from the Quintina water source for domestic consumption in the Shuashi Community, with which it can supply the beneficiary population (30 families).
Map
×2.6 ວັນທີໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າ ບໍ່ຮູ້ຈັກ ປີທີ່ຊັດເຈນ ແມ່ນໃຫ້ປະມານ ວັນທີເອົາ:
- ຕໍ່າກວ່າ 10 ປີ ຜ່ານມາ (ມາເຖິງປະຈຸບັນ)
2.7 ການນໍາສະເໜີ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຖືກຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດຄືແນວໃດ?
- ໂດຍຜ່ານນະວັດຕະກໍາຄິດຄົ້ນຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
- ໃນໄລຍະການທົດລອງ / ການຄົ້ນຄວ້າ
- ໂດຍຜ່ານໂຄງການ / ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອຈາກພາຍນອກ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ (ປະເພດ ໂຄງການ ແລະ ອື່ນໆ):
This practice was established thanks to the management carried out by the "Mancomunidda del Frente Sur Occidental", "Fondo de Páramos de Tungurahua" and "the international organization Figth Against Poverty", with the financing of cooperating entities such as "Consorcio para el Desarrollo de la Ecorregión Andina" (CONDESAN) and the Ministry of the Environment, however, it was also a decision of the community of Shaushi, who assigned the area of implementation of the practice for conservation purposes.The reserve tank stores water from the fog water capture system and from the Quintina water source for domestic consumption in the Shuashi Community, with which it can supply the beneficiary population (30 families).
3. ການໃຈ້ແຍກ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໃນການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
3.1 ຈຸດປະສົງຫຼັກ (ຫຼາຍ) ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ, ປ້ອງກັນ, ຟື້ນຟູ ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
- ການອະນຸລັກ ລະບົບນິເວດ
- ປົກປັກຮັກສານໍ້າ / ນໍ້າພື້ນທີ່ - ປະສົມປະສານກັບ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີອື່ນໆ
- ປົກປັກຮັກສາ / ການປັບປຸງຊີວະນາໆພັນ
- ສ້າງຜົນກະທົບ ທີ່ເປັນທາງບວກ ໃຫ້ແກ່ສັງຄົມ
3.2 ປະເພດການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃນປະຈຸບັນ() ທີ່ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຖືກນໍາໃຊ້

ປະສົມປະສານ (ການປູກພືດ / ທົ່ງຫຍ້າລ້ຽງສັດ / ຕົ້ນໄມ້), ລວມທັງ ປ່າໄມ້ ແບບປະສົມປະສານ
- ກະສິກຳ-ທົ່ງຫຍ້າ
ຜະລິດຕະພັນຫຼັກ / ບໍລິການ:
In the area of implementation of the practice outside the conservation area alternately develops short cycle crops mainly and livestock.

ອື່ນໆ
ລະບຸ ຊະນິດ:
Paramo
ຂໍ້ສັງເກດ:
The practice was implemented in an area that preserves its natural conditions and is in recovery. This area was declared a conservation and protection area. In the area of implementation of the practice outside the conservation area alternately develops short cycle crops mainly and livestock.
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າ ການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ມີການປ່ຽນແປງ ໃນເວລາ ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ, ແມ່ນໃຫ້ລະບຸວ່າ ດິນພື້ນທີ່ດັ່ງກ່າວ ເຄີຍເປັນດິນປະເພດໃດ ກ່ອນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
The area where the practice was implemented was an area that was partially intervened with activities related to agriculture, grazing and forest plantations (native species and pine). Today the area is restricted under a conservation and protection agreement.
3.3 ຂໍ້ມູນເພີ່ມເຕີມກ່ຽວກັບການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
ການສະໜອງນໍ້າ ໃນພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
- ປະສົມປະສານ ກັນລະຫວ່າງ ນໍ້າຝົນ ແລະ ນໍ້າຊົນລະປະທານ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The area where the practice is applied does not require irrigation since it is currently under conservation agreement. The area of direct influence, outside the conservation area, in the Shaushi community uses rainwater and the Mocha - Quero Canal irrigation system as irrigation water.
ຈໍານວນ ລະດູການ ປູກໃນປີໜຶ່ງ:
- 2
ລະບຸ ຊະນິດ:
In the cultivated area the crops (outside the conservation area) are rotated approximately after 4 to 6 months, depending on the product.
ຄວາມໜາແໜ້ນ ຂອງສັດລ້ຽງ (ຖ້າຫາກວ່າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ):
In the Shaushi Community, an average of 5-7 cattle per hectare is evident.
3.4 ການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ຢູ່ໃນກຸ່ມການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
- ການປິດພື້ນທີ່ (ຢຸດການນໍາໃຊ້, ເພື່ອປູກເປັນປ່າຟື້ນຟູ)
- ການເກັບກັກນໍ້າ
- ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ແລະ ປ້ອງກັນເຂດດິນທາມ
3.5 ການຂະຫຍາຍເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ການແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
- ນໍາໃຊ້ໃນຈຸດສະເພາະ / ແນໃສ່ນໍາໃຊ້ໃນພື້ນທີ່ຂະໜາດນ້ອຍ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The practice of applying a water capture system, although installed in specific points, is accompanied by the declaration of the implantation zone as a conservation and protection area.
3.6 ມາດຕະການ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ ປະກອບດ້ວຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ມາດຕະການໂຄງສ້າງ
- S7: ອຸປະກອນເກັບຮັກສາ, ສະໜອງນ້ຳ, ຊົນລະປະທານ

ມາດຕະການ ທາງດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ
- M1: ການປ່ຽນແປງ ປະເພດ ການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ

ມາດຕະການອື່ນໆ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Monitoring of water quality and quantity. The measures chosen correspond in the first case to the water capture system and in the second case refers to the declaration of the area of implantation of the practice as a conservation area.
3.7 ປະເພດດິນເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຫຼັກທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຂອງດິນ ທາງກາຍະພາບ
- Pc: ການອັດແໜ້ນ

ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ທາງຊີວະພາບ
- Bc: ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນການປົກຫຸ້ມຂອງພືດ
- Bq: ປະລິມານ / ອິນຊີວັດຖຸຫຼຸດລົງ
- Bl: ການສູນເສຍ ຈຸລິນຊີໃນດິນ

ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຂອງນໍ້າ
- Ha: ສະພາບແຫ້ງແລ້ງ
- Hs: ການປ່ຽນແປງ ປະລິມານ ນໍ້າໜ້າດິນ
- Hp: ຄຸນນະພາບ ຂອງນ້ຳຊັ້ນໜ້າດິນຫຼຸດລົງ
- Hq: ຄຸນນະພາບ ຂອງນ້ຳໃຕ້ດິນຫຼຸດລົງ
- HW: ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ ຄວາມສາມາດ ໃນການປ້ອງກັນພື້ນທີ່ດິນທາມ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The practice avoids that in the area of conservation and sources of water they are intervened by the inhabitants of the Community of Shaushi and by the cattle of their property, with the development of sustainable activities like the capture of fog water that does not affect the availability of the resource. The water supply for domestic use for the inhabitants of Shaushi is currently provided by the Junta de Shaushi, San Vicente and Pueblo Viejo Drinking Water System. However, service coverage is partial; the inhabitants of the upper area of the Shaushi community do not have access to the water because the population has expanded over time to higher altitudes, making it impossible for the system to provide service for technical and infrastructural reasons. However, the population could not be fully supplied and there was a risk of contamination because there was no adequate infrastructure to distribute water for the two required uses.
3.8 ການປ້ອງກັນ, ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ, ຫຼືການຟື້ນຟູຂອງການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເປົ້າໝາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ພົວພັນ ກັບຄວາມເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ:
- ປ້ອງກັນການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
- ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The practice also includes the sustainable management of soil and territory with the capture of water from the fog, the declaration of this area as an area of conservation and protection that will prevent deep soil degradation.
4. ຂໍ້ກໍາໜົດ, ກິດຈະກໍາການປະຕິບັດ, ວັດຖຸດິບ, ແລະຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
4.1 ເຕັກນິກ ໃນການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
4.2 ການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດອະທິບາຍເຕັກນິກ
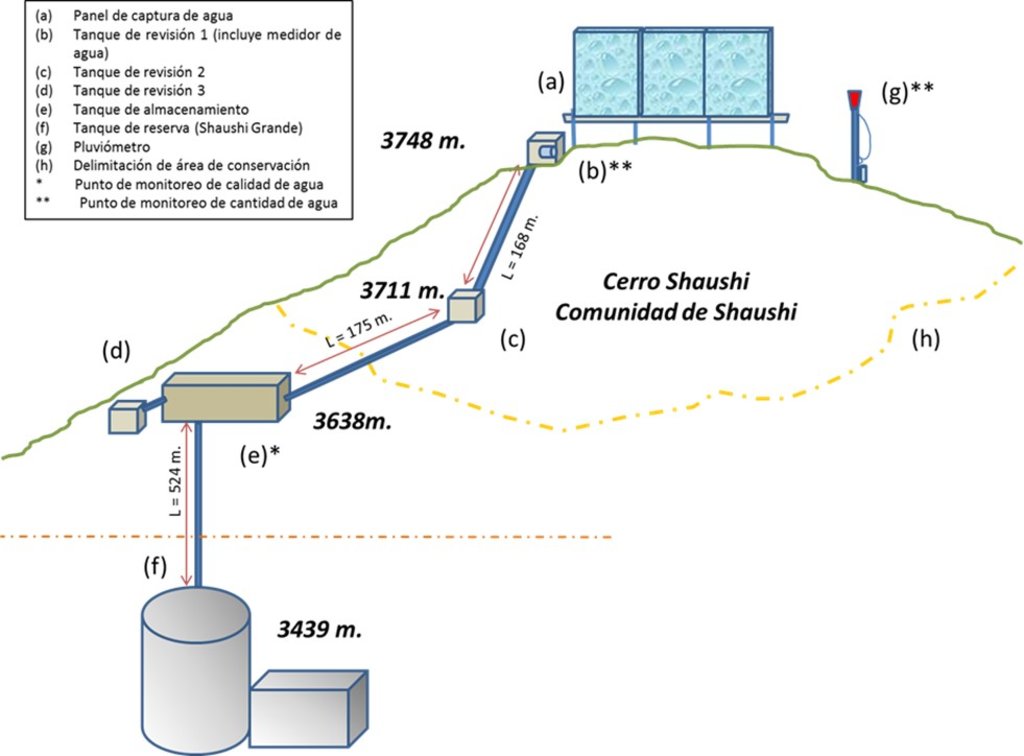
Dimensions
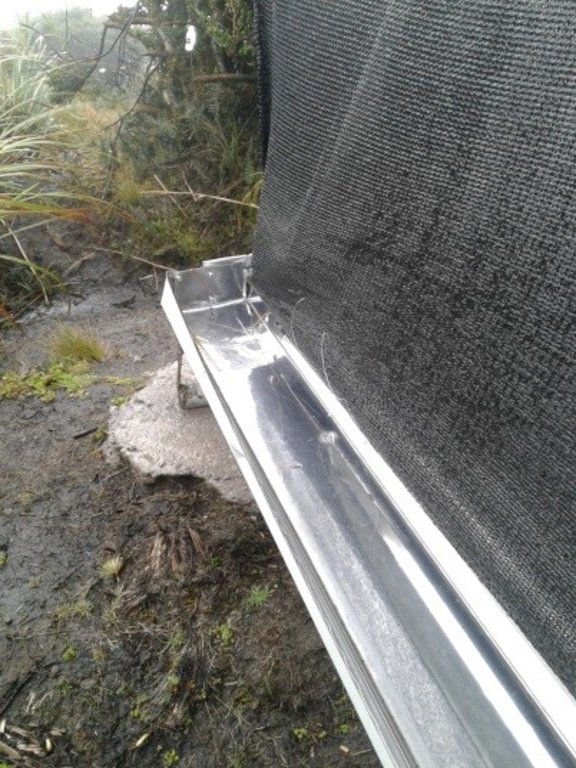
Capture Panel Review and Breakthrough Tanks
Height = 4 m. length = 1.0 m.
Length = 10 m. width = 1.0 m.
depth = 1.0 m.
Driving line storage tank
Length = 343 m. length = 3 m.
Diameter = 32 mm. width = 2 m.
depth = 2 m.
Tank capacity Overhaul and breaker tanks
Volume = 1 m3
Storage tank
Volume = 12 m3
Slope angle: Mostly the terrain of the practice implantation zone is 30-40%.
Construction material used: Galvanized steel pipes, zaran mesh, cement, stone, sand and gravel, PVC pipes, fittings (keys, elbows, valves, etc.), iron stakes for supports, tensioners, tol lids for tanks.
Area 137 ha, owned by Shaushi Community
Altitude range approx. 3400-3700 m
Slope range 30 - 40 %.
Parameters considered: pH, conductivity, total dissolved solids, water temperature, precipitation and flow.
Monitoring points water storage tank.
1) Precipitation: Nearby of the water capture screen (neblinometer).
2) Flow: to one side of the water capture panel (neblinometer).
Monthly frequency
1) Precipitation: Weekly
2) Flow: Weekly
Materials and/or equipment used
1) pH, conductivity, total dissolved solids: Multiparametric equipment.
2) Water temperature: Thermometer and/or multiparametric
equipment
1) Precipitation: Totalizer rain gauge (wooden stake, plastic bottle, mangueta, measuring probe.
2) Flow: Micrometer (water meter).
4.3 ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປກ່ຽວກັບການຄິດໄລ່ປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າໃນການຜະລິດ ແລະ ມູນຄ່າອື່ນໆ
ລະບຸ ວິທີການ ຄຳໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ແລະ ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າ ທີ່ໄດ້ຄິດໄລ່:
- ຕໍ່ພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ລະບຸ ສະກຸນເງິນທີ່ໃຊ້ສໍາລັບ ການຄິດໄລ່ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ:
- ໂດລາສະຫະລັດ
ລະບຸ ຄ່າຈ້າງ ຄ່າແຮງງານສະເລ່ຍ ຕໍ່ ວັນ:
10-20
4.4 ການສ້າງຕັ້ງກິດຈະກໍາ
| ກິດຈະກໍາ | ປະເພດ ມາດຕະການ | ໄລຍະເວລາ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Installation of fog water capture system | ໂຄງສ້າງ | Only once the site has been identified. |
| 2. | Declaration of conservation and protection area in the area of implementation of the practice | ການຈັດການຄຸ້ມຄອງ | Only once the area of interest has been identified. |
| 3. | Participatory monitoring of water quality and quantity. | ມາດຕະການອື່ນໆ | Amount of water: weekly Water quality: monthly |
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The most relevant activities carried out for the implementation of the practice are considered. In the following paragraphs the declaration activity of the conservation area will not be considered due to the fact that it is an inter-institutional management activity only.
4.5 ຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ປັດໄຈຂາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນໃນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ
ຖ້າເປັນໄປໄດ້, ໃຫ້ແຕກຍ່ອຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຕົ້ນທຶນ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕີບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ດັ່ງຕາຕະລາງລຸ່ມນີ້, ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ປັດໄຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ ແລະ ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ ຫົວໜ່ວຍ ຖ້າທ່ານບໍ່ ສາມາດ ແຕກຍ່ອຍລາຍລະອຽດຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນ, ໃຫ້ຄາດຄະເນ ມູນຄ່າທັງໝົດ ທີ່ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
33238.86
| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ແຮງງານ | Construction and installation of the elements of the water capture system. Skilled and unskilled labor. | 1 | 1.0 | 26176.33 | 26176.33 | 3.4 |
| ແຮງງານ | Water quality and quantity monitoring (measurements) | 1 | 1.0 | 500.0 | 500.0 | 100.0 |
| ອຸປະກອນ | Miscellaneous materials for the construction and installation of the water harvesting system | 1 | 1.0 | 2012.53 | 2012.53 | |
| ອຸປະກອນ | Materials and equipment for water quality and quantity sampling and measurements | 1 | 1.0 | 4550.0 | 4550.0 | |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 33238.86 | |||||
ຖ້າຫາກຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ນຳໃຊ້ມູນຄ່າຕ່ຳກວ່າ 100% ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ແມ່ນໃຜເປັນຜູ້ຊ່ວຍ ໃນລາຍຈ່າຍທີ່ເຫຼືອ:
The cooperating entities for the application of the practice were: CONDESAN, Ministry of Environment MAE (Project GIDACC), FMPLPT, Autonomous Decentralized Municipal Government of the canton Santiago Quero and the Commonwealth of FSO.
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The costs were estimated on the basis of the information available from the cooperating entities.
4.6 ບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ / ແຜນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ກິດຈະກໍາ
| ກິດຈະກໍາ | ປະເພດ ມາດຕະການ | ໄລຍະເວລາ / ຄວາມຖີ່ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Review of fog water capture system and additional elements for monitoring. | ມາດຕະການອື່ນໆ | weekly |
| 2. | Repair and/or replacement of deteriorated or damaged elements. | ໂຄງສ້າງ | when necessary |
4.7 ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ແລະ ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນສໍາລັບການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາກິດຈະກໍາ / ແຜນປະຕິບັດ (ຕໍ່ປີ)
ຖ້າເປັນໄປໄດ້, ໃຫ້ແຕກຍ່ອຍລາຍລະອຽດຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນ ໃນການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ດັ່ງຕາຕະລາງລຸ່ມນີ້, ໃຫ້ລະບຸເຖິງ ປັດໄຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ ແລະ ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ ຫົວໜ່ວຍ ຖ້າທ່ານບໍ່ສາມາດ ແຕກຍ່ອຍລາຍລະອຽດຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນ, ໃຫ້ຄາດຄະເນ ມູນຄ່າທັງໝົດ ທີ່ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
4900.0
ຖ້າຫາກຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ນຳໃຊ້ມູນຄ່າຕ່ຳກວ່າ 100% ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ແມ່ນໃຜເປັນຜູ້ຊ່ວຍ ໃນລາຍຈ່າຍທີ່ເຫຼືອ:
The costs so far have been assumed by the Technical Unit of the Commonwealth of Southern Western Front.
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
It is proposed that an agreement be made with the community to establish responsibilities for the maintenance of the practice.
4.8 ປັດໄຈ ທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
ໃຫ້ອະທິບາຍ ປັດໃຈ ທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ຕົ້ນທຶນ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ:
According to the perception of the beneficiaries, the most important factor that can affect the system and therefore the costs, are the environmental conditions of the area, especially the presence of strong winds that could mainly affect the water capture panel fog.
5. ສະພາບແວດລ້ອມທໍາມະຊາດ ແລະ ມະນຸດ
5.1 ອາກາດ
ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນປະຈໍາປີ
- < 250 ມີລິແມັດ
- 251-500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 501-750 ມີລິແມັດ
- 751-1,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,001-1,500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,501-2,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 2,001-3,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 3,001-4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- > 4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸສະເລ່ຍ ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນຕົກປະຈໍາປີ ເປັນມິນລິແມັດ (ຖ້າຫາກຮູ້ຈັກ):
615.00
ຂໍ້ມູນສະເພາະ / ຄວາມເຫັນກ່ຽວກັບ ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນ:
In the Inter-Andean region the Rainy Period presents a bimodal distribution, presenting a Secondary Rainy Period during the months of September to November and the Main Rainy Period during the months of February to May.
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ຊື່ສະຖານີ ອຸຕຸນິຍົມ ເພື່ອເປັນຂໍ້ມູນອ້າງອີງ:
Querochaca and Huambalo from INAMHI
ເຂດສະພາບອາກາດກະສິກໍາ
- ເຄີ່ງຄວາມຊຸ່ມ
The agroclimatic zone was determined based on the information of the biophysical characterization provided in the Diagnosis of the Quero Canton in the Cubillo Paulina Grade Thesis.
5.2 ພູມິປະເທດ
ຄ່າສະເລ່ຍ ຄວາມຄ້ອຍຊັນ:
- ພື້ນທີ່ຮາບພຽງ (0-2%)
- ອ່ອນ (3-5 %)
- ປານກາງ (6-10 %)
- ມ້ວນ (11-15 %)
- ເນີນ(16-30%)
- ໍຊັນ (31-60%)
- ຊັນຫຼາຍ (>60%)
ຮູບແບບຂອງດິນ:
- ພູພຽງ / ທົ່ງພຽງ
- ສັນພູ
- ເປີ້ນພູ
- ເນີນພູ
- ຕີນພູ
- ຮ່ອມພູ
ເຂດລະດັບສູງ:
- 0-100 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 101-500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- > 4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ໄດ້ຖືກນຳໃຊ້:
- ລັກສະນະສວດ
ຄຳເຫັນ ແລະ ຂໍ້ມູນສະເພາະ ເພີ່ມເຕີມ ກ່ຽວກັບ ພູມີປະເທດ:
The actions carried out as part of the practice are located in an area with rugged topography, mostly in convex areas.
5.3 ດິນ
ຄວາມເລິກ ຂອງດິນສະເລ່ຍ:
- ຕື້ນຫຼາຍ (0-20 ຊັງຕີແມັດ)
- ຕື້ນ (21-50 ຊຕມ)
- ເລີກປານກາງ (51-80 ຊຕມ)
- ເລິກ (81-120 ຊມ)
- ເລິກຫຼາຍ (> 120 cm)
ເນື້ອດິນ (ໜ້າດິນ):
- ຫຍາບ / ເບົາ (ດິນຊາຍ)
- ບາງລະອຽດ / ໜັກ (ໜຽວ)
ເນື້ອດິນ (ເລິກຈາກໜ້າດິນ ລົງໄປຫຼາຍກວ່າ 20 ຊັງຕິແມັດ):
- ຫຍາບ / ເບົາ (ດິນຊາຍ)
- ບາງລະອຽດ / ໜັກ (ໜຽວ)
ຊັ້ນອິນຊີວັດຖຸ ເທິງໜ້າດິນ:
- ສູງ (> 3 %)
ຖ້າເປັນໄປໄດ້ ແມ່ນໃຫ້ຕິດຄັດ ການພັນລະນາດິນ ຫຼື ຂໍ້ມູນສະເພາະຂອງດິນ, ຕົວຢ່າງ, ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ປະເພດຂອງດິນ, ຄ່າຄວາມເປັນກົດ / ເປັນດ່າງຂອງດິນ, ສານອາຫານ, ດິນເຄັມ ແລະ ອື່ນໆ.
The soils of Quero are volcanic and are mainly differentiated by the parental material: there are soils formed in recent volcanic ash (Andosoles: northern and central soils) and soils formed in meteorized metamorphic rock (Inceptisoles: southern soils).
Specifically they are evidenced from Udic Eutrandepts soils (Hv) and their characteristics are: isothermal black; francs with fine to medium sand with clear presence of silt; 4 to 5% organic matter from 0 to 20 cm; deep (1m); friable; well drained; water retention from 10 to 20%; neutral pH; medium natural fertility.
In this area, also have an Entic Distrandepts soils (Dny) and their characteristics are: with content of coarse pumice sand in more than 35% over the whole profile. Moderate to high water retention capacity, 50 to 80%; very black; loamy pseudo-silt textures; deep; well drained.
5.4 ມີນໍ້າ ແລະ ຄຸນນະພາບ
ລະດັບ ນໍ້າໃຕ້ດິນ:
ເທິງຊັ້ນໜ້າດິນ
ການມີນໍ້າ ເທິງໜ້າດິນ:
ປານກາງ
ຄຸນນະພາບນໍ້າ (ບໍ່ມີການບໍາບັດ):
ບໍ່ມີນໍ້າດື່ມ (ຮຽກຮ້ອງໃຫ້ມີການບຳບັດນ້ຳ)
ມີບັນຫາ ກ່ຽວກັບນໍ້າເຄັມບໍ່?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
ເກີດມີນໍ້າຖ້ວມ ໃນພື້ນທີ່ບໍ່?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ ແລະ ຂໍ້ກໍານົດ ເພີ່ມເຕີມ ກ່ຽວກັບ ຄຸນນະພາບ ແລະ ປະລິມານ ຂອງນ້ຳ:
The monitoring of the captured water is currently being carried out, with the result that up to now the water is of acceptable quality. There is no specific groundwater information available for the area. It is estimated that the soil is not very permeable and the aquifers are very localized (INAMHI, 2015).
5.5 ຊີວະນາໆພັນ
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ທາງສາຍພັນ:
- ປານກາງ
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ທາງດ້ານ ທີ່ຢູ່ອາໃສ ຂອງສິ່ງທີ່ມີຊີວິດ:
- ປານກາງ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ ແລະ ລັກສະນະສະເພາະ ເພີ່ມເຕີມກ່ຽວກັບ ຊີວະນາໆພັນ:
In order to determine the diversity of the practice area, the following data are considered: The Sierra del Ecuador region is characterized for being crossed by knots and high mountain chains (with their moors), which have their own biodiversity and diversity of environments and habitats, due to isolation. The ecosystem maintains shrub and herbaceous vegetation (Mena and Medina, 2001). The moor in Quero canton has an evident fragility, due to the constant expansion of the agricultural frontier, overgrazing, burning of grasslands, deforestation, etc., so that the area destined for conservation and protection in the Community of Shaushi is only a remnant of this ecosystem (GAD Quero, 2014).
5.6 ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຢູ່ປະຈຳ ຫຼື ເຄື່ອນຍ້າຍຕະຫຼອດ:
- ບໍ່ເຄື່ອນໄຫວ
ລະບົບ ການຕະຫຼາດ ແລະ ຜົນຜະລິດ:
- ປະສົມ (ກຸ້ມຕົນເອງ / ເປັນສິນຄ້າ
ລາຍຮັບ ທີ່ບໍ່ໄດ້ມາຈາກ ການຜະລິດ ກະສິກໍາ:
- ໜ້ອຍກ່ວາ 10 % ຂອງລາຍຮັບທັງໝົດ
ບຸກຄົນ ຫຼື ກຸ່ມ:
- ບຸກຄົນ / ຄົວເຮືອນ
- ກຸ່ມ / ຊຸມຊົນ
ລະດັບ ການຫັນເປັນກົນຈັກ:
- ການໃຊ້ແຮງງານຄົນ
- ເຄື່ອງກົນຈັກ
ເພດ:
- ຜູ້ຍິງ
- ຜູ້ຊາຍ
ອາຍຸ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
- ໄວກາງຄົນ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
In order to determine the relative level of poverty, data are taken from the 2010 National Census conducted by INEC, which indicates that the percentage of poor due to unsatisfied basic needs in Quero canton is 84.5% (GAD Quero, 2014; SNI, 2017). The components or dimensions: (i) quality of housing, (ii) overcrowding, (iii) access to basic services, (iv) access to education and (v) economic capacity (INEC, 2016).
5.7 ພື້ນທີ່ສະເລ່ຍຂອງທີ່ດິນ ຫຼື ເຊົ່າໂດຍຜູ້ໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- <0.5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 0.5-1 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1-2 ເຮັກຕາ
- 2-5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 5-15 ເຮັກຕາ
- 15-50 ເຮັກຕາ
- 50-100 ເຮັກຕາ
- 100-500 ເຮັກຕາ
- 500-1,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1,000-10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- > 10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
ຖືໄດ້ວ່າ ເປັນຂະໜາດນ້ອຍ, ກາງ ຫຼື ໃຫຍ່ (ອີງຕາມເງື່ອນໄຂ ສະພາບຄວາມເປັນຈິງ ຂອງທ້ອງຖີ່ນ)? :
- ຂະໜາດນ້ອຍ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The inhabitants of the Shaushi Community have an average area of less than 3 ha.
5.8 ເຈົ້າຂອງທີ່ດິນ, ສິດໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ, ແລະ ສິດທິການນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ
- mixed
- mixed
ສິດທິ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ:
- ຊຸມຊົນ (ທີ່ມີການຈັດຕັ້ງ)
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
In the area of direct influence (Shaushi Community) the lands are individual property except for the area destined for conservation and protection which is communal.
5.9 ການເຂົ້າເຖິງການບໍລິການ ແລະ ພື້ນຖານໂຄງລ່າງ
ສຸຂະພາບ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການສຶກສາ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ດ້ານວິຊາການ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການຈ້າງງານ (ຕົວຢ່າງ, ການເຮັດກິດຈະກໍາອື່ນ ທີ່ບໍ່ແມ່ນ ການຜະລິດກະສິກໍາ):
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ຕະຫຼາດ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ພະລັງງານ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ຖະໜົນຫົນທາງ ແລະ ການຂົນສົ່ງ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການດື່ມນໍ້າ ແລະ ສຸຂາພິບານ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການບໍລິການ ທາງດ້ານການເງິນ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
6. ຜົນກະທົບ ແລະ ລາຍງານສະຫຼຸບ
6.1 ການສະແດງຜົນກະທົບ ພາຍໃນພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງເສດຖະກິດສັງຄົມ
ມີນໍ້າ ແລະ ຄຸນນະພາບ
ມີນໍ້າດື່ມ
ນໍ້າດື່ມ ມີຄຸນນະພາບ
ຜົນກະທົບດ້ານວັດທະນາທໍາສັງຄົມ
ສະພາບທາງດ້ານສຸຂະພາບ
ສິດທິ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ຫຼື ນໍ້າ
ສະຖາບັນ ການຈັດຕັ້ງຊຸມຊົນ
ຄວາມຮູ້ກ່ຽວກັບ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ / ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ ຂໍ້ຂັດແຍ່ງ
ຜົນກະທົບຕໍ່ລະບົບນິເວດ
ວົງຈອນນໍ້າ / ນໍ້າ
ປະລິມານນໍ້າ
ຄຸນນະພາບນໍ້າ
ການຂຸດຄົ້ນ / ການເກັບກັກນໍ້າ
ດິນ
ຄວາມຊຸ່ມຂອງດິນ
ການປົກຄຸມຂອງດິນ
ການອັດແໜ້ນຂອງດິນ
ຊີວະນານາພັນ: ສັດ, ພືດ
ການປົກຫຸ້ມຂອງພືດ
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍຂອງພືດ
ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ຈາກໄພພິບັດ ແລະ ອາກາດປ່ຽນແປງ
ຜົນກະທົບ ຂອງໄພແຫ້ງແລ້ງ
ການລະເຫີຍອາຍກາກບອນ ແລະ ອາຍຜິດເຮືອນແກ້ວ
ການປ່ຽນແປງ ອາກາດ ໃນວົງແຄບ
6.2 ຜົນກະທົບທາງອ້ອມ ຈາກການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ສາມາດເຂົ້າເຖິງແຫຼ່ງນໍ້າ
ການໄຫຼຂອງນໍ້າໃນລະດູແລ້ງ
ຄໍາເຫັນກ່ຽວກັບ ການປະເມີນ ຜົນກະທົບ:
Impacts that have been classified as insignificant are thus valued because they are impacts expected by the practices considering their scope, but which have not been measured or perceived by the population as opposed to the impacts valued at the time of analysis.
6.3 ການປ້ອງກັນ ແລະ ຄວາມບອບບາງ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢິ ໃນການປ່ຽນແປງສະພາບດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ແລະ ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງກັບອາກາດທີ່ມີການປ່ຽນແປງທີ່ຮຸນແຮງ / ໄພພິບັດທາງທໍາມະຊາດ (ຮັບຮູ້ໄດ້ໂດຍຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ)
ການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ເທື່ອລະກ້າວ
ການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ເທື່ອລະກ້າວ
| ລະດູການ | ຮູບແບບ ການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ / ທີ່ຮ້າຍແຮງ | ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ອຸນຫະພູມປະຈໍາປີ | ເພີ່ມຂື້ນ | ບໍ່ຮູ້ | |
| ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນປະຈໍາປີ | ເພີ່ມຂື້ນ | ດີ | |
| ການປ່ຽນແປງສະພາບດິນຟ້າອາກາດອື່ນໆ | Loss of seasonality | ເພີ່ມຂື້ນ | ບໍ່ຮູ້ |
ອາກາດ ທີ່ກ່ຽວພັນກັບຄວາມຮຸນແຮງ (ໄພພິບັດທາງທໍາມະຊາດ)
ໄພພິບັດທາງພູມອາກາດ
| ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|
| ຄື້ນໜາວ | ດີ |
6.4 ການວິເຄາະຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ຜົນປະໂຫຍດ
ຈະເຮັດປະໂຫຍດເພື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍກັບສິ່ງກໍ່ສ້າງ (ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ) ໄດ້ແນວໃດ?
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກຫຼາຍ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກຫຼາຍ
ຈະໄດ້ຮັບຜົນປະໂຫຍດເມື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບ / ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍໃນການບຳລຸງຮັກສາທີເ່ກີດຂື້ນອິກ (ຈາກທັດສະນະຄະຕິຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ) ໄດ້ແນວໃດ?
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກຫຼາຍ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກຫຼາຍ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The most plausible benefit for the population of the Shaushi Community is the availability of water for human consumption for the inhabitants who did not have it, so the comparison in terms of costs is assumed in the case of not having the practice, which would represent carrying out a project to transport the water from another geographical point, which would be more costly. On the other hand, the perceived benefits also include environmental and health benefits, which are not quantified economically, thanks to the conservation of the area of implantation of the practice.
6.5 ການປັບຕົວຮັບເອົາເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- ຫຼາຍກ່ວາ 50 %
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າມີ, ປະລິມານ (ຈໍານວນຂອງຄົວເຮືອນ / ເນື້ອທີ່ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ):
23
ທັງໝົດນັ້ນ ແມ່ນໃຜ ທີ່ເປັນຜູ້ປັບຕົວ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ, ມີຈັກຄົນ ທີ່ສາມາດເຮັດເອງໄດ້, ຕົວຢ່າງ, ປາດສະຈາກ ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ທາງດ້ານອຸປະກອນ / ການຈ່າຍເປັນເງິນ?
- 90-100%
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The decision to adopt the practice was made within the Shaushi Community (beneficiaries) for those who did not have the service, where the villagers understood the need to allocate the area for conservation and protection considering the benefits it provides, and the advantage of having a system that would provide water for the consumption of the villagers who did not have the resource.
6.6 ການປັບຕົວ
ໄດ້ມີການດັດປັບ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເພື່ອໃຫ້ແທດເໝາະກັບເງື່ອນໄຂ ການປ່ຽນແປງບໍ?
ແມ່ນ
ອື່ນໆ (ລະບຸແຈ້ງ):
Climatic conditions, terrain and structure of the water capture panel.
ລະບຸການຮັບຮອງເອົາ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ການອອກແບບ, ອຸປະກອນການ / ຊະນິດພັນ ແລະ ອື່ນໆ):
The dimensions of the excavations were reviewed to place the holders and turnbuckles, considering the slope and shape of the relief so that the system is stable.
6.7 ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ |
|---|
| The commitment of the inhabitants of the community to preserve the environment and specifically the protection area that provides them with water in quantity and quality. |
| The water capture system provides them with direct benefits in terms of the availability of drinking water for this zone. |
| Participatory monitoring is beneficial because it allows them to control the quality and quantity of water that the system can provide. |
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຈຸດດີ / ໂອກາດ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ |
|---|
| Plant restoration trials can be carried out to improve knowledge in these ecosystems, which were intervened and which are subsequently destined for conservation. |
| It is possible to investigate how a natural ecosystem in conservation interacts with the areas in its surroundings that are highly intervened and how it could affect it. |
| Decrease in dependence on other water sources for sustainable management of soil and other resources. |
| Investigations can be carried out based on the measurements and analysis of water quantity and quality carried out and to be carried out. Analysis of soil moisture and other elements may be included. |
| Implementation of other practices for research and/or sustainable use of soil and water, with high community participation. |
| The community can be strengthened with respect to issues related to the conservation of these ecosystems and the services they provide, so that they can be properly managed and managed. |
6.8 ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແລະ ວິທີການແກ້ໄຂບັນຫາ
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງໃນມຸມມອງຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| Some users do not respect the rules established for the management of the area destined for conservation, and residues from past activities are still observed. | Sanctions can be established for the presence of any improper action, however, in parallel with the practice, training should continue to involve users more in the review and maintenance activities, in order to achieve a better result. |
| The environmental conditions of the site, especially the strength of the wind in the area. | It is being continuously reviewed to detect any impact on the system, especially on the water capture panel, which could break or become dislocated. |
| In the water capture panel fog, due to the height of the water collection gutter, it splashes in heavy rain events allowing soil to enter into the system from the ground. The same factor when the system becomes saturated or plugged the water overflows into the gutter, so collection is sometimes inefficient. | The functionality of the system is being reviewed, if necessary any modifications will be made in coordination with the community. |
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ/ຂໍ້ບົກຜ່ອງ/ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| Lack of a preventive and corrective maintenance plan to maintain optimal conditions. | It is neccesary to include a preventive and corrective maintenance plan that should be agreed between the technical area of the cooperating entities and with the users of the communities for its application. |
| The practice of permanent monitoring is insufficient, because data collection is minimal. | The cooperating entities and community authorities can establish a monitoring action plan that covers several lines, including infrastructure such as monitoring for research purposes. |
7. ເອກະສານອ້າງອີງ ແລະ ການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
7.1 ວິທີການ / ແຫຼ່ງຂໍ້ມູນ
- ການໄປຢ້ຽມຢາມພາກສະໜາມ, ການສໍາຫຼວດພາກສະໜາມ
Land users and technicians from cooperating entities were interviewed.
- ການສໍາພາດ ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
3 land users, one of them is the President of the Junta de Agua Potable.
- ສໍາພາດ ຊ່ຽວຊານ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
Three technicians from the cooperating entities: Mancomunidad FSO and Fondo de Páramos.
- ການລວບລວມ ບົດລາຍງານ ແລະ ເອກະສານ ອື່ນໆ ທີ່ມີຢູ່ແລ້ວ
The documents used include technical reports prepared by the technicians of the Fondo de Páramos, reports and terms of reference prepared by the Technical Unit of the FSO.
7.2 ເອກກະສານອ້າງອີງທີ່ເປັນບົດລາຍງານ
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
"Los páramos del Ecuador". Mena Vásconez Patricio y Medina Galo. 2001. Abya-Yala / Proyecto Páramo, Quito.
ມີຢູ່ໃສ?ມູນຄ່າເທົ່າໃດ?
Available for free online: https://www.portalces.org/sites/default/files/references/044_Mena%20et%20al.%20(Eds.).%20%202001.Paramos%20Ecuador%20PORTADA%2B_%2BHOJA%2BTECNICA%2BY%2BPRESENTACION.pdf
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
"La biodiversidad en el Ecuador". Bravo Velásquez Elizabeth. 2014. Universidad Politécnica Salesiana. Cuenca-Ecuador.
ມີຢູ່ໃສ?ມູນຄ່າເທົ່າໃດ?
Available for free online: https://dspace.ups.edu.ec/handle/123456789/6788
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Actualización Plan de Desarrollo y Ordenamiento Territorial-Quero 2014. Gobierno Autónomo Descentralizado Municipal del Cantón Quero. 2014.
ມີຢູ່ໃສ?ມູນຄ່າເທົ່າໃດ?
Available for free online: http://app.sni.gob.ec/sni-link/sni/PORTAL_SNI/data_sigad_plus/sigadplusdiagnostico/1860000800001_PDYOT%20QUERO%20CONSOLIDADO_19-04-2015_20-19-44.pdf
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Informe de implementación de un sistema de captura de agua niebla en la comunidad de Shaushi, en el cantón Quero. Guevara Rocío. 2017. Fondo de Manejo de Páramos y Lucha contra la pobreza Tungurahua.
ມີຢູ່ໃສ?ມູນຄ່າເທົ່າໃດ?
In the archives of the Tungurahua Wetland Fund and Fight against Poverty in the GAD of the province of Tungurahua.
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Informe y base de datos de Shaushi y Llimpes, que incluye la línea base llena y estructurada de acuerdo a los lineamientos de CONDESAN. Calle Juan. 2017. CONDESAN.
ມີຢູ່ໃສ?ມູນຄ່າເທົ່າໃດ?
In the archives of the Consortium for Sustainable Development of the Andean Ecoregion CONDESAN.
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Informe final de “Construcción de un sistema de captura de agua niebla en la comunidad de Shaushi, cantón Quero”. Mancomunidad de GADs municipales “Frente Sur Occidental” de la provincia de Tungurahua. 2017.
ມີຢູ່ໃສ?ມູນຄ່າເທົ່າໃດ?
In the archives of the Technical Unit of the Mancomunidad de GADs municipales "Frente Sur Occidental" of the province of Tungurahua.
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Manual de monitoreo hídrico participativo. Calles Juan. 2016. CONDESAN.
ມີຢູ່ໃສ?ມູນຄ່າເທົ່າໃດ?
In the archives of the Consortium for Sustainable Development of the Andean Ecoregion CONDESAN.
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Reporte de Pobreza y Desigualdad. Diciembre 2016. INEC. Dirección responsable de la información estadística y contenidos: Dirección de Innovación en Métricas y Metodologías.
ມີຢູ່ໃສ?ມູນຄ່າເທົ່າໃດ?
Available for free online: https://www.ecuadorencifras.gob.ec/documentos/web-inec/POBREZA/2016/Diciembre_2016/Reporte%20pobreza%20y%20desigualdad-dic16.pdf
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Ubicación del Nuevo Relleno Sanitario en base a criterios ambientales, socioeconómicos y técnicos, y propuesta de Plan de Reciclaje en la ciudad de Quero, Cantón Quero Provincia del Tungurahua. Cubillo Paulina. 2005. Escuela Politécnica del Ejército.
ມີຢູ່ໃສ?ມູນຄ່າເທົ່າໃດ?
Available for free online: http://repositorio.espe.edu.ec/xmlui/handle/21000/722
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Introducción a la Hidrogeología del Ecuador (Segunda Versión). Burbano Napoléon, Becerra Simón, Pasquel Efrén. 2014. INAMHI
ມີຢູ່ໃສ?ມູນຄ່າເທົ່າໃດ?
Available for free online: http://www.serviciometeorologico.gob.ec/Publicaciones/Hidrologia/HIDROGEOLOGIA_2%20EDICION_2014.pdf
7.3 ສາມາດເຊື່ອມໂຍງ ຂໍ້ມູນຂ່າວສານ ໄດ້ໂດຍຜ່ານການອອນລາຍ
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
Anuarios meteorológicos del Instituto Nacional de Meteorología e Hidrología INAMHI.
URL:
http://www.forosecuador.ec/forum/ecuador/educaci%C3%B3n-y-ciencia/35393-inamhi-anuarios-metereol%C3%B3gicos-en-pdf
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
Boletín Anual del Instituto Nacional de Meteorología e Hidrología INAMHI.
URL:
http://www.serviciometeorologico.gob.ec/boletin-anual/
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
Indicadores de pobreza del INEC 2010. Sistema Nacional de Información.
URL:
http://indestadistica.sni.gob.ec/QvAJAXZfc/opendoc.htm?document=SNI.qvw&host=QVS@kukuri&anonymous=truehttp://indestadistica.sni.gob.ec/QvAJAXZfc/opendoc.htm?document=SNI.qvw&host=QVS@kukuri&anonymous=true&bookmark=Document/BM27
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
Sistema Nacional de Información. Página de la Secretaría Nacional de Planificación y Desarrollo del Ecuador
URL:
http://app.sni.gob.ec/web/menu/
ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ ແລະ ເນື້ອໃນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ບໍ່ມີຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ເນື້ອໃນ
ບໍ່ມີເນື້ອໃນ